2006 SUZUKI SWIFT ig 2 sig
[x] Cancel search: ig 2 sigPage 262 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-212 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Troubleshooting
WARNING!
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from engine cooling fan to help prevent personal injury. This fan
is electric and can come on whether or not the engi ne is running. The fan can start automatically in
response to the ECT sensor with the ig nition switch at the “ON” position.
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
StepAction YesNo
1 Is there DTC(s) of ECT sensor circuit (DTC P0116 / P0117 /
P0118) and/or radiator cooling fan circuit (DTC P0480)? Go to corresponding
DTC flow.Go to Step 2.
2 Low speed radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
3) Warm up engine until coolant temp. is 97.5 °C, 207.5 °F
or higher and A/C switch turns OFF (if equipped with A/
C). (If engine coolant temp. dose not rise, check engine
cooling system or ECT sensor.)
Is radiator cooling fan started at low speed when engine
coolant temp. reached above temp.? Radiator cooling fan low
speed control system is
in good condition.
Perform from Step 2 to
Step 8 in DTC P0480
diag. flow. If OK, Go to
Ste p 3.
3 Radiator cooling fan control check
1) Disconnect radiator cooling fan control relays No. 2, and
No. 3 from individual circuit fuse box No.1 with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Run engine when ECT is over 97.5 °C, 207.5 °F.
3) Measure voltage between vehicle body ground and “BLU/RED” wire terminal of disconnected radiator
cooling fan motor connector.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 4.
“BLU/RED” wire is open
or high resistance
circuit.
4 Check radiator cooling fan wire circuit check
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Measure resistance between “BLK” wire terminal of
disconnected radiator coolin g fan motor connector and
vehicle body ground.
Is resistance below 1
Ω? Go to Step 5. “BLK” wire is open or
high resistance circuit.
5 Radiator cooling fan check
1) Check radiator cooling fan referring to “Radiator Cooling
Fan Motor On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1F”.
Is it in good condition? Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Faulty radiator cooling
fan.
Page 264 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-214 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Troubleshooting
WARNING!
Keep hands, tools, and clothing away from engine cooling fan to help prevent personal injury. This fan
is electric and can come on whether or not the engi ne is running. The fan can start automatically in
response to the ECT sensor with the ig nition switch at the “ON” position.
NOTE
When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referri ng to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
StepAction YesNo
1 Is there DTC(s) of ECT sensor circuit (DTC P0116 / P0117 /
P0118) and/or radiator cooling fan circuit (DTC P0480)? Go to corresponding
DTC flow.Go to Step 2.
2 Low speed radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition switch turned
OFF.
2) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
3) Warm up engine until coolant temp. is 97.5 °C, 207.5 °F
or higher and A/C switch turns OFF (if equipped with A/
C). (If engine coolant temp. dose not rise, check engine
cooling system or ECT sensor.)
Is radiator cooling fan started at low speed when engine
coolant temp. reached above temp.? Go to Step 3.
Perform from Step 2 to
Step 5 in “Radiator
Cooling Fan Low Speed
Control System Check”.
3 High speed radiator cooling fan control circuit check
1) Start engine and select “DATA LIST” mode on scan tool.
2) Warm up engine until coolant temp. is 102.5 °C, 216.5 °F
or higher and A/C switch turns OFF (if equipped with A/
C). (If engine coolant temp. dose not rise, check engine
cooling system or ECT sensor.)
Is radiator cooling fan started at high speed when engine
coolant temp. reached above temp? Radiator cooling fan
control system is in
good condition.
Perform from Step 9 to
Step 14 in DTC P0480
diag. flow.
If OK, Go to Step 4.
4 Radiator cooling fan control No. 2 and No. 3 check
1) Run engine when ECT is over 102.5 °C, 216.5 °F.
2) Measure voltage between vehicle body ground and “E23-48” terminal of ECM connector.
Is voltage lower than 1.5 V? Go to Step 5.
Faulty ECM.
5 Radiator cooling fan No. 2 wire circuit check
1) Remove radiator cooling fan control relay No.2 with
ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Measure voltage between “GRY” wire terminal of disconnected radiator cooling fan control relay No. 2
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V? Go to Step 6.
“GRY” wire is open or
high resistance circuit.
6 Radiator cooling fan No. 2 wire circuit check
1) Disconnect connector from radiator cooling fan motor
with ignition swit ch turned OFF.
2) Measure resistance between “BLU/BLK” wire terminal of disconnected radiator cooling fan control relay No. 2
connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance infinity? Go to Step 7.
“BLU/BLK” wire is
shorted to ground
circuit.
Page 280 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1C-8 Engine Electrical Devices:
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Tighten heated oxygen sensor to specified torque.Tightening torque
Heated oxygen sensor (a): 45 N·m (4.5 kgf-m,
32.5 lb-ft)
• Install exhaust manifold referring to “Exhaust Manifold Removal and Installation in Section 1K”, if removed.
• Connect connector of heated oxygen sensor and clamp wire harness securely.
• After installing heated oxygen sensor, start engine and check that no exhaust gas leakage exists.
CMP Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306012
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connector from CMP sensor.
3) Remove CMP sensor from cylinder head.
Installation 1) Install CMP sensor to cylinder head.
Tightening torque
CMP sensor bolt (a): 10 N·m (1.0 kgf-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to CMP sensor securely.
3) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
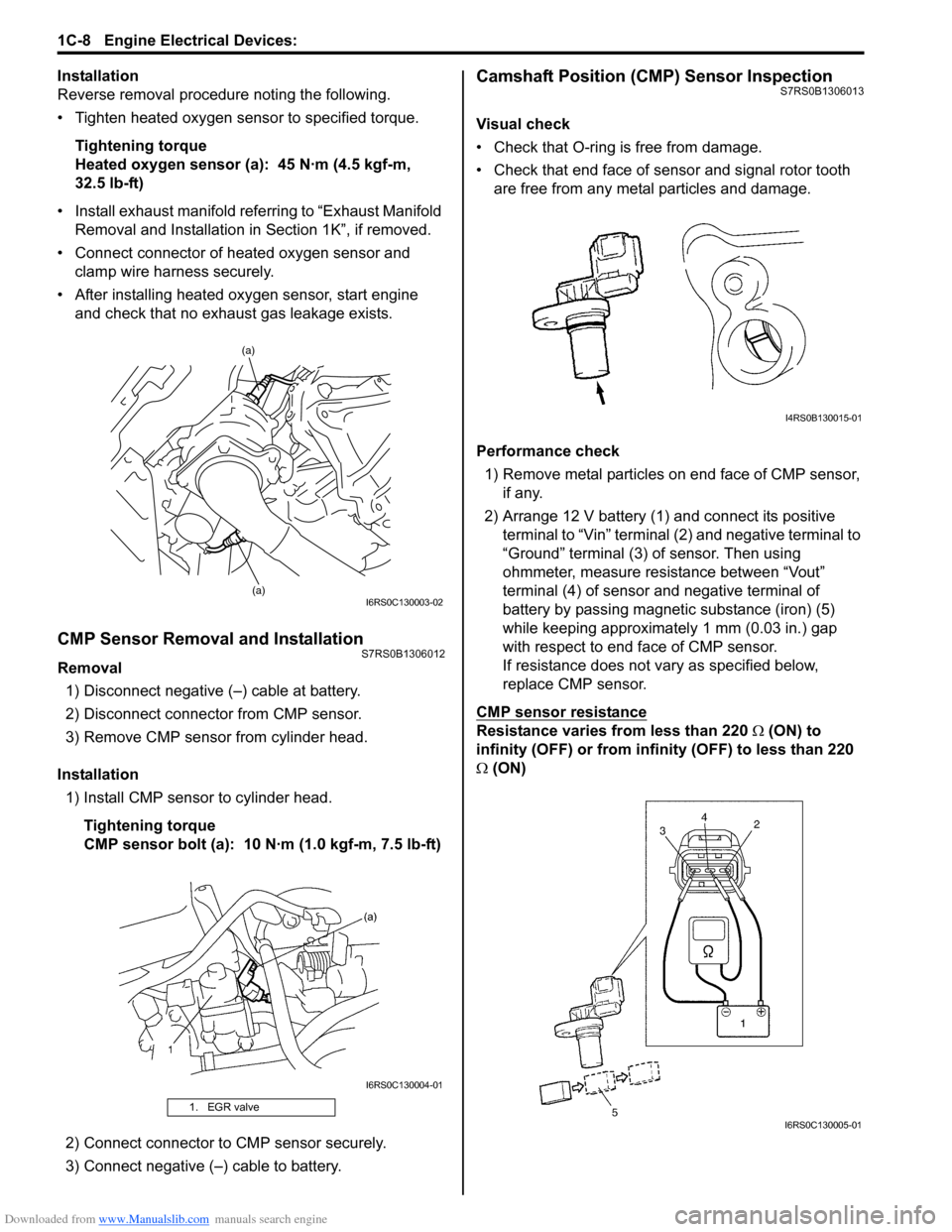
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306013
Visual check
• Check that O-ring is free from damage.
• Check that end face of sensor and signal rotor tooth are free from any metal particles and damage.
Performance check 1) Remove metal particles on end face of CMP sensor, if any.
2) Arrange 12 V battery (1) and connect its positive terminal to “Vin” terminal (2) and negative terminal to
“Ground” terminal (3) of sensor. Then using
ohmmeter, measure resistance between “Vout”
terminal (4) of sensor and negative terminal of
battery by passing magnetic substance (iron) (5)
while keeping approximately 1 mm (0.03 in.) gap
with respect to end face of CMP sensor.
If resistance does not vary as specified below,
replace CMP sensor.
CMP sensor resistance
Resistance varies from less than 220 Ω (ON) to
infinity (OFF) or from infinity (OFF) to less than 220
Ω (ON)
1. EGR valve
(a)
(a)
I6RS0C130003-02
I6RS0C130004-01
I4RS0B130015-01
I6RS0C130005-01
Page 281 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-9
CKP Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306014
Removal1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Remove generator drive belt refer to “Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Remo val and Installation in
Section 1J”.
3) Remove generator bracket bolt (1) and move generator rearward.
4) Disconnect connector from CKP sensor.
5) Remove CKP sensor (2) from cylinder block.
Installation 1) Install CKP sensor to cylinder block. Tighten CKP sensor bolt to specified torque.
Tightening torque
CKP sensor bolt (a): 10 N·m (1.0 kgf-m, 7.5 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to CKP sensor securely.
3) Adjust generator drive belt tension referring to “Water Pump / Generator Drive Belt Tension
Inspection and Adjustment in Section 1J”.
4) Connect negative (–) cable to battery.
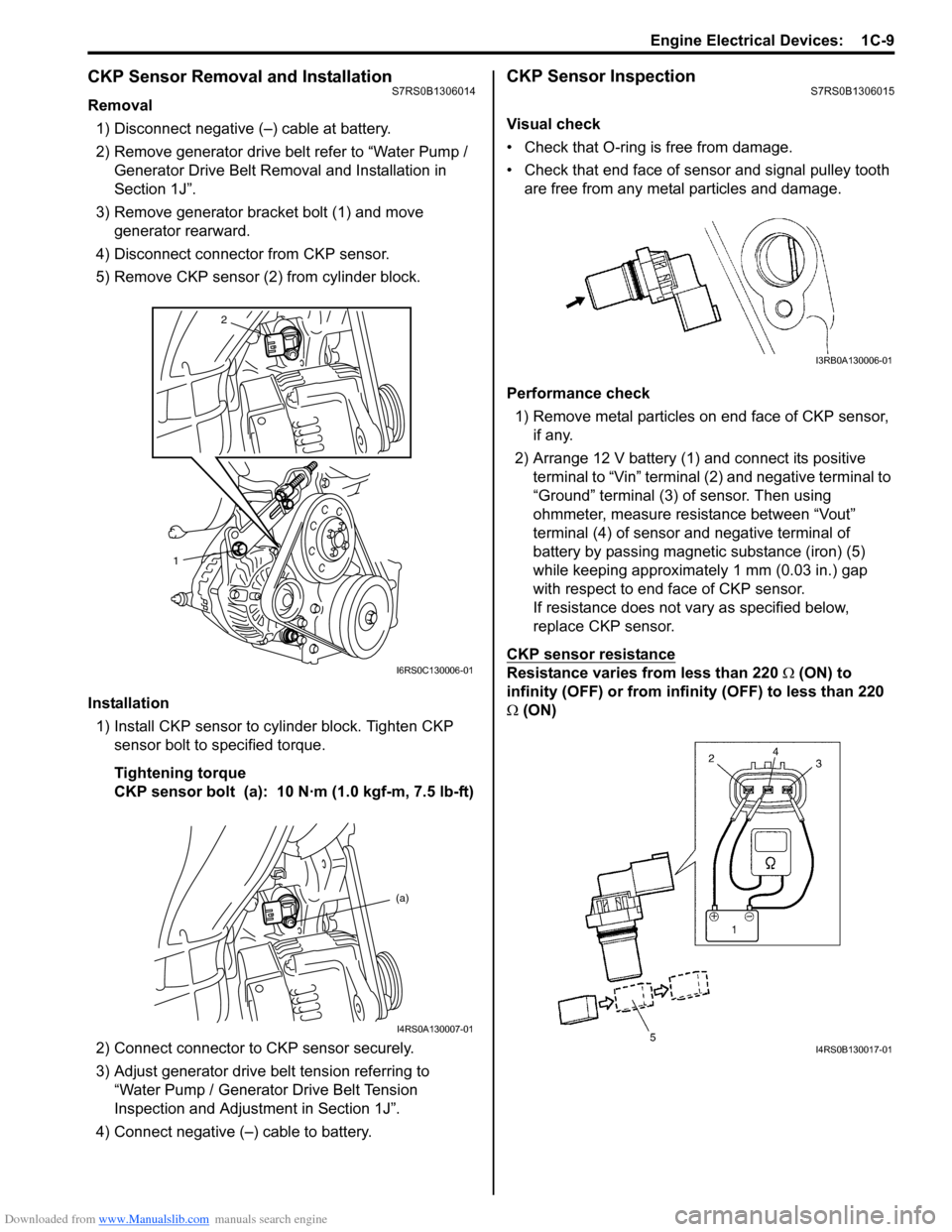
CKP Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306015
Visual check
• Check that O-ring is free from damage.
• Check that end face of sensor and signal pulley tooth are free from any metal particles and damage.
Performance check 1) Remove metal particles on end face of CKP sensor, if any.
2) Arrange 12 V battery (1) and connect its positive terminal to “Vin” terminal (2) and negative terminal to
“Ground” terminal (3) of sensor. Then using
ohmmeter, measure resistance between “Vout”
terminal (4) of sensor and negative terminal of
battery by passing magnetic substance (iron) (5)
while keeping approximately 1 mm (0.03 in.) gap
with respect to end face of CKP sensor.
If resistance does not vary as specified below,
replace CKP sensor.
CKP sensor resistance
Resistance varies from less than 220 Ω (ON) to
infinity (OFF) or from infinity (OFF) to less than 220
Ω (ON)
2
1
I6RS0C130006-01
(a)
I4RS0A130007-01
I3RB0A130006-01
I4RS0B130017-01
Page 283 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-11
MAF and IAT Sensor On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B1306018
NOTE
Before performed this inspection, be sure to
read the “Precautions of ECM Circuit
Inspection in Section 1A”.
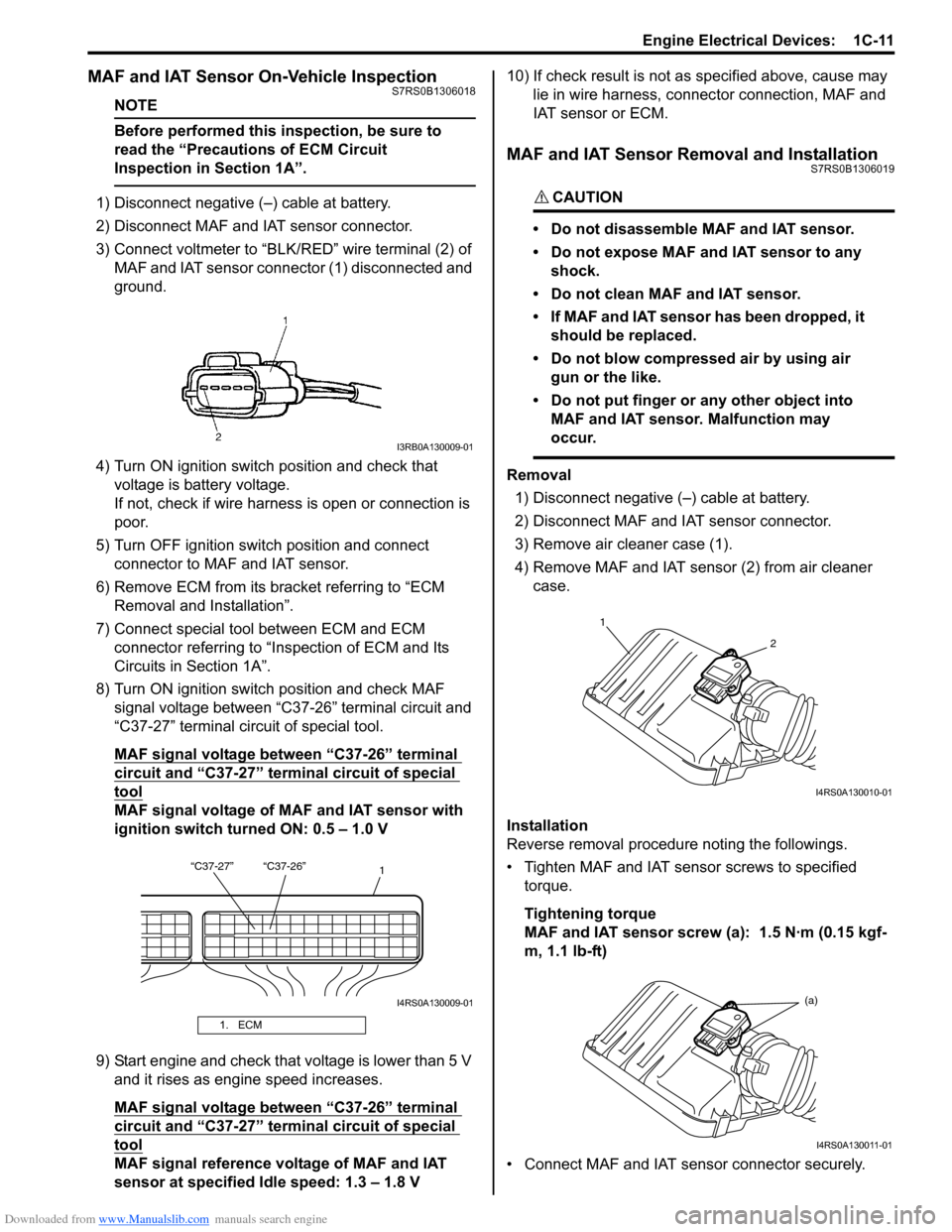
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect MAF and IAT sensor connector.
3) Connect voltmeter to “BLK/RED” wire terminal (2) of
MAF and IAT sensor connector (1) disconnected and
ground.
4) Turn ON ignition switch position and check that voltage is battery voltage.
If not, check if wire harness is open or connection is
poor.
5) Turn OFF ignition switch position and connect connector to MAF and IAT sensor.
6) Remove ECM from its bracket referring to “ECM Removal and Installation”.
7) Connect special tool between ECM and ECM connector referring to “Inspection of ECM and Its
Circuits in Section 1A”.
8) Turn ON ignition switch position and check MAF signal voltage between “C37-26” terminal circuit and
“C37-27” terminal circuit of special tool.
MAF signal voltage between “C37-26” terminal
circuit and “C37-27” termi nal circuit of special
tool
MAF signal voltage of MAF and IAT sensor with
ignition switch turned ON: 0.5 – 1.0 V
9) Start engine and check that voltage is lower than 5 V and it rises as engine speed increases.
MAF signal voltage between “C37-26” terminal
circuit and “C37-27” termi nal circuit of special
tool
MAF signal reference voltage of MAF and IAT
sensor at specified Idle speed: 1.3 – 1.8 V 10) If check result is not as
specified above, cause may
lie in wire harness, connec tor connection, MAF and
IAT sensor or ECM.
MAF and IAT Sensor Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306019
CAUTION!
• Do not disassemble MAF and IAT sensor.
• Do not expose MAF and IAT sensor to any shock.
• Do not clean MAF and IAT sensor.
• If MAF and IAT sensor has been dropped, it should be replaced.
• Do not blow compressed air by using air gun or the like.
• Do not put finger or any other object into MAF and IAT sensor. Malfunction may
occur.
Removal
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect MAF and IAT sensor connector.
3) Remove air cleaner case (1).
4) Remove MAF and IAT sensor (2) from air cleaner case.
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the followings.
• Tighten MAF and IAT sensor screws to specified torque.
Tightening torque
MAF and IAT sensor screw (a): 1.5 N·m (0.15 kgf-
m, 1.1 lb-ft)
• Connect MAF and IAT sensor connector securely.
1. ECM
I3RB0A130009-01
“C37-27” “C37-26” 1
I4RS0A130009-01
1
2
I4RS0A130010-01
(a)
I4RS0A130011-01
Page 287 of 1496
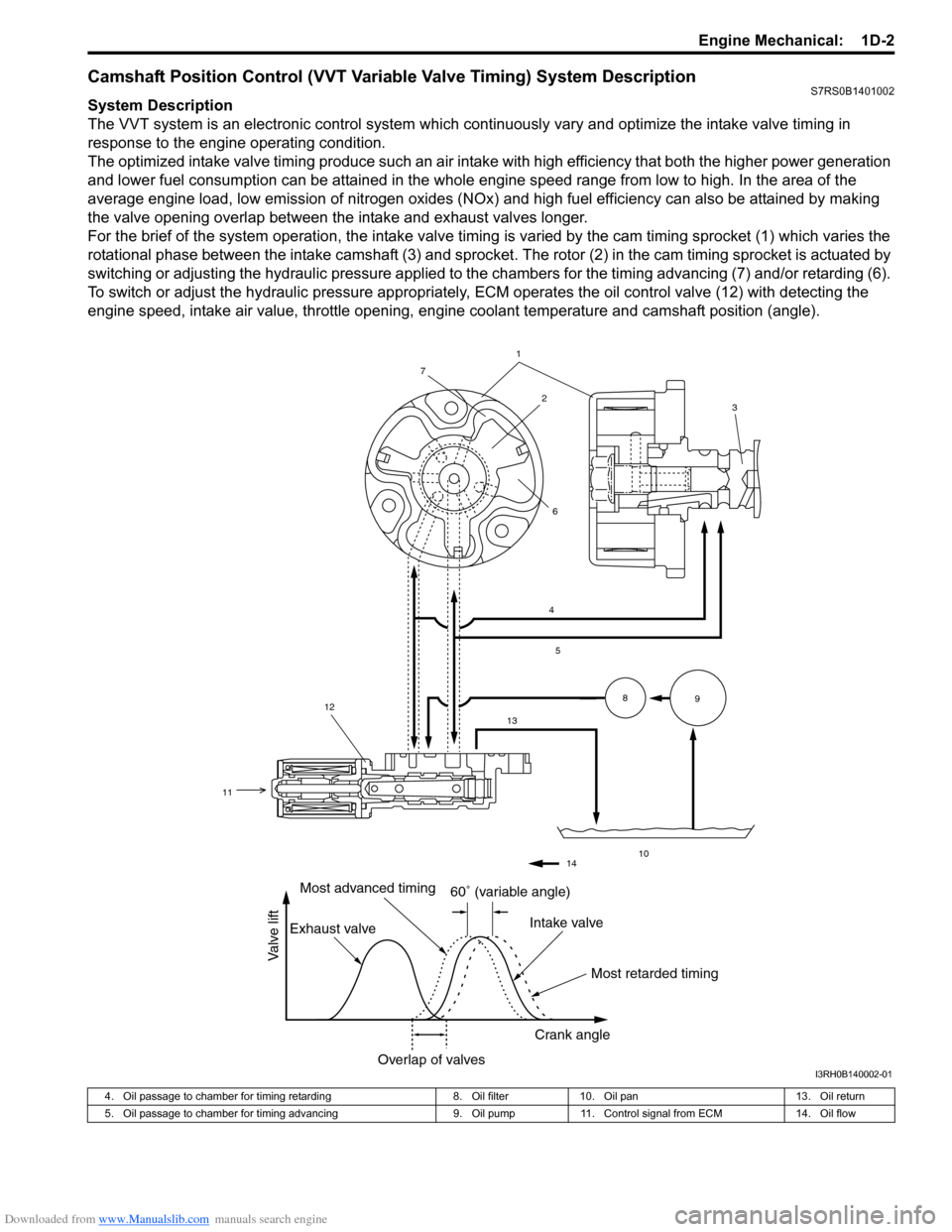
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-2
Camshaft Position Control (VVT Variable Valve Timing) System DescriptionS7RS0B1401002
System Description
The VVT system is an electronic control system which continuously vary and optimize the intake valve timing in
response to the engine operating condition.
The optimized intake valve timing produce such an air intake with high efficiency that both the higher power generation
and lower fuel consumption can be attained in the whole engine speed range from low to high. In the area of the
average engine load, low emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and high fuel efficiency can also be attained by making
the valve opening overlap between the intake and exhaust valves longer.
For the brief of the system operation, the intake valve timing is varied by the cam timing sprocket (1) which varies the
rotational phase between the intake camshaft (3) and sprocket . The rotor (2) in the cam timing sprocket is actuated by
switching or adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied to the chambers for the timing advancing (7) and/or retarding (6).
To switch or adjust the hydraulic pressure appropriately, ECM operates the oil control valve (12) with detecting the
engine speed, intake air value, throttle opening, engine coolant temperature and camshaft position (angle).
1
4
5
13
10
89
2
7
6
12
11
3
14
60� (variable angle)
Most retarded timing
Most advanced timing
Exhaust valve Intake valve
Crank angle
Overlap of valves
Valve lift
I3RH0B140002-01
4. Oil passage to chamber for timing retarding 8. Oil filter10. Oil pan 13. Oil return
5. Oil passage to chamber for timing advancing 9. Oil pump11. Control signal from ECM 14. Oil flow
Page 288 of 1496
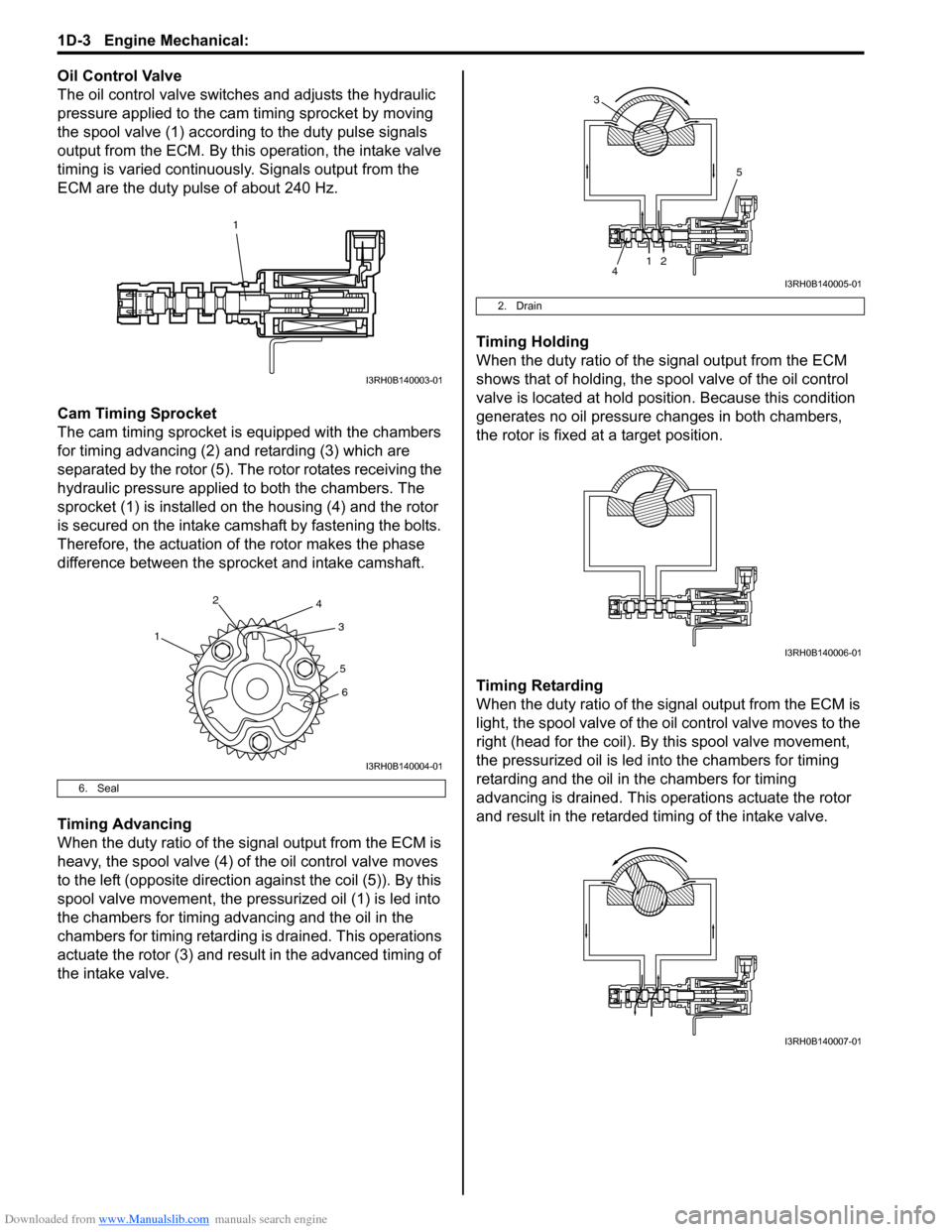
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-3 Engine Mechanical:
Oil Control Valve
The oil control valve switches and adjusts the hydraulic
pressure applied to the cam timing sprocket by moving
the spool valve (1) according to the duty pulse signals
output from the ECM. By this operation, the intake valve
timing is varied continuously. Signals output from the
ECM are the duty pulse of about 240 Hz.
Cam Timing Sprocket
The cam timing sprocket is equipped with the chambers
for timing advancing (2) and retarding (3) which are
separated by the rotor (5). The rotor rotates receiving the
hydraulic pressure applied to both the chambers. The
sprocket (1) is installed on the housing (4) and the rotor
is secured on the intake camshaft by fastening the bolts.
Therefore, the actuation of the rotor makes the phase
difference between the sprocket and intake camshaft.
Timing Advancing
When the duty ratio of the signal output from the ECM is
heavy, the spool valve (4) of the oil control valve moves
to the left (opposite direction against the coil (5)). By this
spool valve movement, the pressurized oil (1) is led into
the chambers for timing advancing and the oil in the
chambers for timing retarding is drained. This operations
actuate the rotor (3) and result in the advanced timing of
the intake valve. Timing Holding
When the duty ratio of the si
gnal output from the ECM
shows that of holding, the sp ool valve of the oil control
valve is located at hold posi tion. Because this condition
generates no oil pressure changes in both chambers,
the rotor is fixed at a target position.
Timing Retarding
When the duty ratio of the sig nal output from the ECM is
light, the spool valve of the o il control valve moves to the
right (head for the coil). By this spool valve movement,
the pressurized oil is led into the chambers for timing
retarding and the oil in the chambers for timing
advancing is drained. This operations actuate the rotor
and result in the retarded timing of the intake valve.
6. Seal
1
I3RH0B140003-01
1 2
3
4
56
I3RH0B140004-01
2. Drain
12
5
4
3
I3RH0B140005-01
I3RH0B140006-01
I3RH0B140007-01
Page 335 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-50
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt deformation
(Plastic deformation tightening bolt)
Measure each thread diameter of connecting rod
bearing cap bolt (1) at “A” on 32 mm (1.25 in.) from bolt
mounting surface and “B” on 40 mm (1.57 in.) from bolt
mounting surface by using a micrometer (2).
Calculate difference in diameters (“A” – “B”). If it is
exceeds limit, replace connecting rod bearing cap bolt
(1).
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt measurement
points
“a”: 25 mm (0.98 in.)
“b”: 40 mm (1.57 in.)
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt diameter difference
Limit (“A” – “B”): 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
Crank Pin and Connecting Rod Bearings
Inspection
S7RS0B1406034
Crank Pin Diameter
Inspect crank pin for uneven wear or damage. Measure
crank pin for out-of-round or taper with a micrometer. If
crank pin is damaged or out-of round or taper is out of
limit, replace crankshaft or regrind crank pin to undersize
and use undersize bearing.
Crank pin diameter
Out-of-round
A – B
Ta p e r
a – b
Crank pin taper and out-of-round
Limit: 0.01 mm (0.0004 in.)
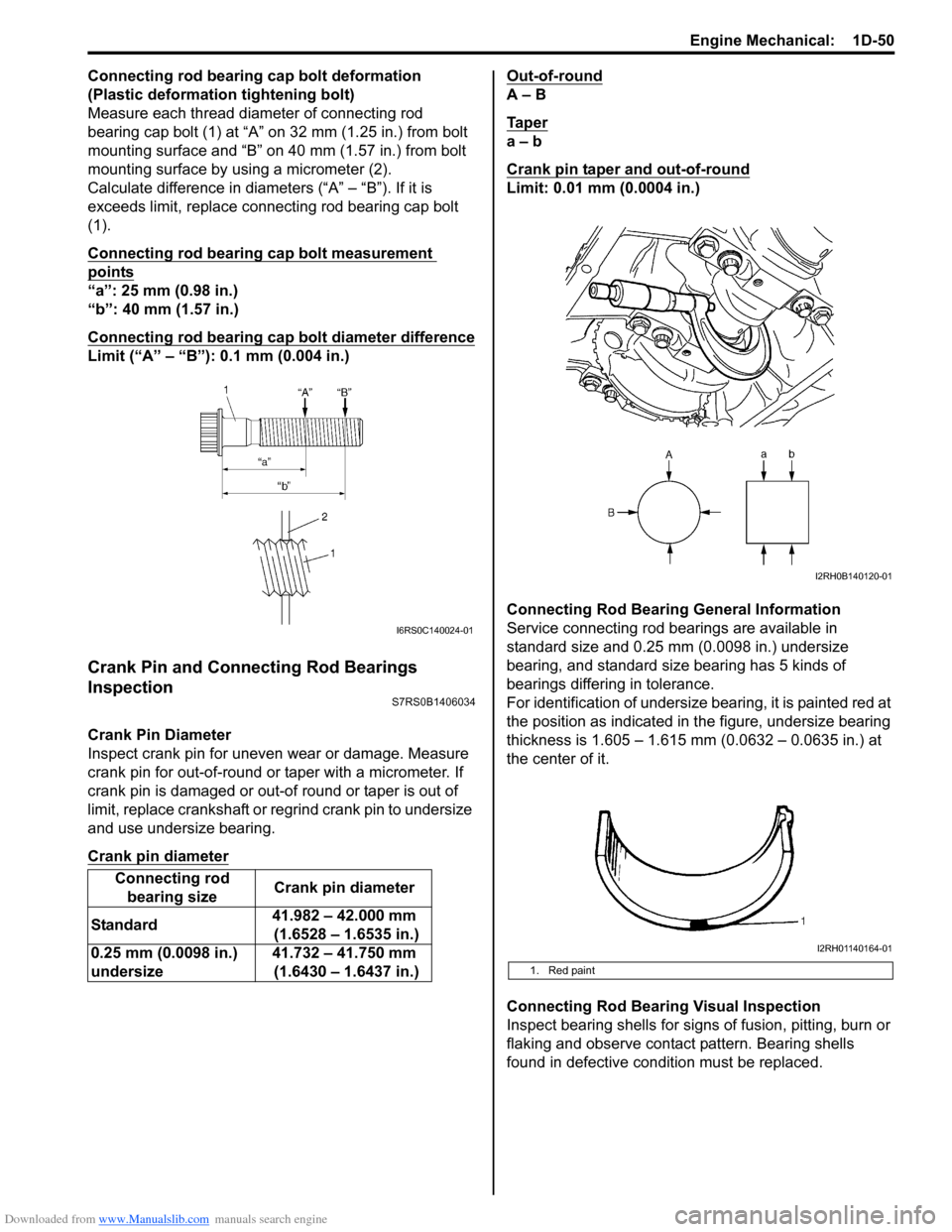
Connecting Rod Bearing General Information
Service connecting rod be arings are available in
standard size and 0.25 mm (0.0098 in.) undersize
bearing, and standard size bearing has 5 kinds of
bearings differing in tolerance.
For identification of undersize bearing, it is painted red at
the position as indicated in the figure, undersize bearing
thickness is 1.605 – 1.615 mm (0.0632 – 0.0635 in.) at
the center of it.
Connecting Rod Bearing Visual Inspection
Inspect bearing shells for signs of fusion, pitting, burn or
flaking and observe contact pattern. Bearing shells
found in defective condition must be replaced.
Connecting rod
bearing size Crank pin diameter
Standard 41.982 – 42.000 mm
(1.6528 – 1.6535 in.)
0.25 mm (0.0098 in.)
undersize 41.732 – 41.750 mm
(1.6430 – 1.6437 in.)
I6RS0C140024-01
1. Red paint
I2RH0B140120-01
I2RH01140164-01