2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN ors
[x] Cancel search: orsPage 1657 of 2339

(69) Install and tighten solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-transaxle case bolts to 12 N´m (110 in.
lbs.) (Fig. 158).
(70) Install and torque input and output speed
sensors to case to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If transaxle assembly has been replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perfrom the ªQuick-Learnº procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Using a transmission jack and a helper, posi-
tion transaxle assembly to engine. Install and torque
bellhousing bolts to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install upper mount assembly to transaxle and
torque bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 159).
(3) Raise engine/transaxle assembly into position.
Install and torque upper mount-to-bracket thru-bolt
to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 159).
(4) Remove transmission jack and screw jack.
(5) Secure left wheelhouse splash shield.
(6) Install torque converter-to-drive plate bolts and
torque to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
(7) Install inspection cover.
(8) Install lateral bending brace.
(9) Install starter motor.
(10) Install front mount/bracket assembly.
(11) Align and install rear mount bracket-to-case
bolts by hand (Fig. 160). Torque horizontal bolt to
102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).(12) AWD models: Install power transfer unit.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
POWER TRANSFER UNIT - INSTALLATION)
(13) Install left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(14) Install front wheel/tire assemblies.
(15) Lower vehicle.
(16) Torque remaining rear mount bracket-to-tran-
saxle vertical bolts (Fig. 160) to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(17) Install transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts and torque to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(18) Install and connect crank position sensor (if
equipped).
(19) Connect gearshift cable to upper mount
bracket and transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 161).
(20) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 162).
(21) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 162).
(22) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 162).
(23) Remove plugs and connect transaxle oil cooler
lines. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(24) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly.
Fig. 158 Solenoid Pack-to-Transaxle Bolts
1 - BOLTS
2 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 159 Left Mount to Bracket and Transaxle
1 - BOLT - BRACKET TO FRAME RAIL 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
2 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL THRU 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.)
3 - BOLT - LEFT MOUNT TO TRANSAXLE 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
4 - TRANSAXLE
5 - MOUNT - LEFT
6 - BRACKET - LEFT MOUNT
21 - 196 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1679 of 2339
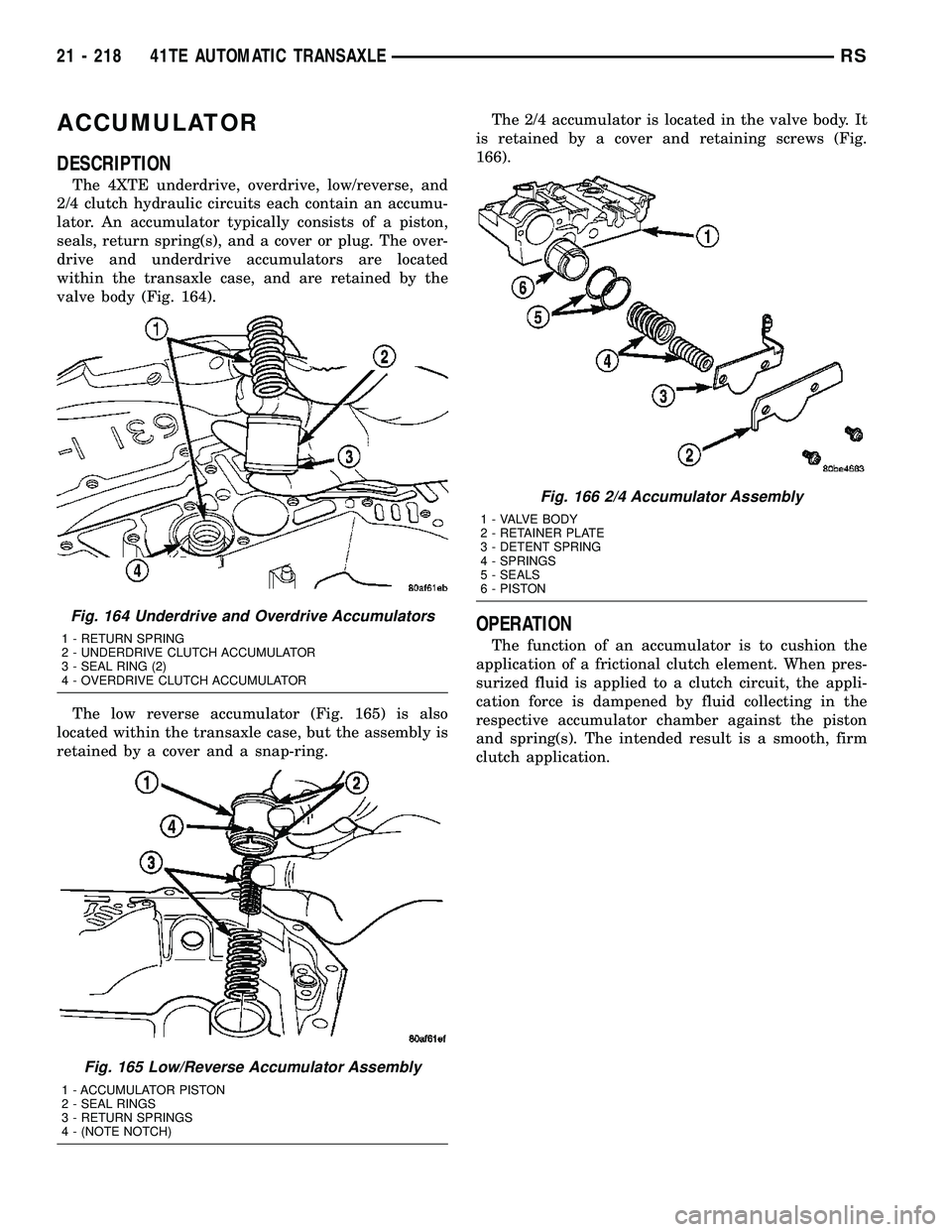
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The 4XTE underdrive, overdrive, low/reverse, and
2/4 clutch hydraulic circuits each contain an accumu-
lator. An accumulator typically consists of a piston,
seals, return spring(s), and a cover or plug. The over-
drive and underdrive accumulators are located
within the transaxle case, and are retained by the
valve body (Fig. 164).
The low reverse accumulator (Fig. 165) is also
located within the transaxle case, but the assembly is
retained by a cover and a snap-ring.The 2/4 accumulator is located in the valve body. It
is retained by a cover and retaining screws (Fig.
166).
OPERATION
The function of an accumulator is to cushion the
application of a frictional clutch element. When pres-
surized fluid is applied to a clutch circuit, the appli-
cation force is dampened by fluid collecting in the
respective accumulator chamber against the piston
and spring(s). The intended result is a smooth, firm
clutch application.
Fig. 164 Underdrive and Overdrive Accumulators
1 - RETURN SPRING
2 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
3 - SEAL RING (2)
4 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
Fig. 165 Low/Reverse Accumulator Assembly
1 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
2 - SEAL RINGS
3 - RETURN SPRINGS
4 - (NOTE NOTCH)
Fig. 166 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - SPRINGS
5 - SEALS
6 - PISTON
21 - 218 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1691 of 2339

CAUTION: Do not damage the transaxle case and/or
differential retainer sealing surface.
(9) Using the end play measurement that was
determined, add 0.18mm (0.007 inch). This should
give you between 5-18 inch pounds of bearing pre-
load. Refer to the Differential Bearing Shim Chart to
determine which shim to use.
(10) Remove the differential bearing retainer.
Remove the bearing cup.
(11) Install the oil baffle. Install the proper shim
combination under the bearing cup.
(12) Install the differential bearing retainer. Seal
the retainer to the housing with MopartSilicone
Rubber Adhesive Sealant. Torque bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.).
(13) Using Miller Special Tool L-4436-A and an
inch-pound torque wrench, check the turning torque
of the differential (Fig. 204). The turning torque
should be between 5-18 inch-pounds.
NOTE: If turning torque is too high install a 0.05mm
(0.002 inch) thicker shim. If the turning torque is too
low, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
Repeat until 5-18 inch-pounds of turning torque is
obtained.
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 205). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.
(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 206).
(6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart.
(7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
Fig. 205 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21 - 230 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1730 of 2339
should be detected by the PCM/TCM during this test.
It no spike is detected, the circuit is tested again to
verify the failure. In addition to the periodic testing,
the solenoid circuits are tested if a speed ratio or
pressure switch error occurs.
PRESSURE SWITCHES
The PCM/TCM relies on three pressure switches to
monitor fluid pressure in the L/R, 2/4, and OD
hydraulic circuits. The primary purpose of these
switches is to help the PCM/TCM detect when clutch
circuit hydraulic failures occur. The range for the
pressure switch closing and opening points is 11-23
psi. Typically the switch opening point will be
approximately one psi lower than the closing point.
For example, a switch may close at 18 psi and open
at 17 psi. The switches are continuously monitored
by the PCM/TCM for the correct states (open or
closed) in each gear as shown in the following chart:
PRESSURE SWITCH STATES
GEAR L/R 2/4 OD
ROPOPOP
P/N CL OP OP
1st CL OP OP
2nd OP CL OP
DOPOPCL
OD OP CL CL
OP = OPEN
CL = CLOSED
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set if the
PCM/TCM senses any switch open or closed at the
wrong time in a given gear.
The PCM/TCM also tests the 2/4 and OD pressure
switches when they are normally off (OD and 2/4 are
tested in 1st gear, OD in 2nd gear, and 2/4 in 3rd
gear). The test simply verifies that they are opera-
tional, by looking for a closed state when the corre-
sponding element is applied. Immediately after a
shift into 1st, 2nd, or 3rd gear with the engine speed
above 1000 rpm, the PCM/TCM momentarily turns
on element pressure to the 2/4 and/or OD clutch cir-
cuits to identify that the appropriate switch has
closed. If it doesn't close, it is tested again. If the
switch fails to close the second time, the appropriate
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, the ªQuick-Learnº procedure must
be performed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(3) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 305).
(4) Disconnect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
305).
Fig. 305 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 269
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
Page 1733 of 2339
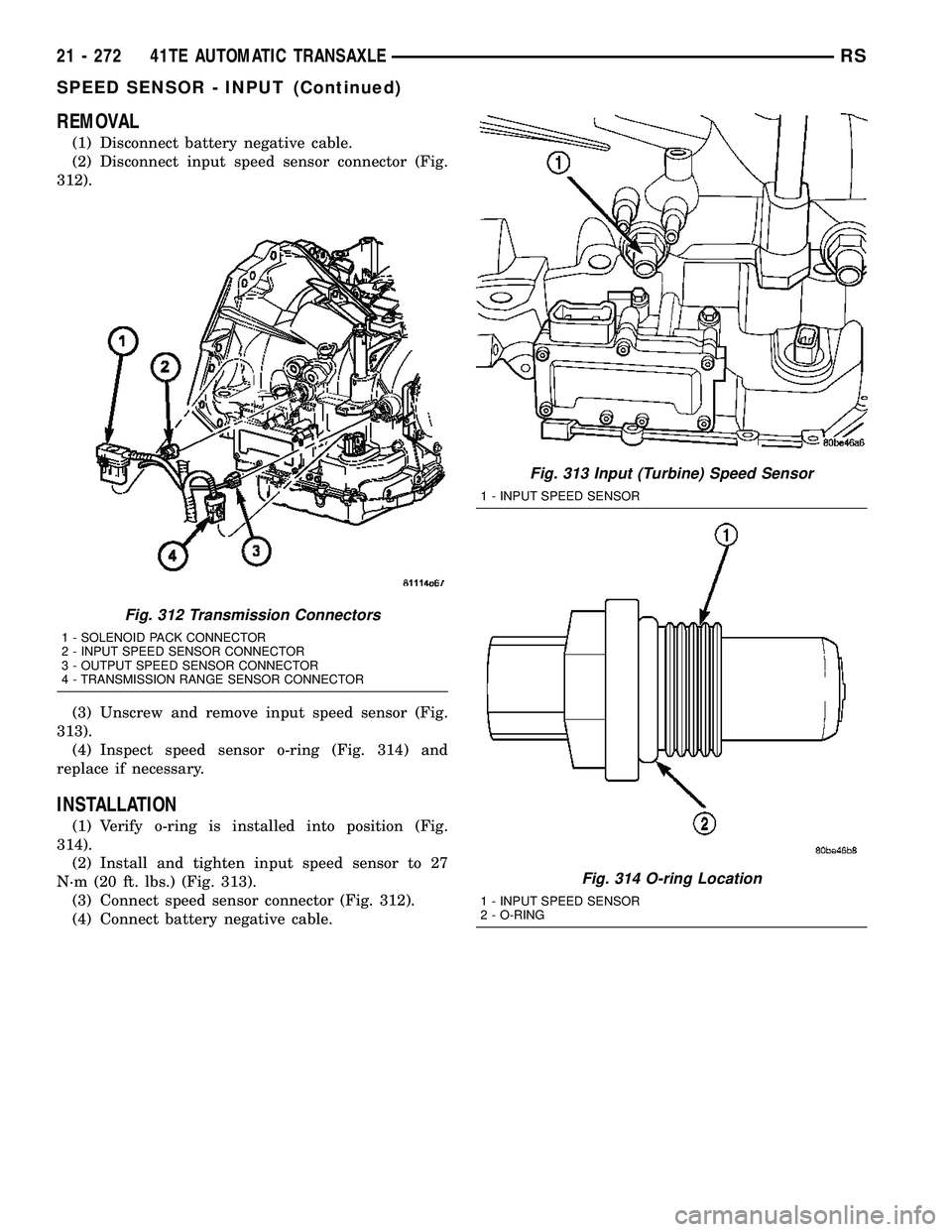
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
312).
(3) Unscrew and remove input speed sensor (Fig.
313).
(4) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 314) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
314).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 313).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 312).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 312 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 313 Input (Turbine) Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 314 O-ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
21 - 272 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT (Continued)
Page 1735 of 2339
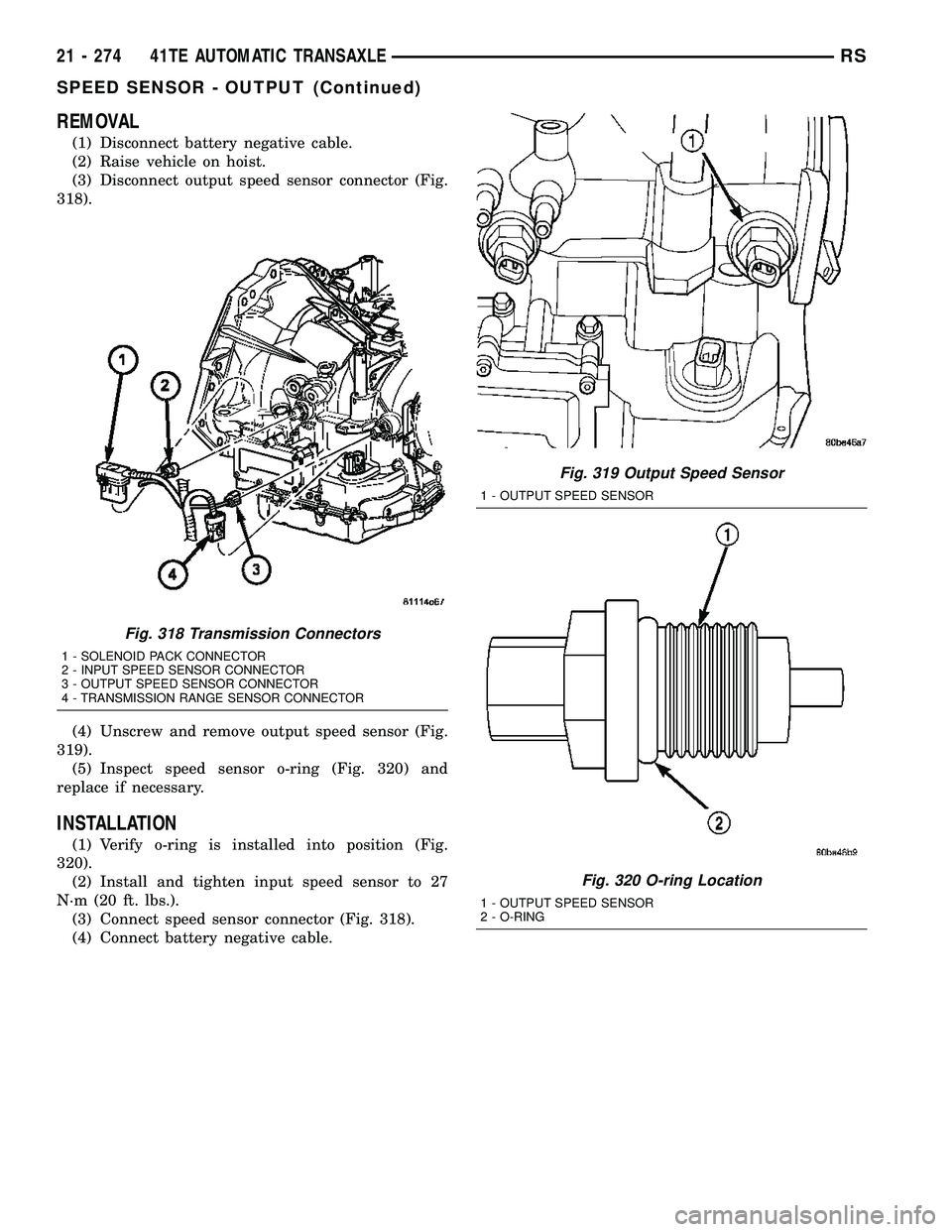
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect output speed sensor connector (Fig.
318).
(4) Unscrew and remove output speed sensor (Fig.
319).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 320) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
320).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 318).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 318 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 319 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 320 O-ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
21 - 274 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT (Continued)
Page 1742 of 2339
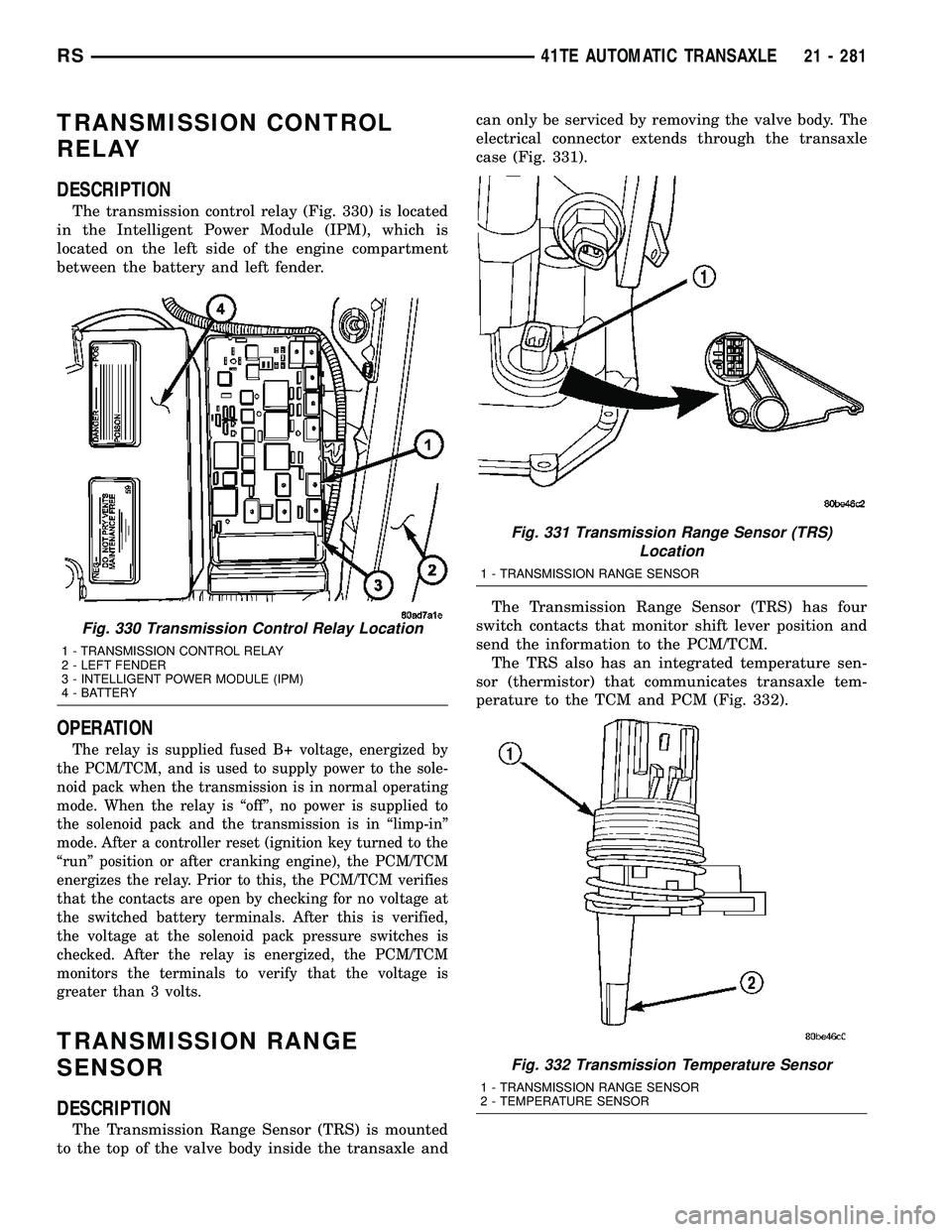
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 330) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized by
the PCM/TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal operating
mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to
the solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset (ignition key turned to the
ªrunº position or after cranking engine), the PCM/TCM
energizes the relay. Prior to this, the PCM/TCM verifies
that the contacts are open by checking for no voltage at
the switched battery terminals. After this is verified,
the voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the PCM/TCM
monitors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle andcan only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 331).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 332).
Fig. 330 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 331 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 332 Transmission Temperature Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - TEMPERATURE SENSOR
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 281
Page 1743 of 2339
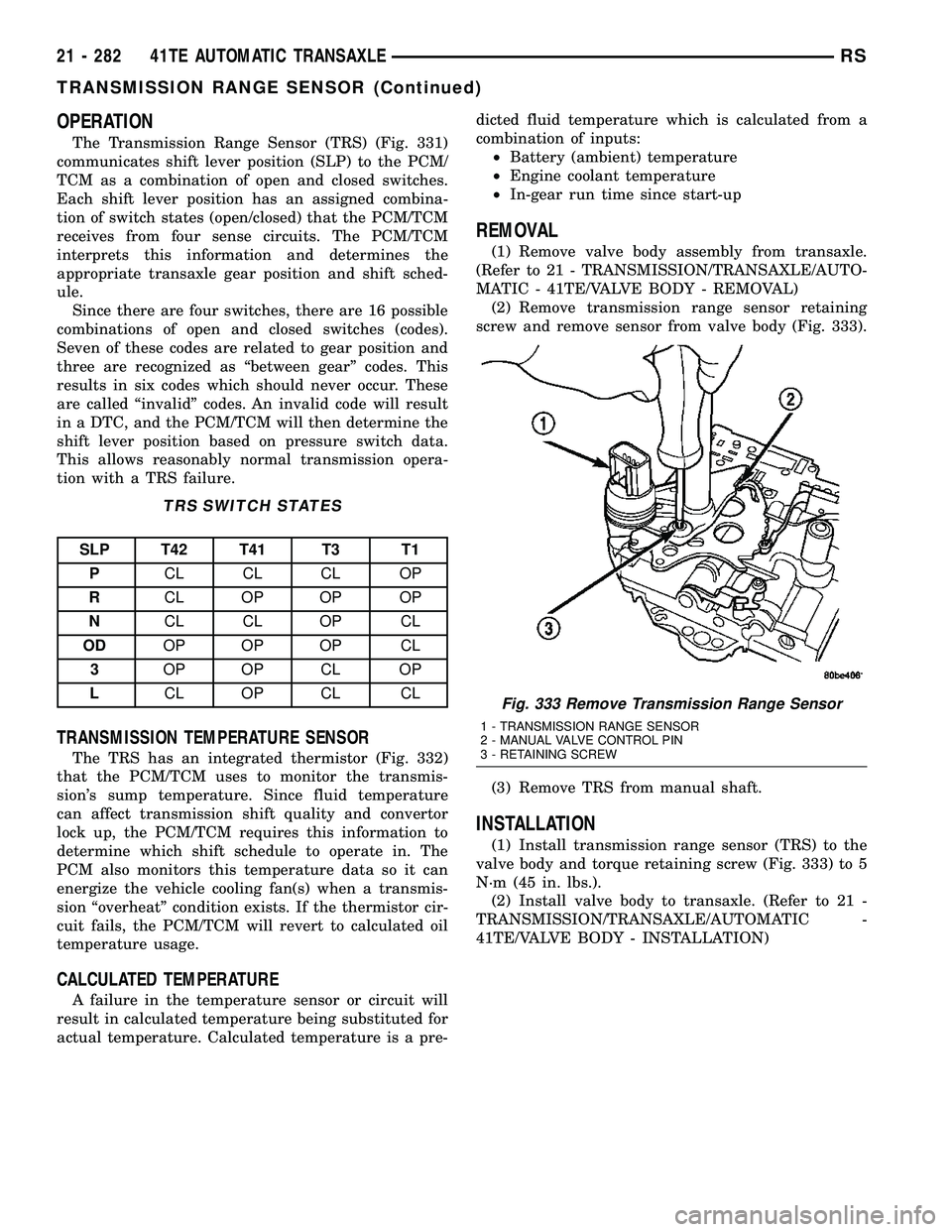
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 331)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combina-
tion of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM
interprets this information and determines the
appropriate transaxle gear position and shift sched-
ule.
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 332)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 333).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 333) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 333 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
21 - 282 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)