2005 SUZUKI SWIFT Turn indicator
[x] Cancel search: Turn indicatorPage 415 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-5
Generator Test (Undercharged Battery Check)S7RS0B1A04003
This condition, as evidenced by slow cranking or
indicator clear with dark or light yellow dot can be
caused by one or more of the following conditions even
though indicator lamp may be operating normal.
The following procedure also applies to cars with
voltmeter and ammeter.1) Make sure that undercharged condition has not been caused by accessories left on for extended period of
time.
2) Check drive belt for proper tension.
3) If battery defect is suspected, refer to “Battery Description”.
4) Inspect wiring for defects. Check all connections for tightness and cleanliness, battery cable connections
at battery, starting motor, ignition ground cable and
no “C” terminal circuit at ground.
5) Connect switch (6), load (5), battery (4), voltmeter (3) and ammeter (2) to generator (1) as shown in
figure.
Voltmeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and ground.
Ammeter: Set between generator “B” terminal
and battery (+) terminal.
NOTE
Use fully charged battery.
6) Measure current and voltage.
No-Load Check 1) Run engine from idling up to 2000 rpm and read meters.
NOTE
Turn off switches of all accessories (wiper,
heater etc.).
Specification for undercharged battery (No-load
check)
Current: 10 A
Voltage: 14.2 – 14.8 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
NOTE
Consideration should be taken that voltage
will differ somewhat with regulator case
temperature as shown in figure.
2) Using service wire, ground “C” terminal (1) of
generator.
3) Measure voltage between “B” terminal of generator and body ground.
Voltage: 12.5 – 13.1 V (at 20 °C, 68 °F)
• If voltage is higher than standard value
If voltage is higher than standard value, check ground
of brushes.
If brushes are not grounded, replace IC regulator.
If voltage is lower than standard value, proceed to the
following check.
Load Check 1) Run engine at 2000 rpm and turn on head light and blower motor.
2) Measure current. If measure current is less than 30 A, repair or
replace generator.
IYSQ011A0007-01
[A]: Regulated voltage (V)
[B]: Heat sink temperature ( °C)
16.0
15.5
15.0
14.5
14.0
13.5
13.0
-30 0 20
[A]
[B]
68
22120 (˚C)
248 (˚F)
(V)
I6RS0B1A1002-01
I5JB0A1A0011-01
Page 469 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-2
Lower than recommended pressure can cause:
• Tire squeal on turns
• Hard Steering
• Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
• Tire rim bruises and rupture
• Tire cord breakage
• High tire temperature
• Reduced handling
• High fuel consumption
Replacement Tires
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment
type tire should be used. Refer to the Tire Placard.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load
range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride,
handling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the
body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on
the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to
equalize braking traction.
WARNING!
Do not mix different types of tires on the
same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-
belted tires except in emergencies, because
handling may be seriously affected and may
result in loss of control.
The metric term for tire infl ation pressure is the kilo
pascal (kPa). Tire pressures is usually printed in both
kPa and kgf/cm
2 on the “Tire Placard”.
Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The chart, shown the table, converts commonly used
inflation pressures from kPa to kgf/cm
2 and psi.
Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401002
Wheel Maintenance
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are
not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
Replacement Wheels
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, air leak through welds,
have elongated bolt holes, if lug wheel bolts won’t stay
tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater
runout than shown in the following may cause
objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original
equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim with
offset and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper
size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire clearance to body and
chassis.
How to Measure Wheel Runout
To measure the wheel runout, it is necessary to use an
accurate dial indicator. The tire may be on or off the
wheel. The wheel should be installed to the wheel
balancer of the like for proper measurement.
Take measurements of both lateral runout “a” and radial
runout “b” at both inside an d outside of the rim flange.
With the dial indicator set in place securely, turn the
wheel one full revolution slowly and record every reading
of the indicator.
When the measured runout exceeds the specification
and correction by the balancer adjustment is impossible,
replace the wheel. If the reading is affected by welding,
paint or scratch, it should be ignored.
Lateral runout limit “a”
: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
Radial runout limit “b”
: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
kPa kgf/cm2psi
Conversion: 1 psi =
6.895 kPa 1 kgf/cm
2 =
98.066 kPa 160 1.6 23
180 1.8 26
200 2.0 29
220 2.2 32
240 2.4 35
260 2.6 38
280 2.8 41
300 3.0 44
I4RS0A240001-01
Page 503 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Brake Control System and Diagnosis: 4A-5
If deterioration of rubber is evident, disassemble all
hydraulic parts and wash with alcohol. Dry these parts
with compressed air before assembly to keep alcohol out
of the system. Replace all rubber parts in the system,
including hoses. Also, when working on the brake
mechanisms, check for fluid on the linings.
If excessive fluid is found, replace the pads. If master cylinder piston seals
are satisfactory, check for
leakage or excessive heat co nditions. If leakage is not
found, drain fluid, flush with brake fluid, refill and bleed
system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been used
which contained parts that have been subjected to
contaminated fluid.
Brakes Symptom DiagnosisS7RS0B4104002
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Not enough braking force Brake oil leakage from brake lines Locate leaking point and repair.
Brake disc or brake pad stained with oil Clean or replace.
Overheated brakes Determine cause and repair.
Badly worn brake pad Replace.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Repair or replace.
Malfunctioning brake booster Check system and replace assembly.
Malfunctioning brake master cylinder Check system and replace as necessary.
Air in system Bleed system.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®). Check system and replace as necessary.
Brake pull (Brakes not
working in unison) Brake pad and disc are wet with water or
stained with oil in some brakes Clean or replace.
Disc is out of round in some brakes Replace.
Tires are inflated unequally Inflate equally.
Disturbed front wheel alignment Adjust as prescribed.
Unmatched tires on same axle Tires with approximately the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses and damaged lines.
Replace with new hoses and new double-
walled steel brake tubing.
Malfunctioning caliper assembly Caliper should slide.
Check for stuck or sluggish pistons and proper
lubrication of caliper slide pin.
Loose suspension parts Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers Check and torque bolts to specifications.
Noise (High pitched
squeak without brake
applied) Contact wear indicator to brake disc
Replace brake pads.
Worn brake pad Replace brake pads.
Excessive pedal travel
(Pedal stroke too large) Partial brake system failure
Check brake systems and repair as necessary.
Brake fluid leaking Repair the leaking point and bleed air.
Air in system (soft / spongy pedal) Bleed system.
Brake locked Malfunctioning ABS (ESP®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
Dragging brakes (A very
light drag is present in all
brakes immediately after
pedal is released.) Master cylinder pistons not returning
correctly
Replace master cylinder.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses Check for soft hoses or damaged pipes and
replace with new hoses and/or new brake
piping.
Incorrect parking brake adjustment on
rear brakes Check and adjust to correct specifications.
Weakened or broken return springs in
rear brakes. Replace.
Sluggish parking brake cables or linkage Repair or replace.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Badly worn piston seal in caliper Replace piston seal.
Improper brake pedal free height Check brake pedal free height.
Page 504 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4A-6 Brake Control System and Diagnosis:
Pedal pulsation (Pedal
pulsates when depressed
for braking)Damaged or loose wheel bearings
Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted steering knuckle or rear wheel
spindle Replace knuckle or rear wheel spindle.
Excessive disc lateral runout Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Parallelism between brake pad and disc
not within specifications Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine disc.
Brake caliper piston sticking Repair as necessary.
Braking noise Worn or distorted brake pad Replace pads.
Loose front wheel bearings Replace wheel bearings.
Distorted backing plates or loose
mounting bolts Replace or retighten securing bolts.
Contact wear indicator to brake disc Replace brake pad.
Brake warning light lights
after engine start Parking brake applied
Release parking brake and check that brake
warning light turns off.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake fluid leaking Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light circuit faulty Repair circuit.
Malfunctioning EBD system Check system referring to “EBD Warning Light
(Brake Warning Light) Comes ON Steady in
Section 4E”.
Brake warning light turns
on when brake is applied Brake fluid leaking
Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Insufficient amount of brake fluid Investigate leaky point, correct it and add
brake fluid.
Brake warning light fails
to turn on even when
parking brake is applied Brake warning light circuit faulty
Replace bulb or repair circuit.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on after engine start Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light turns
on when brake is applied Malfunctioning ABS (ESP
®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light or
ESP
® warning light does
not turn on for 2 sec. after
ignition switch has turned
ON Bulb burnt out
Replace bulb.
Malfunctioning ABS (ESP ®) Check system referri ng to “ABS Check in
Section 4E” or “Electronic Stability Program
System Check in Section 4F”.
ABS warning light flashes New ABS hydraulic unit / control module
assembly installed. Perform “ABS Hydraulic
Unit Operation Check
in Section 4E”.
Condition Possible cause Correction / Reference Item
Page 579 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-5
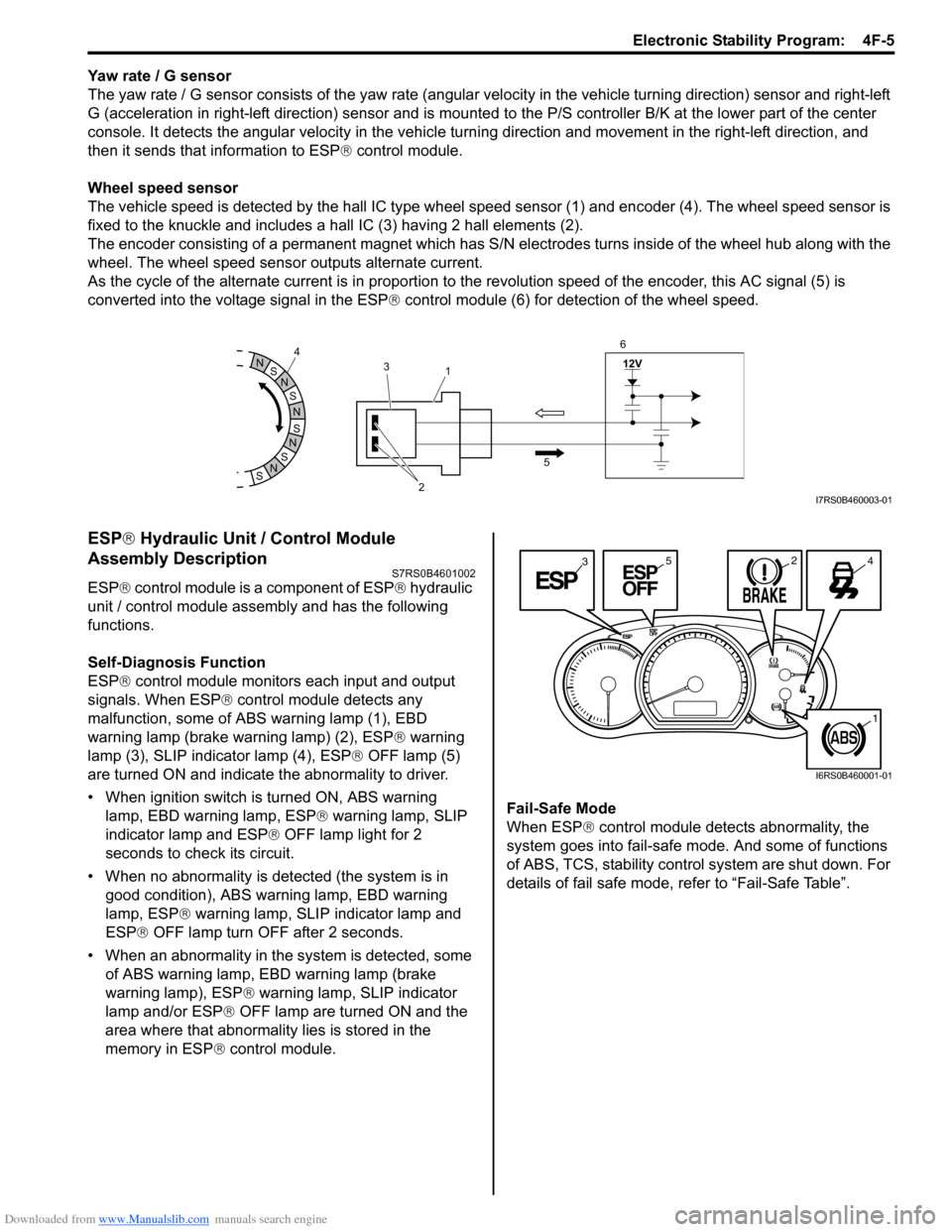
Yaw rate / G sensor
The yaw rate / G sensor consists of the yaw rate (angular velocity in the vehicle turning direction) sensor and right-left
G (acceleration in right-left direction) sensor and is mounted to the P/S controller B/K at the lower part of the center
console. It detects the angular velocity in the vehicle turn ing direction and movement in the right-left direction, and
then it sends that information to ESP ® control module.
Wheel speed sensor
The vehicle speed is detected by the hall IC type wheel speed sensor (1) and encoder (4). The wheel speed sensor is
fixed to the knuckle and includes a hall IC (3) having 2 hall elements (2).
The encoder consisting of a permanent ma gnet which has S/N electrodes turns inside of the wheel hub along with the
wheel. The wheel speed sensor outputs alternate current.
As the cycle of the alternate current is in proportion to the revolution speed of the encoder, this AC signal (5) is
converted into the voltage signal in the ESP ® control module (6) for detection of the wheel speed.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly Description
S7RS0B4601002
ESP ® control module is a component of ESP ® hydraulic
unit / control module assembly and has the following
functions.
Self-Diagnosis Function
ESP ® control module monitors each input and output
signals. When ESP ® control module detects any
malfunction, some of ABS warning lamp (1), EBD
warning lamp (brake warning lamp) (2), ESP ® warning
lamp (3), SLIP indicator lamp (4), ESP ® OFF lamp (5)
are turned ON and indicate the abnormality to driver.
• When ignition switch is turned ON, ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP
indicator lamp and ESP ® OFF lamp light for 2
seconds to check its circuit.
• When no abnormality is detected (the system is in good condition), ABS warning lamp, EBD warning
lamp, ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator lamp and
ESP ® OFF lamp turn OFF after 2 seconds.
• When an abnormality in the system is detected, some of ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp (brake
warning lamp), ESP ® warning lamp, SLIP indicator
lamp and/or ESP ® OFF lamp are turned ON and the
area where that abnormality lies is stored in the
memory in ESP ® control module. Fail-Safe Mode
When ESP
® control module detects abnormality, the
system goes into fail-safe mode. And some of functions
of ABS, TCS, stability control system are shut down. For
details of fail safe mode, re fer to “Fail-Safe Table”.
S
N
S
N
S
N
N
S
N
S
12V
2
3
1
5
4
6I7RS0B460003-01
3245
1
I6RS0B460001-01
Page 580 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-6 Electronic Stability Program:
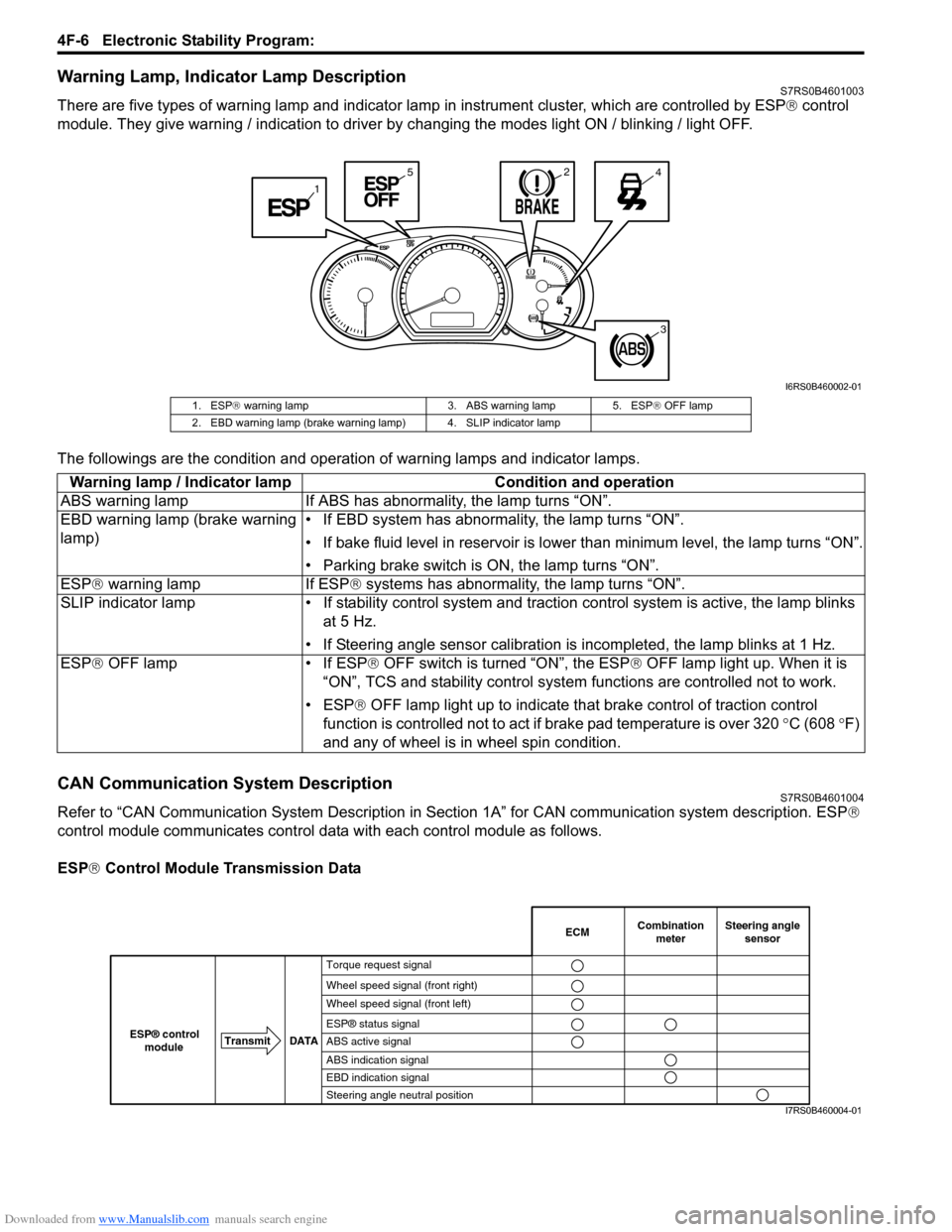
Warning Lamp, Indicator Lamp DescriptionS7RS0B4601003
There are five types of warning lamp and indicator lamp in instrument cluster, which are controlled by ESP ® control
module. They give warning / indication to driver by changing the modes light ON / blinking / light OFF.
The followings are the condition and operation of warning lamps and indicator lamps.
CAN Communication System DescriptionS7RS0B4601004
Refer to “CAN Communication System Description in Section 1A” for CAN communication system description. ESP ®
control module communicates control data with each control module as follows.
ESP ® Control Module Transmission Data
1
245
3
I6RS0B460002-01
1. ESP ® warning lamp 3. ABS warning lamp 5. ESP ® OFF lamp
2. EBD warning lamp (brake warning lamp) 4. SLIP indicator lamp
Warning lamp / Indicator lamp Condition and operation
ABS warning lamp If ABS has abnor mality, the lamp turns “ON”.
EBD warning lamp (brake warning
lamp) • If EBD system has abnormality, the lamp turns “ON”.
• If bake fluid level in reservoir is lower
than minimum level, the lamp turns “ON”.
• Parking brake switch is ON, the lamp turns “ON”.
ESP ® warning lamp If ESP ® systems has abnormality, the lamp turns “ON”.
SLIP indicator lamp • If stability cont rol system and traction control system is active, the lamp blinks
at 5 Hz.
• If Steering angle sensor calibration is incompleted, the lamp blinks at 1 Hz.
ESP ® OFF lamp • If ESP ® OFF switch is turned “ON”, the ESP ® OFF lamp light up. When it is
“ON”, TCS and stability control system functions are controlled not to work.
• ESP® OFF lamp light up to indicate th at brake control of traction control
function is controlled not to act if brake pad temperature is over 320 °C (608 °F)
and any of wheel is in wheel spin condition.
Combination
meter
Transmit DATA
ESP® control
moduleECMSteering angle sensor
Torque request signal
Wheel speed signal (front right)
Wheel speed signal (front left)
ESP® status signal
ABS active signal
ABS indication signal
EBD indication signal
Steering angle neutral position
I7RS0B460004-01
Page 592 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4F-18 Electronic Stability Program:
NOTE
•“�{” in ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp and ESP ® warning lamp column of the above table
means warning lamp is li t when DTC is detected.
• *1: If two or more wheel speed sensor are defective, ABS warning lamp, EBD warning lamp and ESP ® warning lamp are lit and all the control functions are deactivated. If one wheel speed sensor is
defective, ABS warning lamp and ESP ® warning lamp are lit and ABS and TCS / stability control are
deactivated.
• *2: SLIP indicator lamp and ESP ® OFF lamp turn ON when power supply circuit voltage is low.
• *3: SLIP indicator lamp flashes continuously at Intervals of 1 Hz.
• *4: EBD warning lamp is lit when power supply circuit voltage is too low.
DTC ClearanceS7RS0B4604006
WARNING!
When performing a driving test, select a safe place where there is neither any traffic nor any traffic
accident possibility and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector in the same manner as when making this connection for DTC
check.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position.
3) Erase DTC according to instructions displayed on scan t ool. Refer to scan tool operator’s manual for further
derails.
4) After completing the clearance, tu rn ignition switch OFF and disconnec t scan tool from data link connector.
5) Perform “Driving Test” (Step 2 of “E lectronic Stability Program System Check” ) and “DTC Check” and confirm that
NO DTC is displayed on scan tool. �)
U1100 Lost communication with
ECM (reception error) ECM message data is missing from
CAN communication.
——
�{
�) U1126 Lost communication with
steering angle sensor
(reception error) Steering angle sensor message
data is missing from CAN
communication.
——
�{
�) U1140 Lost communication with
BCM (reception error) BCM message data is missing from
CAN communication.
——
�{
DTC (displayed
on SUZUKI scan tool) Diagnostic Items
Detecting condition (DTC will
beset when detecting) ABS
warning lamp EBD
warning lamp ESP
®
warning lamp
Page 629 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Electronic Stability Program: 4F-55
Sensor Calibration (Using SUZUKI Scan Tool)1) Set steering wheel in straight-ahead position.
2) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to data link connector (DLC) (1) with ignition switch OFF.
Special tool
(A): SUZUKI scan tool
3) Turn ignition switch to ON position and confirm that
only any of DTC(s) C1075, C1076 and/or C1077 is
detected. If any other DTC are detected, repair the
detected DTC.
4) Park and level the vehicle with parking brake, stop engine with ignition switch ON, set steering in
straight and without step ping on the brake pedal.
NOTE
Hold the above condition in Step 4) to
calibrate sensor correctly until sensor
calibration is completed.
5) Select menu “SENSOR CALIBRATION” under
“MISC. TEST” mode of SUZUKI scan tool and
calibrate sensor. Refer to scan tool operator's
manual for further derails.
6) After completing the calibra tion, turn ignition switch
to OFF position and disconnect SUZUKI scan tool
from DLC. Steering Angle Sensor Calibration (Not Using
SUZUKI Scan Tool)
1) Set steering wheel in straight-ahead position.
2) Connect battery terminals and/or fuse and start engine.
NOTE
When power is not supplied to the steering
angle sensor by removing battery or fuse,
DTC C1075 is detected and SLIP indicator
lamp (1) flashes.
If DTC other than C1075 is detected, SLIP
indicator lamp flushes and other indicator
illuminate. In that case, repair the detected
DTC first.
3) Drive vehicle straight on level ground at 15 km/h (9.5 mph) or above for few seconds without spinning
wheels. And confirm that SLIP indicator lamp is OFF.
ESP ® Hydraulic Unit / Control Module
Assembly On-Vehicle Inspection
S7RS0B4606027
CAUTION!
Never disassemble ESP ® hydraulic unit /
control module assembly, loosen blind plug
or remove motor. Pe rforming any of these
prohibited services will affect original
performance of ESP ® hydraulic unit / control
module assembly.
Check hydraulic unit for fluid leakage.
If any, repair or replace.
(A)
1
I4RS0B450003-01
1
I6RS0B460028-02