2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN display
[x] Cancel search: displayPage 287 of 2339

When a PCM (SBEC) and the SKIM are replaced
at the same time perform the following steps in
order:
(1) Program the new PCM (SBEC)
(2) Program the new SKIM
(3) Replace all ignition keys and program them to
the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING THE PCM (SBEC)
The SKIS Secret Key is an ID code that is unique
to each SKIM. This code is programmed and stored
in the SKIM, PCM and transponder chip (ignition
keys). When replacing the PCM it is necessary to
program the secret key into the new PCM using the
DRB III. Perform the following steps to program the
secret key into the PCM.
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRB III and select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE).
(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
(5) Select ENTER to update PCM VIN.
NOTE: If three attempts are made to enter secure
access mode using an incorrect PIN, secured
access mode will be locked out for one hour. To
exit this lockout mode, turn the ignition to the RUN
position for one hour then enter the correct PIN.
(Ensure all accessories are turned off. Also monitor
the battery state and connect a battery charger if
necessary).
(6) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
SKIM will send the secret key to the PCM).
(7) Press Page Back to get to the Select System
menu and select ENGINE, MISCELLANEOUS, and
SRI MEMORY CHECK.
(8) The DRB III will ask, Is odometer reading
between XX and XX? Select the YES or NO button on
the DRB III. If NO is selected, the DRB III will read,
Enter odometer Reading
the odometer reading from the Instrument Panel and
press ENTER.
PROGRAMMING THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRB III and select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE).
(4) Program the vehicle four-digit PIN into SKIM.
(5) Select COUNTRY CODE and enter the correct
country.NOTE: Be sure to enter the correct country code. If
the incorrect country code is programmed into
SKIM, the SKIM must be replaced.
(6) Select YES to update VIN (the SKIM will learn
the VIN from the PCM).
(7) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
PCM will send the secret key to the SKIM).
(8) Program ignition keys to SKIM.
NOTE: If the PCM and the SKIM are replaced at the
same time, all vehicle keys will need to be replaced
and programmed to the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING IGNITION KEYS TO THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch on (transmission in
park/neutral).
(2) Use the DRB III and select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PROGRAM IGNITION KEY'S.
(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
NOTE: A maximum of eight keys can be learned to
each SKIM. Once a key is learned to a SKIM it (the
key) cannot be transferred to another vehicle.
If ignition key programming is unsuccessful, the
DRB III will display one of the following messages:
Programming Not Attempted - The DRB III
attempts to read the programmed key status and
there are no keys programmed into SKIM memory.
Programming Key Failed (Possible Used Key From
Wrong Vehicle) - SKIM is unable to program key due
to one of the following:
²faulty ignition key transponder
²ignition key is programmed to another vehicle.
8 Keys Already Learned, Programming Not Done -
SKIM transponder ID memory is full.
(5) Obtain ignition keys to be programmed from
customer (8 keys maximum).
(6) Using the DRB III, erase all ignition keys by
selecting MISCELLANEOUS and ERASE ALL CUR-
RENT IGN. KEYS.
(7) Program all ignition keys.
Learned Key In Ignition - Ignition key transponder
ID is currently programmed in SKIM memory.
BODY CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Body Control Module (BCM) is located in the
passenger compartment, attached to the bulkhead
underneath the left side of the instrument panel.
8E - 2 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES (Continued)
Page 298 of 2339

By comparing the two inputs, the PCM can deter-
mine transaxle gear ratio. This is important to the
CVI calculation because the PCM determines CVIs
by monitoring how long it takes for a gear change to
occur (Fig. 10).
Gear ratios can be determined by using the DRB
Scan Tool and reading the Input/Output Speed Sen-
sor values in the ªMonitorsº display. Gear ratio can
be obtained by dividing the Input Speed Sensor value
by the Output Speed Sensor value.
For example, if the input shaft is rotating at 1000
rpm and the output shaft is rotating at 500 rpm,
then the PCM can determine that the gear ratio is
2:1. In direct drive (3rd gear), the gear ratio changes
to 1:1. The gear ratio changes as clutches are applied
and released. By monitoring the length of time it
takes for the gear ratio to change following a shift
request, the PCM can determine the volume of fluid
used to apply or release a friction element.
The volume of transmission fluid needed to apply
the friction elements are continuously updated for
adaptive controls. As friction material wears, the vol-
ume of fluid need to apply the element increases.
Certain mechanical problems within the clutch
assemblies (broken return springs, out of position
snap rings, excessive clutch pack clearance, improper
assembly, etc.) can cause inadequate or out-of-range
clutch volumes. Also, defective Input/Output Speed
Sensors and wiring can cause these conditions. The
following chart identifies the appropriate clutch vol-
umes and when they are monitored/updated:
CLUTCH VOLUMES
ClutchWhen Updated
Proper Clutch
Volume
Shift Sequence Oil Temperature Throttle Angle
L/R2-1 or 3-1 coast
downshift>70É <5É 35to83
2/4 1-2 shift
> 110É5 - 54É20 to 77
OD 2-3 shift 48 to 150
UD 4-3 or 4-2 shift > 5É 24 to 70
SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the PCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the PCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Fig. 10 Example of CVI Calculation
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - CLUTCH PACK
4 - SEPARATOR PLATE
5 - FRICTION DISCS
6 - INPUT SHAFT
7 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
8 - PISTON AND SEAL
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-13
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 320 of 2339
(2) Wearing safety glasses, look through the bat-
tery cell cap holes to determine the level of the elec-
trolyte in the battery. The electrolyte should be above
the hooks inside the battery cells (Fig. 10).
(3)Add only distilled wateruntil the electrolyte
is above the hooks inside the battery cells (Fig. 10).
MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER
Always use the Micro 420 Instruction Manual that
was supplied with the tester as a reference. If the
Instruction Manual is not available the following pro-
cedure can be used:
WARNING: ALWAYS WEAR APPROPRIATE EYE
PROTECTION AND USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN
WORKING WITH BATTERIES.
BATTERY TESTING
(1) If testing the battery OUT-OF-VEHICLE, clean
the battery terminals with a wire brush before test-
ing. If the battery is equipped with side post termi-
nals, install and tighten the supplied lead terminal
stud adapters. Do not use steel bolts. Failure to prop-
erly install the stud adapters, or using stud adapters
that are dirty or worn-out may result in false test
readings.
(2) If testing the battery IN-THE-VEHICLE, make
certain all of the vehicle accessory loads are OFF,
including the ignition.The preferred test positionis at the battery terminal. If the battery is not
accessible, you may test using both the positive and
negative jumper posts. Select TESTING AT JUMPER
POST when connecting to that location.
(3) Connect the tester to the battery or jumper
posts, the red clamp to positive (+) and the black
clamp to negative (±).
NOTE: Multiple batteries connected in parallel must
have the ground cable disconnected to perform a
battery test. Failure to disconnect may result in
false battery test readings.
(4) Using the ARROW key selectinoroutof vehi-
cle testing and press ENTER to make a selection.
(5) If not selected, choose the Cold Cranking Amp
(CCA) battery rating. Or select the appropriate bat-
tery rating for your area (see menu). The tester will
then run its self programmed test of the battery and
display the results. Refer to the test result table
noted below.
CAUTION: If REPLACE BATTERY is the result of the
test, this may mean a poor connection between the
vehicle's cables and battery exists. After discon-
necting the vehicle's battery cables from the bat-
tery, retest the battery using the OUT-OF-VEHICLE
test before replacing.
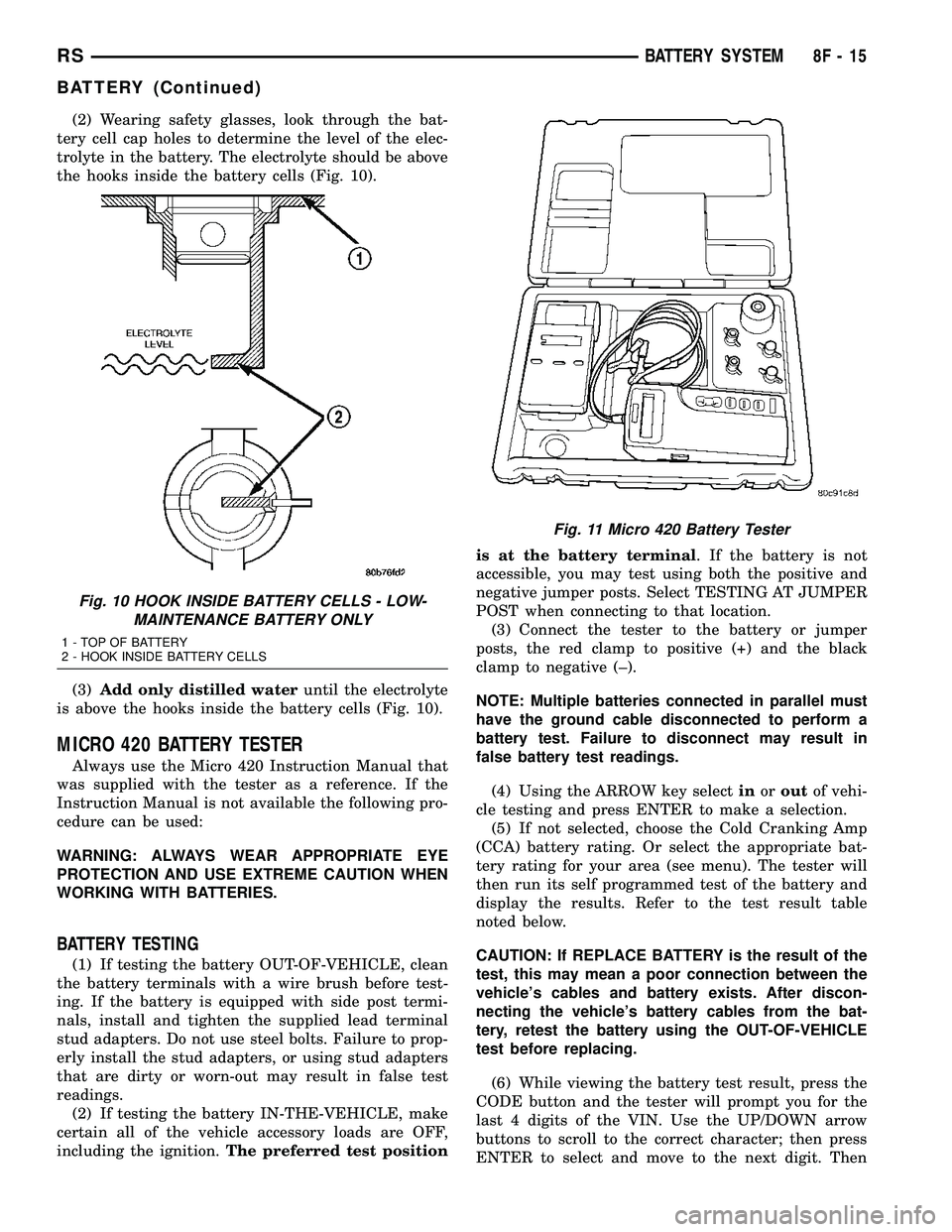
(6) While viewing the battery test result, press the
CODE button and the tester will prompt you for the
last 4 digits of the VIN. Use the UP/DOWN arrow
buttons to scroll to the correct character; then press
ENTER to select and move to the next digit. Then
Fig. 10 HOOK INSIDE BATTERY CELLS - LOW-
MAINTENANCE BATTERY ONLY
1 - TOP OF BATTERY
2 - HOOK INSIDE BATTERY CELLS
Fig. 11 Micro 420 Battery Tester
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-15
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 367 of 2339

CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The camshaft position sensor for the 3.3/3.8L is
mounted in the front of the timing case cover (Fig. 6)
and the camshaft position sensor for the 2.4L is
mounted on the end of the cylinder head (Fig. 3).
OPERATION
The camshaft position sensor provides cylinder
identification to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) (Fig. 1). The sensor generates pulses as
groups of notches on the camshaft sprocket pass
underneath it (Fig. 2). The PCM keeps track of
crankshaft rotation and identifies each cylinder by
the pulses generated by the notches on the camshaft
sprocket. Four crankshaft pulses follow each group of
camshaft pulses.
When the PCM receives 2 cam pulses followed by
the long flat spot on the camshaft sprocket, it knows
that the crankshaft timing marks for cylinder 1 are
next (on driveplate). When the PCM receives one
camshaft pulse after the long flat spot on the
sprocket, cylinder number 2 crankshaft timing marks
are next. After 3 camshaft pulses, the PCM knows
cylinder 4 crankshaft timing marks follow. One cam-shaft pulse after the 3 pulses indicates cylinder 5.
The 2 camshaft pulses after cylinder 5 signals cylin-
der 6 (Fig. 2). The PCM can synchronize on cylinders
1or4.
When metal aligns with the sensor, voltage goes
low (less than 0.3 volts). When a notch aligns with
the sensor, voltage switches high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the voltage
switches from low (metal) to high (notch) then back
to low. The number of notches determine the amount
of pulses. If available, an oscilloscope can display the
square wave patterns of each timing event.
Top Dead Center (TDC) does not occur when
notches on the camshaft sprocket pass below the sen-
sor. TDC occurs after the camshaft pulse (or pulses)
and after the 4 crankshaft pulses associated with the
particular cylinder. The arrows and cylinder call outs
on (Fig. 2) represent which cylinder the flat spot and
notches identify, they do not indicate TDC position.
Fig. 1 Camshaft Position Sensor
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - PAPER SPACER
Fig. 2 Camshaft Sprocket
1 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
2 - CYL #6
3 - CYL #5
4 - CYL #4
5 - CYL #3
6 - CYL #2
7 - CYL #1
8I - 4 IGNITION CONTROLRS
Page 374 of 2339

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS.........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUSTER
DIAGNOSIS...........................3REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
CLUSTER LENS
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION
The instrumentation gauges are contained in a
subdial assembly within the instrument cluster. The
individual gauges are not serviceable. If one of the
cluster gauges becomes faulty, the entire cluster
would require replacement.
The Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC) with a
tachometer is equipped with a electronic vacuum flu-
orescent transmission range indicator (PRND3L),
odometer, and trip odometer display.
The MIC without a tachometer is equipped with a
Light Emitting Diode (LED) transmission range indi-
cator (PRND3L) and a vacuum fluorescent odometer
display.
The MIC is equipped with the following warning
lamps.
²Lift Gate Ajar
²Low Fuel Level
²Low Windshield Washer Fluid Level
²Cruise
²Battery Voltage
²Fasten Seat Belt
²Door Ajar
²Coolant Temperature
²Anti-Lock Brake
²Brake
²Oil Pressure
²MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
²VTSS/SKIS Indicator
²Airbag
²Traction Control
²Autostick
Export Only- uses a message center that displays
the following telltales:
²Turns Signals
²High Beam
²Tire Pressure Monitoring (TPM)²Glow Plug (Export Only)
²Supplemental Cabin Heater (Export Only)WATER IN FUEL LAMP - EXPORT
The Water In Fuel Lamp is located in the message
center. When moisture is found within the fuel sys-
tem, the sensor sends a message via the PCI data
bus to the instrument cluster. The MIC illuminates
the bulb in the message center, The sensor is located
underneath the vehicle, directly above the rear axle.
The sensor is housed within the fuel filter/water sep-
arator assembly cover. The sensor is not serviced sep-
arately. If found defective, the entire assembly cover
must be replaced.
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for operation
instructions and conditions for the Instrument Clus-
ter Gauges.
WATER IN FUEL LAMP/SENSOR - EXPORT
The Water In Fuel Sensor is a resistive type
switch. It is calibrated to sense the different resis-
tance between diesel fuel and water. When water
enters the fuel system, it is caught in the bottom of
the fuel filter/water separator assembly, where the
sensor is located. Water has less resistance than die-
sel fuel. The sensor then sends a PCI data bus mes-
sage to the instrument cluster to illuminate the
lamp.
If the lamp is inoperative, perform the self diag-
nostic test on the instrument cluster to check the
lamp operation before continuing diagnosis.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-1
Page 375 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS
The instrument clusters are equipped with a self
diagnostic test feature to help identify electronic
problems. Prior to any test, perform the Self-Diag-
nostic Test. The self diagnostic system displays
instrument cluster stored fault codes in the odometer
display, sweeps the gauges to the calibration points,
and bulb checks the warning indicators. When the
key is in the ON position with the engine not run-
ning, the MIL will remain illuminated for regulatory
purposes.
To activate the Self-Diagnostic program:
(1) With the ignition switch in the OFF position,
depress the TRIP ODOMETER RESET button.
(2) Continue to hold the TRIP ODOMETER
RESET button untilSofand a number (software ver-
sion number (i.e.Sof 3.2) appears in the odometer
window then release the button. If a fault code is
present, the cluster will display it in the odometer
display. When all fault codes have been displayed,
the cluster will displayªendºin the odometer dis-
play. Refer to the INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DTC'S
table to determine what each trouble code means.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DTC'S
DTC DESCRIPTION
100.0 LOOP-BACK FAILURE
100.1 ABS COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.2 BCM COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.3 EATX COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.4 FCM COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.5 ORC COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.6SBEC/DEC/MCM COMMUNICATION
FAULT
200.0 AIRBAG LED SHORT
200.1 AIRBAG LED OPEN
200.2 ABS LED SHORT
200.3 ABS LED OPEN
200.6 EL INVERTER TIME-OUT
200.7 EATX MISMATCH
400.0 EEPROM READ/WRITE FAILURE
400.1IMPROPER POWER DOWN
DETECTED
CALIBRATION TEST
The CLUSTER CALIBRATION table contains the
proper calibration points for each gauge. If the gauge
pointers are not calibrated, a problem exists in the
cluster. If any gauge is out of calibration, replace the
cluster.
CLUSTER CALIBRATION
SPEEDOMETER CALIBRATION POINT
1 0 MPH (0 KM/H)
2 20 MPH (40 KM/H)
3 60 MPH (100 KM/H)
4 100 MPH (160 KM/H)
TACHOMETER
1 0 RPM
2 1000 RPM
3 3000 RPM
4 6000 RPM
FUEL GAUGE
1 EMPTY
2 1/4 FILLED
3 1/2 FILLED
4 FULL
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
1 COLD
2 1/4
3 3/4
4 HOT
ODOMETER SEGMENT TEST
If a segment in the odometer does not illuminate
normally, a problem exists in the display.
ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR
SEGMENT TEST
If a segment in the transmission range indicator
does not illuminate normally, a problem exists in the
display.
8J - 2 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERRS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 376 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUSTER
DIAGNOSIS
CONDITIONS
Refer to the following tables for possible problems,
causes, and corrections.
²INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
²SPEEDOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²TACHOMETER DIAGNOSIS²FUEL GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
²TEMPERATURE GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
²ODOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²ELECTRONIC GEAR INDICATOR DISPLAY
DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Always check the functionality of the cluster
by running the self test prior to troubleshooting.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
INOPERATIVE. NO
RESPONSE FROM
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER.NO PCI BUS MESSAGES
FROM THE BCM.USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO CHECK THE BCM.
IF OK, LOOK FOR ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE
FOR CLUSTER FAILURE. IF NOT OK, REFER TO
THE PROPER BODY DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
MANUAL.
SPREAD TERMINAL(S)
ON WIRING HARNESS
CLUSTER CONNECTOR.REMOVE CLUSTER FROM INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND CHECK WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR FOR
SPREAD TERMINAL. IF OK, LOOK FOR ANOTHER
POSSIBLE CAUSE FOR THE CLUSTER FAILURE. IF
NOT OK, REPAIR CONNECTOR.
BCM IS NOT RECEIVING
PROPER INPUT FROM
THE IGNITION SWITCH.1. USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO VERIFY IGNITION
SWITCH STATUS INTO THE BCM. IF NOT OK, GO
TO STEP (2). IF OK, LOOK AT ANOTHER POSSIBLE
CAUSE OF FAILURE.
2. CHECK IGNITION SWITCH FUNCTION AND
WIRING.
INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.REPLACE CLUSTER.
WAKE UP CIRCUIT
FAULTY.VERIFY CONTINUITY OF WAKE UP CIRCUIT FROM
BCM TO MIC. CIRCUIT SHALL BE LOW WHENEVER
BCM IS AWAKE.
POWER OR GROUND
MISSING.IF NO RESPONSE FROM THE MIC, CHECK FOR
POWER AND GROUND AT THE MIC CONNECTOR.
REFER TO WIRING DIAGRAMS FOR CONNECTOR
CALL OUTS.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-3
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 382 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ERRATIC POINTER
MOVEMENT.1. BAD PCI BUS
MESSAGE FROM THE
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE.1.A. CHECK PCM FAULT CODES USING A DRB IIIT
SCAN TOOL. IF THERE ARE NO FAULTS, GO TO
STEP 1.B. IF THERE ARE FAULTS, REFER TO THE
PROPER POWERTRAIN DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO PROPERLY DIAGNOSE
AND REPAIR.
1.B. REFER TO FUEL, COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING. REPAIR
SENSOR AS NEEDED.
2. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.2. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF THE POINTER MOVES DURING TEST BUT
STILL APPEARS ERRATIC, REPLACE CLUSTER
ASSEMBLY.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
INACCURATE.1. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE OUT OF
CALIBRATION.1. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST.
²IF POINTER IS ACCURATE TO THE CALIBRATION
POINTS LOOK FOR ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE
OF FAILURE.
²IF POINTER IS INACCURATE TO THE
CALIBRATION POINTS, REPLACE CLUSTER
ASSEMBLY.
2. COOLANT SENSOR
OUT OF CALIBRATION.2. REFER TO FUEL, COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR FOR TEST AND REPAIR PROCEDURE.
ODOMETER DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO DISPLAY. 1. NO PCI BUS
ODOMETER MESSAGE
FROM BCM.1. USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO CHECK THE BCM.
REFER TO THE PROPER BODY DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO PROPERLY DIAGNOSE
AND REPAIR.
2. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.2. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF ODOMETER PASSES THE SEGMENT CHECK,
LOOK FOR ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE OF
FAILURE. IF IT FAILS VERIFY POWER AND
GROUND ARE BEING PROVIDED TO THE
CLUSTER. IF YES, REPLACE CLUSTER. IF NO,
DETERMINE CAUSE OF NO POWER OR GROUND.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-9
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)