2005 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1692 of 2339
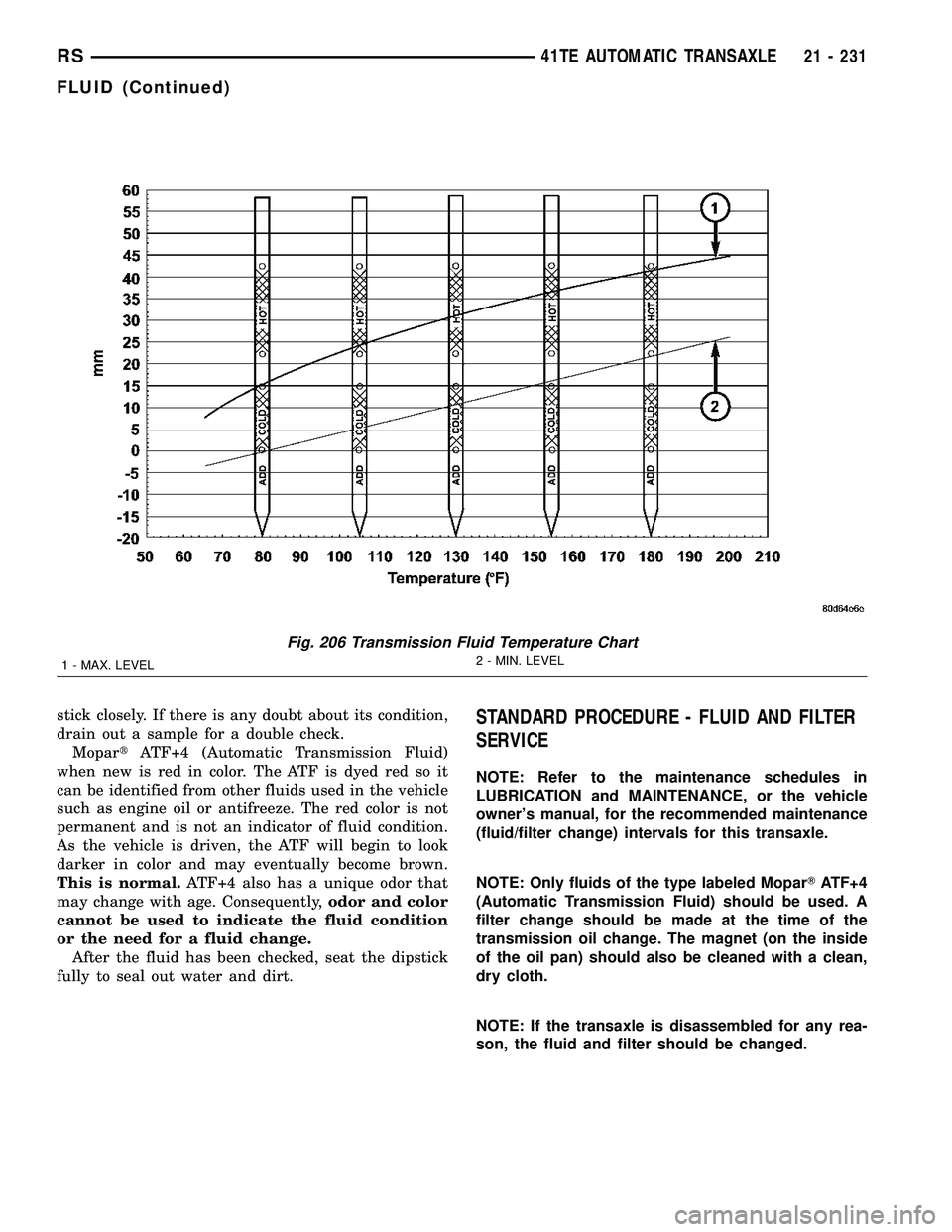
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed red so it
can be identified from other fluids used in the vehicle
such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red color is not
permanent and is not an indicator of fluid condition.
As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin to look
darker in color and may eventually become brown.
This is normal.ATF+4 also has a unique odor that
may change with age. Consequently,odor and color
cannot be used to indicate the fluid condition
or the need for a fluid change.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
(Automatic Transmission Fluid) should be used. A
filter change should be made at the time of the
transmission oil change. The magnet (on the inside
of the oil pan) should also be cleaned with a clean,
dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
Fig. 206 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
1 - MAX. LEVEL2 - MIN. LEVEL
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 231
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1693 of 2339
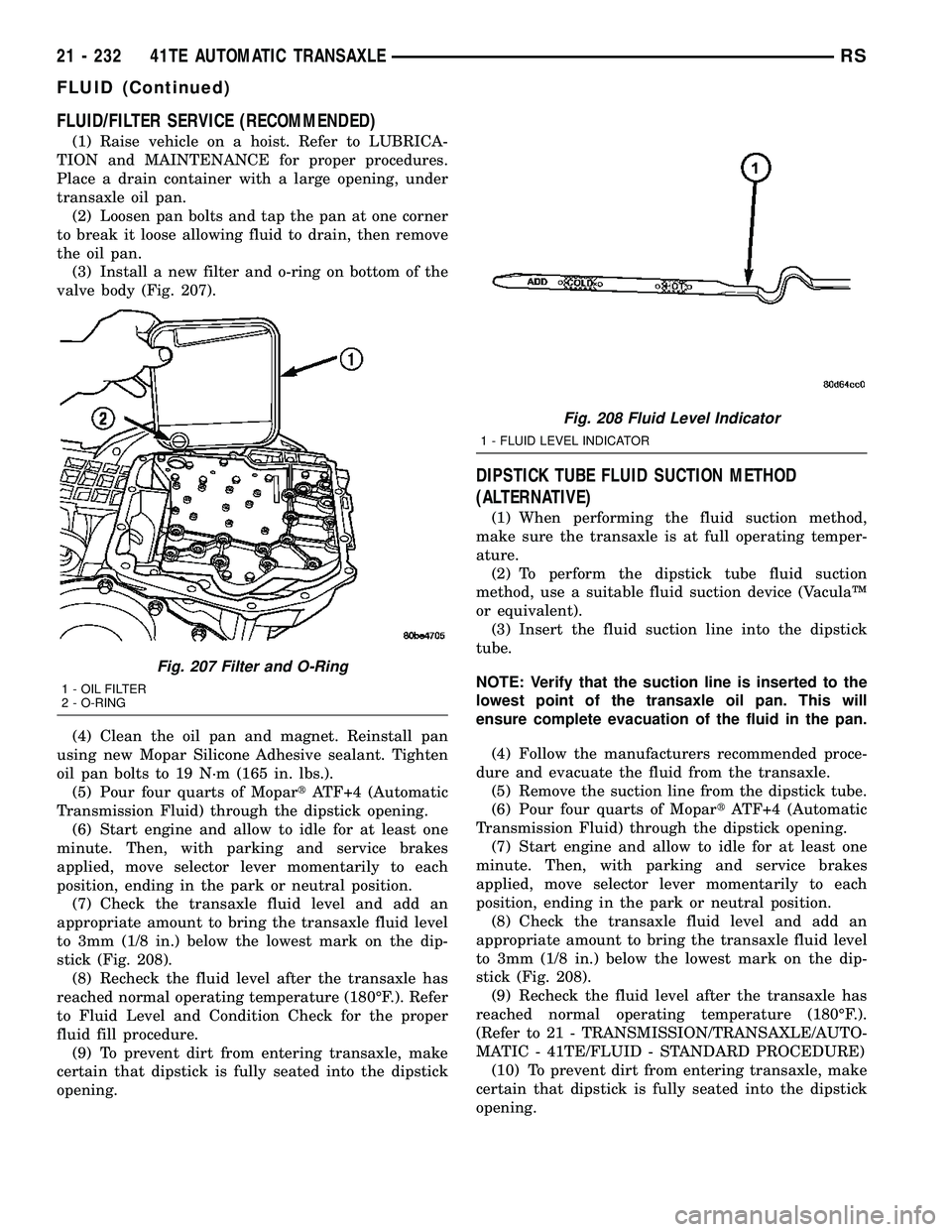
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan.
(2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan.
(3) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 207).
(4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.).
(5) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) through the dipstick opening.
(6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(7) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 208).
(8) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure.
(9) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) through the dipstick opening.
(7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 208).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
Fig. 207 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 208 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21 - 232 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1732 of 2339
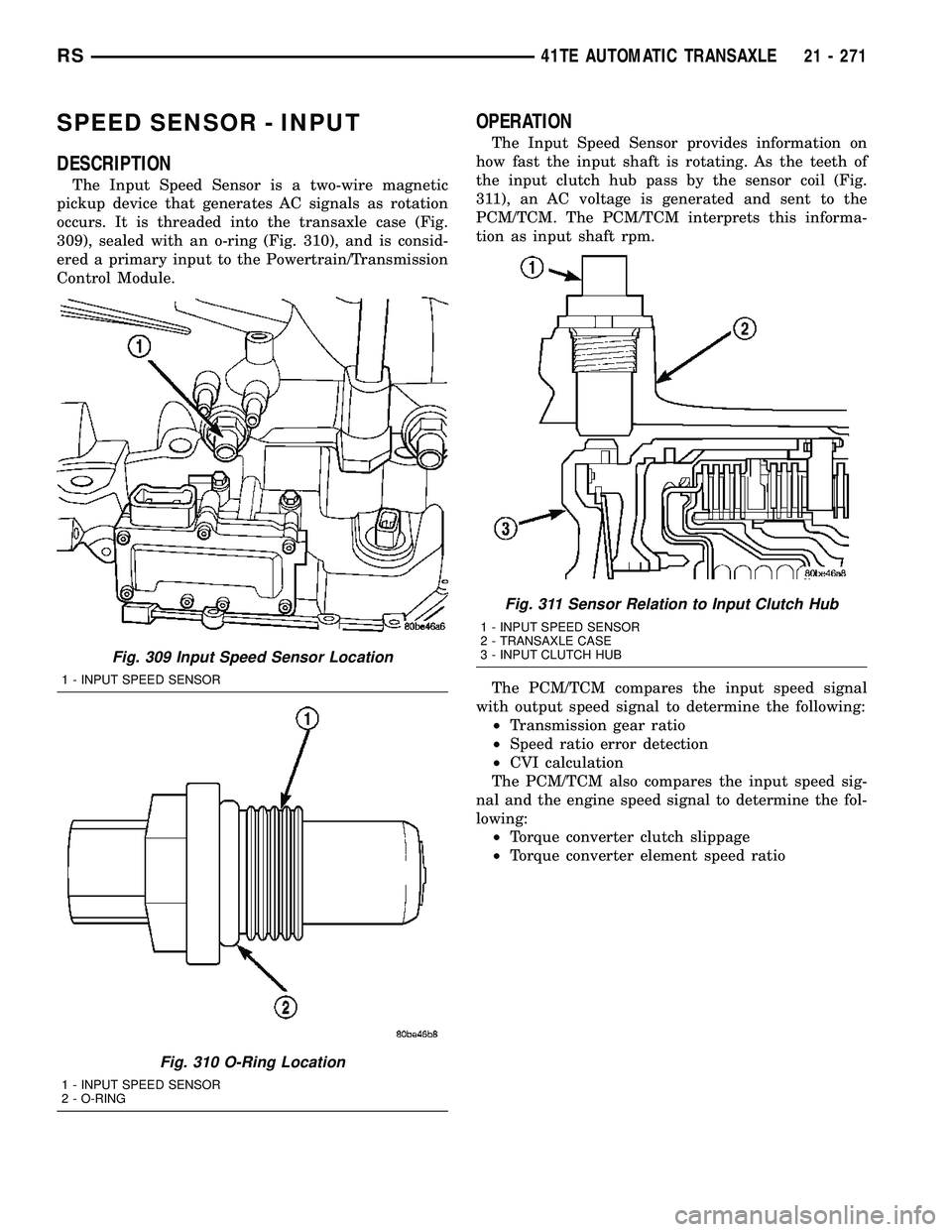
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Input Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates AC signals as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
309), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 310), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powertrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
311), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
Fig. 309 Input Speed Sensor Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 310 O-Ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 311 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 271
Page 1736 of 2339
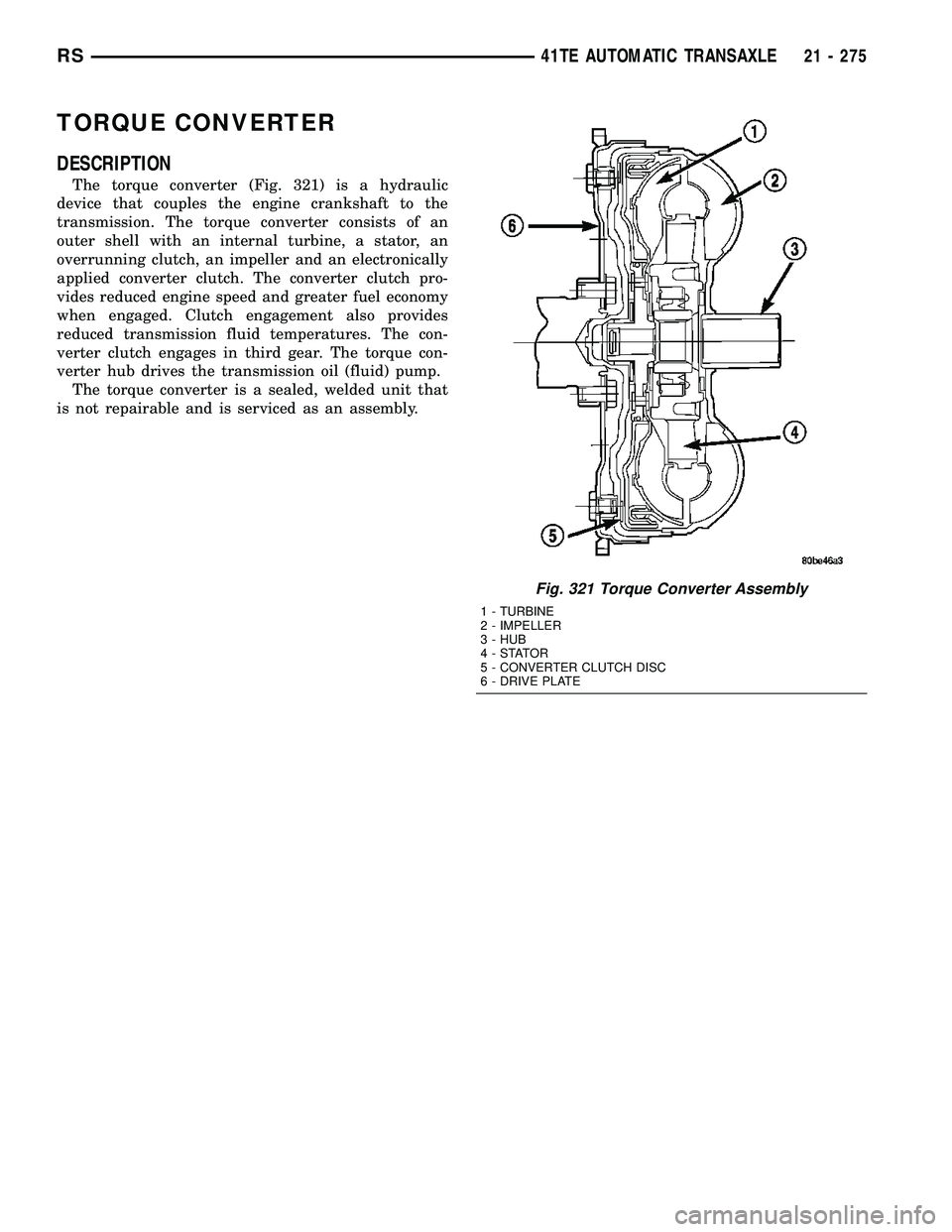
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 321) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 321 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 275
Page 1737 of 2339
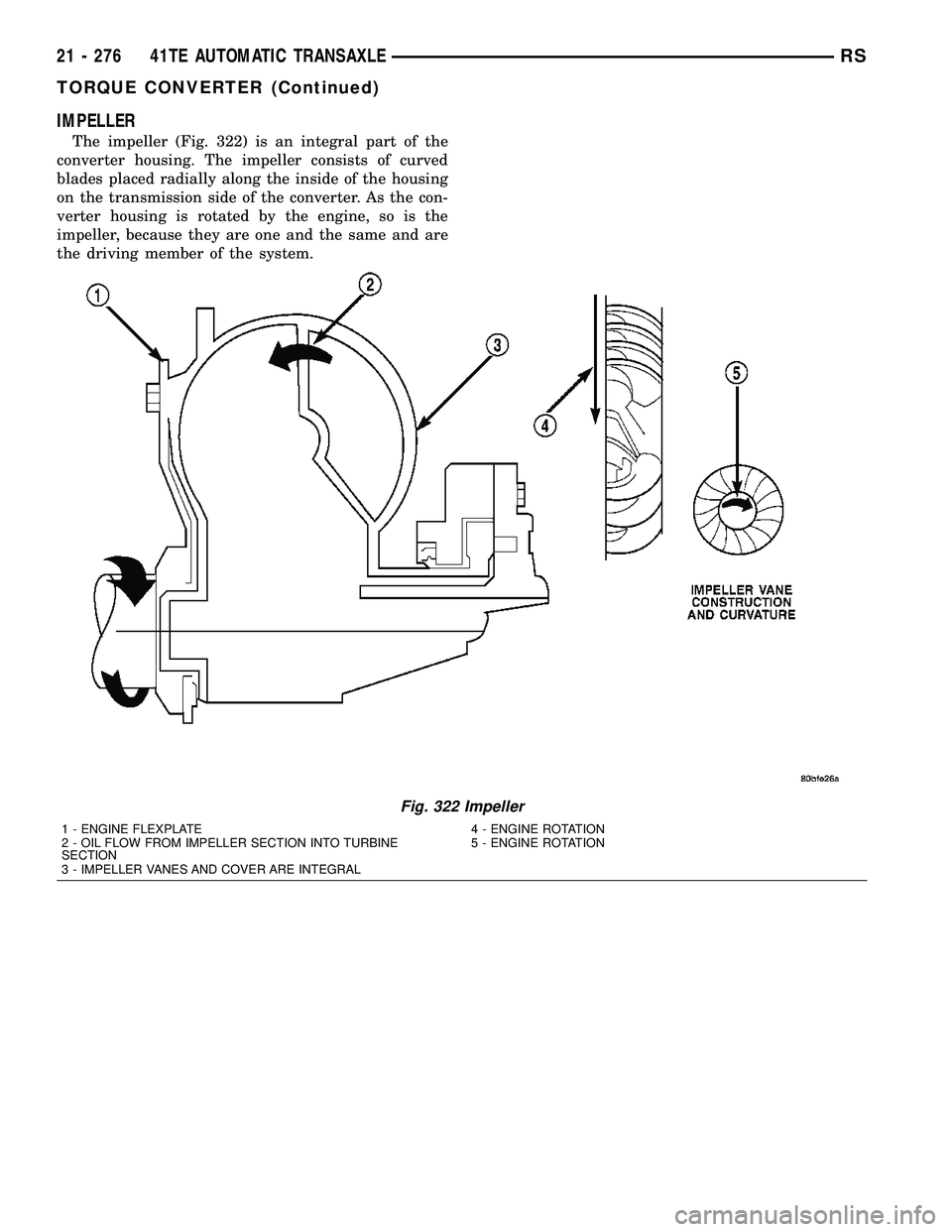
IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 322) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving member of the system.
Fig. 322 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
21 - 276 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1738 of 2339

TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 323) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 323 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE
2 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
5 - ENGINE ROTATION
6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 277
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1739 of 2339
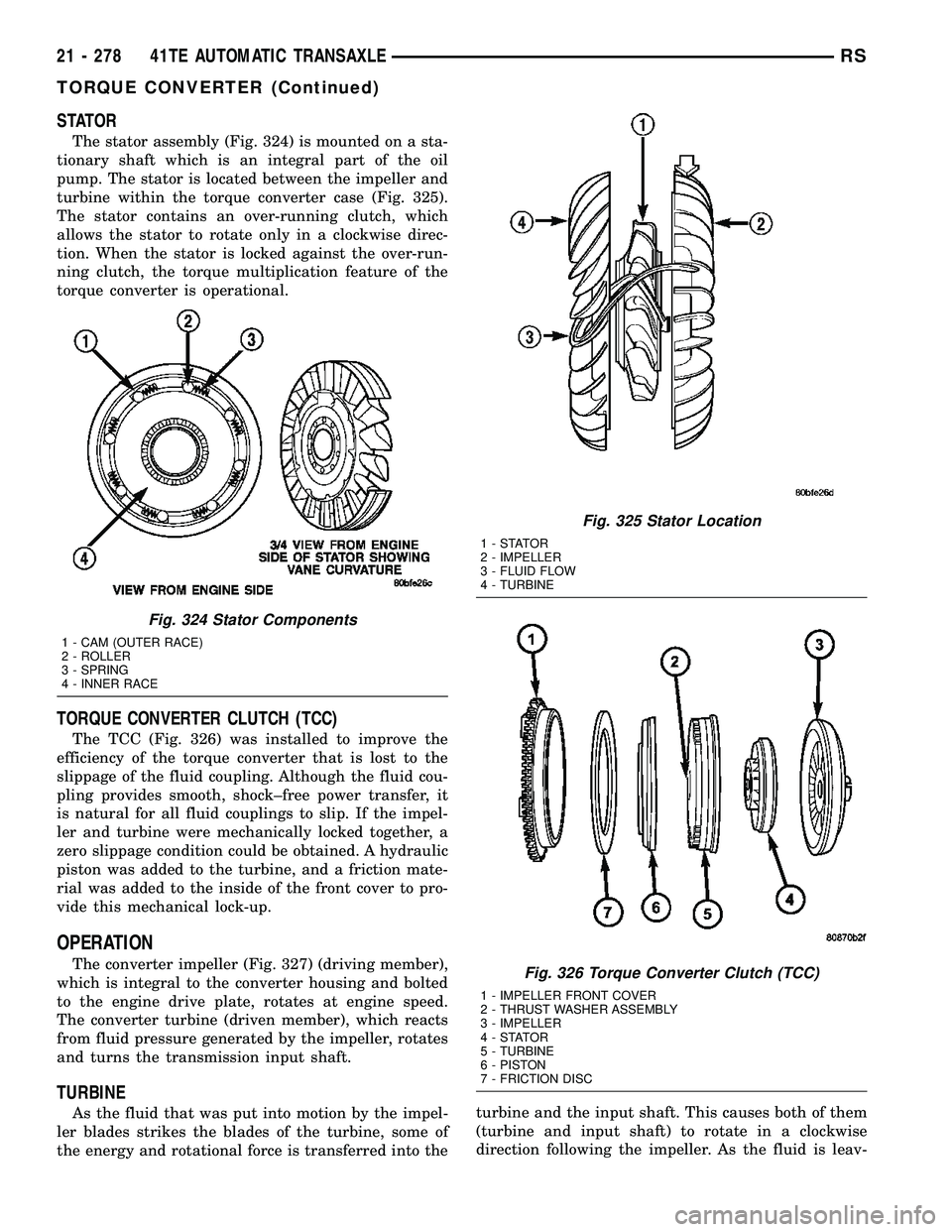
STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 324) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 325).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 326) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock±free power transfer, it
is natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impel-
ler and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 327) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into theturbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
Fig. 324 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 325 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 326 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
21 - 278 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1740 of 2339
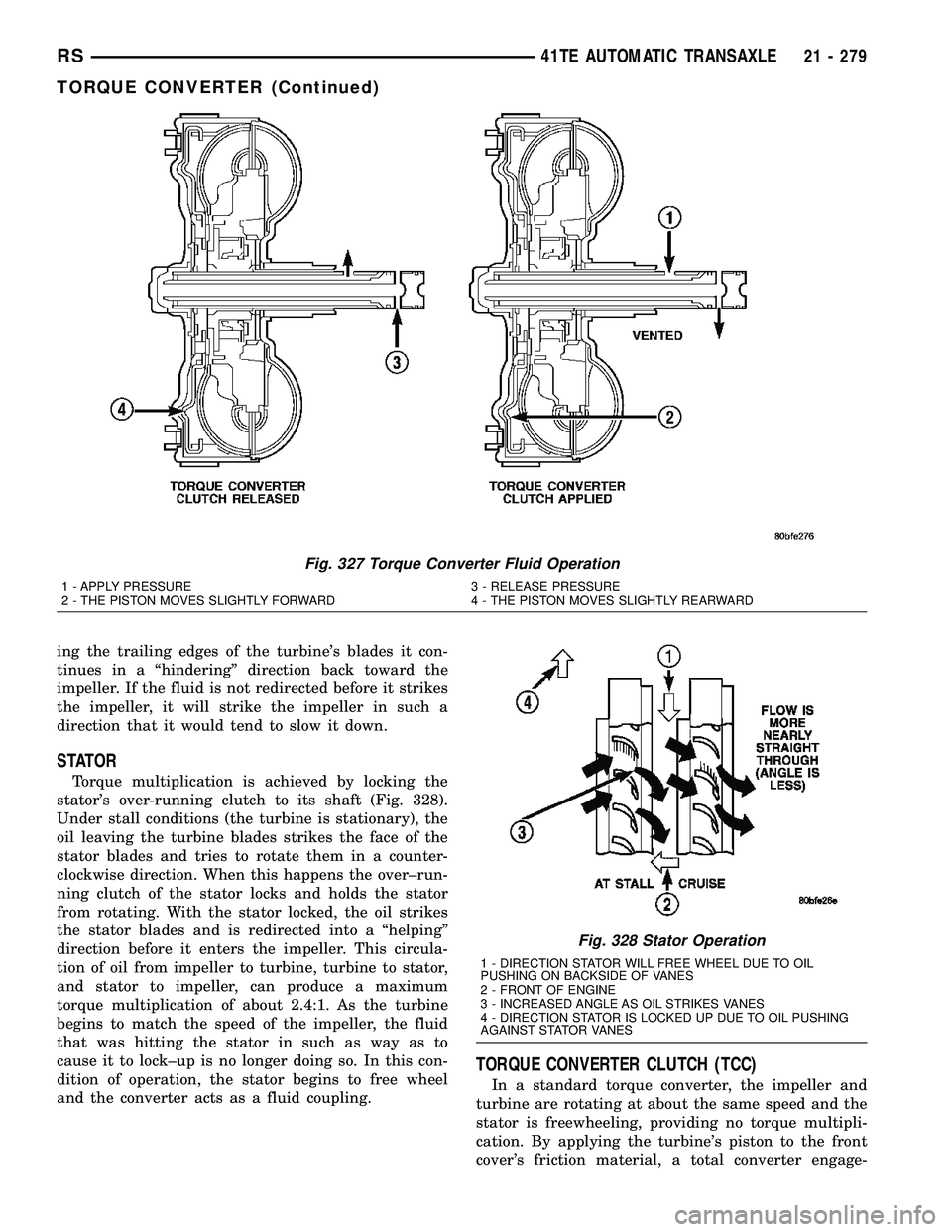
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 328).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
Fig. 327 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
Fig. 328 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 279
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)