2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 303 of 2339

SLIDING DOOR CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with a power sliding door system
utilize a sliding door control module. The sliding door
control module is located behind the sliding door trim
panel in the center of the door, just above the sliding
door motor (Fig. 15). This module controls the opera-
tion of the door through the Programmable Commu-
nication Interface (PCI) data bus circuit and the
Body Control Module (BCM). The sliding door control
module contains software technology which enables it
to detect resistance to door travel and to reverse door
travel in order to avoid damage to the door or to
avoid possible personal injury if the obstruction is a
person. This feature functions in both the opening
and closing cycles. If the power sliding door system
develops any problems the control module will store
and recall Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC). The use
of a diagnostic scan tool, such as the DRB IIItis
required to read and troubleshoot these trouble
codes. The sliding door control module can be
reflashed if necessary. Refer to the latest Technical
Service Bulletin (TSB) Information for any updates.The power door control module is a replaceable
component and cannot be repaired, if found to be
faulty it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The power sliding door control module serves as
the main computer for the power sliding door system.
All power door functions are processed through the
power sliding door control module and/or the vehicles
Body Control Module (BCM). At the start of a power
open command, a signal is sent to the BCM and then
to the power sliding door control module via the Pro-
grammable Communication Interface (PCI) data bus
circuit. This signal, generated by any of the power
door command switches, tells the power sliding door
control module to activate a power latch release,
engage the clutch assembly and drive the door into
the full open position. If an obstacle is felt during
this power open cycle, the module will reverse direc-
tion and close the door. This process is also enabled
during a power close cycle. This process will repeat
three times, and if a fourth obstacle is detected, the
door will go into full manual mode. Once the full
open position is obtained, a hold open latch assembly
mounted full open switch tells the power sliding door
control module that the door has reached the full
open position. If the power sliding door system devel-
ops any problems the power sliding door control mod-
ule will store and recall Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(DTC). The use of a diagnostic scan tool, such as the
DRB IIItis required to read and troubleshoot these
trouble codes.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
Any diagnosis of the power sliding door sys-
tem should begin with the use of the DRB IIIt
diagnostic tool. For information on the use of
the DRB IIIt, refer to the appropriate Diagnos-
tic Procedures information.
Inspect the related wiring harness connectors for
broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded terminals.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the appropriate door trim panel from
the vehicle. (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOORS - SLIDING/
TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove the weather shield.
Fig. 15 Power Side Door Components
1 - SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
2 - MODULE RETAINING SCREW
3 - MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
4 - DOOR MOTOR ASSEMBLY
5 - FLEX DRIVE ASSEMBLY
6 - DOOR MOTOR RETAINING FASTENERS
7 - DOOR MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
8E - 18 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
Page 304 of 2339

(4) Disconnect the power door control module elec-
trical connectors. Slide the red locking tab out (away
from module) and depress connector retaining tab,
while pulling straight apart.
(5) Remove the control module retaining screw
(Fig. 16).
(6) Remove the module from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the sliding door control module and
install the retaining screw.
(2) Connect the electrical connectors. Slide the
locking tab into the locked position.
(3) Install the weather shield.
(4) Install the appropriate door trim panel on the
vehicle. (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOORS - SLIDING/
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION)
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
(6) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any power door control module diagnostic trou-
ble codes.
(7) Verify power door system operation. Cycle the
power door through one complete open and close
cycle.
Fig. 16 Power Side Door Components
1 - SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
2 - MODULE RETAINING SCREW
3 - MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
4 - DOOR MOTOR ASSEMBLY
5 - FLEX DRIVE ASSEMBLY
6 - DOOR MOTOR RETAINING FASTENERS
7 - DOOR MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-19
SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 306 of 2339

ENGINE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM......................... 1
CHARGING.............................. 21STARTING............................... 31
BATTERY SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY SYSTEM.....................2
CLEANING.............................5
INSPECTION...........................5
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY............................6
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS.......7
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY............................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE
SPIRAL PLATE BATTERY CHARGING......10
CONVENTIONAL BATTERY CHARGING....11
OPEN-CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST..........13IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST.............13
CHECKING BATTERY ELECTROLYTE
LEVEL..............................14
MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER...........15
REMOVAL - BATTERY...................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BATTERY HOLDDOWN
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BATTERY CABLES
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY CABLES....................17
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION.........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................20
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a single 12-volt bat-
tery. All of the components of the battery system are
located within the engine compartment. The battery
system for this vehicle contains the following related
components:
²Battery- The storage battery provides a reli-
able means of storing a renewable source of electrical
energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cable- The battery cables connect the
battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Thermowrap- The battery thermow-
rap insulates the battery to protect it from engine
compartment temperature extremes.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
RSENGINE SYSTEMS8F-1
Page 307 of 2339

OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-
sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a complete system. In order for the engine to start
and the battery to maintain its charge properly, all of
the components that are used in these systems must
perform within specifications. It is important that
the battery, starting, and charging systems be thor-
oughly tested and inspected any time a battery needs
to be charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal bat-
tery discharge, overcharging or early battery failuremust be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) for the proper charging system on-board
diagnostic test procedures.MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER
The Micro 420 automotive battery tester is
designed to help the dealership technicians diagnose
the cause of a defective battery. Follow the instruc-
tion manual supplied with the tester to properly
diagnose a vehicle. If the instruction manual is not
available refer to the standard procedure in this sec-
tion, which includes the directions for using the
Micro 420 battery tester.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 308 of 2339
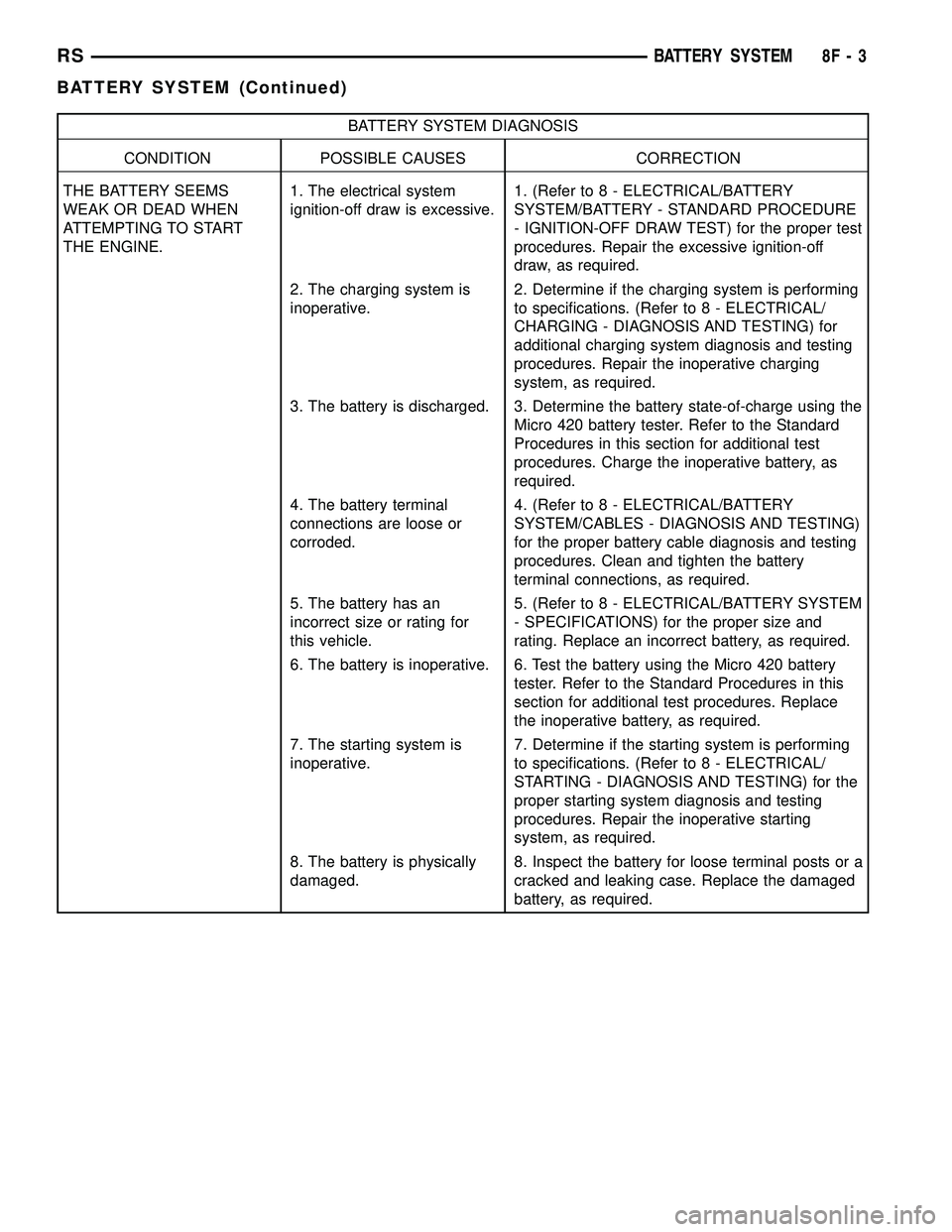
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY SEEMS
WEAK OR DEAD WHEN
ATTEMPTING TO START
THE ENGINE.1. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST) for the proper test
procedures. Repair the excessive ignition-off
draw, as required.
2. The charging system is
inoperative.2. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
additional charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative charging
system, as required.
3. The battery is discharged. 3. Determine the battery state-of-charge using the
Micro 420 battery tester. Refer to the Standard
Procedures in this section for additional test
procedures. Charge the inoperative battery, as
required.
4. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
for the proper battery cable diagnosis and testing
procedures. Clean and tighten the battery
terminal connections, as required.
5. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM
- SPECIFICATIONS) for the proper size and
rating. Replace an incorrect battery, as required.
6. The battery is inoperative. 6. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester. Refer to the Standard Procedures in this
section for additional test procedures. Replace
the inoperative battery, as required.
7. The starting system is
inoperative.7. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative starting
system, as required.
8. The battery is physically
damaged.8. Inspect the battery for loose terminal posts or a
cracked and leaking case. Replace the damaged
battery, as required.
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-3
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 309 of 2339
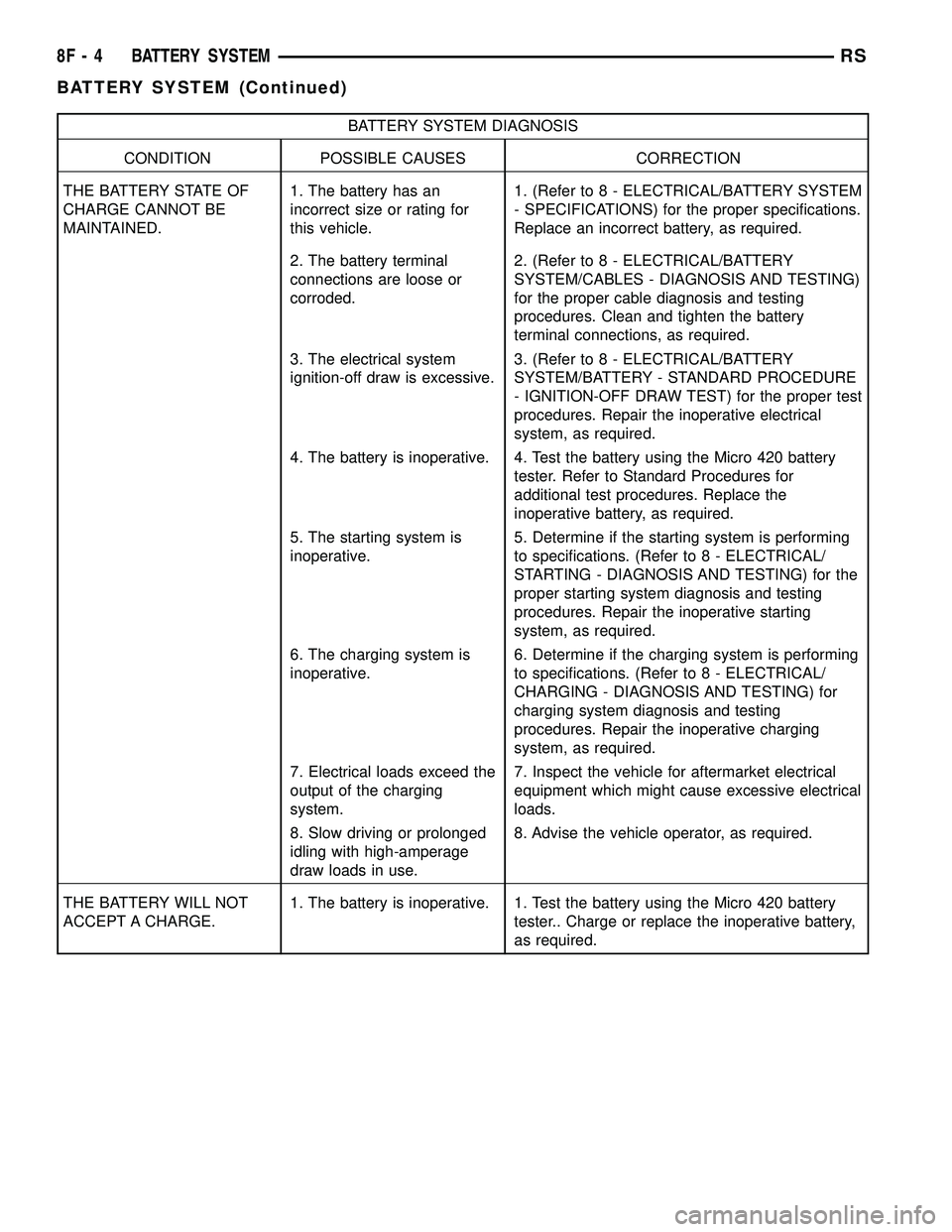
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY STATE OF
CHARGE CANNOT BE
MAINTAINED.1. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM
- SPECIFICATIONS) for the proper specifications.
Replace an incorrect battery, as required.
2. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/CABLES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
for the proper cable diagnosis and testing
procedures. Clean and tighten the battery
terminal connections, as required.
3. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE
- IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST) for the proper test
procedures. Repair the inoperative electrical
system, as required.
4. The battery is inoperative. 4. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester. Refer to Standard Procedures for
additional test procedures. Replace the
inoperative battery, as required.
5. The starting system is
inoperative.5. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative starting
system, as required.
6. The charging system is
inoperative.6. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
CHARGING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for
charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the inoperative charging
system, as required.
7. Electrical loads exceed the
output of the charging
system.7. Inspect the vehicle for aftermarket electrical
equipment which might cause excessive electrical
loads.
8. Slow driving or prolonged
idling with high-amperage
draw loads in use.8. Advise the vehicle operator, as required.
THE BATTERY WILL NOT
ACCEPT A CHARGE.1. The battery is inoperative. 1. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester.. Charge or replace the inoperative battery,
as required.
8F - 4 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 310 of 2339
CLEANING
The following information details the recommended
cleaning procedures for the battery and related com-
ponents. In addition to the maintenance schedules
found in this service manual and the owner's man-
ual, it is recommended that these procedures be per-
formed any time the battery or related components
must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Clean the battery cable terminal clamps of all
corrosion. Remove any corrosion using a wire brush
or a post and terminal cleaning tool, and a sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda) and warm water cleaning
solution (Fig. 1).
(2) Clean the battery tray and battery holddown
hardware of all corrosion. Remove any corrosion
using a wire brush and a sodium bicarbonate (baking
soda) and warm water cleaning solution. Paint any
exposed bare metal.
(3) If the removed battery is to be reinstalled,
clean the outside of the battery case and the top
cover with a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
warm water cleaning solution using a stiff bristle
parts cleaning brush to remove any acid film (Fig. 2).
Rinse the battery with clean water. Ensure that the
cleaning solution does not enter the battery cells
through the vent holes. If the battery is being
replaced, refer to Battery System Specifications for
the factory-installed battery specifications. Confirm
that the replacement battery is the correct size and
has the correct ratings for the vehicle.(4) Clean the battery thermowrap with a sodium
bicarbonate (baking soda) and warm water cleaning
solution using a soft bristle parts cleaning brush to
remove any acid film.
(5) Clean any corrosion from the battery terminal
posts with a wire brush or a post and terminal
cleaner, and a sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and
warm water cleaning solution (Fig. 3).
INSPECTION
The following information details the recommended
inspection procedures for the battery and related
components. It is recommended that these proce-
dures be performed any time the battery or related
components must be removed for vehicle service.
(1) Inspect the battery cable terminal clamps for
damage. Replace any battery cable that has a dam-
aged or deformed terminal clamp.
(2) Inspect the battery tray and battery holddown
hardware for damage. Replace any damaged parts.
(3) Slide the thermowrap off of the battery case.
Inspect the battery case for cracks or other damage
that could result in electrolyte leaks. Also, check the
battery terminal posts for looseness. Batteries with
damaged cases or loose terminal posts must be
replaced.
(4) Inspect the battery thermowrap for tears,
cracks, deformation or other damage. Replace any
battery thermal wrap that has been damaged.
Fig. 1 Clean Battery Cable Terminal Clamp - Typical
1 - TERMINAL BRUSH
2 - BATTERY CABLE
Fig. 2 Clean Battery - Typical
1 - CLEANING BRUSH
2 - WARM WATER AND BAKING SODA SOLUTION
3 - BATTERY
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-5
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 311 of 2339

(5) Inspect the battery built-in test indicator sight
glass (if equipped) for an indication of the battery
condition. If the battery is discharged, charge as
required. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYS-
TEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE - BAT-
TERY CHARGING) for the proper battery charging
procedures.
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY
The battery Group Size number, the Cold Cranking
Amperage (CCA) rating, and the Reserve Capacity(RC) rating or Ampere-Hours (AH) rating can be
found on the original equipment battery label. Be
certain that a replacement battery has the correct
Group Size number, as well as CCA, and RC or AH
ratings that equal or exceed the original equipment
specification for the vehicle being serviced. Battery
sizes and ratings are discussed in more detail below.
²Group Size- The outside dimensions and ter-
minal placement of the battery conform to standards
established by the Battery Council International
(BCI). Each battery is assigned a BCI Group Size
number to help identify a correctly-sized replace-
ment.
²Cold Cranking Amperage- The Cold Crank-
ing Amperage (CCA) rating specifies how much cur-
rent (in amperes) the battery can deliver for thirty
seconds at -18É C (0É F). Terminal voltage must not
fall below 7.2 volts during or after the thirty second
discharge period. The CCA required is generally
higher as engine displacement increases, depending
also upon the starter current draw requirements.
²Reserve Capacity- The Reserve Capacity (RC)
rating specifies the time (in minutes) it takes for bat-
tery terminal voltage to fall below 10.5 volts, at a
discharge rate of 25 amperes. RC is determined with
the battery fully-charged at 26.7É C (80É F). This rat-
ing estimates how long the battery might last after a
charging system failure, under minimum electrical
load.
²Ampere-Hours- The Ampere-Hours (AH) rat-
ing specifies the current (in amperes) that a battery
can deliver steadily for twenty hours, with the volt-
age in the battery not falling below 10.5 volts. This
rating is also sometimes identified as the twenty-
hour discharge rating.
BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS & RATINGS
Part NumberBCI Group Size
ClassificationCold Cranking
AmperageReserve
CapacityAmpere -
HoursLoad Test
Amperage
4686158AD 34 500 110 Minutes 60 250
4727159AD 34 600 120 Minutes 66 300
4727242AD DIN H6 600 120 Minutes 66 300
4868999AA 34 700 90 Minutes 50 350
Fig. 3 Clean Battery Terminal Post - Typical
1 - TERMINAL BRUSH
2 - BATTERY CABLE
3 - BATTERY
8F - 6 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)