2005 SUZUKI SWIFT spec
[x] Cancel search: specPage 325 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-40
Valves and Valve Guides InspectionS7RS0B1406026
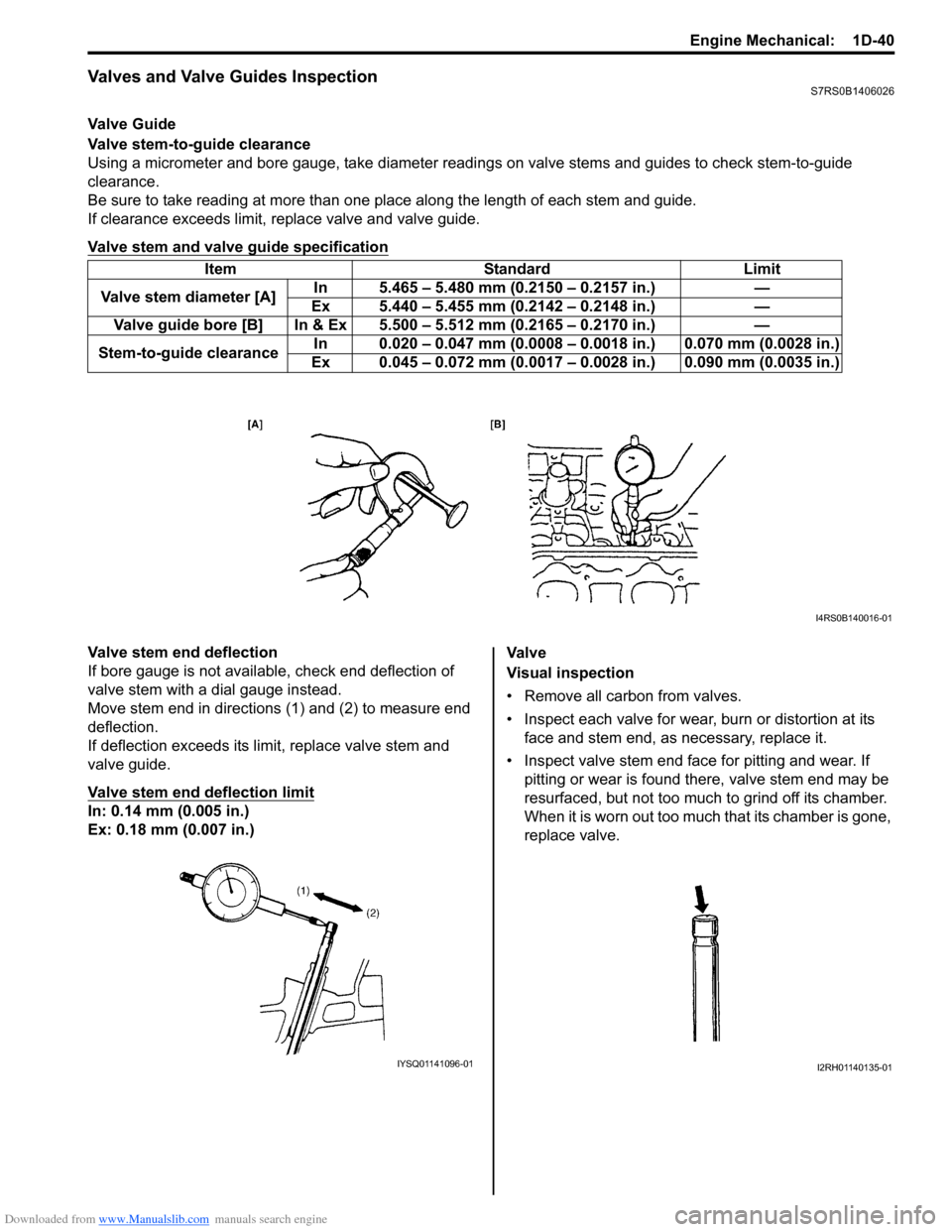
Valve Guide
Valve stem-to-guide clearance
Using a micrometer and bore gauge, take diameter readings on valve stems and guides to check stem-to-guide
clearance.
Be sure to take reading at more than one place along the length of each stem and guide.
If clearance exceeds limit, replace valve and valve guide.
Valve stem and valve guide specification
Valve stem end deflection
If bore gauge is not available, check end deflection of
valve stem with a dial gauge instead.
Move stem end in directions (1) and (2) to measure end
deflection.
If deflection exceeds its limit, replace valve stem and
valve guide.
Valve stem end deflection limit
In: 0.14 mm (0.005 in.)
Ex: 0.18 mm (0.007 in.) Va l v e
Visual inspection
• Remove all carbon from valves.
• Inspect each valve for wear, burn or distortion at its
face and stem end, as necessary, replace it.
• Inspect valve stem end face for pitting and wear. If pitting or wear is found there, valve stem end may be
resurfaced, but not too much to grind off its chamber.
When it is worn out too much that its chamber is gone,
replace valve.
Item Standard Limit
Valve stem diameter [A] In 5.465 – 5.480 mm (0.2150 – 0.2157 in.) —
Ex 5.440 – 5.455 mm (0.2142 – 0.2148 in.) —
Valve guide bore [B] In & Ex 5.500 – 5.512 mm (0.2165 – 0.2170 in.) —
Stem-to-guide clearance In 0.020 – 0.047 mm (0.0008 – 0.
0018 in.) 0.070 mm (0.0028 in.)
Ex 0.045 – 0.072 mm (0.0017 – 0. 0028 in.) 0.090 mm (0.0035 in.)
I4RS0B140016-01
IYSQ01141096-01I2RH01140135-01
Page 326 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-41 Engine Mechanical:
Valve head radial runout
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and
“V” block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping)
must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551
in.)Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing
a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
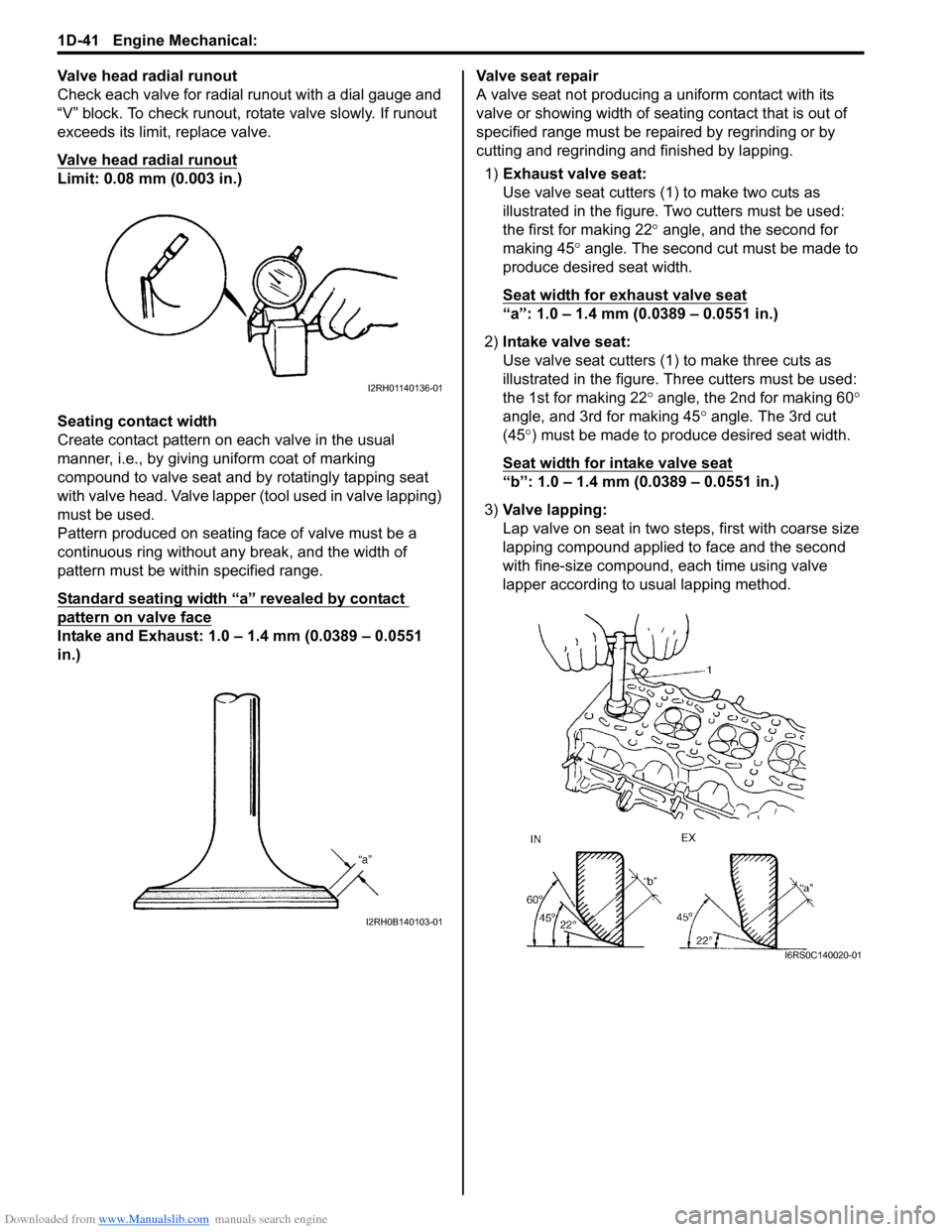
1) Exhaust valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1 ) to make two cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Two cutters must be used:
the first for making 22 ° angle, and the second for
making 45 ° angle. The second cut must be made to
produce desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
2) Intake valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Th ree cutters must be used:
the 1st for making 22 ° angle, the 2nd for making 60 °
angle, and 3rd for making 45 ° angle. The 3rd cut
(45 °) must be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
3) Valve lapping:
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse size
lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve
lapper according to usual lapping method.
I2RH01140136-01
I2RH0B140103-01
I6RS0C140020-01
Page 327 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-42
Cylinder Head InspectionS7RS0B1406027
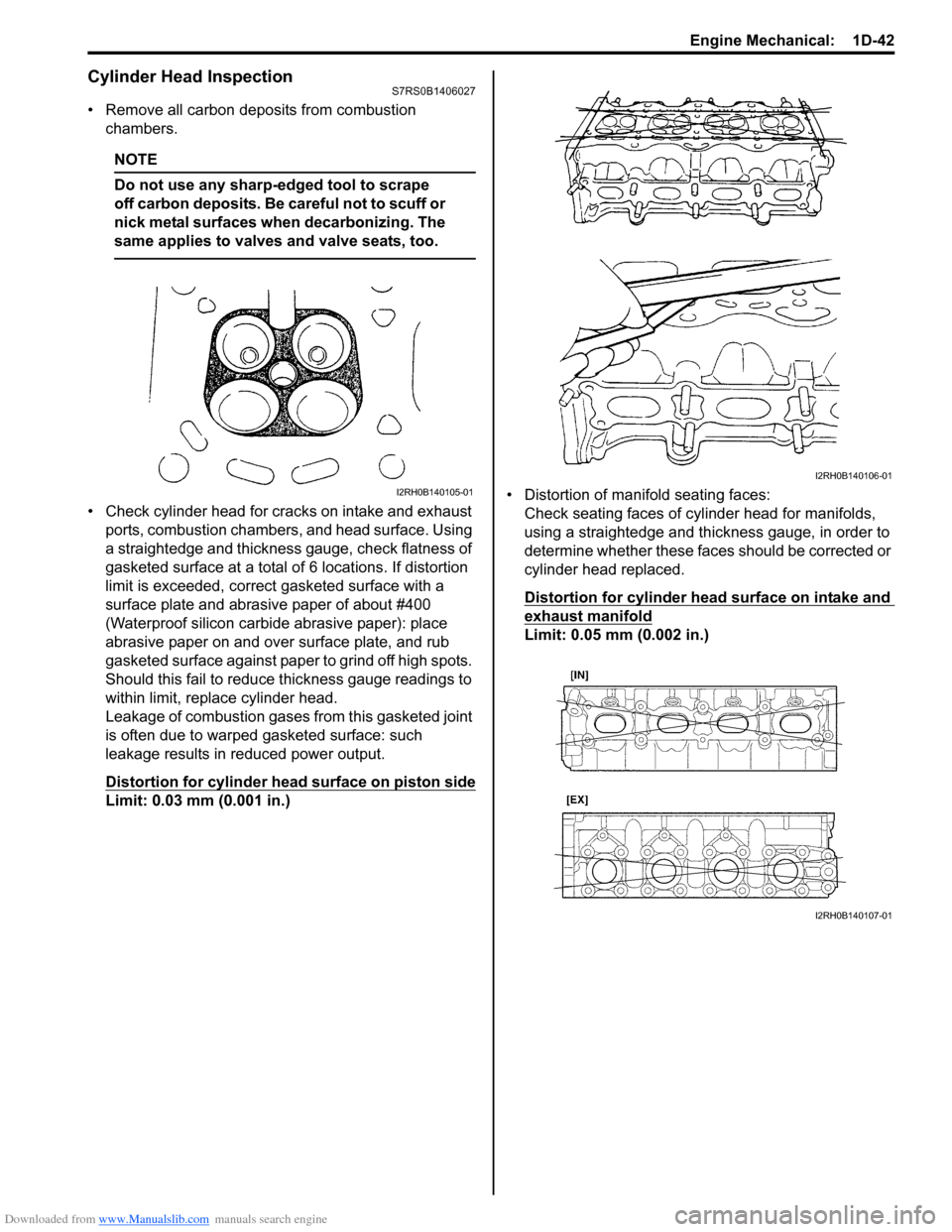
• Remove all carbon deposits from combustion chambers.
NOTE
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to scrape
off carbon deposits. Be careful not to scuff or
nick metal surfaces when decarbonizing. The
same applies to valves and valve seats, too.
• Check cylinder head for cracks on intake and exhaust ports, combustion chambers, and head surface. Using
a straightedge and thickness gauge, check flatness of
gasketed surface at a total of 6 locations. If distortion
limit is exceeded, correct gasketed surface with a
surface plate and abrasive paper of about #400
(Waterproof silicon carbide abrasive paper): place
abrasive paper on and over surface plate, and rub
gasketed surface against paper to grind off high spots.
Should this fail to reduce thickness gauge readings to
within limit, replace cylinder head.
Leakage of combustion gases from this gasketed joint
is often due to warped gasketed surface: such
leakage results in reduced power output.
Distortion for cylinder head surface on piston side
Limit: 0.03 mm (0.001 in.) • Distortion of manifold seating faces:
Check seating faces of cylinder head for manifolds,
using a straightedge and thickness gauge, in order to
determine whether these faces should be corrected or
cylinder head replaced.
Distortion for cylinder head surface on intake and
exhaust manifold
Limit: 0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
I2RH0B140105-01
I2RH0B140106-01
I2RH0B140107-01
Page 328 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-43 Engine Mechanical:
Valve Spring InspectionS7RS0B1406028
Valve Spring Free Length and Preload
Referring to data, check to be sure that each spring is in
sound condition, free of any evidence of breakage or
weakening. Remember, weakened valve springs can
cause chatter, not to mention possibility of reducing
power output due to gas leakage caused by decreased
seating pressure.
Valve spring free length
Standard: 39.37 mm (1.550 in.)
Limit: 36.49 mm (1.437 in.)
Valve spring preload
Standard: 161– 185 N (16.1 – 18.5 kg)
(35.4 – 40.7 lb / 1.240 in.)
Limit: 159 N (15.9 kg) for 31.50 mm (35.1 lb / 1.240 in.) Spring Squareness
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring for
squareness in terms of clearance between end of valve
spring and square. Valve springs found to exhibit a
larger clearance than limit must be replaced.
Valve spring squareness
Limit: 1.7 mm (0.067 in.)
I2RH01140143-01
I2RH01140144-01
Page 329 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-44
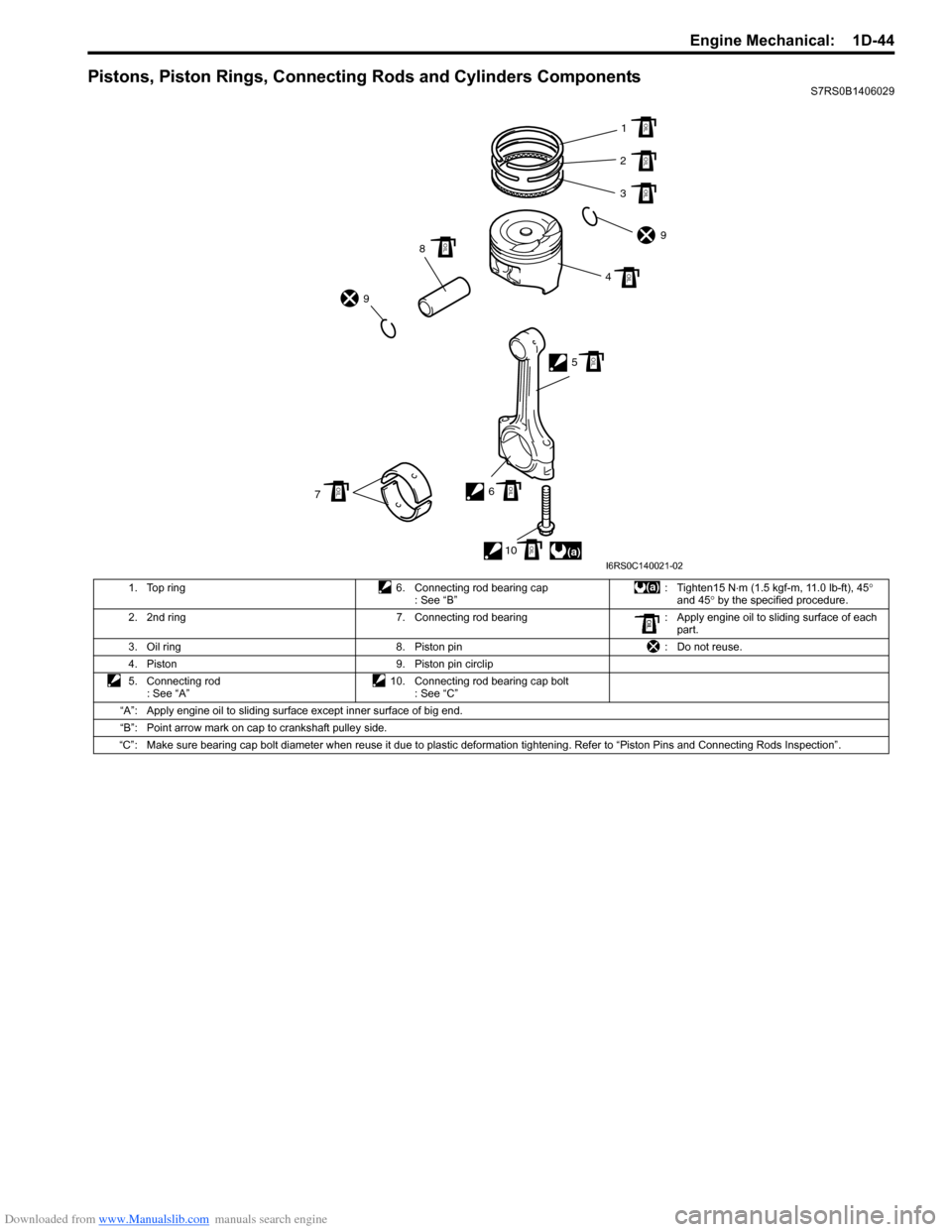
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and Cylinders ComponentsS7RS0B1406029
1. Top ring 6. Connecting rod bearing cap : See “B”: Tighten15 N
⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft), 45 °
and 45 ° by the specified procedure.
2. 2nd ring 7. Connecting rod bearing : Apply engine oil to sliding surface of each
part.
3. Oil ring 8. Piston pin : Do not reuse.
4. Piston 9. Piston pin circlip
5. Connecting rod : See “A” 10. Connecting rod bearing cap bolt
: See “C”
“A”: Apply engine oil to sliding surface except inner surface of big end.
“B”: Point arrow mark on cap to crankshaft pulley side.
“C”: Make sure bearing cap bolt diameter when reuse it due to plastic deformation tightening. Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecti ng Rods Inspection”.
(a)1
2
3
9
4
5
6 10
7 8
9
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
OIL
I6RS0C140021-02
Page 330 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-45 Engine Mechanical:
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Removal and Installation
S7RS0B1406030
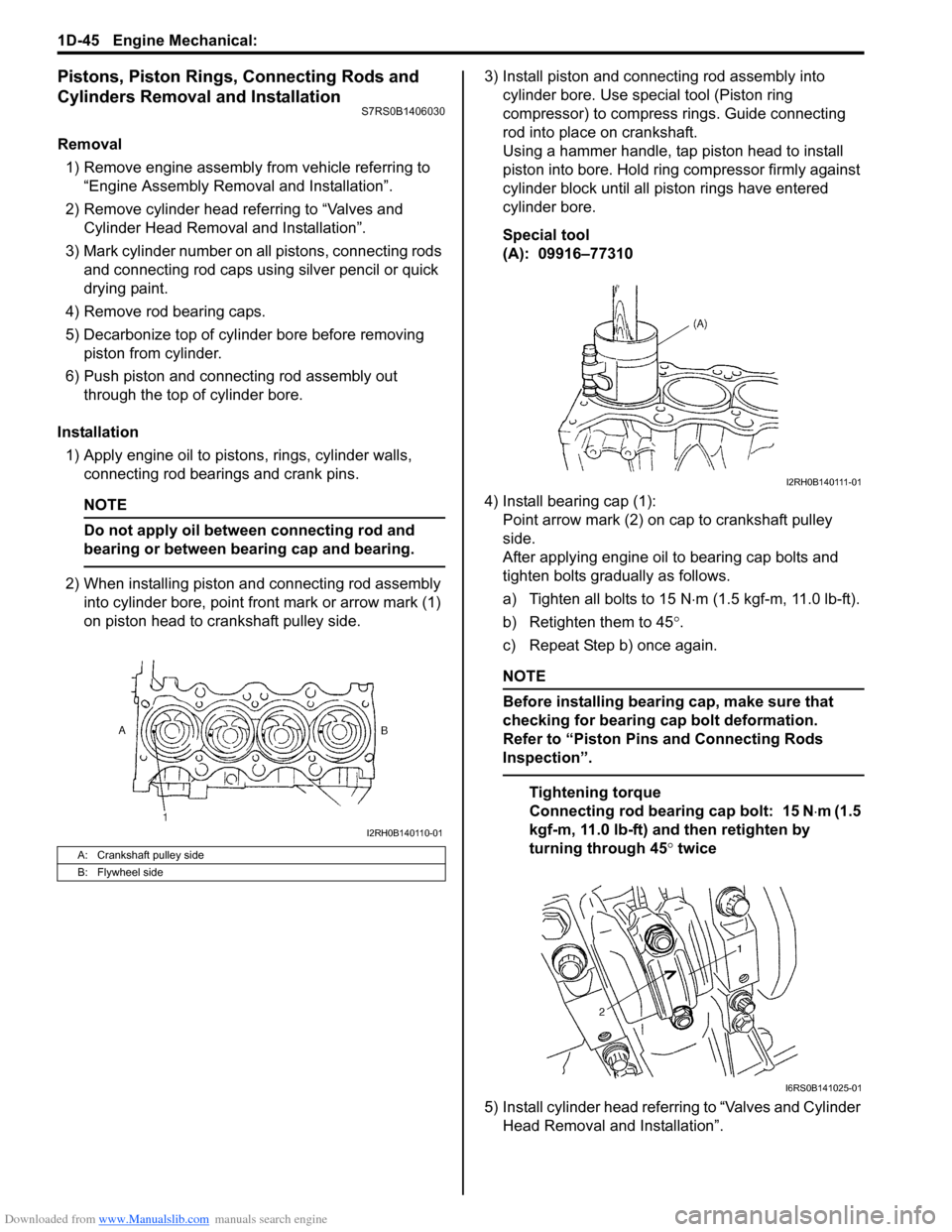
Removal1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle referring to “Engine Assembly Removal and Installation”.
2) Remove cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
3) Mark cylinder number on all pistons, connecting rods
and connecting rod caps using silver pencil or quick
drying paint.
4) Remove rod bearing caps.
5) Decarbonize top of cylinder bore before removing piston from cylinder.
6) Push piston and connecting rod assembly out through the top of cylinder bore.
Installation 1) Apply engine oil to pistons, rings, cylinder walls, connecting rod bearings and crank pins.
NOTE
Do not apply oil between connecting rod and
bearing or between bearing cap and bearing.
2) When installing piston and connecting rod assembly into cylinder bore, point front mark or arrow mark (1)
on piston head to crankshaft pulley side. 3) Install piston and connecting rod assembly into
cylinder bore. Use special tool (Piston ring
compressor) to compress rings. Guide connecting
rod into place on crankshaft.
Using a hammer handle, tap piston head to install
piston into bore. Hold ring compressor firmly against
cylinder block until all piston rings have entered
cylinder bore.
Special tool
(A): 09916–77310
4) Install bearing cap (1): Point arrow mark (2) on cap to crankshaft pulley
side.
After applying engine oil to bearing cap bolts and
tighten bolts gradually as follows.
a) Tighten all bolts to 15 N ⋅m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft).
b) Retighten them to 45 °.
c) Repeat Step b) once again.
NOTE
Before installing bearing cap, make sure that
checking for bearing cap bolt deformation.
Refer to “Piston Pins and Connecting Rods
Inspection”.
Tightening torque
Connecting rod bearing cap bolt: 15 N ⋅m (1.5
kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft) and then retighten by
turning through 45 ° twice
5) Install cylinder head referring to “Valves and Cylinder Head Removal and Installation”.
A: Crankshaft pulley side
B: Flywheel side
I2RH0B140110-01
I2RH0B140111-01
I6RS0B141025-01
Page 331 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-46
Pistons, Piston Rings, Connecting Rods and
Cylinders Disassembly and Assembly
S7RS0B1406031
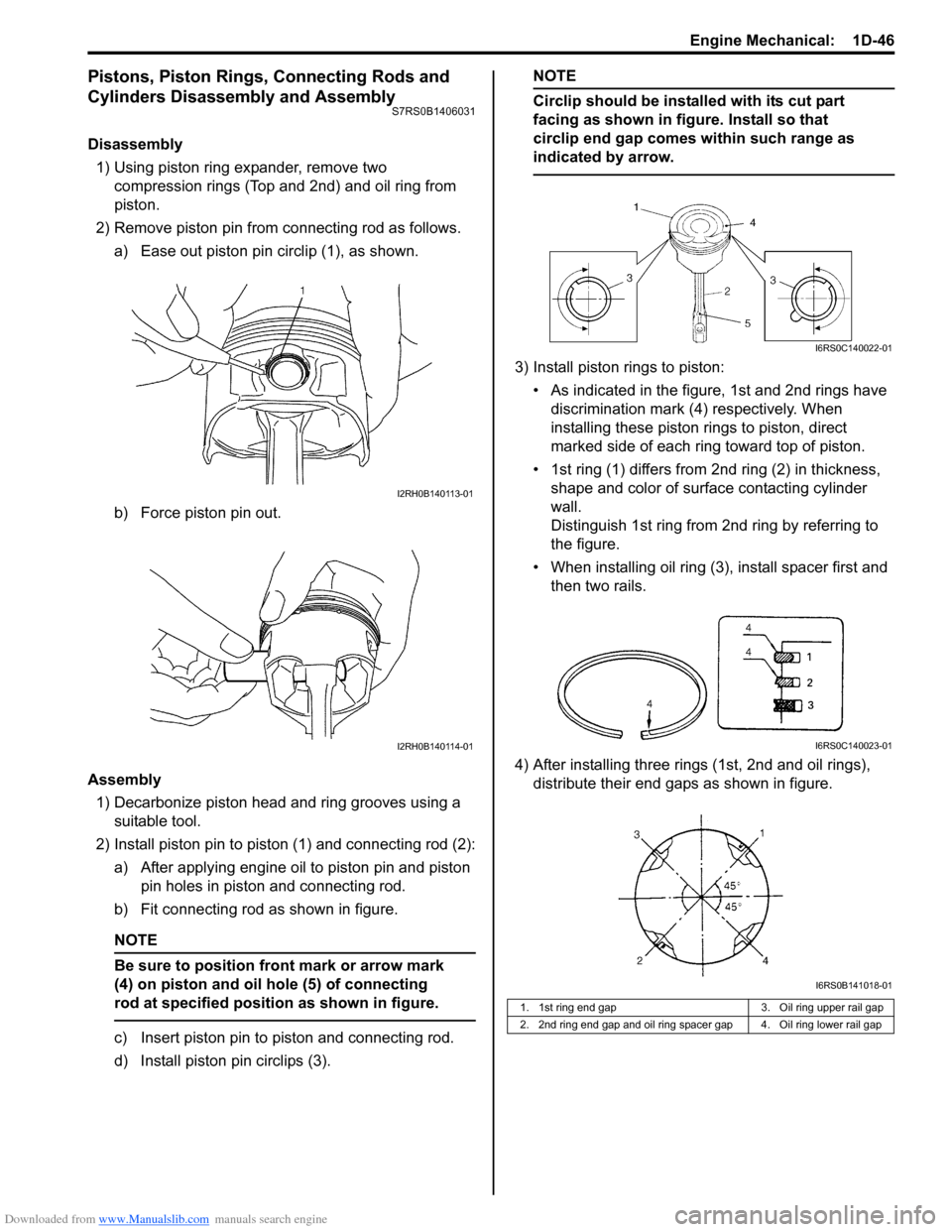
Disassembly1) Using piston ring expander, remove two compression rings (Top and 2nd) and oil ring from
piston.
2) Remove piston pin from connecting rod as follows. a) Ease out piston pin circlip (1), as shown.
b) Force piston pin out.
Assembly 1) Decarbonize piston head and ring grooves using a suitable tool.
2) Install piston pin to piston (1) and connecting rod (2): a) After applying engine oil to piston pin and piston pin holes in piston and connecting rod.
b) Fit connecting rod as shown in figure.
NOTE
Be sure to position front mark or arrow mark
(4) on piston and oil hole (5) of connecting
rod at specified position as shown in figure.
c) Insert piston pin to piston and connecting rod.
d) Install piston pin circlips (3).
NOTE
Circlip should be installed with its cut part
facing as shown in figure. Install so that
circlip end gap comes within such range as
indicated by arrow.
3) Install piston rings to piston:
• As indicated in the figure, 1st and 2nd rings have discrimination mark (4) respectively. When
installing these piston rings to piston, direct
marked side of each ring toward top of piston.
• 1st ring (1) differs from 2nd ring (2) in thickness, shape and color of surface contacting cylinder
wall.
Distinguish 1st ring from 2nd ring by referring to
the figure.
• When installing oil ring (3), install spacer first and then two rails.
4) After installing three rings (1st, 2nd and oil rings), distribute their end gaps as shown in figure.
I2RH0B140113-01
I2RH0B140114-01
1. 1st ring end gap 3. Oil ring upper rail gap
2. 2nd ring end gap and oil ring spacer gap 4. Oil ring lower rail gap
I6RS0C140022-01
I6RS0C140023-01
I6RS0B141018-01
Page 332 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-47 Engine Mechanical:
Cylinders, Pistons and Piston Rings InspectionS7RS0B1406032
Cylinder
Visual inspection
Inspect cylinder walls for scratches, roughness or ridges
which indicate excessive wear. If cylinder bore is very
rough or deeply scratched, or ridged, rebore cylinder and
use over size piston.
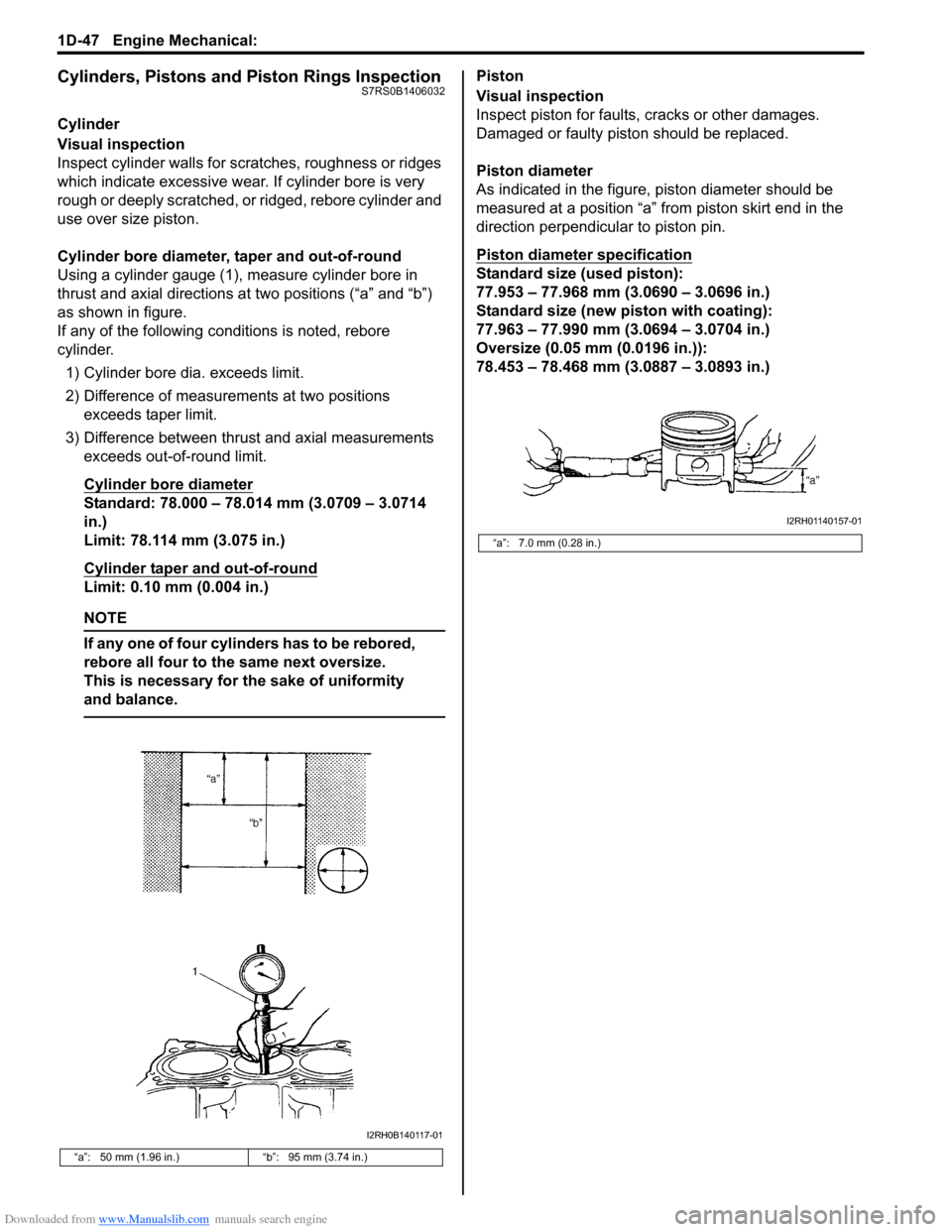
Cylinder bore diameter, taper and out-of-round
Using a cylinder gauge (1), measure cylinder bore in
thrust and axial directions at two positions (“a” and “b”)
as shown in figure.
If any of the following conditions is noted, rebore
cylinder.1) Cylinder bore dia. exceeds limit.
2) Difference of measurements at two positions exceeds taper limit.
3) Difference between thrust and axial measurements exceeds out-of-round limit.
Cylinder bore diameter
Standard: 78.000 – 78.014 mm (3.0709 – 3.0714
in.)
Limit: 78.114 mm (3.075 in.)
Cylinder taper and out-of-round
Limit: 0.10 mm (0.004 in.)
NOTE
If any one of four cylinders has to be rebored,
rebore all four to the same next oversize.
This is necessary for the sake of uniformity
and balance.
Piston
Visual inspection
Inspect piston for faults, cracks or other damages.
Damaged or faulty piston should be replaced.
Piston diameter
As indicated in the figure, piston diameter should be
measured at a position “a” from piston skirt end in the
direction perpendicular to piston pin.
Piston diameter specification
Standard size (used piston):
77.953 – 77.968 mm (3.0690 – 3.0696 in.)
Standard size (new piston with coating):
77.963 – 77.990 mm (3.0694 – 3.0704 in.)
Oversize (0.05 mm (0.0196 in.)):
78.453 – 78.468 mm (3.0887 – 3.0893 in.)
“a”: 50 mm (1.96 in.) “b”: 95 mm (3.74 in.)
I2RH0B140117-01
“a”: 7.0 mm (0.28 in.)
I2RH01140157-01