2005 MITSUBISHI 380 brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 1164 of 1500

35-1
GROUP 35
SERVICE BRAKES
CONTENTS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35A
ANTI-LOCK BRAKING SYSTEM (ABS). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35B
Page 1167 of 1500
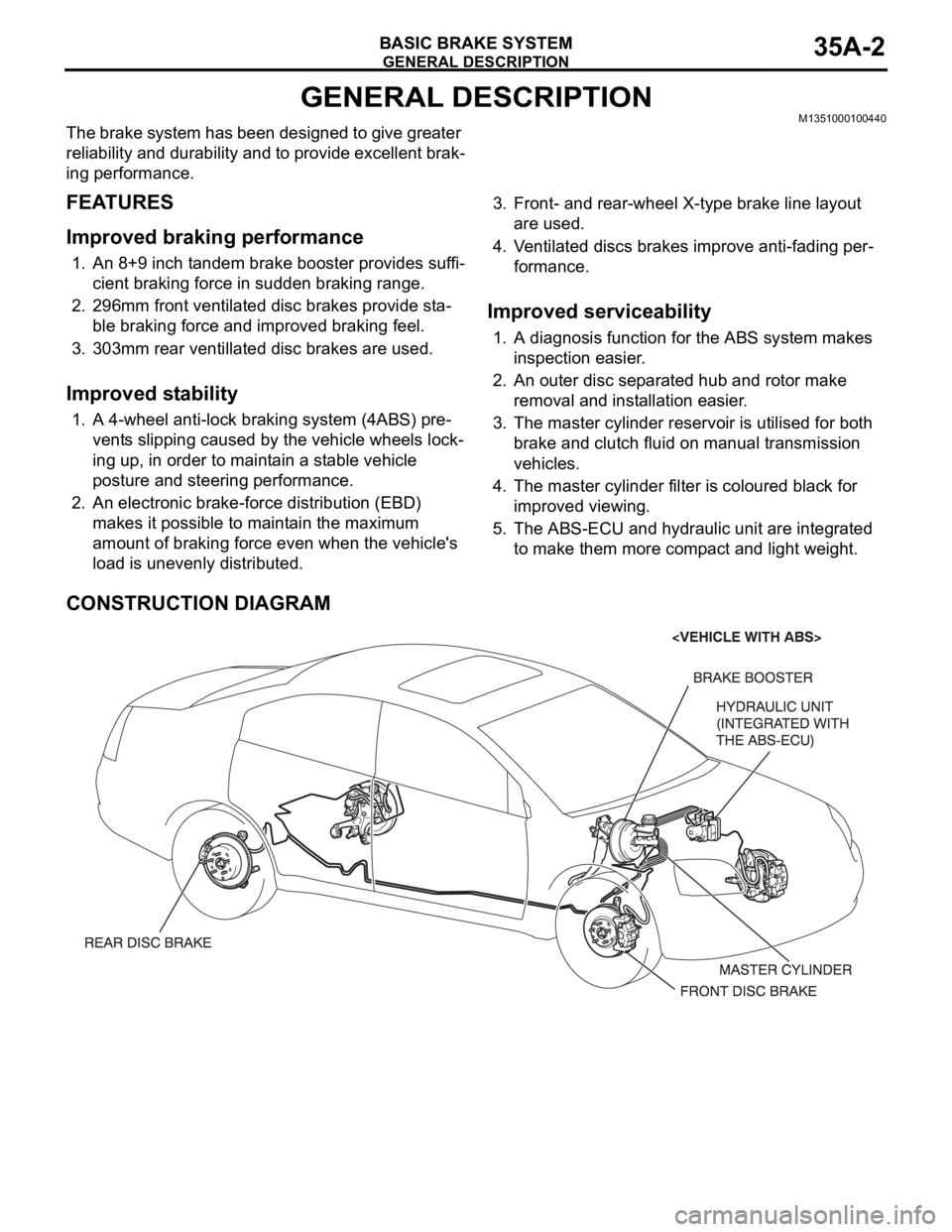
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1351000100440
The brake system has been designed to give greater
reliability and durability and to provide excellent brak-
ing performance.
FEATURES
.
Improved braking performance
1. An 8+9 inch tandem brake booster provides suffi-
cient braking force in sudden braking range.
2. 296mm front ventilated disc brakes provide sta-
ble braking force and improved braking feel.
3. 303mm rear ventillated disc brakes are used.
.
Improved stability
1. A 4-wheel anti-lock braking system (4ABS) pre-
vents slipping caused by the vehicle wheels lock-
ing up, in order to maintain a stable vehicle
posture and steering performance.
2. An electronic brake-force distribution (EBD)
makes it possible to maintain the maximum
amount of braking force even when the vehicle's
load is unevenly distributed. 3. Front- and rear-wheel X-type brake line layout
are used.
4. Ventilated discs brakes improve anti-fading per-
formance.
.
Improved serviceability
1. A diagnosis function for the ABS system makes
inspection easier.
2. An outer disc separated hub and rotor make
removal and installation easier.
3. The master cylinder reservoir is utilised for both
brake and clutch fluid on manual transmission
vehicles.
4. The master cylinder filter is coloured black for
improved viewing.
5. The ABS-ECU and hydraulic unit are integrated
to make them more compact and light weight.
CONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
Page 1168 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-3
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION TO BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSISM1351009700319
Hydraulic brakes are composed of the brake pedal,
master cylinder, brake booster and disc brakes. Mal-
functions such as insufficient braking power or the
generation of noise may occur due to wear, damage
or incorrect adjustment of these components.
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1351009800316
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find a
basic brake system fault.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the symptom
chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
SYMPTOM CHARTM1351009900324
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: Vehicle Pulls to One Side when Brakes are Applied
.DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check for oil, water, etc., on the pad
contact surface of all brakes.
Q: Is oil, water, etc., on the pad contact surface?
YES :
Replace the part and determine the
source/cause of foreign material. Then go to
St e p 5.
NO : Go to Step 2. SYMPTOM INSPECTION
PROCEDUREREFERENCE
PA G E
Vehicle pulls to one side when brakes are applied 1
P.35A-3
Insufficient braking power 2
P.35A-4
Increased pedal stroke (Reduced pedal-to-floor board clearance)3
P.35A-5
Brake drag 4
P.35A-6
Scraping or grinding noise when brake are applied 5
P.35A-7
Squealing, groaning or chattering noise when brake are applied 6
P.35A-8
Squealing noise when brakes are not applied 7
P.35A-9
Groaning, clicking or rattling noise when brakes are not applied8
P.35A-11
Page 1169 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-4
STEP 2. Check disc brake pistons for smooth
operation.
(1) With engine not running, depress the brake pedal
rapidly several times to deplete booster vacuum
reserves.
(2) Test each disc brake assembly one at a time.
a. Remove the lower caliper bolt, then remove
caliper from mount.
b. Have an assistant slowly depress the brake
pedal. Confirm piston(s) extend slowly and
smoothly with no jumpiness. Repeat for each
disc brake assembly.
Q: Do (does) the piston(s) move correctly?
YES :
Go to Step 3.
NO : Disassemble and inspect the brake
assembly (Front: refer to P.35A-33, Rear:
refer to P.35A-36). Then go to Step 5.
STEP 3. Check brake disc(s) for runout.
Refer to P.35A-19.
Q: Is runout outside of specifications?
YES :
Repair or replace the brake disc(s) as
necessary. Then go to Step 5.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check brake discs for correct thickness.
Refer to P.35A-19.
Q: Is the thickness outside of specifications?
YES :
Repair or replace the brake disc(s) as
necessary. Then go to Step 5.
NO : Perform the brake line bleeding. Then go to
St e p 5.
STEP 5. Retest the system.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at Step 1. If a new symptom
appears, refer to the appropriate symptom
chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 2: Insufficient Braking Power
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check that the specified brake fluid is
used, its level is correct, and no contamination is
found.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES :
Refill or replace with the specified brake
fluid DOT 3 or DOT 4. Bleed the brakes if
necessary (Refer to P.35A-16). Then go to
Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check for spongy (not firm) brakes.
(1) With engine not running, depress the brake pedal
rapidly several times to deplete the booster
vacuum reserve.
(2) With the brake pedal fully released, depress the
brake pedal slowly until it stops.
(3) With a measuring device (ruler, etc.) next to the
brake pedal, depress the pedal firmly and
measure the distance the pedal traveled.
Q: Is the distance greater than 20 mm (0.8 inch)?
YES :
Bleed the brakes to remove air in the fluid
(Refer to P.35A-16). Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the brake booster function.
Refer to P.35A-14.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES :
Replace the brake booster. Then go to Step
7.
NO : Go to Step 4.
Page 1170 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-5
STEP 4. Check for pinched or restricted brake
tube or hose.
Q: Is there a pinched or restricted brake tube or hose?
YES :
Replace that complete section of brake tube
or brake hose. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check for oil, water, etc., on the pad
contact surfaces of all brakes.
Q: Is oil, water, etc., on the pad contact surface?
YES :
Replace the part and determine the
source/cause of foreign material. Recheck
symptom. Then go to Step 7.
NO : The procedure is complete. If condition
persists for vehicles without ABS, go to Step
6.
STEP 7. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom
surfaces, refer to the appropriate symptom
chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3: Increased Pedal Stroke (Reduced Pedal-to-Floor Board Clearance)
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check for spongy (not firm) brakes.
(1) With engine not running, depress the brake pedal
rapidly several times to deplete booster vacuum
reserve.
(2) With the brake pedal fully released, depress the
brake pedal slowly until it stops.
(3) With a measuring device (ruler, etc.) next to the
brake pedal, depress the pedal firmly and
measure the distance the pedal traveled.
Q: Is the distance greater than 20 mm (0.8 inch)?
YES :
Bleed the brakes to remove air in the fluid
(Refer to P.35A-16). Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check the pad for wear.
Refer to P.35A-17.
Q: Is the pad thickness outside of specifications?
YES :
Replace the part. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the vacuum hose and check valve
for damage.
Refer to P.35A-15.
Q: Is there a damage?
YES :
Replace the part. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check the master cylinder function.
Refer to P.35A-23.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES :
Repair it. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check for brake fluid leaks.
Q: Is there a leak?
YES :
Check the connection for looseness,
corrosion, etc. Clean and repair as
necessary. If leaking in any tube or hose
section, replace the complete tube or hose.
Then go to Step 7 .
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Check for excessive clearance between
the push rod and primary piston.
Refer to P.35A-26.
Q: Is the clearance outside of specifications?
YES :
Adjust the clearance. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 7.
STEP 7. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom
surfaces, refer to the symptom chart.
Page 1172 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-7
STEP 6. Check the master cylinder piston return spring for
damage and return port for clogging.
Refer to P.35A-28.
Q: Is there damage?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 9.
NO : Go to Step 7.
STEP 7. Check port for clogging.
Q: Is the port clogged?
YES : Repair it. Then go to Step 9.
NO : Go to Step 8.
STEP 8. Check disc brake pistons for sticking.
Depress the brake pedal, then release. Confirm each wheel
spins freely.
Q: Does any wheel stick?
YES : Inspect that brake assembly. Then go to Step 9.
NO : Go to Step 9.
STEP 9. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES : The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom surfaces, refer
to the symptom chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 5: Scraping or Grinding Noise when Brakes are Applied
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the front brakes, then rear brakes, for
metal-to-metal condition.
Q: Is any metal-to-metal contact evident?
YES : Repair or replace the components. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check for interference between the caliper and
wheel.
Q: Is there any interference?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 3.
Page 1173 of 1500
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-8
STEP 3. Check for interference between the dust cover and
brake disc.
Q: Is there any interference?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check the brake drums or discs for cracks.
Q: Are there cracks?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check for bent backing plate(s).
Q: Is (Are) the backing plate(s) bent?
YES : Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step 6.
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES : The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom surfaces, refer
to the symptom chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE6: Squealing, Groaning or Chattering Noise when Brakes are Applied
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check the brake disc and pads for wear
or cutting.
Q: Is there wear or cutting?
YES :
Repair or replace the part. Then go to Step
4.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check the calipers for rust.
Q: Is there any rust?
YES :
Remove the rust. Then go to Step 4.
NO : Go to Step 3.
Page 1174 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-9
STEP 3. Adjust the brake pedal or brake booster
pushrod.
Refer to P.35A-13 or P.35A-26.
Q: Are the brake pedal and the brake booster pushrod
adjusted correctly?
YES :
Go to Step 4.
NO : Adjust the brake pedal or the brake booster
pushrod. Then go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom
surfaces, refer to the symptom chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 7: Squealing Noise when Brakes are not Applied
DIAGNOSIS
.
STEP 1. Check whether the backing plate is bent or loose
and interfering with the drum.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check whether the drum is damaged due to
interference with the backing plate or shoe.
Q: Is there any damage?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the brake drum for wear and the shoe
spring for damage.
Q: Is there any wear or damage?
YES : Replace the part. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check the brake discs for rust.
Q: Are the brake discs rusted?
YES : Remove the rust by using sand paper. If still rusted,
turn the rotors with an on-the-car brake lathe. Then go
to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check the brake pads for correct installation.
Q: Are the pads installed incorrectly?
YES : Repair the pads. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Check the calipers for correct installation.
Q: Are the calipers installed incorrectly?
YES : Repair the calipers. Then go to Step 10.
NO : Go to Step 7.