Page 1580 of 2339
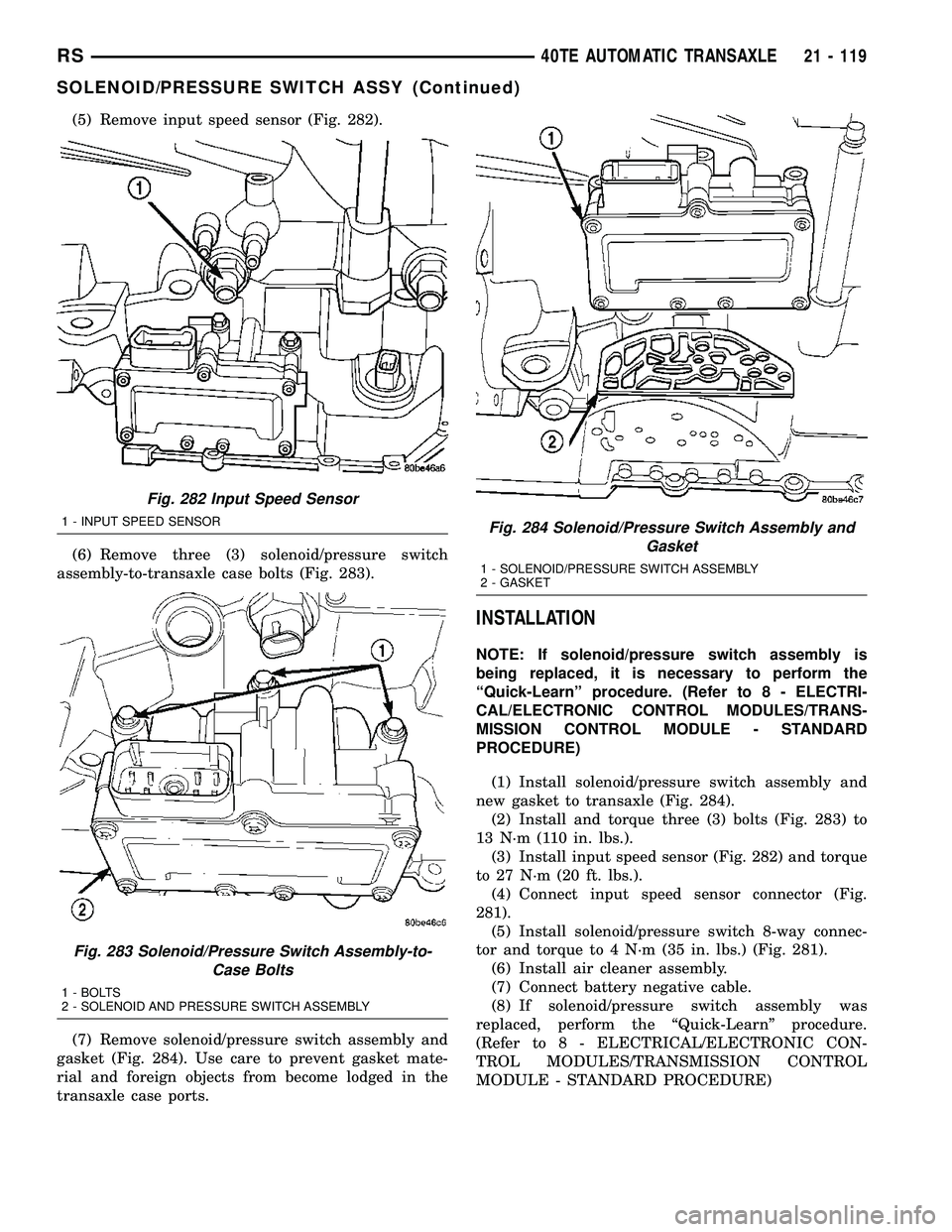
(5) Remove input speed sensor (Fig. 282).
(6) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 283).
(7) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 284). Use care to prevent gasket mate-
rial and foreign objects from become lodged in the
transaxle case ports.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, it is necessary to perform the
ªQuick-Learnº procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANS-
MISSION CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(1) Install solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
new gasket to transaxle (Fig. 284).
(2) Install and torque three (3) bolts (Fig. 283) to
13 N´m (110 in. lbs.).
(3) Install input speed sensor (Fig. 282) and torque
to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(4) Connect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
281).
(5) Install solenoid/pressure switch 8-way connec-
tor and torque to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) (Fig. 281).
(6) Install air cleaner assembly.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) If solenoid/pressure switch assembly was
replaced, perform the ªQuick-Learnº procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 282 Input Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 283 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly-to-
Case Bolts
1 - BOLTS
2 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 284 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly and
Gasket
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - GASKET
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 119
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
Page 1581 of 2339
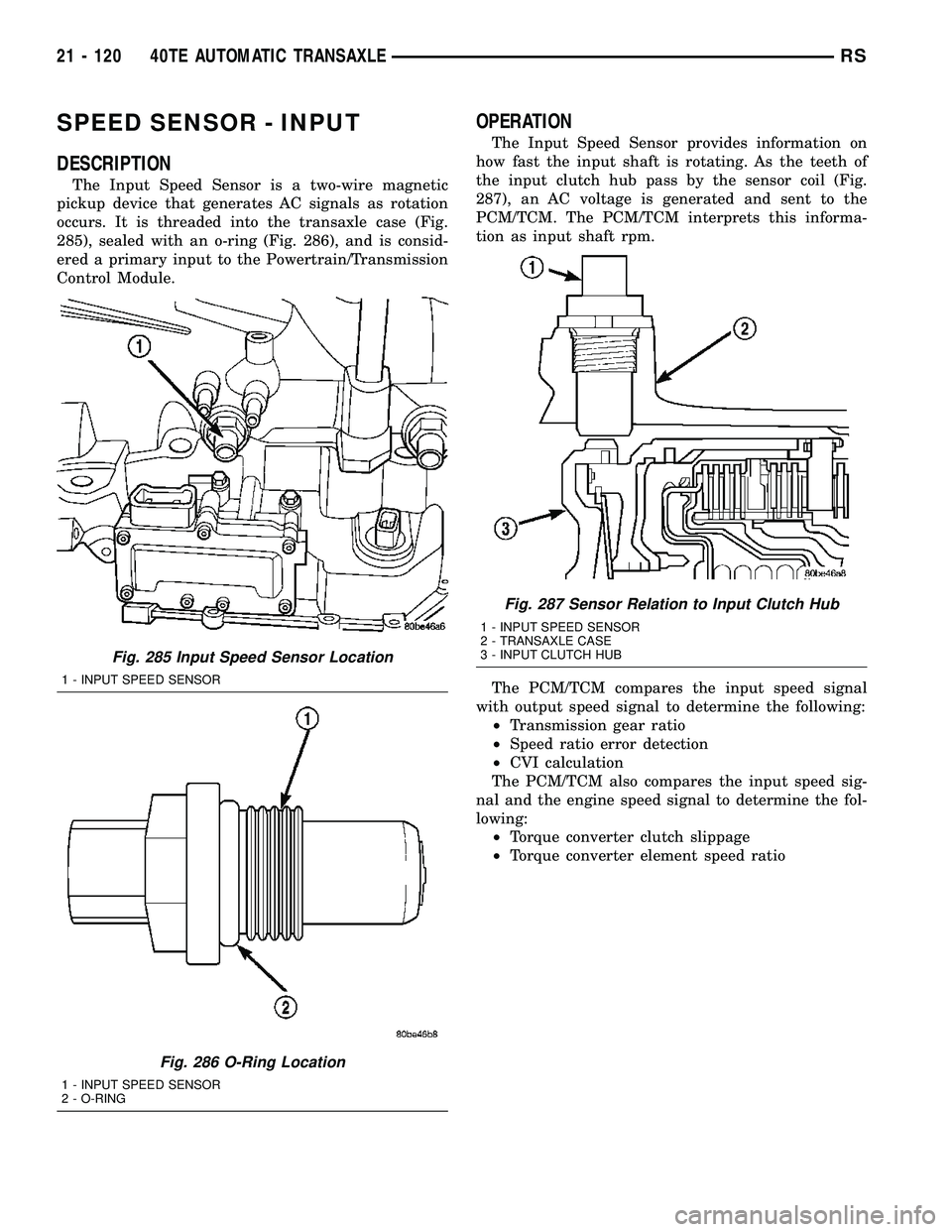
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Input Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates AC signals as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
285), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 286), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powertrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
287), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
Fig. 285 Input Speed Sensor Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 286 O-Ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 287 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
21 - 120 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1582 of 2339
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
288).
(3) Unscrew and remove input speed sensor (Fig.
289).
(4) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 290) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
290).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 289).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 288).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 288 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 289 Input (Turbine) Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 290 O-ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 121
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT (Continued)
Page 1583 of 2339
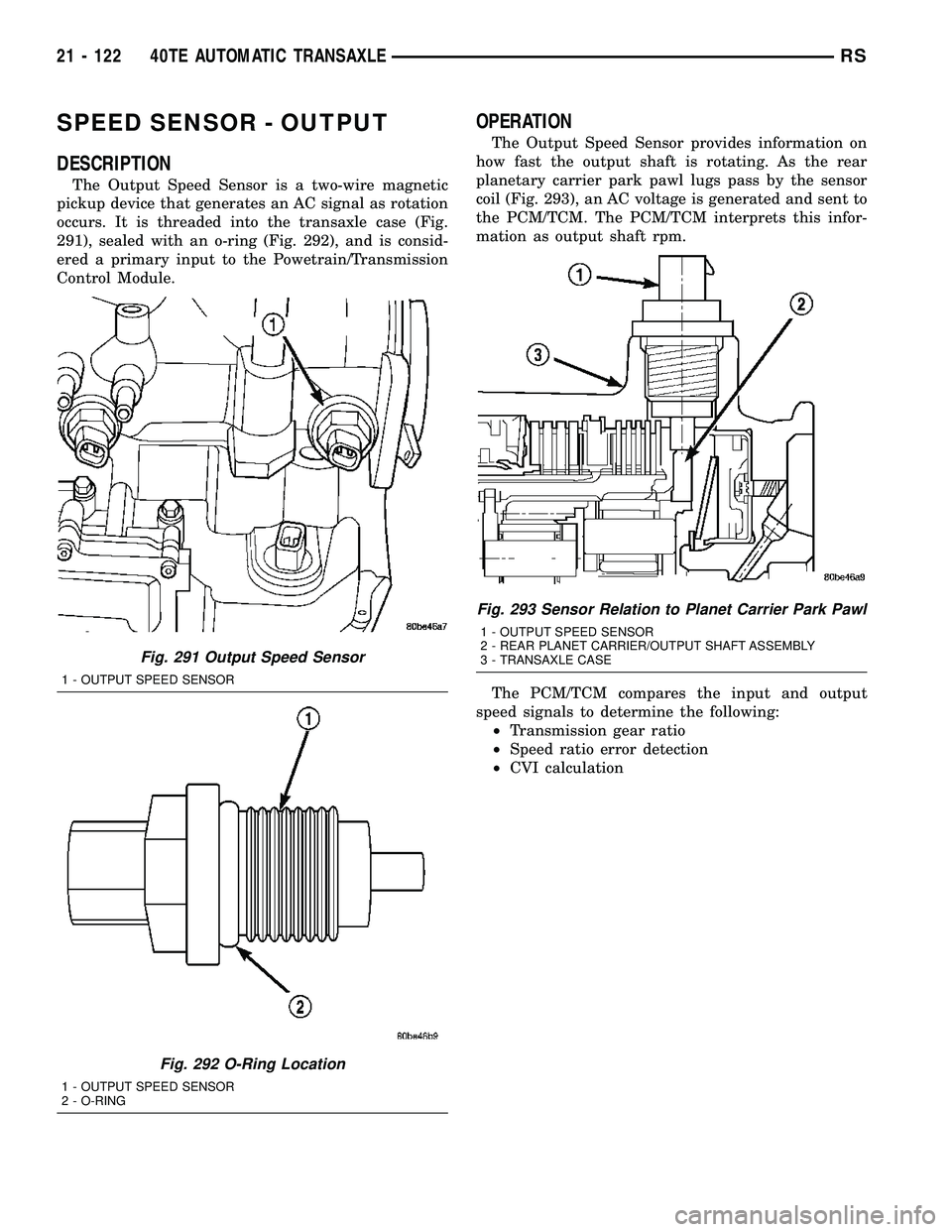
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Output Speed Sensor is a two-wire magnetic
pickup device that generates an AC signal as rotation
occurs. It is threaded into the transaxle case (Fig.
291), sealed with an o-ring (Fig. 292), and is consid-
ered a primary input to the Powetrain/Transmission
Control Module.
OPERATION
The Output Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the output shaft is rotating. As the rear
planetary carrier park pawl lugs pass by the sensor
coil (Fig. 293), an AC voltage is generated and sent to
the PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this infor-
mation as output shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input and output
speed signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
Fig. 291 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 292 O-Ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
Fig. 293 Sensor Relation to Planet Carrier Park Pawl
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - REAR PLANET CARRIER/OUTPUT SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - TRANSAXLE CASE
21 - 122 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1584 of 2339
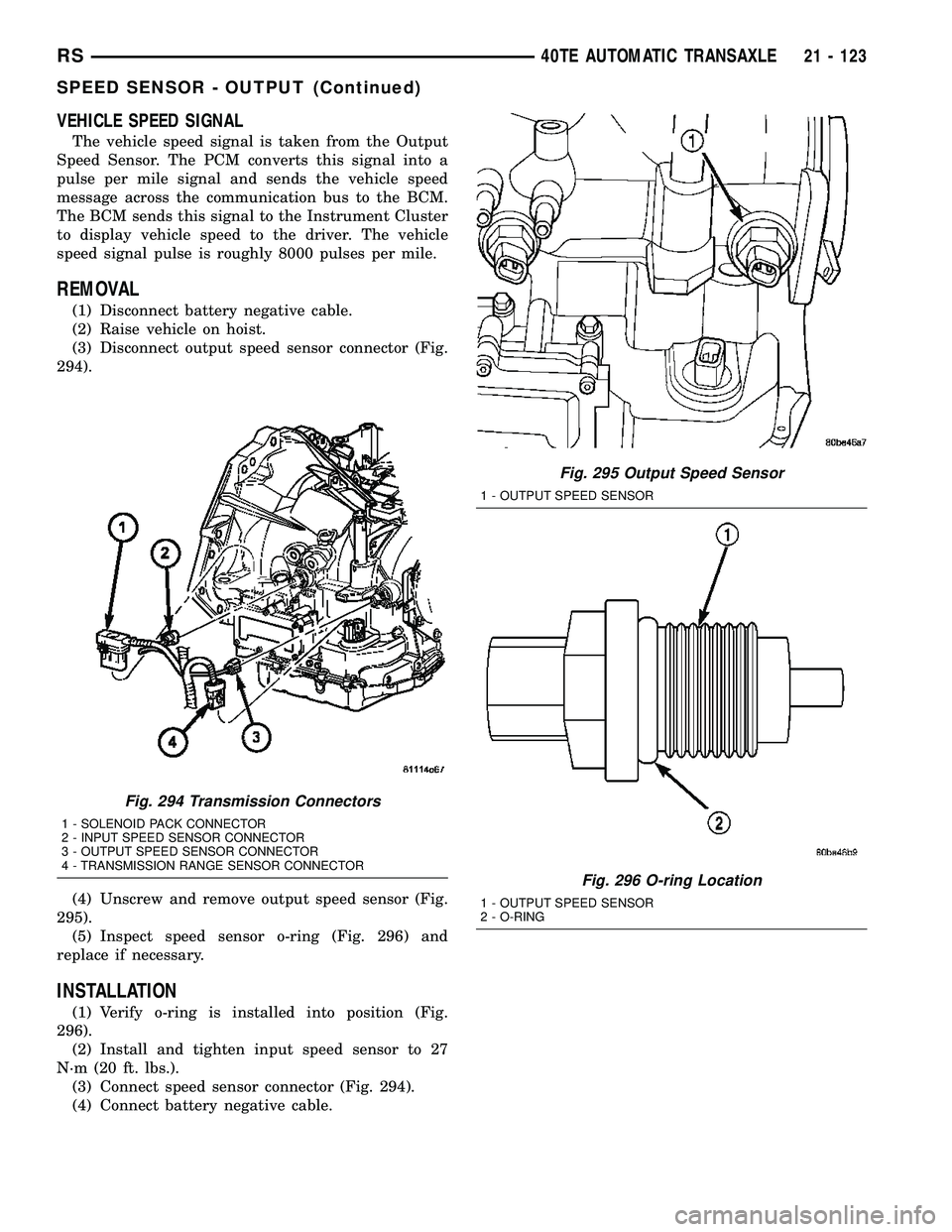
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
The vehicle speed signal is taken from the Output
Speed Sensor. The PCM converts this signal into a
pulse per mile signal and sends the vehicle speed
message across the communication bus to the BCM.
The BCM sends this signal to the Instrument Cluster
to display vehicle speed to the driver. The vehicle
speed signal pulse is roughly 8000 pulses per mile.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect output speed sensor connector (Fig.
294).
(4) Unscrew and remove output speed sensor (Fig.
295).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 296) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
296).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 294).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 294 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 295 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 296 O-ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 123
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT (Continued)
Page 1585 of 2339
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 297) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 297 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 124 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1586 of 2339
IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 298) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving member of the system.
Fig. 298 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 125
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1589 of 2339
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 303) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impeller
blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of the
energy and rotational force is transferred into the tur-
bine and the input shaft. This causes both of them (tur-
bine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise direction
following the impeller. As the fluid is leaving the trail-
ing edges of the turbine's blades it continues in a ªhin-
deringº direction back toward the impeller. If the fluid
is not redirected before it strikes the impeller, it will
strike the impeller in such a direction that it would
tend to slow it down.
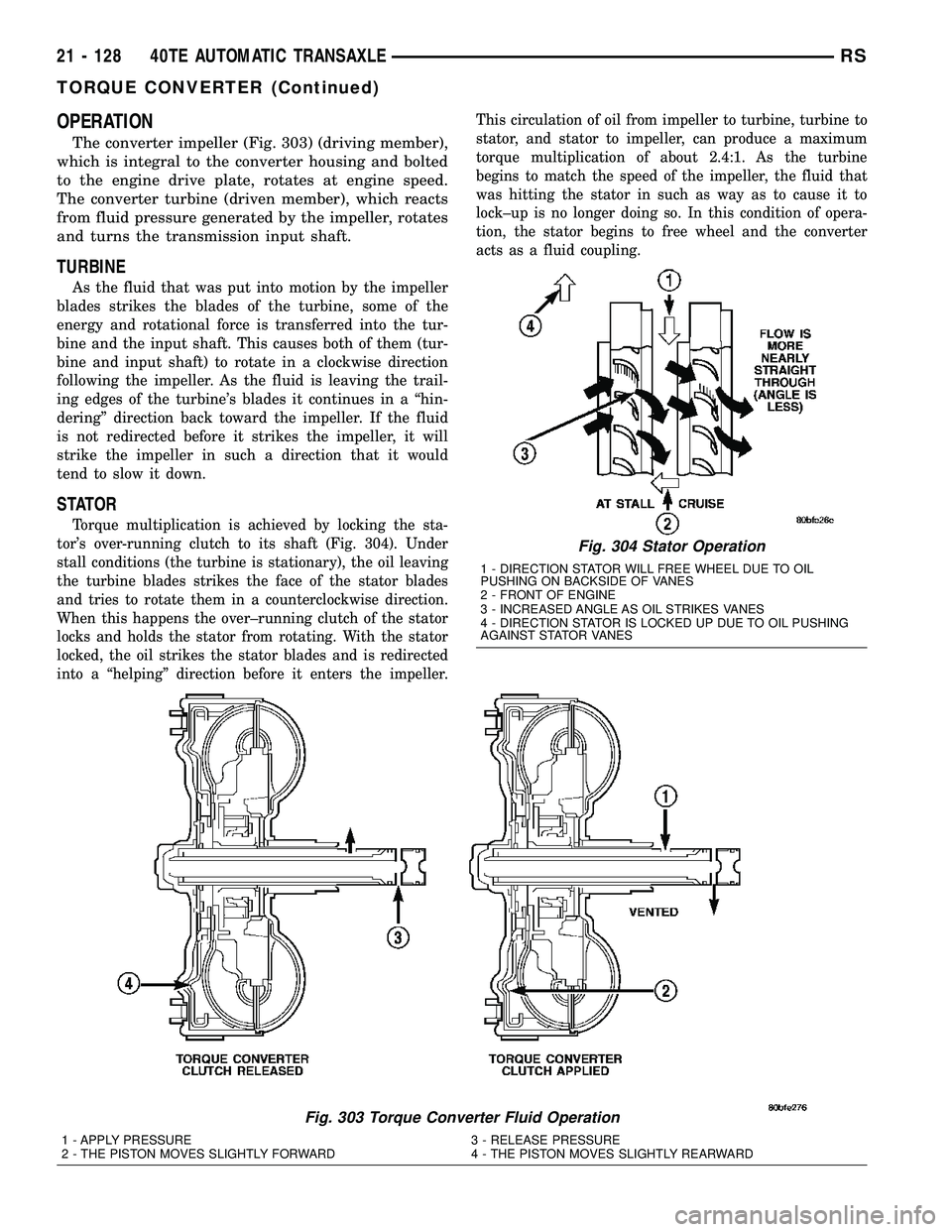
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the sta-
tor's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 304). Under
stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the oil leaving
the turbine blades strikes the face of the stator blades
and tries to rotate them in a counterclockwise direction.
When this happens the over±running clutch of the stator
locks and holds the stator from rotating. With the stator
locked, the oil strikes the stator blades and is redirected
into a ªhelpingº direction before it enters the impeller.This circulation of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to
stator, and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid that
was hitting the stator in such as way as to cause it to
lock±up is no longer doing so. In this condition of opera-
tion, the stator begins to free wheel and the converter
acts as a fluid coupling.
Fig. 303 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
Fig. 304 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 128 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)