2006 FORD TRANSIT load capacity
[x] Cancel search: load capacityPage 4 of 234

3.7Exhaust System..........................86
3.7.1Extensions and Optional Exhausts....
86
3.7.2Exhaust Pipes and Supports.............86
3.7.3Exhaust Heat Shields..........................86
3.8Fuel System.................................88
4 Electrical
4.1Communications Network..........90
4.1.1CAN-Bus System Description and
Interface................................................90
4.1.2Central Junction Box (CJB)................91
4.1.3Circuit Diagram....................................93
4.2Module Communications
Network—Specifications.............94
4.2.1Circit Diagram......................................94
4.3Charging System.........................95
4.3.1General Information and Specific
Warnings...............................................95
4.3.2Power Management Settings...........95
4.3.3Electrical Conversions........................95
4.3.4Fitting of Equipment Containing an
Electric Motor.......................................97
4.3.5Vehicle Electrical Capacity -
Alternator..............................................97
4.3.6Charge Balance Guidelines...............97
4.3.7Circuit Diagrams..................................97
4.4Battery and Cables.....................98
4.4.1Battery Information.............................98
4.4.2Generator and Alternator.................103
4.5Climate Control System.............106
4.6Instrument Cluster.....................107
4.7Horn...........................................108
4.8Tachograph................................109
4.8.1Legislation...........................................109
4.8.2Tachograph Mounting.......................110
4.9Information and Entertainment
System - General
Information—Specifications.......112
4.9.1Radio Connector................................112
4.9.2Possible Accessories.........................113
4.10Cellular Phone............................115
4.11Exterior Lighting.........................116
4.11.1Reversing Lamps...............................116
4.11.2Additional External Lamps................116
4.11.3Lamps – Hazard / Direction
Indication..............................................117
4.11.4Lamps – Front and Rear Fog Lights....
117
4.11.5Lamps for Wide Vehicles...................117
4.11.6Electrically operated Door Mirrors....
117
4.12Interior Lighting..........................118
4.12.1Additional Internal Lamps .................118
4.12.2Additional 'Theatre Lighting' for rear
of vehicle interior................................118
4.13Fuses and Relays.......................119
4.13.1Wiring Specification............................119
4.13.2Auxiliary Fuses, Fuse Box and Relays
(Fuses - Standard).............................119
4.13.3Customer Connection Points..........120
4.13.4Special Vehicle Option Auxiliary Fuse
Box........................................................121
4.13.5Additional Ignition, Instrument Panel
Illumination and Air Conditioning On
Signals.................................................124
4.13.6Relays and Switches.........................127
4.13.7Windscreen wipers...........................130
4.14Special Conversions..................131
4.14.1Vehicle Speed Output (Signal).........131
4.14.2Engine Run Signal (D+ Alternative)....
132
4.14.3Connectors.........................................133
4.14.4Installation and Routing Guides.......134
4.14.5Electrics for Tow bar.........................136
4.14.6Ground Points....................................140
4.14.7Special Vehicle Options (SVO) and
Aftermarket Kits.................................146
4.14.8Additional Vehicle Signals / Features..
147
4.14.9Engine RPM (Revs Per Minute) Speed
Controller.............................................157
4.14.10Adding Connectors, Terminals and
Wiring...................................................162
5 Body and Paint
5.1Body...........................................175
5.1.1Body Structures - General
Information..........................................175
5.1.2Back Panel Removal.........................177
5.1.3Integrated Bodies and Conversions...
177
5.1.4Chassis Cab........................................179
5.1.5Cab Van Floor.....................................185
5.1.6Hydraulic Lifting Equipment for Van,
Bus, Kombi and Chassis Cab..........186
5.1.7Partitions (Bulkhead) - Driver and
Front Passenger(s) Protection on Van,
Bus and Kombi..................................192
5.1.8Racking Systems...............................194
5.1.9Front End Integrity for Cooling, Crash,
Aerodynamics and Lighting.............198
5.1.10Tipper Bodies.....................................199
5.1.11Tank and Dry Bulk Carriers...............199
5.2Body System - General
Information—Specifications......200
5.2.1Van Floor - Load Compartment Tie
Downs for Van ,Bus and Kombi.....200
5.3Body Closures..........................203
5.3.1Load Compartment Interior Lining....
203
5.3.2Security, Anti Theft and Locking
System Security ...............................203
5.4Rear View Mirrors.....................208
5.4.1Mirrors for Wide Vehicles.................208
5.5Seats.........................................209
5.5.1Rear Seat Fixings Positions - Kombi...
209
5.5.2Heated Seats.....................................210
5.6Glass, Frames and Mechanisms...
211
5.6.1Rear Windows....................................211
Table of Contents
4
Page 36 of 234
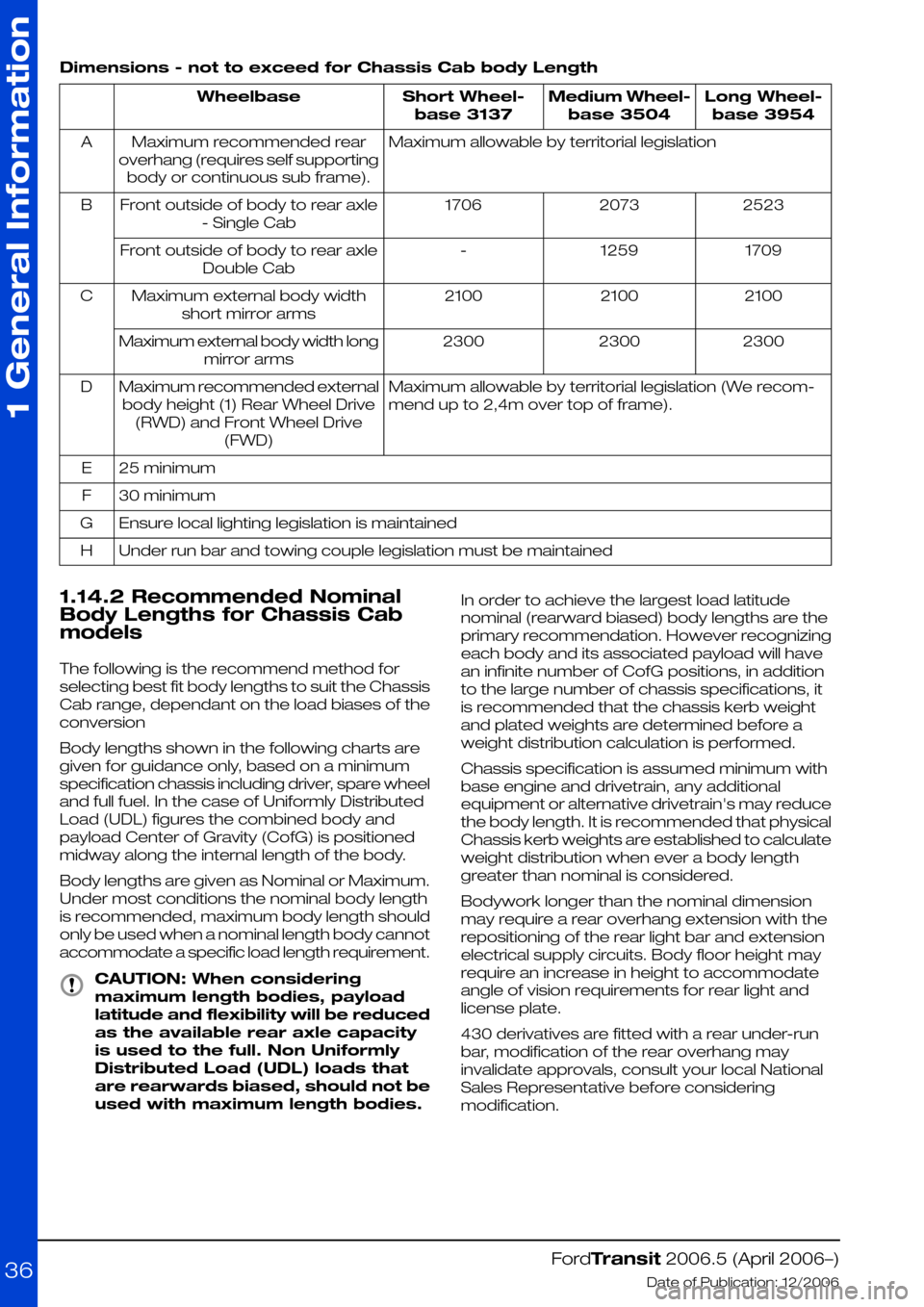
Dimensions - not to exceed for Chassis Cab body Length
Long Wheel-
base 3954
Medium Wheel-
base 3504
Short Wheel-
base 3137
Wheelbase
Maximum allowable by territorial legislationMaximum recommended rear
overhang (requires self supporting
body or continuous sub frame).
A
252320731706Front outside of body to rear axle
- Single Cab
B
17091259-Front outside of body to rear axle
Double Cab
210021002100Maximum external body width
short mirror arms
C
230023002300Maximum external body width long
mirror arms
Maximum allowable by territorial legislation (We recom-
mend up to 2,4m over top of frame).
Maximum recommended external
body height (1) Rear Wheel Drive
(RWD) and Front Wheel Drive
(FWD)
D
25 minimumE
30 minimumF
Ensure local lighting legislation is maintainedG
Under run bar and towing couple legislation must be maintainedH
1.14.2 Recommended Nominal
Body Lengths for Chassis Cab
models
The following is the recommend method for
selecting best fit body lengths to suit the Chassis
Cab range, dependant on the load biases of the
conversion
Body lengths shown in the following charts are
given for guidance only, based on a minimum
specification chassis including driver, spare wheel
and full fuel. In the case of Uniformly Distributed
Load (UDL) figures the combined body and
payload Center of Gravity (CofG) is positioned
midway along the internal length of the body.
Body lengths are given as Nominal or Maximum.
Under most conditions the nominal body length
is recommended, maximum body length should
only be used when a nominal length body cannot
accommodate a specific load length requirement.
CAUTION: When considering
maximum length bodies, payload
latitude and flexibility will be reduced
as the available rear axle capacity
is used to the full. Non Uniformly
Distributed Load (UDL) loads that
are rearwards biased, should not be
used with maximum length bodies.
In order to achieve the largest load latitude
nominal (rearward biased) body lengths are the
primary recommendation. However recognizing
each body and its associated payload will have
an infinite number of CofG positions, in addition
to the large number of chassis specifications, it
is recommended that the chassis kerb weight
and plated weights are determined before a
weight distribution calculation is performed.
Chassis specification is assumed minimum with
base engine and drivetrain, any additional
equipment or alternative drivetrain's may reduce
the body length. It is recommended that physical
Chassis kerb weights are established to calculate
weight distribution when ever a body length
greater than nominal is considered.
Bodywork longer than the nominal dimension
may require a rear overhang extension with the
repositioning of the rear light bar and extension
electrical supply circuits. Body floor height may
require an increase in height to accommodate
angle of vision requirements for rear light and
license plate.
430 derivatives are fitted with a rear under-run
bar, modification of the rear overhang may
invalidate approvals, consult your local National
Sales Representative before considering
modification.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
1 General Information
36
Page 95 of 234

4.3 Charging System
4.3.1 General Information and
Specific Warnings
The Transit electrical system is a 12-Volt supply
with a negative earth return. The alternator and
battery equipment used as standard are
designed for normal operations with the type of
engine fitted. Higher capacity batteries are
available as standard production options and
special vehicle options. Before installing additional
electrical equipment check that the battery
capacity, harness load capability, and alternator
output are suitable for the extra load.
The battery capacity and charge available from
the alternator must be adequate to ensure
engine cranking in unfavorable climatic conditions
but excessive battery capacity could damage
the starter motor.
The Transit utilizes multiplexed vehicle electronics
- it is recommended that the appropriate Ford
proprietary accessory systems are used.
Inappropriate or incorrect connection of
additional equipment could cause mis-operation,
or damage to the vehicle, and so invalidate any
warranty.
Additional connection points are provided
specifically for customer use (except M1 and M2
Bus), and are located on the outside of the
driver's seat base.
Do not jump-start the vehicle directly from the
battery. Use designated jump-start points. Refer
to the owners literature.
4.3.2 Power Management
Settings
There are four Power Management Settings
available:
•Factory
•Transport
•Normal
•Crash
Factory and Transport modes are only active
with ignition off; with ignition on, the vehicle
operates with full functionality. When in Transport
mode, the interior lights, clocks, and power
locking and alarms (where fitted) do not work.
It is possible to switch from Transport Mode to
Normal Mode without the use of any ancillary
equipment, but not vice versa. To change mode,
the brake pedal must be depressed five times,
and the hazard warning switch operated twice
(in any combination) within 10 seconds.
WARNING: It is not possible to return
the transport setting without using
the vehicle's diagnostics.
At the end of production, the vehicle is
configured to the transport setting to minimize
power consumption. As part of the Pre Delivery
Inspection process at the Ford dealership, the
vehicle is reconfigured to normal operation.
4.3.3 Electrical Conversions
Operator requirements for additional and
specialised electrical equipment varies. The
vehicle converter/modifier must, therefore,
consider the following points when designing the
installation:
•Legality and regulatory conformity of the base
vehicle.
•Drive-ability and serviceability of the base
vehicle.
•The effect of regulations governing the
proposed conversion including National
Legislation in the country of sale.
•The method of integrating the circuit into the
base vehicle.
•No additional circuits are to be run alongside
the electrical circuits (shown in blue in the
figure below) associated with the
Management System (shown in green in the
figure below), due to the possible Electro
Motive Force (EMF) effect on the circuits.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
95
Page 98 of 234

4.4 Battery and Cables
4.4.1 Battery Information
In order to protect the battery system from direct
ground shorts, a special fuse is incorporated into
the battery positive feed, in the pre-fuse box
under the driver’s seat.
This fuse is not repairable – use only a Ford
replacement part.
Where extra batteries are required on vehicles
with a single battery installation, the battery
disconnect switch (split charge relay) and
associated wiring/hardware — fitted as standard
to vehicles equipped with dual batteries — can
be added.
Batteries – Additional – Heavy Duty
High current consumption may require a
heavy-duty battery or an additional battery.
Factory fitted Special Vehicle Options are available
for heavy-duty and/or extra batteries with the
battery disconnect switch (split charge relay).
The batteries can be retrofitted.
See diagram E74522 - Battery disconnect switch
(split charge relay) circuit.
Deep Cycle Battery (not for use as
primary, start-relevant battery)
A Special Vehicle Option is available. Please
contact your local National Sales Company
representative for availability and details.
•The deep cycle battery is used in conjunction
with the battery disconnect switch (split charge
relay) in applications where power to ancillary
circuits would heavily discharge the main
vehicle battery(s).
•Installation should be under the driver's seat.
When the deep cycle battery is installed, the
battery disconnect switch (split charge relay)
must be used.
•When the Deep Cycle Battery is installed it is
recommended that the Special Vehicle Option
auxiliary fuse box is fed from the customer
connection points.
Battery Part Numbers and Usage
SizeQuantityTypeBattery Part Number
Single Battery Installation Front Wheel Drive
T71680 CCA (70Ah @20 hour rate)98AB-10655-D_ (Turkey)
T71700 CCA (80Ah @20 hour rate)6G9N 10655 P_ (Southampton)
Dual Battery Installation Rear Wheel Drive and Front Wheel Drive with specific options
T62590 CCA (60Ah @20 hour rate)98AB-10655-C_ (Turkey)
T62590 CCA (60Ah @20 hour rate)6G9N 10655 N_ (Southampton)
Dual Battery Installation Rear Wheel Drive -29°C Territories
T72680 CCA (70Ah @20 hour rate)98AB-10655-D_ (Turkey)
T72700 CCA (80Ah @20 hour rate)6G9N 10655 P_ (Southampton)
Deep Cycle Battery
H82(90Ah @20 hour rate;70Ah@5 hour rate)V3C15-10655-A_
Battery Rules:
•Batteries in parallel must be of the same type
and capacity.
•Starter and deep cycle batteries may only be
mixed through an isolator.
•For External charging of batteries ensure that
the maximum voltage of 14.6V is not
exceeded.
NOTE: Deep cycle batteries can be drained but
high loads can damage them. Always observe
circuit set-up outlined in diagram E74522 -
Battery disconnect switch (split charge relay).
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
4 Electrical
98
Page 191 of 234

•Sub-frame ends must be relieved at forward
end to minimize local contact stress
concentrations, see Figure E74575.
Refer to: 5.11 Frame and Body Mounting (page
222).
(However it is recommended to mount the
longitudinal onto the mounting brackets with
a clearance to the chassis frame top surface).
•Stiff sub-frames, for example closed section
Longitudinal rigidly connected with similar
section cross members, may damage the
chassis frame by preventing its natural flexing.
Therefore compliant mounts should be used
with up to plus and minus (+/-) 12mm
compliance, vehicle laden or un-laden
which-ever is worst case, rated at 2.0mm
deflection minimum per 200kg mass at each
chassis frame forward mount, please refer to
Figure E74696 for example of compliant
mount and Figure E75880 for location.
•Each set of brackets must use two (2) x M10
bolts grade 8.8 minimum
•For safety device on outriggers/legs please
refer to Van, Kombi and Bus
Hydraulic tail lift
DescriptionItem
1000mmA
It is recommended to fix lift framework on bottom
and on top side by using reinforcing plates and
through bolts. It is also recommended to design
and/or locate the reinforcing plates in a way that
load can be routed into adjacent reinforced body
structure. If mounted at rear door symmetrical
to the vehicle center line load capacity is up to
1000kg at 1000mm from floor edge to center of
load.
If mounted asymmetrical to the vehicle center
line or if mounted at side load door load capacity
is up to 500kg at 1000mm from floor edge to
center of load. For pillar lifts with adjustable reach
swing jib fixed only to one rear door pillar load
capacity is reduced to 100kg at maximum
1000mm reach.
For load conditions as described above additional
stabilizing equipment is not necessary. Hydraulic
under-slung tail lifts are not recommended for
Transit Van, bus and Kombi.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
191E75918A
Page 192 of 234

For Chassis Cab with tail lift design as described
above it is recommended to use unique body
sub-frame for fixing to Chassis Cab structure. For
connection between sub-frame Chassis Cab
body structure please refer to Figure E74696.
For Chassis Cab with under-slung tail lift load
capacity is up to 1000kg at 1000mm from rear
end of chassis frame to center of load if mounted
and functioning on centre line of vehicle. If
mounted and functioning off center line or at the
side of the vehicle load capacity is reduced to
500kg at 1000mm from side/rear end to center
of load.
Greater off-sets and/or loads require additional
stabilizing equipment such as outriggers or
ground jacks. It is recommended not to increase
vehicle body stress over limit as given by load
factors above. If uncertain please consult your
local national sales representative or the Vehicle
Converter Advisory Service [email protected].
It is the Vehicle converters responsibility to fit a
decal to the converted vehicle stating that the
equipment must not be used without
outriggers/ground jacks in operating position. It
is also the vehicle converters responsibility to
guarantee safe functioning of the equipment.
For hydraulic tail lifts as used for general loading
or more specialized for wheel-chair lifts please
refer to Figure E75874.
5.1.7 Partitions (Bulkhead) - Driver
and Front Passenger(s)
Protection on Van, Bus and Kombi
The following two figures show the standard
bulkhead fixing locations on B-pillar. These are
hexagonal holes for M6 thin sheet rivet type nuts.
The standard range of Ford Regular Production
Option bulkheads can be retro-fitted at these
points.
Conversely a Ford Regular Production Option
bulkheads can also be removed.
Ford Regular Production Option bulkheads do
have a clearance between bulkhead and body
structure to allow natural body flexing and an air
circulation from the cab to the rear load space
for ventilation control.
Air circulation and body flexing must be also given
consideration when engineering an alternative
bulkhead. It is not recommended to restrict
driver’s or passengers’s seat adjustment travel.
It is the vehicle converter’s responsibility to ensure
local current legislation, governing bulkheads and
protective window grilles, is met. It is also the
converter’s responsibility to ensure legal load
constraint requirements if using a non Ford
Regular Production Option bulkhead.
Low Roof Bulkhead Fixing Holes
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
192E75919
Page 232 of 234

Special Vehicle Options (SVO) and Aftermarket
Kits....................................................................146
Springs and Spring Mounting....................58, 59
Suspension System...........................................57
T
Tachograph Mounting......................................110
Tachograph.......................................................109
Tank and Dry Bulk Carriers..............................199
Terminology...........................................................7
Tipper Bodies....................................................199
Tire Manufacturers.............................................60
Towing Requirements.......................................54
Towing..................................................................54
U
Under Body Protection and Material.............221
V
Van Floor - Load Compartment Tie Downs for
Van ,Bus and Kombi......................................200
Vehicle Duty Cycle Guidelines..........................25
Vehicle Electrical Capacity - Alternator...........97
Vehicle Ride and Handling Attributes..............25
Vehicle Speed Output (Signal)........................131
Vehicle Transportation Aids and Vehicle
Storage..............................................................32
W
Warnings, Cautions and Notes in This Manual..
6
Warranty on Ford Vehicles..................................7
Wheel Clearance................................................60
Wheels and Tires................................................60
Windscreen wipers..........................................130
Wiring Specification...........................................119
Index
232