2005 CHRYSLER VOYAGER oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 1263 of 2339

Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 3). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap/bed plate bolts of the
bearing being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare the clearance measurements to specsifica-
tions found in the engine specifications table(Refer to
9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).Plastigage gen-
erally is accompanied by two scales. One scale
is in inches, the other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances.
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN IIis used to seal
components exposed to engine oil. This material is a
specially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTVis a specifically designed
black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and
sealing properties to seal components exposed to
automatic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKERis an anaerobic type
gasket material. The material cures in the absence of
air when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It
will not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The
anaerobic material is for use between two machined
surfaces. Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
Fig. 3 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIGAGE
9 - 86 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1264 of 2339

MOPARtBED PLATE SEALANTis a unique
(green-in-color) anaerobic type gasket material that
is specially made to seal the area between the bed
plate and cylinder block without disturbing the bear-
ing clearance or alignment of these components. The
material cures slowly in the absence of air when
torqued between two metallic surfaces, and will rap-
idly cure when heat is applied.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANTis a slow drying,
permanently soft sealer. This material is recom-
mended for sealing threaded fittings and gaskets
against leakage of oil and coolant. Can be used on
threaded and machined parts under all tempera-
tures. This material is used on engines with multi-
layer steel (MLS) cylinder head gaskets. This
material also will prevent corrosion. MopartGasket
Sealant is available in a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16
oz. can w/applicator.
SEALER APPLICATION
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE GASKET
SURFACE PREPARATION
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean gasket surfaces:
²Metal scraper²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 4)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 4)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocŸ Bristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 4)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
Fig. 4 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCŸ BRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-87
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1266 of 2339
(13) Disconnect the EGR transducer electrical con-
nector (if equipped).
(14) Disconnect the vacuum hoses from throttle
body.
(15) Disconnect the brake booster and speed con-
trol vacuum hoses.
(16) Disengage wire harness clip from the right
side engine mount.
(17) Remove the power steering reservoir from
mounting position and set aside.Do notdisconnect
hose.
(18) Disconnect ground strap from rear of cylinder
head.
(19) Disconnect engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor and ignition coil electrical connectors.
(20) Disconnect the fuel injector electrical harness
connector and disengage clip from support bracket.
(21) Disconnect camshaft and crankshaft position
sensor electrical connectors.
(22) Evacuate air conditioning system. Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING.
(23) Disconnect A/C compressor electrical connec-
tor.
(24) Disconnect the A/C lines from compressor.
Cover and seal all openings of hoses and compressor.
(25) Remove the radiator upper hose.
(26) Disengage electrical harness clip at transaxle
dipstick tube.
(27) Remove transaxle dipstick tube. Seal opening
using a suitable plug.
NOTE: When the transaxle cooler lines are removed
from the rolled-groove type fittings at the transaxle,
damage to the inner wall of the hose will occur. To
prevent prevent potential leakage, the cooler hoses
must be cut off flush at the transaxle fitting, and a
service cooler hose splice kit must be installed
upon reassembly.
(28) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut
transaxle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug
cooler lines and fittings to prevent debris from enter-
ing transaxle or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will
be installed upon reassembly.
(29) Disconnect transaxle shift linkage and electri-
cal connectors.
(30) Raise vehicle on hoist and drain the engine
oil.
(31) Remove the axle shafts. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - REMOVAL)
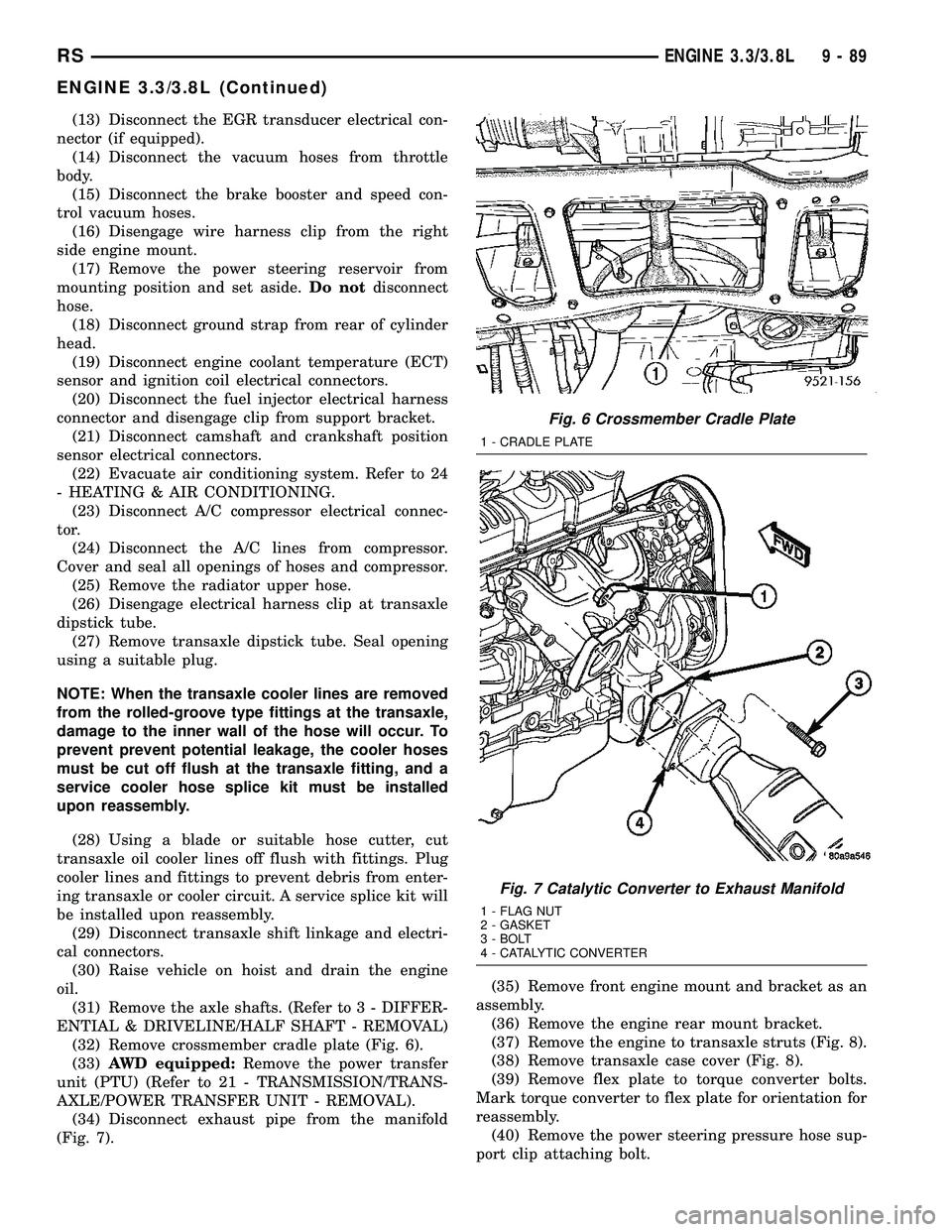
(32) Remove crossmember cradle plate (Fig. 6).
(33)AWD equipped:Remove the power transfer
unit (PTU) (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/POWER TRANSFER UNIT - REMOVAL).
(34) Disconnect exhaust pipe from the manifold
(Fig. 7).(35) Remove front engine mount and bracket as an
assembly.
(36) Remove the engine rear mount bracket.
(37) Remove the engine to transaxle struts (Fig. 8).
(38) Remove transaxle case cover (Fig. 8).
(39) Remove flex plate to torque converter bolts.
Mark torque converter to flex plate for orientation for
reassembly.
(40) Remove the power steering pressure hose sup-
port clip attaching bolt.
Fig. 6 Crossmember Cradle Plate
1 - CRADLE PLATE
Fig. 7 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - FLAG NUT
2 - GASKET
3 - BOLT
4 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-89
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1270 of 2339
(49) Install the radiator upper support crossmem-
ber (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/GRILLE OPEN-
ING REINFORCEMENT - INSTALLATION).
(50) Install the wiper module (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
INSTALLATION).
(51) Connect the fuel line to fuel rail (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL LINES -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(52) Install the air cleaner and hoses.
(53) Install new oil filter. Fill engine crankcase
with proper oil to correct level.
(54) Connect negative cable to battery.
(55) Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(56) Start engine and run until operating temper-
ature is reached.
(57) Adjust transmission linkage, if necessary.
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Engine Type 60É V-6 Engine
Number of
Cylinders6
Displacement
3.3L3.3Liters 201 cu.in.
Displacement
3.8L3.8 Liters 231 cu. in.
Bore 3.3L 93.0 mm 201 cu.in.
Bore 3.8L 96.0 mm 3.779 cu.in.
Stroke 3.3L 81 mm 3.188 in.
Stroke 87 mm 3.425 in.
Compression
Ratio 3.3L- 9.35:1
Compression
Ratio 3.8L- 9.6:1
Firing Order - 1-2-3-4-5-6
Compression
Pressure-
Minimum689.5 kPa 100 psi.
Cylinder
Compression
(Max. Difference
Between
Cylinders- 25%
CYLINDER BLOCK
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Cylinder Bore
Diameter
(Standard) 3.3L92.993-93.007
mm3.661-3.6617 in.
Cylinder Bore
Diameter
(Standard) 3.8L95.993-96.007
mm3.7792-3.780 in.
Out of Round
(Service Limits)0.076 mm 0.003 in.
Taper (Service
Limits)0.051 mm 0.002 in.
Lifter Bore
Diameter22.980-23.010
mm0.905-0.906 in.
Deck Surface
Flatness (Max.)0.1 mm 0.004 in.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Connecting Rod
Journal
Diameter57.979-58.005
mm2.2827-2.2837
in.
Main Bearing
Journal
Diameter63.993-64.013
mm2.5194-2.5202
in.
Journal
Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.025 mm 0.001 in.
Journal Taper
(Max.)0.025 mm 0.001 in
End Play 0.09-0.24 mm 0.0036-0.0095
in.
Wear Limit 0.381 mm 0.015 in.
Main Bearing
Diametrical
Clearance
1-2-3-40.011-0.055
mm0.0005-0.0022
in.
Wear Limit 0.076 mm 0.003 in.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-93
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1271 of 2339
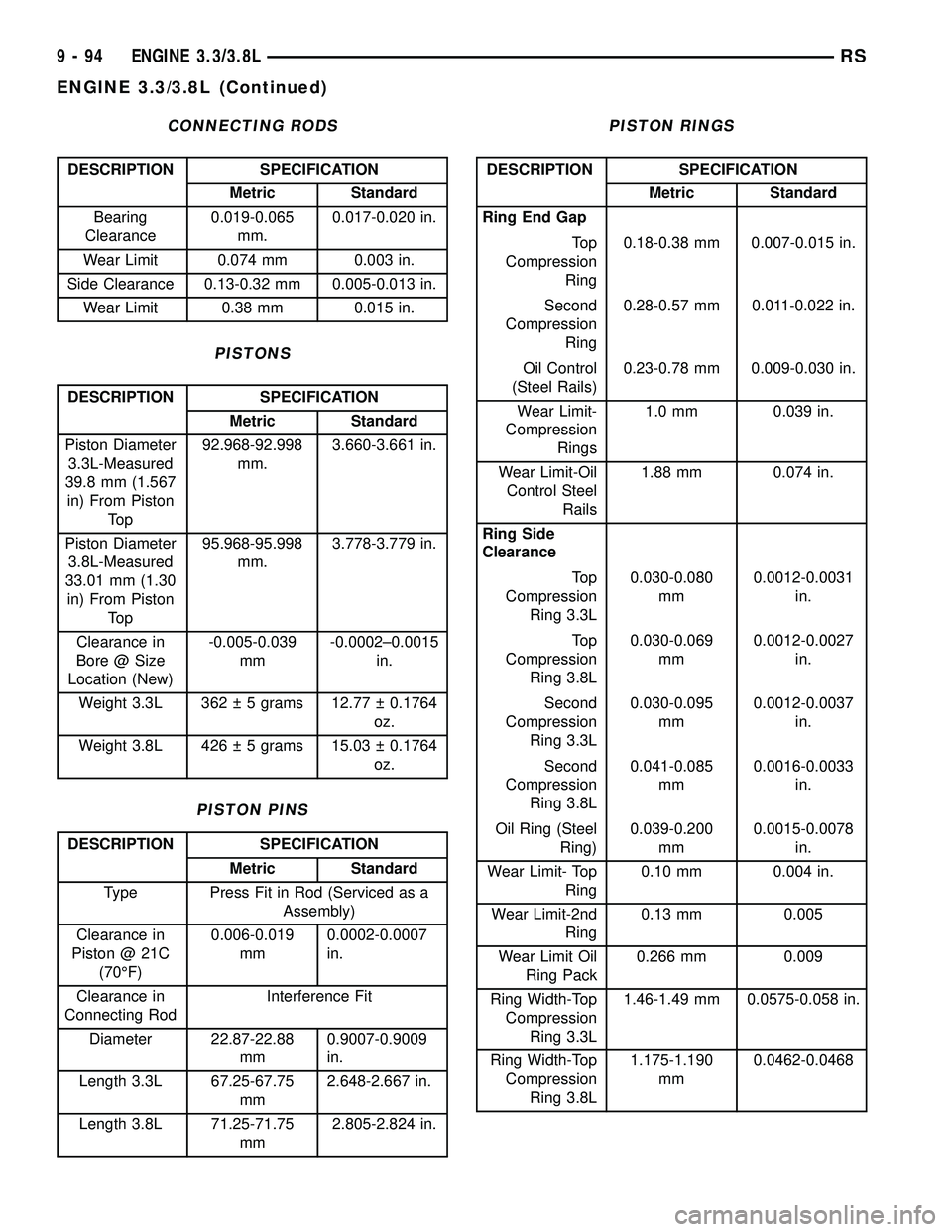
CONNECTING RODS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Bearing
Clearance0.019-0.065
mm.0.017-0.020 in.
Wear Limit 0.074 mm 0.003 in.
Side Clearance 0.13-0.32 mm 0.005-0.013 in.
Wear Limit 0.38 mm 0.015 in.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Piston Diameter
3.3L-Measured
39.8 mm (1.567
in) From Piston
To p92.968-92.998
mm.3.660-3.661 in.
Piston Diameter
3.8L-Measured
33.01 mm (1.30
in) From Piston
To p95.968-95.998
mm.3.778-3.779 in.
Clearance in
Bore @ Size
Location (New)-0.005-0.039
mm-0.0002±0.0015
in.
Weight 3.3L 362 5 grams 12.77 0.1764
oz.
Weight 3.8L 426 5 grams 15.03 0.1764
oz.
PISTON PINS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Type Press Fit in Rod (Serviced as a
Assembly)
Clearance in
Piston @ 21C
(70ÉF)0.006-0.019
mm0.0002-0.0007
in.
Clearance in
Connecting RodInterference Fit
Diameter 22.87-22.88
mm0.9007-0.9009
in.
Length 3.3L 67.25-67.75
mm2.648-2.667 in.
Length 3.8L 71.25-71.75
mm2.805-2.824 in.
PISTON RINGS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Ring End Gap
To p
Compression
Ring0.18-0.38 mm 0.007-0.015 in.
Second
Compression
Ring0.28-0.57 mm 0.011-0.022 in.
Oil Control
(Steel Rails)0.23-0.78 mm 0.009-0.030 in.
Wear Limit-
Compression
Rings1.0 mm 0.039 in.
Wear Limit-Oil
Control Steel
Rails1.88 mm 0.074 in.
Ring Side
Clearance
To p
Compression
Ring 3.3L0.030-0.080
mm0.0012-0.0031
in.
To p
Compression
Ring 3.8L0.030-0.069
mm0.0012-0.0027
in.
Second
Compression
Ring 3.3L0.030-0.095
mm0.0012-0.0037
in.
Second
Compression
Ring 3.8L0.041-0.085
mm0.0016-0.0033
in.
Oil Ring (Steel
Ring)0.039-0.200
mm0.0015-0.0078
in.
Wear Limit- Top
Ring0.10 mm 0.004 in.
Wear Limit-2nd
Ring0.13 mm 0.005
Wear Limit Oil
Ring Pack0.266 mm 0.009
Ring Width-Top
Compression
Ring 3.3L1.46-1.49 mm 0.0575-0.058 in.
Ring Width-Top
Compression
Ring 3.8L1.175-1.190
mm0.0462-0.0468
9 - 94 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1272 of 2339
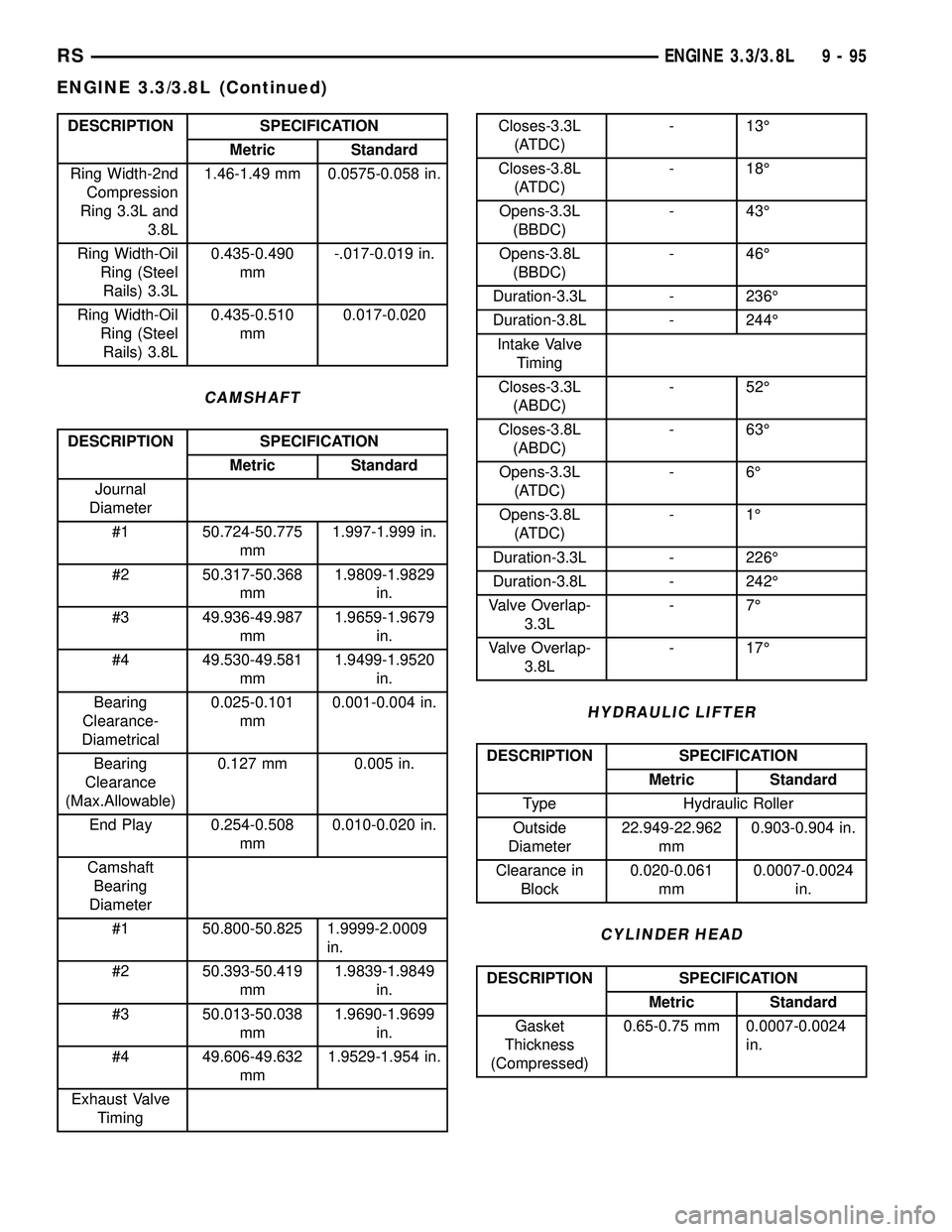
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Ring Width-2nd
Compression
Ring 3.3L and
3.8L1.46-1.49 mm 0.0575-0.058 in.
Ring Width-Oil
Ring (Steel
Rails) 3.3L0.435-0.490
mm-.017-0.019 in.
Ring Width-Oil
Ring (Steel
Rails) 3.8L0.435-0.510
mm0.017-0.020
CAMSHAFT
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Journal
Diameter
#1 50.724-50.775
mm1.997-1.999 in.
#2 50.317-50.368
mm1.9809-1.9829
in.
#3 49.936-49.987
mm1.9659-1.9679
in.
#4 49.530-49.581
mm1.9499-1.9520
in.
Bearing
Clearance-
Diametrical0.025-0.101
mm0.001-0.004 in.
Bearing
Clearance
(Max.Allowable)0.127 mm 0.005 in.
End Play 0.254-0.508
mm0.010-0.020 in.
Camshaft
Bearing
Diameter
#1 50.800-50.825 1.9999-2.0009
in.
#2 50.393-50.419
mm1.9839-1.9849
in.
#3 50.013-50.038
mm1.9690-1.9699
in.
#4 49.606-49.632
mm1.9529-1.954 in.
Exhaust Valve
Timing
Closes-3.3L
(ATDC)- 13É
Closes-3.8L
(ATDC)- 18É
Opens-3.3L
(BBDC)- 43É
Opens-3.8L
(BBDC)- 46É
Duration-3.3L - 236É
Duration-3.8L - 244É
Intake Valve
Timing
Closes-3.3L
(ABDC)- 52É
Closes-3.8L
(ABDC)- 63É
Opens-3.3L
(ATDC)-6É
Opens-3.8L
(ATDC)-1É
Duration-3.3L - 226É
Duration-3.8L - 242É
Valve Overlap-
3.3L-7É
Valve Overlap-
3.8L- 17É
HYDRAULIC LIFTER
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Type Hydraulic Roller
Outside
Diameter22.949-22.962
mm0.903-0.904 in.
Clearance in
Block0.020-0.061
mm0.0007-0.0024
in.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Gasket
Thickness
(Compressed)0.65-0.75 mm 0.0007-0.0024
in.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-95
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1274 of 2339
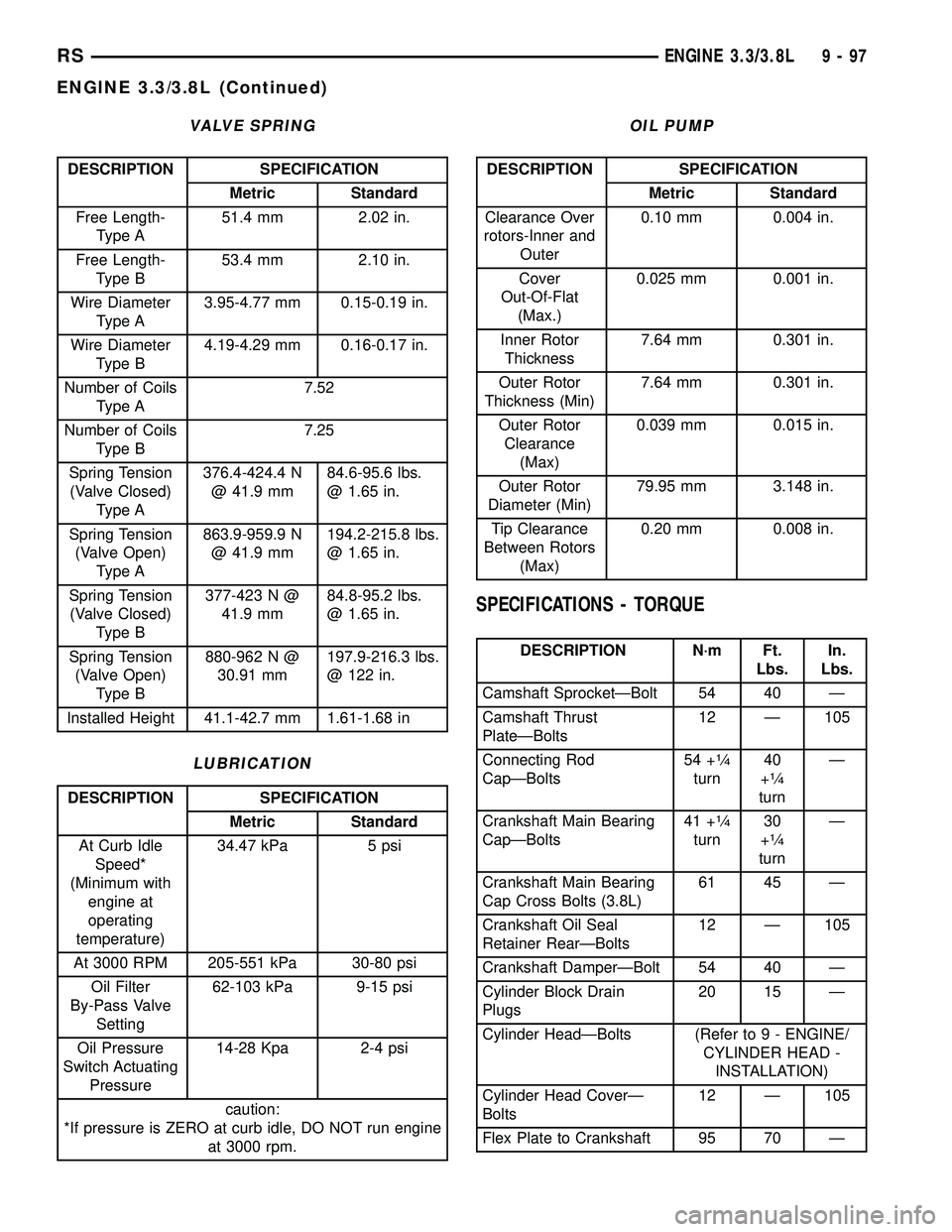
VALVE SPRING
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Free Length-
Type A51.4 mm 2.02 in.
Free Length-
Type B53.4 mm 2.10 in.
Wire Diameter
Type A3.95-4.77 mm 0.15-0.19 in.
Wire Diameter
Type B4.19-4.29 mm 0.16-0.17 in.
Number of Coils
Type A7.52
Number of Coils
Type B7.25
Spring Tension
(Valve Closed)
Type A376.4-424.4 N
@ 41.9 mm84.6-95.6 lbs.
@ 1.65 in.
Spring Tension
(Valve Open)
Type A863.9-959.9 N
@ 41.9 mm194.2-215.8 lbs.
@ 1.65 in.
Spring Tension
(Valve Closed)
Type B377-423 N @
41.9 mm84.8-95.2 lbs.
@ 1.65 in.
Spring Tension
(Valve Open)
Type B880-962 N @
30.91 mm197.9-216.3 lbs.
@ 122 in.
Installed Height 41.1-42.7 mm 1.61-1.68 in
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
At Curb Idle
Speed*
(Minimum with
engine at
operating
temperature)34.47 kPa 5 psi
At 3000 RPM 205-551 kPa 30-80 psi
Oil Filter
By-Pass Valve
Setting62-103 kPa 9-15 psi
Oil Pressure
Switch Actuating
Pressure14-28 Kpa 2-4 psi
caution:
*If pressure is ZERO at curb idle, DO NOT run engine
at 3000 rpm.
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Clearance Over
rotors-Inner and
Outer0.10 mm 0.004 in.
Cover
Out-Of-Flat
(Max.)0.025 mm 0.001 in.
Inner Rotor
Thickness7.64 mm 0.301 in.
Outer Rotor
Thickness (Min)7.64 mm 0.301 in.
Outer Rotor
Clearance
(Max)0.039 mm 0.015 in.
Outer Rotor
Diameter (Min)79.95 mm 3.148 in.
Tip Clearance
Between Rotors
(Max)0.20 mm 0.008 in.
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 54 40 Ð
Camshaft Thrust
PlateÐBolts12 Ð 105
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts54 +
1¤4
turn40
+1¤4
turnÐ
Crankshaft Main Bearing
CapÐBolts41 +
1¤4
turn30
+1¤4
turnÐ
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap Cross Bolts (3.8L)61 45 Ð
Crankshaft Oil Seal
Retainer RearÐBolts12 Ð 105
Crankshaft DamperÐBolt 54 40 Ð
Cylinder Block Drain
Plugs20 15 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION)
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
Flex Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-97
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1286 of 2339
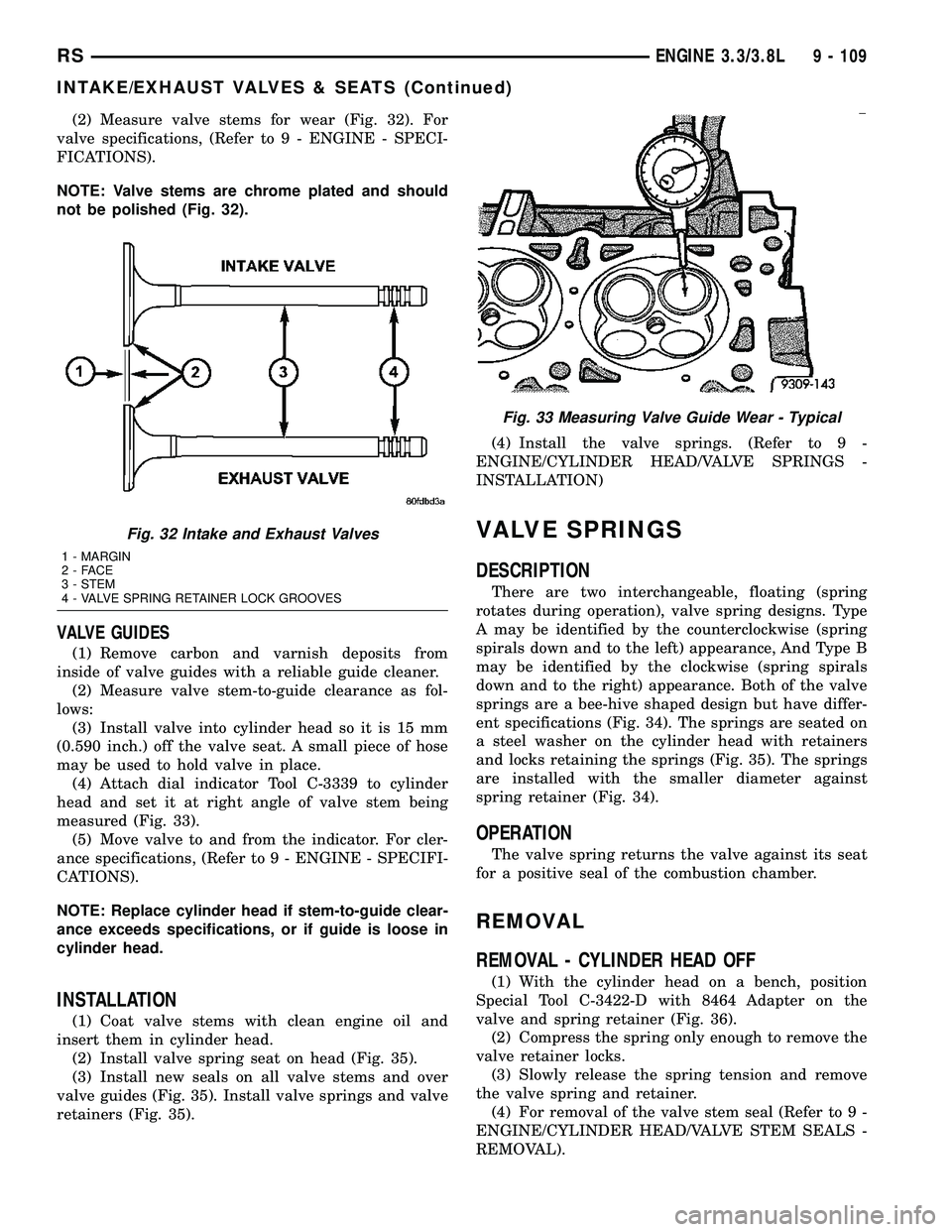
(2) Measure valve stems for wear (Fig. 32). For
valve specifications, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).
NOTE: Valve stems are chrome plated and should
not be polished (Fig. 32).
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Measure valve stem-to-guide clearance as fol-
lows:
(3) Install valve into cylinder head so it is 15 mm
(0.590 inch.) off the valve seat. A small piece of hose
may be used to hold valve in place.
(4) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angle of valve stem being
measured (Fig. 33).
(5) Move valve to and from the indicator. For cler-
ance specifications, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFI-
CATIONS).
NOTE: Replace cylinder head if stem-to-guide clear-
ance exceeds specifications, or if guide is loose in
cylinder head.
INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert them in cylinder head.
(2) Install valve spring seat on head (Fig. 35).
(3) Install new seals on all valve stems and over
valve guides (Fig. 35). Install valve springs and valve
retainers (Fig. 35).(4) Install the valve springs. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS -
INSTALLATION)
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
There are two interchangeable, floating (spring
rotates during operation), valve spring designs. Type
A may be identified by the counterclockwise (spring
spirals down and to the left) appearance, And Type B
may be identified by the clockwise (spring spirals
down and to the right) appearance. Both of the valve
springs are a bee-hive shaped design but have differ-
ent specifications (Fig. 34). The springs are seated on
a steel washer on the cylinder head with retainers
and locks retaining the springs (Fig. 35). The springs
are installed with the smaller diameter against
spring retainer (Fig. 34).
OPERATION
The valve spring returns the valve against its seat
for a positive seal of the combustion chamber.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) With the cylinder head on a bench, position
Special Tool C-3422-D with 8464 Adapter on the
valve and spring retainer (Fig. 36).
(2) Compress the spring only enough to remove the
valve retainer locks.
(3) Slowly release the spring tension and remove
the valve spring and retainer.
(4) For removal of the valve stem seal (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE STEM SEALS -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 32 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2-FACE
3 - STEM
4 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVES
Fig. 33 Measuring Valve Guide Wear - Typical
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 109
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)