2005 SKODA FABIA height
[x] Cancel search: heightPage 69 of 260

Seats and Stowage
68
Adjusting the front seats
Adjusting a seat in a fo rward/back direction
– Pull the lever ⇒fig. 46 up and push the seat into the
desired position.
– Release the lever and push the seat further until the lock is heard to engage.
Adjusting height of seat*
– Lift the seat if required by pulling or pumping lever upwards.
– Lower the seat if required by pushing or pumping lever downwards. Adjusting angle of backrest
– Relieve any pressure on the backrest (do not lean on it) and
turn the handwheel to adjust the angle of the backrest.
The driver's seat should be adjusted in such a way that the pedals can be
pressed to the floor with slightly bent legs.
The backrest on the driver's seat should be adjusted in such a way that
the upper point of the steering wheel can be easily reached with slightly
bent arms.
WARNING
•Only adjust the driver seat when the vehicle is stationary - risk
of injury!
•Take care when adjusting the seat! Adjusting the seat without
care can lead to bruises or injuries.
•The backrests must not be angled too far back when driving
otherwise this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of
the airbag system - risk of injury!
Fig. 46 Controls at
seat
A1
A1
A2
A2
A3
sqc.1.book Seite 68 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 70 of 260
Seats and Stowage69
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assist-
anceTechnical DataFabia Praktik
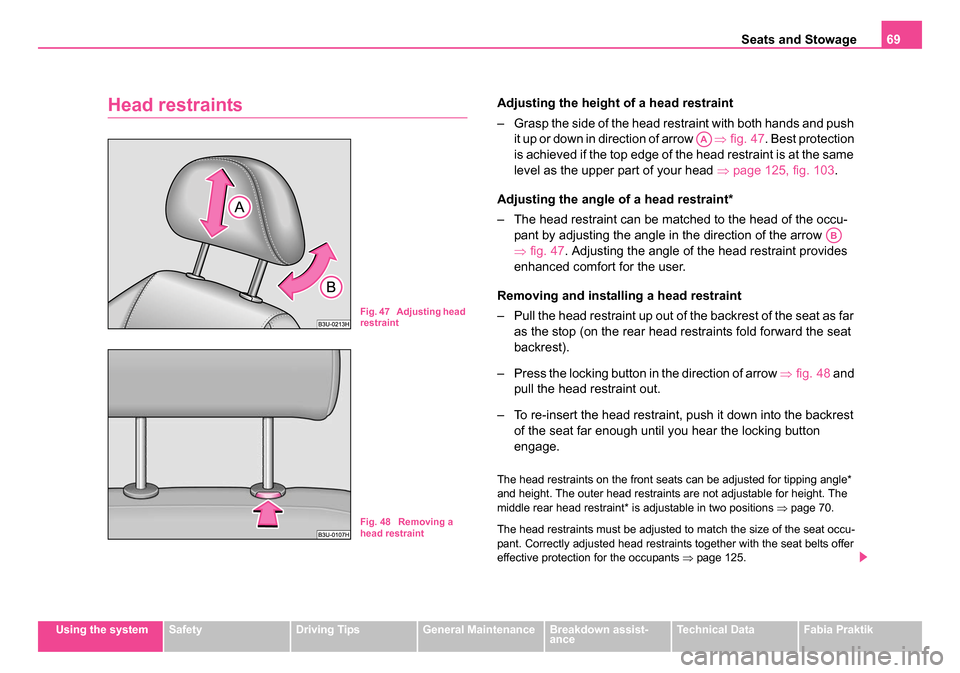
Head restraintsAdjusting the height of a head restraint
– Grasp the side of the head restraint with both hands and push it up or down in direction of arrow ⇒fig. 47. Best protection
is achieved if the top edge of the head restraint is at the same
level as the upper part of your head ⇒page 125, fig. 103 .
Adjusting the angle of a head restraint*
– The head restraint can be matched to the head of the occu- pant by adjusting the angle in the direction of the arrow
⇒fig. 47 . Adjusting the angle of the head restraint provides
enhanced comfort for the user.
Removing and installing a head restraint
– Pull the head restraint up out of the backrest of the seat as far as the stop (on the rear head restraints fold forward the seat
backrest).
– Press the locking button in the direction of arrow ⇒fig. 48 and
pull the head restraint out.
– To re-insert the head restraint, push it down into the backrest of the seat far enough until you hear the locking button
engage.
The head restraints on the front seats can be adjusted for tipping angle*
and height. The outer head restraints are not adjustable for height. The
middle rear head restraint* is adjustable in two positions ⇒page 70.
The head restraints must be adjusted to match the size of the seat occu-
pant. Correctly adjusted head restraints together with the seat belts offer
effective protection for the occupants ⇒page 125.
Fig. 47 Adjusting head
restraint
Fig. 48 Removing a
head restraint
AA
AB
sqc.1.book Seite 69 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 103 of 260

Starting-off and Driving
102
Starting-off and Driving
Setting steering wheel position*You can set the height and the forward/back position of the
steering wheel to the desired position.
– Adjust the driver seat ⇒page 67.
– Pull the lever below the steering column ⇒fig. 89 down
⇒ .
– Set the steering wheel to the desired position (concerning height and forward/back position).
– Then push the lever up against the steering column until it locks into place.
WARNING
•You must not adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is
moving!
•The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the
steering wheel ⇒fig. 90 . Not maintaining this minimum distance
will mean that the airbag system will not be able to properly protect
you - hazard!
•For safety reasons the lever must always be firmly pushed up to
avoid the steering wheel altering its position unintentionally when
driving - risk of accident!
•If you adjust the steering wheel further towards the head, you
will reduce the protection offered by the driver airbag in the event
of an accident. Check that the steering wheel is aligned to the
chest.
•When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on
the outer edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold
Fig. 89 Adjustable
steering wheel: Lever
below steering column
Fig. 90 Safe distance
to steering wheel
sqc.1.book Seite 102 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 124 of 260

Passive Safety123
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assist-
anceTechnical DataFabia Praktik
Safety
Passive Safety
Basic information
Driving the safe way
Passive safety measures reduce the risk of injury in acci-
dent situations.
In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the
subject of passive safety in your vehicle. We have combined everything
here which you should be familiar with, for example, regarding seat belts,
airbags, child seats and safety of children. It is therefore important, in
particular, to comply with the notes and warnings in this section for your
own interest and in the interest of those travelling with you.
WARNING
•This chapter contains important information on how to use the
vehicle for the driver and his occupants. You will find further infor-
mation on safety, which concerns you and those travelling with
you, in the following chapters of this Owner's Manual.
•The complete on-board literature should always be in the
vehicle. This applies in particular, if you rent out or sell the
vehicle.
Safety equipment
The safety equipment is part of the occupant protection
and it can reduce the risk of injuries in accident situations.
“Do not put at risk” your safety and the safety of those travelling with you.
In the event of an accident, the safety equipment can reduce the risk of
injuries. The following list contains part of the safety equipment in your
vehicle:
•Three-point seat belts for all the seats*,
•belt force limiter for front seats*,
•belt tensioner for front seats,
•seat belt height adjuster for front seats,
•front airbags*,
•Side airbags*,
•anchoring points for child seat using the “ISOFIX” system,
•head restraint adjustable for height,
•adjustable steering column.
The specified safety equipment works together, in order to optimally
protect you and those travelling with you in accident situations. The safety
equipment does not protect you or the people travelling with you, if you or
your occupants adopt an incorrect seated position or the equipment is not
correctly adjusted or used.
For this reason you will be provided with information on why this equip-
ment is very important, how it protects you and the occupants, what
sqc.1.book Seite 123 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 134 of 260

Seat belts133
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assist-
anceTechnical DataFabia Praktik
•A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as
your body is moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an
accident and is then suddenly held firm by the belt.
•Only insert the lock tongue into the lock which is the correct one
for your seat. This will affect the protection which the belt offers
and increase the risk of an injury.
Seat belt height adjuster
The seat belt height adjuster makes it possible for you to adapt
the routing of the three-point seat belt in the area of the shoulder
to match your body size.
– To adjust the belt height press the height adjuster and move it up or down ⇒fig. 109 . – Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height
adjuster has correctly locked in place.
WARNING
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of
the belt is positioned approximately across the middle of your
shoulder - on no account across your neck.
Note
It is also possible to adapt the routing of the belt webbing on the front seats
by adjusting the height of the seat*.
Taking seat belts off
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 109 Front seat:
Seat belt height
adjuster
Fig. 110 Releasing
lock tongue from belt
lock
sqc.1.book Seite 133 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 148 of 260
Transporting children safely 147
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assist-
anceTechnical DataFabia Praktik
Transporting children safely
What you should know about
transporting children!
An introduction to the subject
Accident statistics have revealed that children are gener-
ally more safely transported on the rear seats than on the
front passenger seat.
Children younger than 12 years of age should normally travel on the rear
seat of the vehicle (take note of any national legal provisions which differ
from this). They should be secured there by means of a child restraint
system or by using the existing seat belts depending on their age, body
size and weight. The child seat should be mounted behind the front
passenger seat for safety reasons.
The physical principle of an accident does, of course, also apply to chil-
dren ⇒page 130, “The physical principle of a frontal collision”. They differ
from adults in that their muscles and bone structure of children are not yet
fully developed. Thus children are exposed to increased risk of injury.
Children should be transported by using special child safety seats in order
to reduce this risk of injury.
Only use child safety seats which are officially approved, suitable for chil-
dren and which comply with the ECE-R 44 standard, which classifies child
safety seats into 5 groups ⇒page 151, “Classification of child seats into
groups”. Child restraint systems which have been tested for conformity
with ECE-R 44 have a non-detachable test seal (a large E within a circle
and below this the test number) attached to the seat. We recommend that you use child safety seats from the Škoda genuine
accessories. These child seats were developed and also tested for use in
Škoda vehicles. They fulfil the standard ECE-R 44.
WARNING
Always comply with national lega
l provisions and instructions
from the relevant child safety seat manufacturer when installing
and using a child seat ⇒ in “Important safety information on
using child safety seats”.
Note
Any national legal provisions which vary from the information contained in
this Owner's Manual take precedence over the information contained
herein.
Important safety informat ion on using child safety
seats
Correct use of child safety seats considerably reduces the
risk of injury!
WARNING
•All the occupants of the car - in particular children - must wear
a seat belt when the car is moving!
•Children less than 1.50 m in height or younger than 12 years
must not use a normal seat belt without a child restraint system
sqc.1.book Seite 147 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 152 of 260

Transporting children safely 151
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assist-
anceTechnical DataFabia Praktik
•Do not place any objects within th e deployment area of the side
airbag - risk of injury!
Child seat
Classification of child seats into groups
Only child safety seats which have an official approval and
are suitable for the child, may be used.
ECE-R 44 standard applies to child safety seats. ECE-R means:
Economic Commission of Europe - Regulation.
Child safety seats which have been tested for conformity with ECE-R 44
have a non-detachable test seal (a large E within a circle and below this
the test number) attached to the seat.
Child safety seats are classified in 5 groups:
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the
vehicle without a seat bolster.
Use of child seats
An overview of the usefulness of child seats on each of the seats
according to the EG guidelines 77/541 and ECE 44 standard:
Universal category - seat is suitable for all approved types of child
safety seats.
The seat can be fitted with fixing eyes for the “ ISOFIX”system*.
GroupWeight
00 - 10 kg⇒ page 152
0+up to 13 kg⇒page 152
19 - 18 kg⇒page 152
215 - 25 kg⇒page 153
322 - 36 kg⇒page 154
WARNING (continued)
Child seat
according to groupFront passenger
seatRear seat outsideRear seat middle
0
0+
1
2 and 3
AUAUA+AU
AUAUA+AU
AUAUA+AU
AUAUAU
AU
A+
sqc.1.book Seite 151 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13
Page 155 of 260

Transporting children safely
154
•Please comply with any differ ing national legal regulations
regarding the use of child safety seats.
Child safety seats in Group 3
For children of about 7 years of age weighing between 22 and 36 kg and
of a height of less than 150 cm, the optimal solution is a child safety seat
(seat bolster) in combination with the three-point seat belt ⇒fig. 127 .
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the
vehicle without a seat bolster.
WARNING
•When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please
comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats. Switch off the front passenger airbag if neces-
sary at a specialist garage or switch it off with the switch front front
passenger airbag(s)*
⇒page 145.
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately
across the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
It must on no account run across the neck. The lap part of the seat
belt must run across the pelvis and fits snugly; it must not run over
the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if necessary.
•Please comply with any differ ing national legal regulations
regarding the use of child safety seats.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 127 Child seat in
Group 3 installed on
the rear seat facing the
direction of travel
WARNING (continued)
sqc.1.book Seite 154 Mittwoch, 13. April 2005 1:09 13