2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 1303 of 2339
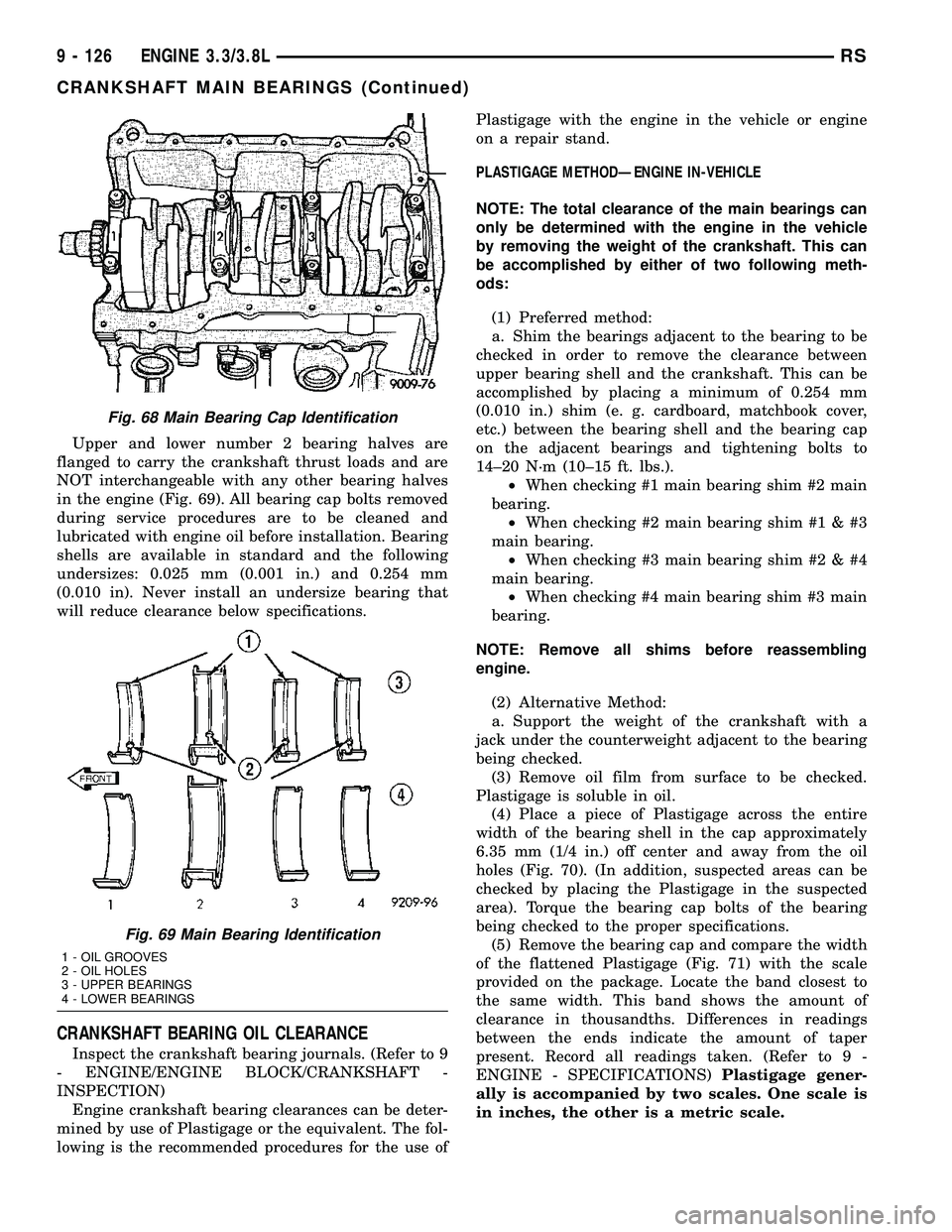
Upper and lower number 2 bearing halves are
flanged to carry the crankshaft thrust loads and are
NOT interchangeable with any other bearing halves
in the engine (Fig. 69). All bearing cap bolts removed
during service procedures are to be cleaned and
lubricated with engine oil before installation. Bearing
shells are available in standard and the following
undersizes: 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) and 0.254 mm
(0.010 in). Never install an undersize bearing that
will reduce clearance below specifications.
CRANKSHAFT BEARING OIL CLEARANCE
Inspect the crankshaft bearing journals. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT -
INSPECTION)
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or the equivalent. The fol-
lowing is the recommended procedures for the use ofPlastigage with the engine in the vehicle or engine
on a repair stand.
PLASTIGAGE METHODÐENGINE IN-VEHICLE
NOTE: The total clearance of the main bearings can
only be determined with the engine in the vehicle
by removing the weight of the crankshaft. This can
be accomplished by either of two following meth-
ods:
(1) Preferred method:
a. Shim the bearings adjacent to the bearing to be
checked in order to remove the clearance between
upper bearing shell and the crankshaft. This can be
accomplished by placing a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 in.) shim (e. g. cardboard, matchbook cover,
etc.) between the bearing shell and the bearing cap
on the adjacent bearings and tightening bolts to
14±20 N´m (10±15 ft. lbs.).
²When checking #1 main bearing shim #2 main
bearing.
²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & #3
main bearing.
²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & #4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 main
bearing.
NOTE: Remove all shims before reassembling
engine.
(2) Alternative Method:
a. Support the weight of the crankshaft with a
jack under the counterweight adjacent to the bearing
being checked.
(3) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(4) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 70). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 71) with the scale
provided on the package. Locate the band closest to
the same width. This band shows the amount of
clearance in thousandths. Differences in readings
between the ends indicate the amount of taper
present. Record all readings taken. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)Plastigage gener-
ally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is
in inches, the other is a metric scale.
Fig. 68 Main Bearing Cap Identification
Fig. 69 Main Bearing Identification
1 - OIL GROOVES
2 - OIL HOLES
3 - UPPER BEARINGS
4 - LOWER BEARINGS
9 - 126 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1304 of 2339

NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
PLASTIGAGE METHODÐENGINE OUT-OF-VEHICLE
(1) With engine in the inverted position (crank-
shaft up) and mounted on a repair stand, remove
main journal cap.
(2) Remove oil from journal and bearing shell.
(3) Cut Plastigage to same length as width of the
bearing and place it in parallel with the journal axis
(Fig. 70).
(4) Carefully install the main bearing cap and
tighten the bolts to specified torque.
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the Plasti-
gage will be smeared.
(5) Carefully remove the bearing cap and measure
the width of the Plastigage at the widest part using
the scale on the Plastigage package (Fig. 71). Refer
to Engine Specifications for proper clearances (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). If the clearance
exceeds the specified limits, replace the main bear-
ing(s) with the appropriate size, and if necessary,
have the crankshaft machined to next undersize.
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
(1) Remove the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)(2) Identify main bearing caps before removal.
(3) Remove bearing caps one at a time. Remove
upper half of bearing by inserting Special Main Bear-
ing Tool C-3059 (Fig. 72) into the oil hole of crank-
shaft.
(4) Slowly rotate crankshaft clockwise, forcing out
upper half of bearing shell.
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
NOTE: One main bearing should be selectively fit-
ted while all other main bearing caps are properly
tightened.
(1) For main bearing fitting procedure, (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Start bearing in place, and insert Main Bearing
Tool C-3059 into oil hole of crankshaft (Fig. 72).
(3) Slowly rotate crankshaft counterclockwise slid-
ing the bearing into position. Remove Special Main
Bearing Tool C-3059.
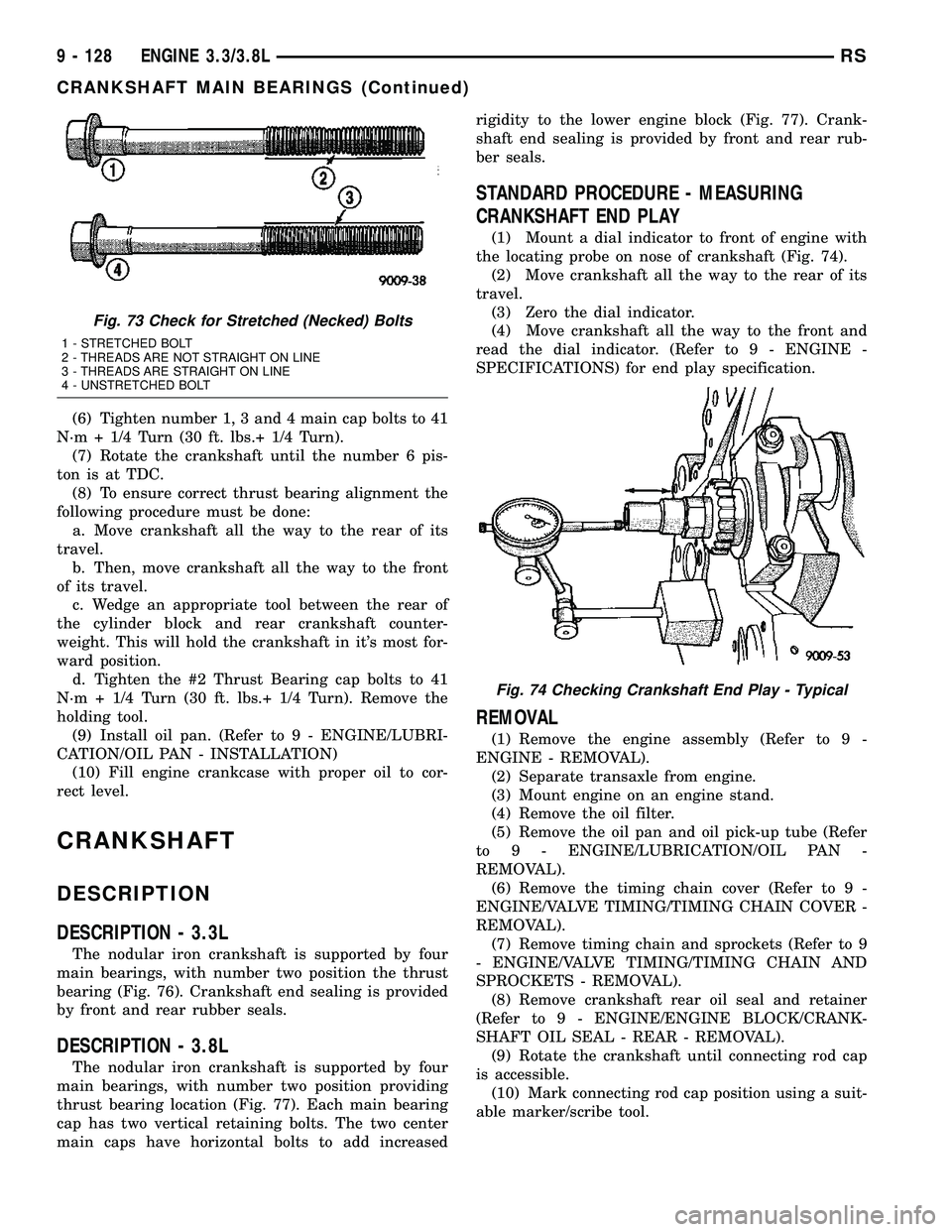
(4) Inspect main cap bolts for stretching (Fig. 73).
Replace bolts that are stretched.
NOTE: The main cap bolts should be examined
before reuse. Bolt stretch can be checked by hold-
ing a scale or straight edge against the threads. If
all the threads do not contact the scale the bolt
must be replaced (Fig. 73).
(5) Install each main cap and tighten bolts finger
tight.
Fig. 70 Plastigage Placed in Lower
1 - PLASTIGAGE
Fig. 71 Clearance Measurement
Fig. 72 Upper Main Bearing Removing/Installing
With Special Tool C-3059
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3059
2 - BEARING
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3059
4 - BEARING
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 127
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1305 of 2339
(6) Tighten number 1, 3 and 4 main cap bolts to 41
N´m + 1/4 Turn (30 ft. lbs.+ 1/4 Turn).
(7) Rotate the crankshaft until the number 6 pis-
ton is at TDC.
(8) To ensure correct thrust bearing alignment the
following procedure must be done:
a. Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
b. Then, move crankshaft all the way to the front
of its travel.
c. Wedge an appropriate tool between the rear of
the cylinder block and rear crankshaft counter-
weight. This will hold the crankshaft in it's most for-
ward position.
d. Tighten the #2 Thrust Bearing cap bolts to 41
N´m + 1/4 Turn (30 ft. lbs.+ 1/4 Turn). Remove the
holding tool.
(9) Install oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION)
(10) Fill engine crankcase with proper oil to cor-
rect level.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 3.3L
The nodular iron crankshaft is supported by four
main bearings, with number two position the thrust
bearing (Fig. 76). Crankshaft end sealing is provided
by front and rear rubber seals.
DESCRIPTION - 3.8L
The nodular iron crankshaft is supported by four
main bearings, with number two position providing
thrust bearing location (Fig. 77). Each main bearing
cap has two vertical retaining bolts. The two center
main caps have horizontal bolts to add increasedrigidity to the lower engine block (Fig. 77). Crank-
shaft end sealing is provided by front and rear rub-
ber seals.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine with
the locating probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 74).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
SPECIFICATIONS) for end play specification.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine assembly (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - REMOVAL).
(2) Separate transaxle from engine.
(3) Mount engine on an engine stand.
(4) Remove the oil filter.
(5) Remove the oil pan and oil pick-up tube (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN -
REMOVAL).
(6) Remove the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING CHAIN COVER -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove timing chain and sprockets (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove crankshaft rear oil seal and retainer
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANK-
SHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR - REMOVAL).
(9) Rotate the crankshaft until connecting rod cap
is accessible.
(10) Mark connecting rod cap position using a suit-
able marker/scribe tool.
Fig. 73 Check for Stretched (Necked) Bolts
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 74 Checking Crankshaft End Play - Typical
9 - 128 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1317 of 2339
(11) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(12) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
NOTE: Care should be exercised when disposing
used engine oil after it has been drained from a
vehicle engine. Refer to the WARNING listed above.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL LEVEL
CHECK
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,
allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading (Fig. 97). Add only when the level is at or
below the ADD mark.
Fig. 97 Engine Oil Level Dipstick and Fill Locations
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER 3 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP 4 - RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 96 Engine Oil Drain Plug and Oil Filter
1 - DRAIN PLUG
2 - OIL FILTER
9 - 140 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
OIL (Continued)
Page 1322 of 2339
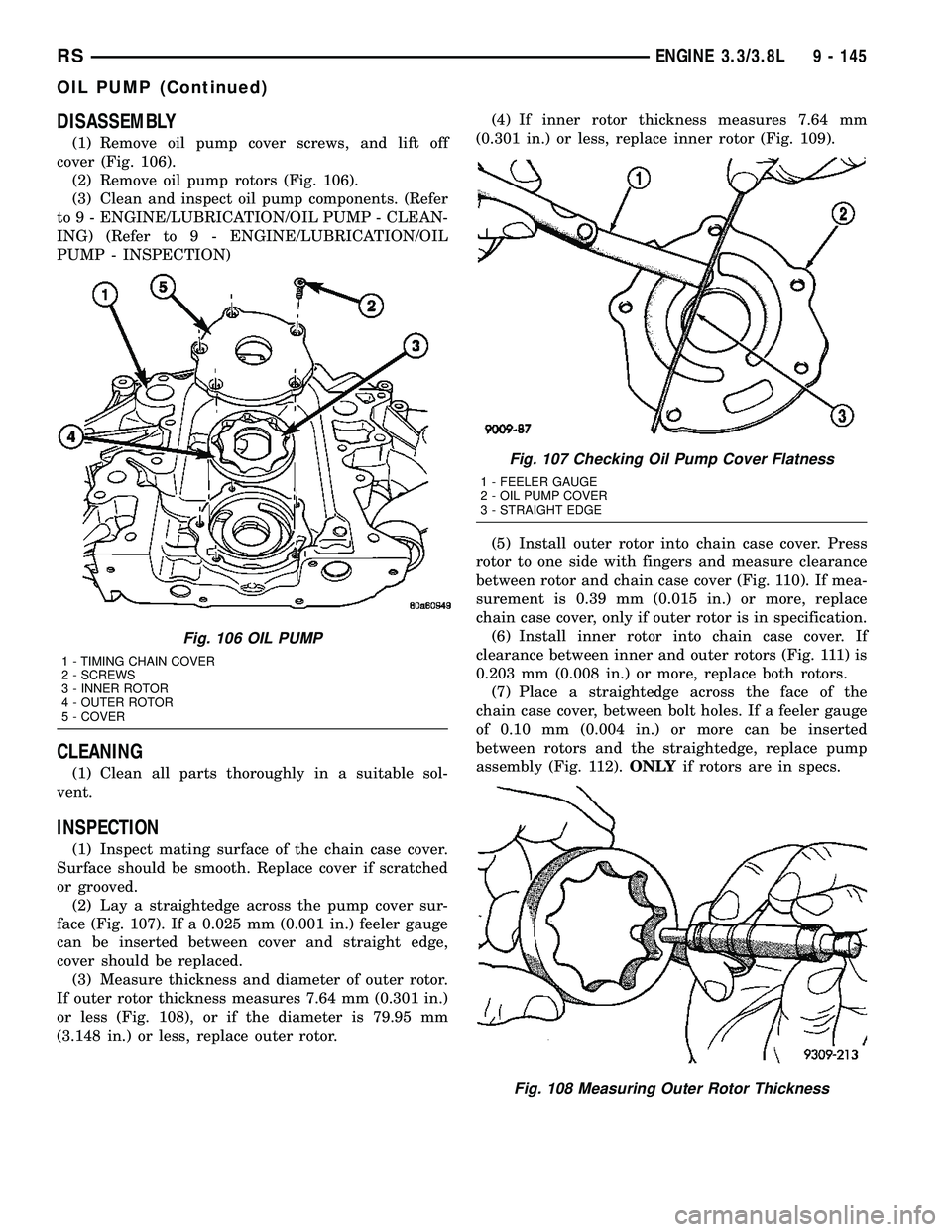
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove oil pump cover screws, and lift off
cover (Fig. 106).
(2) Remove oil pump rotors (Fig. 106).
(3) Clean and inspect oil pump components. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - CLEAN-
ING) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PUMP - INSPECTION)
CLEANING
(1) Clean all parts thoroughly in a suitable sol-
vent.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect mating surface of the chain case cover.
Surface should be smooth. Replace cover if scratched
or grooved.
(2) Lay a straightedge across the pump cover sur-
face (Fig. 107). If a 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) feeler gauge
can be inserted between cover and straight edge,
cover should be replaced.
(3) Measure thickness and diameter of outer rotor.
If outer rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm (0.301 in.)
or less (Fig. 108), or if the diameter is 79.95 mm
(3.148 in.) or less, replace outer rotor.(4) If inner rotor thickness measures 7.64 mm
(0.301 in.) or less, replace inner rotor (Fig. 109).
(5) Install outer rotor into chain case cover. Press
rotor to one side with fingers and measure clearance
between rotor and chain case cover (Fig. 110). If mea-
surement is 0.39 mm (0.015 in.) or more, replace
chain case cover, only if outer rotor is in specification.
(6) Install inner rotor into chain case cover. If
clearance between inner and outer rotors (Fig. 111) is
0.203 mm (0.008 in.) or more, replace both rotors.
(7) Place a straightedge across the face of the
chain case cover, between bolt holes. If a feeler gauge
of 0.10 mm (0.004 in.) or more can be inserted
between rotors and the straightedge, replace pump
assembly (Fig. 112).ONLYif rotors are in specs.
Fig. 106 OIL PUMP
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - SCREWS
3 - INNER ROTOR
4 - OUTER ROTOR
5 - COVER
Fig. 107 Checking Oil Pump Cover Flatness
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - OIL PUMP COVER
3 - STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 108 Measuring Outer Rotor Thickness
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 145
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1541 of 2339
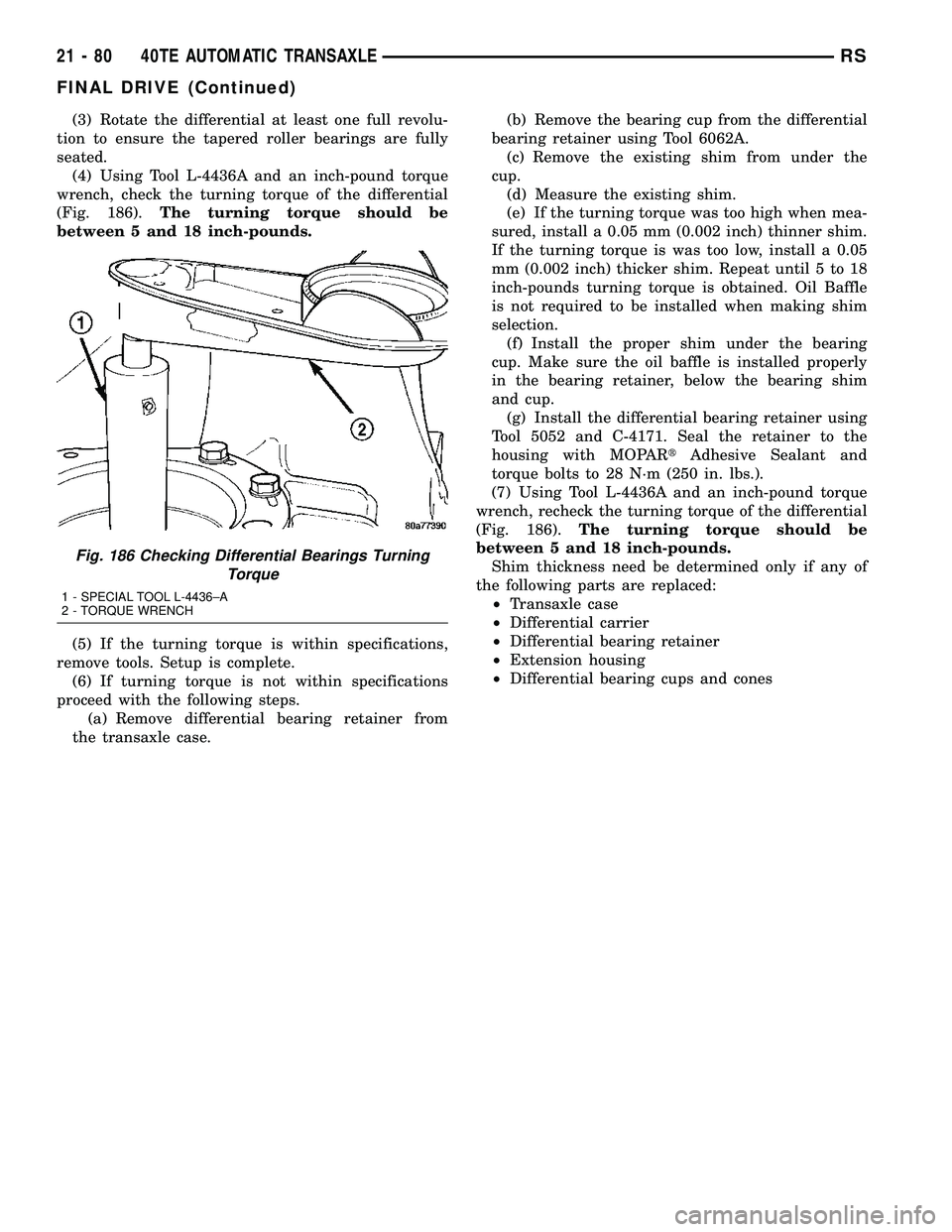
(3) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
(4) Using Tool L-4436A and an inch-pound torque
wrench, check the turning torque of the differential
(Fig. 186).The turning torque should be
between 5 and 18 inch-pounds.
(5) If the turning torque is within specifications,
remove tools. Setup is complete.
(6) If turning torque is not within specifications
proceed with the following steps.
(a) Remove differential bearing retainer from
the transaxle case.(b) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Tool 6062A.
(c) Remove the existing shim from under the
cup.
(d) Measure the existing shim.
(e) If the turning torque was too high when mea-
sured, install a 0.05 mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
If the turning torque is was too low, install a 0.05
mm (0.002 inch) thicker shim. Repeat until 5 to 18
inch-pounds turning torque is obtained. Oil Baffle
is not required to be installed when making shim
selection.
(f) Install the proper shim under the bearing
cup. Make sure the oil baffle is installed properly
in the bearing retainer, below the bearing shim
and cup.
(g) Install the differential bearing retainer using
Tool 5052 and C-4171. Seal the retainer to the
housing with MOPARtAdhesive Sealant and
torque bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(7) Using Tool L-4436A and an inch-pound torque
wrench, recheck the turning torque of the differential
(Fig. 186).The turning torque should be
between 5 and 18 inch-pounds.
Shim thickness need be determined only if any of
the following parts are replaced:
²Transaxle case
²Differential carrier
²Differential bearing retainer
²Extension housing
²Differential bearing cups and cones
Fig. 186 Checking Differential Bearings Turning
Torque
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4436±A
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
21 - 80 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1590 of 2339

TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 305). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
Fig. 305 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 129
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1689 of 2339
(18) Install and torque cover-to-case bolts to 19
N´m (165 in. lbs.) (Fig. 202).
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
PRELOAD
NOTE: Perform all differential bearing preload mea-
surements with the transfer shaft and gear
removed.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOAD ADJUSTMENT
USING EXISTING SHIM
(1) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand, differential bearing retainer side
up.
(2) Install Tool L-4436A into the differential and
onto the pinion mate shaft (Fig. 203).
(3) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
(4) Using Tool L-4436A and an inch-pound torque
wrench, check the turning torque of the differential
(Fig. 204).The turning torque should be
between 5 and 18 inch-pounds.
(5) If the turning torque is within specifications,
remove tools. Setup is complete.
(6) If turning torque is not within specifications
proceed with the following steps.
(a) Remove differential bearing retainer from
the transaxle case.
(b) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Tool 6062A.
(c) Remove the existing shim from under the
cup.(d) Measure the existing shim.
(e) If the turning torque was too high when mea-
sured, install a 0.05 mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
If the turning torque is was too low, install a 0.05
mm (0.002 inch) thicker shim. Repeat until 5-18
inch-pounds turning torque is obtained. Oil Baffle
is not required to be installed when making shim
selection.
(f) Install the proper shim under the bearing
cup. Make sure the oil baffle is installed properly
in the bearing retainer, below the bearing shim
and cup.
(g) Install the differential bearing retainer using
Tool 5052 and C-4171. Seal the retainer to the
Fig. 202 Differential Cover Bolts
1 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER BOLTS
2 - DIFFERENTIAL COVER
Fig. 203 Tool L-4436 and Torque Wrench
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4436±A
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING RETAINER
Fig. 204 Checking Differential Bearings Turning
Torque
1 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4436±A
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
21 - 228 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)