2005 CHRYSLER VOYAGER ipm
[x] Cancel search: ipmPage 2158 of 2339

rator initial temperature, then the cool down test has
been failed and further A/C system diagnosis is
required. If the test is failed, the snowflake icon and
the DELAY text will continue to blink across ignition
cycles until the vehicle has been driven for greater
than 13 km (8 miles).
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST
The A/C system is designed to remove heat and
humidity from the air entering the passenger com-
partment. The evaporator, located in the HVAC hous-
ing, is cooled to temperatures near the freezing point.
As warm damp air passes over the fins in the A/C
evaporator, moisture in the air condenses to water,
dehumidifying the air. Condensation on the evapora-
tor fins reduces the evaporators ability to absorb
heat. During periods of high heat and humidity, an
A/C system will be less effective. With the instru-
ment control set to recirculation mode, only air from
the passenger compartment passes through the A/C
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, A/C performance levels rise.
Humidity has an important bearing on the temper-
ature of the air delivered to the interior of the vehi-
cle. It is important to understand the effect that
humidity has on the performance of the A/C system.
When humidity is high, the A/C evaporator has to
perform a double duty. It must lower the air temper-
ature, and it must lower the temperature of the
moisture in the air that condenses on the evaporator
fins. Condensing the moisture in the air transfers
heat energy into the evaporator fins and tubing. This
reduces the amount of heat the A/C evaporator can
absorb from the air. High humidity greatly reduces
the ability of the A/C evaporator to lower the temper-
ature of the air.
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Wring-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from their
A/C system on humid days. A performance test is the
best way to determine whether the system is per-
forming up to design standards. This test also pro-
vides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the A/C system. The ambient air tem-perature in the location where the vehicle will be
tested must be a minimum of 21É C (70É F) for this
test.
PERFORMANCE TEST PROCEDURE
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
coupling to the line fitting, verify that the valve of
the coupling is fully closed. This will reduce the
amount of effort required to make the connection.
(1) Connect a tachometer and a manifold gauge
set.
(2) Set the mode control to the Recirculation Mode
position, the temperature control to the full cool posi-
tion and the blower to the highest speed position.
(3) Start the engine and hold at 1,000 rpm with
the A/C compressor clutch engaged.
(4) The engine should be warmed up to operating
temperature with the doors closed and windows
open.
(5) Insert a thermometer in the driver's side center
panel A/C-heater outlet and operate the engine for
five minutes.
(6) If the compressor clutch does not engage, pro-
ceed with diagnosis of the compressor clutch coil.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
CONTROLS - FRONT/COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(7) With the A/C compressor clutch engaged, com-
pare the air temperature at the center panel outlet
and the compressor discharge pressure to the A/C
Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. The
compressor clutch may cycle, depending upon the
ambient temperature and humidity. If the clutch
cycles, use the readings obtained before the clutch
disengaged.
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-7
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2165 of 2339
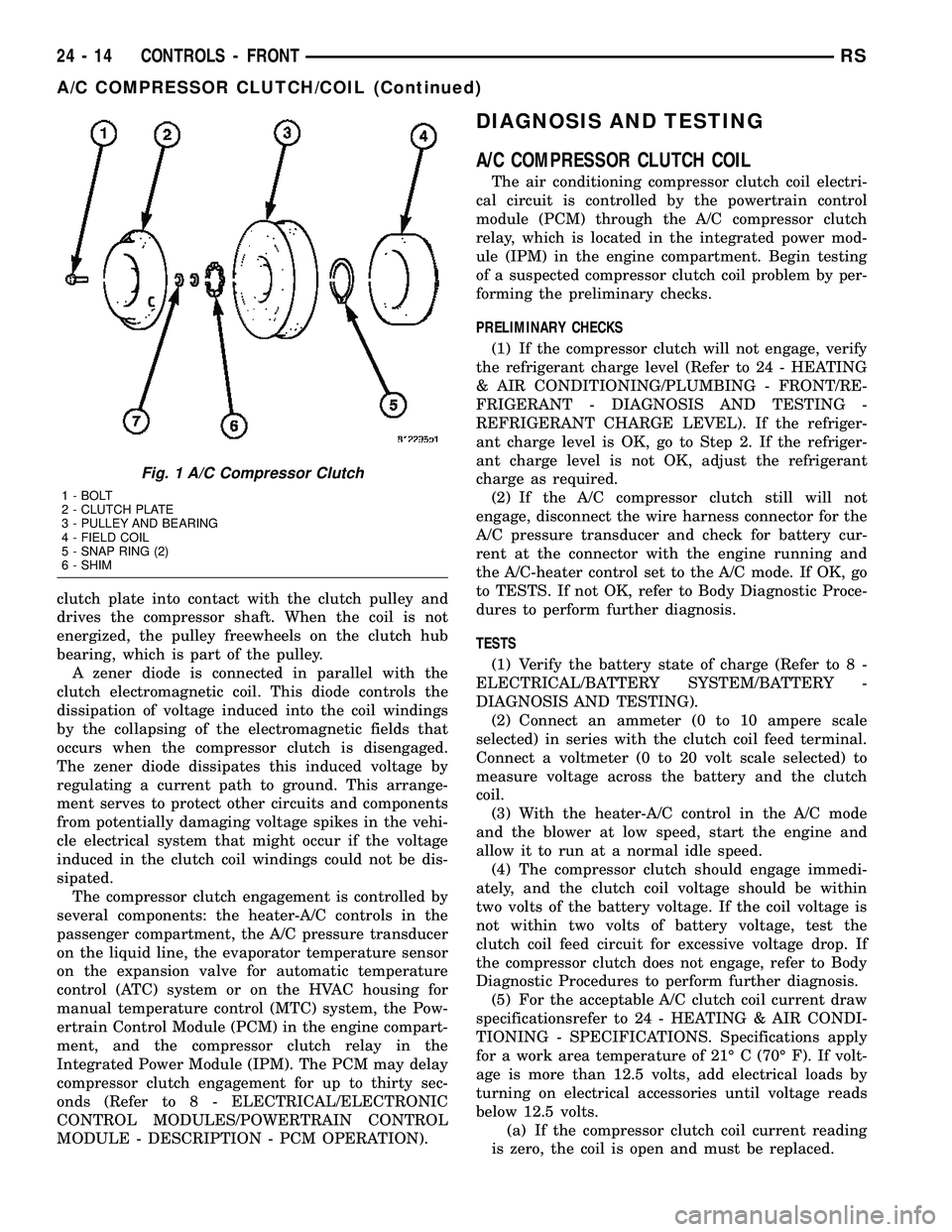
clutch plate into contact with the clutch pulley and
drives the compressor shaft. When the coil is not
energized, the pulley freewheels on the clutch hub
bearing, which is part of the pulley.
A zener diode is connected in parallel with the
clutch electromagnetic coil. This diode controls the
dissipation of voltage induced into the coil windings
by the collapsing of the electromagnetic fields that
occurs when the compressor clutch is disengaged.
The zener diode dissipates this induced voltage by
regulating a current path to ground. This arrange-
ment serves to protect other circuits and components
from potentially damaging voltage spikes in the vehi-
cle electrical system that might occur if the voltage
induced in the clutch coil windings could not be dis-
sipated.
The compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the heater-A/C controls in the
passenger compartment, the A/C pressure transducer
on the liquid line, the evaporator temperature sensor
on the expansion valve for automatic temperature
control (ATC) system or on the HVAC housing for
manual temperature control (MTC) system, the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) in the engine compart-
ment, and the compressor clutch relay in the
Integrated Power Module (IPM). The PCM may delay
compressor clutch engagement for up to thirty sec-
onds (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE - DESCRIPTION - PCM OPERATION).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH COIL
The air conditioning compressor clutch coil electri-
cal circuit is controlled by the powertrain control
module (PCM) through the A/C compressor clutch
relay, which is located in the integrated power mod-
ule (IPM) in the engine compartment. Begin testing
of a suspected compressor clutch coil problem by per-
forming the preliminary checks.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
(1) If the compressor clutch will not engage, verify
the refrigerant charge level (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - FRONT/RE-
FRIGERANT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
REFRIGERANT CHARGE LEVEL). If the refriger-
ant charge level is OK, go to Step 2. If the refriger-
ant charge level is not OK, adjust the refrigerant
charge as required.
(2) If the A/C compressor clutch still will not
engage, disconnect the wire harness connector for the
A/C pressure transducer and check for battery cur-
rent at the connector with the engine running and
the A/C-heater control set to the A/C mode. If OK, go
to TESTS. If not OK, refer to Body Diagnostic Proce-
dures to perform further diagnosis.
TESTS
(1) Verify the battery state of charge (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(2) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale
selected) in series with the clutch coil feed terminal.
Connect a voltmeter (0 to 20 volt scale selected) to
measure voltage across the battery and the clutch
coil.
(3) With the heater-A/C control in the A/C mode
and the blower at low speed, start the engine and
allow it to run at a normal idle speed.
(4) The compressor clutch should engage immedi-
ately, and the clutch coil voltage should be within
two volts of the battery voltage. If the coil voltage is
not within two volts of battery voltage, test the
clutch coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop. If
the compressor clutch does not engage, refer to Body
Diagnostic Procedures to perform further diagnosis.
(5) For the acceptable A/C clutch coil current draw
specificationsrefer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING - SPECIFICATIONS. Specifications apply
for a work area temperature of 21É C (70É F). If volt-
age is more than 12.5 volts, add electrical loads by
turning on electrical accessories until voltage reads
below 12.5 volts.
(a) If the compressor clutch coil current reading
is zero, the coil is open and must be replaced.
Fig. 1 A/C Compressor Clutch
1 - BOLT
2 - CLUTCH PLATE
3 - PULLEY AND BEARING
4 - FIELD COIL
5 - SNAP RING (2)
6 - SHIM
24 - 14 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2169 of 2339

A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 7) is a Interna-
tional Standards Organization (ISO) mini-relay.
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
mini-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO mini-relay ter-
minal pattern (or footprint) is different, the current
capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions are
smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay. The
A/C compressor clutch relay is located in the inte-
grated power module (IPM) in the engine compart-
ment. See the fuse and relay map molded into the
inner surface of the cover of the IPM for A/C com-
pressor clutch relay identification and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the A/C compressor clutch relay. Five
male spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the powertrain control module (PCM) to control the
high current output to the compressor clutch electro-
magnetic coil. The movable common feed contact
point is held against the fixed normally closed con-
tact point by spring pressure. When the relay coil is
energized, an electromagnetic field is produced by the
coil windings. This electromagnetic field draws the
movable relay contact point away from the fixed nor-
mally closed contact point, and holds it against the
fixed normally open contact point. When the relay
coil is de-energized, spring pressure returns the mov-
able contact point back against the fixed normally
closed contact point. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and
helps to dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic
interference that can be generated as the electromag-
netic field of the relay coil collapses.
The compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input from the PCM through the compressor clutch
relay control circuit only when the PCM electroni-
cally pulls the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the PCM through a fused ignition
switch output (run-start) circuit only when the igni-
tion switch is in the On or Start positions.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the compressor clutch coil
through the compressor clutch relay output circuit
only when the compressor clutch relay coil is ener-
gized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the compressor
clutch relay coil is de-energized.
The A/C compressor clutch relay cannot be
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced. Refer to the appropriate wiring information
for diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for
complete HVAC wiring diagrams.
Fig. 7 A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
24 - 18 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
Page 2170 of 2339
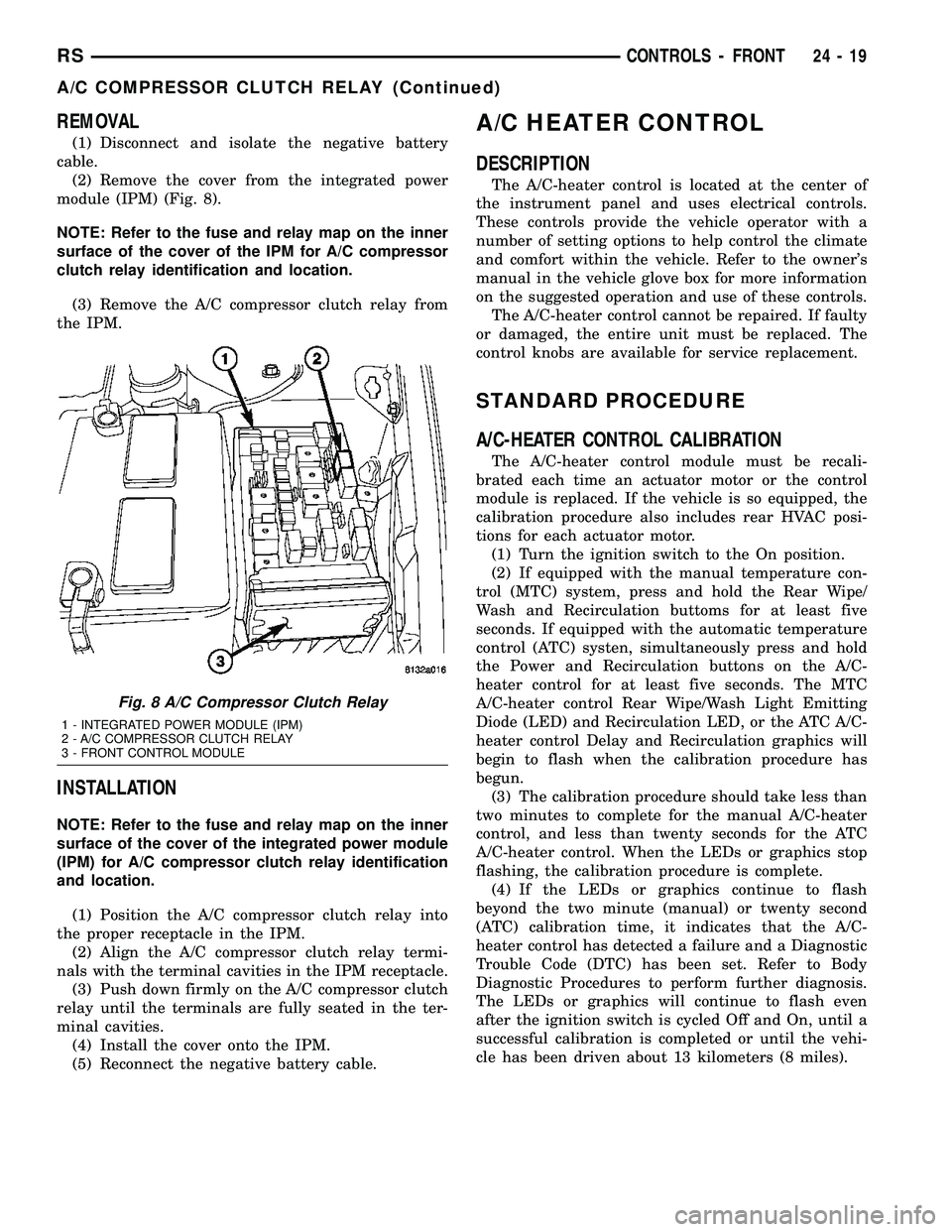
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 8).
NOTE: Refer to the fuse and relay map on the inner
surface of the cover of the IPM for A/C compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(3) Remove the A/C compressor clutch relay from
the IPM.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Refer to the fuse and relay map on the inner
surface of the cover of the integrated power module
(IPM) for A/C compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(1) Position the A/C compressor clutch relay into
the proper receptacle in the IPM.
(2) Align the A/C compressor clutch relay termi-
nals with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(3) Push down firmly on the A/C compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities.
(4) Install the cover onto the IPM.
(5) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The A/C-heater control is located at the center of
the instrument panel and uses electrical controls.
These controls provide the vehicle operator with a
number of setting options to help control the climate
and comfort within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's
manual in the vehicle glove box for more information
on the suggested operation and use of these controls.
The A/C-heater control cannot be repaired. If faulty
or damaged, the entire unit must be replaced. The
control knobs are available for service replacement.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
A/C-HEATER CONTROL CALIBRATION
The A/C-heater control module must be recali-
brated each time an actuator motor or the control
module is replaced. If the vehicle is so equipped, the
calibration procedure also includes rear HVAC posi-
tions for each actuator motor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
(2) If equipped with the manual temperature con-
trol (MTC) system, press and hold the Rear Wipe/
Wash and Recirculation buttoms for at least five
seconds. If equipped with the automatic temperature
control (ATC) systen, simultaneously press and hold
the Power and Recirculation buttons on the A/C-
heater control for at least five seconds. The MTC
A/C-heater control Rear Wipe/Wash Light Emitting
Diode (LED) and Recirculation LED, or the ATC A/C-
heater control Delay and Recirculation graphics will
begin to flash when the calibration procedure has
begun.
(3) The calibration procedure should take less than
two minutes to complete for the manual A/C-heater
control, and less than twenty seconds for the ATC
A/C-heater control. When the LEDs or graphics stop
flashing, the calibration procedure is complete.
(4) If the LEDs or graphics continue to flash
beyond the two minute (manual) or twenty second
(ATC) calibration time, it indicates that the A/C-
heater control has detected a failure and a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) has been set. Refer to Body
Diagnostic Procedures to perform further diagnosis.
The LEDs or graphics will continue to flash even
after the ignition switch is cycled Off and On, until a
successful calibration is completed or until the vehi-
cle has been driven about 13 kilometers (8 miles).
Fig. 8 A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-19
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2174 of 2339

(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the blend door actuator.
(4) Install the silencer under the driver side end of
the instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL SILENCER -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(6) Perform the heater-A/C control calibration pro-
cedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CONTROL
- STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C CON-
TROL CALIBRATION).
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The front blower motor relay is an International
Standards Organization (ISO)-type relay (Fig. 12).
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The front
blower motor relay is located in the integrated power
module (IPM) in the engine compartment. See the
fuse and relay map on the inner surface of the cover
of the IPM for front blower motor relay identification
and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the front blower motor relay. Five male
spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of the
base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem, and the ISO designation for each terminal ismolded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
The front blower motor relay cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If the relay is damaged or faulty, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The blower motor relay is an electromechanical
switch that uses a low current input from the Front
Control Module (FCM) to control the high current
output to the blower motor resistor (manual heater-
A/C control) or blower power module (ATC control).
The movable common feed contact point is held
against the fixed normally closed contact point by
spring pressure. When the relay coil is energized, an
electromagnetic field is produced by the coil wind-
ings. This electromagnetic field draws the movable
relay contact point away from the fixed normally
closed contact point, and holds it against the fixed
normally open contact point. When the relay coil is
de-energized, spring pressure returns the movable
contact point back against the fixed normally closed
contact point. The resistor or diode is connected in
parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic interfer-
ence that can be generated as the electromagnetic
field of the relay coil collapses.
Fig. 11 Blend Door Actuator - LHD Shown, RHD
Typical
1 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - SCREW (2)
4 - DRIVER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (DUAL-ZONE)
5 - HEATER CORE
6 - BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (SINGLE ZONE) OR PASSENGER
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (DUAL-ZONE)
Fig. 12 Front Blower Motor Relay
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-23
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2175 of 2339
The blower motor relay terminals are connected to
the vehicle electrical system through a receptacle in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM). The inputs and
outputs of the blower motor relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from the battery through a B(+)
circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input through the front/rear blower motor relay con-
trol circuit only when the FCM electronically pulls
the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the battery through a B(+) circuit
at all times.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the blower motor resistor
(manual heater-A/C control) or blower power module
(automatic heater-A/C control) through a fuse in the
IPM on the fused front blower motor relay output cir-
cuit only when the blower motor relay coil is ener-
gized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the blower motor
relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
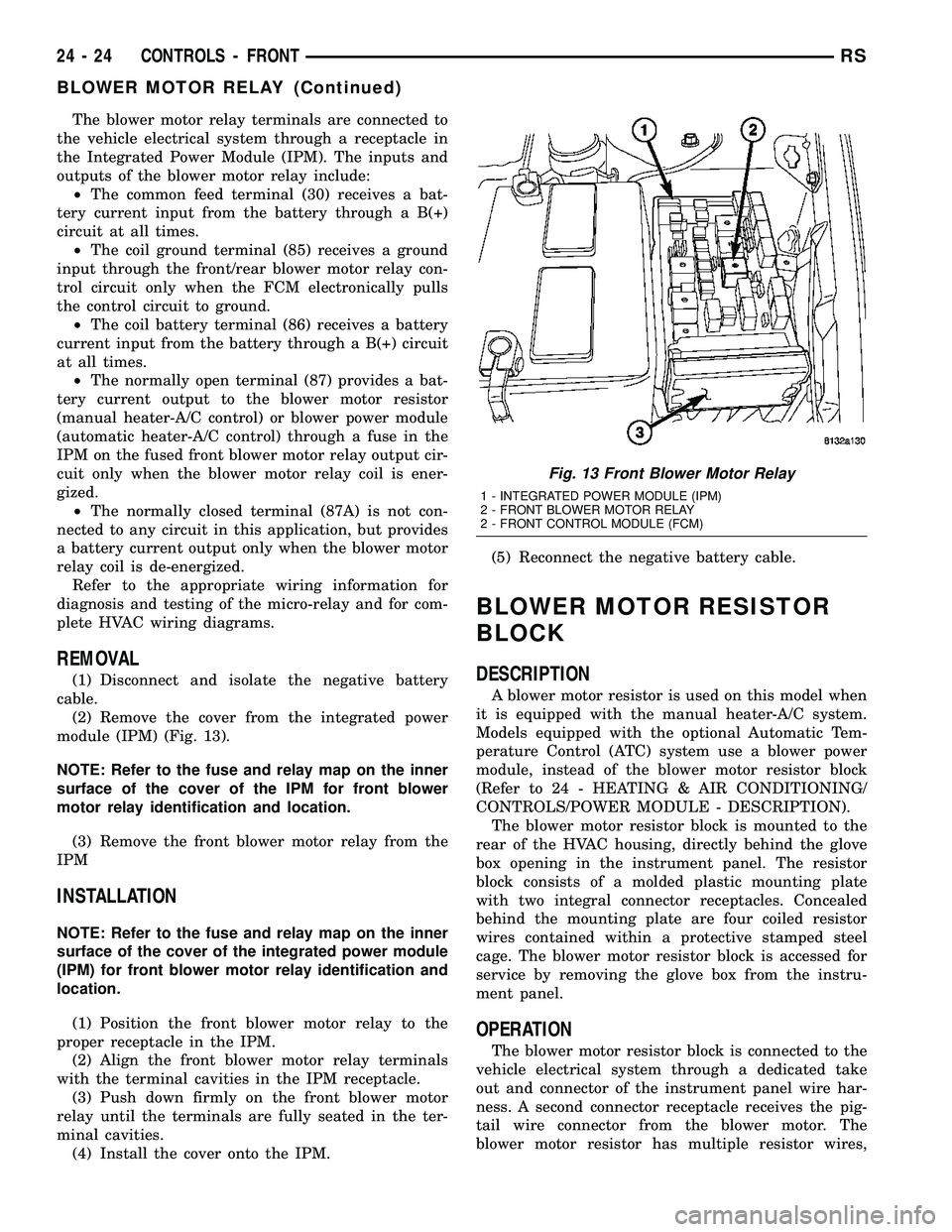
module (IPM) (Fig. 13).
NOTE: Refer to the fuse and relay map on the inner
surface of the cover of the IPM for front blower
motor relay identification and location.
(3) Remove the front blower motor relay from the
IPM
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Refer to the fuse and relay map on the inner
surface of the cover of the integrated power module
(IPM) for front blower motor relay identification and
location.
(1) Position the front blower motor relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(2) Align the front blower motor relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(3) Push down firmly on the front blower motor
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities.
(4) Install the cover onto the IPM.(5) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
A blower motor resistor is used on this model when
it is equipped with the manual heater-A/C system.
Models equipped with the optional Automatic Tem-
perature Control (ATC) system use a blower power
module, instead of the blower motor resistor block
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
CONTROLS/POWER MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
The blower motor resistor block is mounted to the
rear of the HVAC housing, directly behind the glove
box opening in the instrument panel. The resistor
block consists of a molded plastic mounting plate
with two integral connector receptacles. Concealed
behind the mounting plate are four coiled resistor
wires contained within a protective stamped steel
cage. The blower motor resistor block is accessed for
service by removing the glove box from the instru-
ment panel.
OPERATION
The blower motor resistor block is connected to the
vehicle electrical system through a dedicated take
out and connector of the instrument panel wire har-
ness. A second connector receptacle receives the pig-
tail wire connector from the blower motor. The
blower motor resistor has multiple resistor wires,
Fig. 13 Front Blower Motor Relay
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
2 - FRONT BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
2 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE (FCM)
24 - 24 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
Page 2187 of 2339
(6) Install the screw that secures the front of the
rear HVAC housing to the right quarter inner panel.
Tighten the screw to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(7) Install the screw that secures the back of the
rear HVAC housing to the right D-pillar. Tighten the
screw to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(8) Install the two screws that secure the top of
the quarter trim panel attaching bracket to the quar-
ter inner panel. Tighten the screws to 2 N´m (17 in.
lbs.).
(9) Reinstall the right quarter trim panel and
right D-pillar trim panel onto the quarter inner
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/QUARTER
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(10) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(11) Perform the heater-A/C control calibration
procedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CON-
TROL - STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C
CONTROL CALIBRATION).
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The rear blower motor relay is a International
Standards Organization (ISO)-type relay (Fig. 4).
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The rear
blower motor relay is located in the integrated power
module (IPM) in the engine compartment. See the
fuse and relay map on the inner surface of the cover
of the IPM for rear blower motor relay identification
and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the rear blower motor relay. Five male
spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of the
base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical sys-tem, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
The rear blower motor relay cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If the relay is damaged or faulty, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The rear blower motor relay is an electromechani-
cal switch that uses a low current input from the
Front Control Module (FCM) to control the high cur-
rent output to the rear blower motor resistor (man-
ual heater-A/C control) or rear blower motor power
module (ATC heater-A/C control). The movable com-
mon feed contact point is held against the fixed nor-
mally closed contact point by spring pressure. When
the relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic field is
produced by the coil windings. This electromagnetic
field draws the movable relay contact point away
from the fixed normally closed contact point, and
holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. The
resistor or diode is connected in parallel with the
relay coil in the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage
spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be
generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The rear blower motor relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the Integrated Power Module (IPM).
The inputs and outputs of the rear blower motor
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from the battery through a B(+)
circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input through the front/rear blower motor relay con-
trol circuit only when the FCM electronically pulls
the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the battery through a B(+) circuit
at all times.
Fig. 4 Rear Blower Motor Relay
24 - 36 CONTROLS - REARRS
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2188 of 2339
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the blower motor resistor
(manual heater-A/C control) or blower power module
(ATC heater-A/C control) through a fuse in the IPM
on the fused rear blower motor relay output circuit
only when the blower motor relay coil is energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the rear blower
motor relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
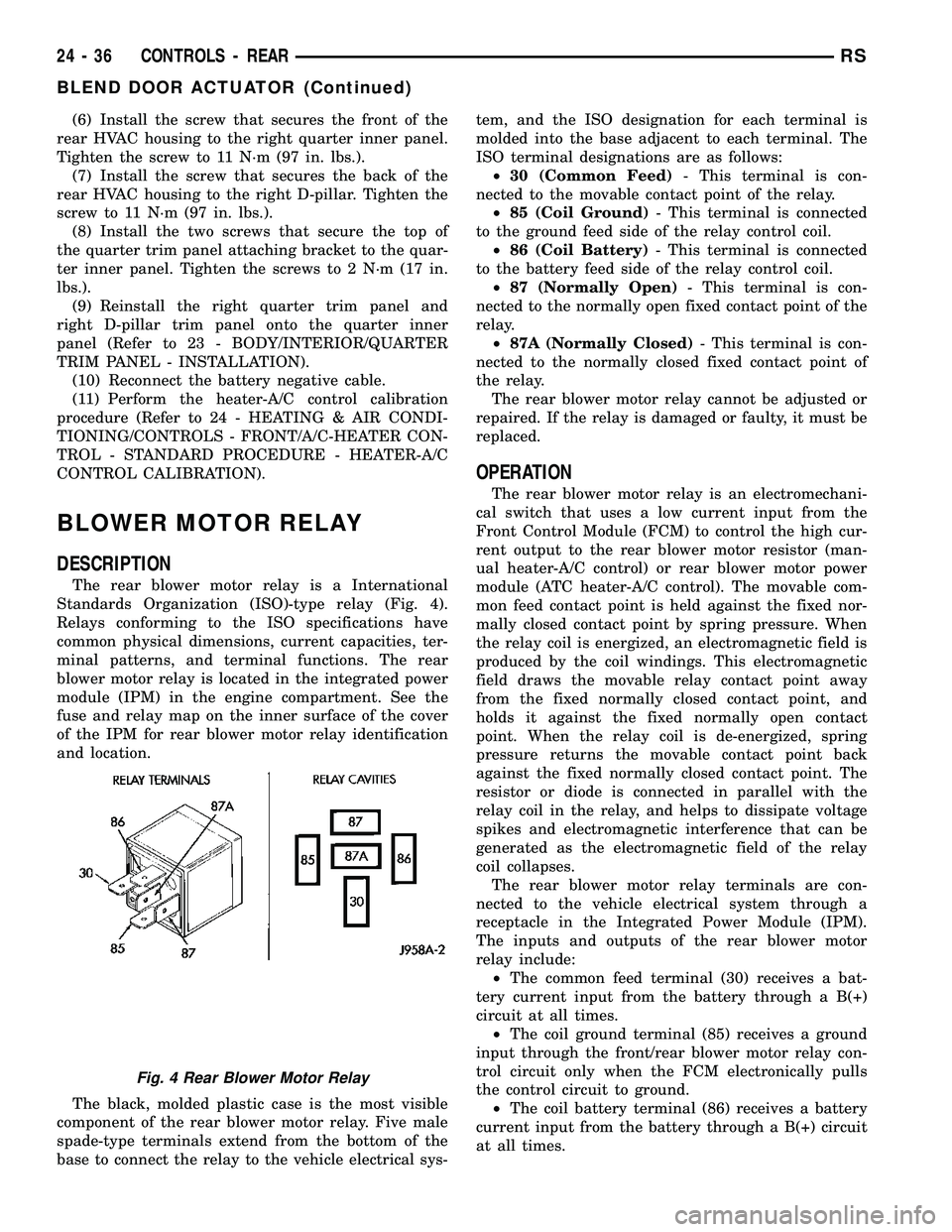
module (IPM) (Fig. 5).
NOTE: Refer to the fuse and relay map on the inner
surface of the cover of the IPM for rear blower
motor relay identification and location.
(3) Remove the rear blower motor relay from the
IPM.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Refer to the fuse and relay map on the inner
surface of the cover of the integrated power module
(IPM) for rear blower motor relay identification and
location.
(1) Position the rear blower motor relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(2) Align the rear blower motor relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(3) Push down firmly on the rear blower motor
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities.
(4) Install the cover onto the IPM.
(5) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
A rear blower motor resistor is used on this model
when it is equipped with the manual heater-A/C sys-
tem. Models equipped with the optional Automatic
Temperature Control (ATC) system use a rear blower
motor power module, instead of the blower motor
resistor block (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/CONTROLS/POWER MODULE -
DESCRIPTION). The rear blower motor resistor
block is mounted to the rear HVAC housing, directly
above the expansion valve. The resistor block con-
sists of a molded plastic mounting plate with an inte-
gral connector receptacle. Concealed behind the
mounting plate is an electrical circuit board with two
resistors and a thermal fuse. The rear blower motor
resistor block is accessed for service by removing the
right quarter and D-pillar trim panels.
OPERATION
The rear blower motor resistor block is connected
to the vehicle electrical system through a dedicated
take out and connector of the rear HVAC wire har-
ness. The blower motor resistor has an electrical cir-
cuit board with two resistors, each of which will
reduce the current flow through the blower motor to
change the blower motor speed. The blower motor
switch in the manual heater-A/C system directs the
ground path for the rear blower motor through the
correct resistor to obtain the selected speed.
Fig. 5 Rear Blower Motor Relay
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
2 - REAR BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE (FCM)
RSCONTROLS - REAR24-37
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)