2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN spark plugs
[x] Cancel search: spark plugsPage 33 of 2339

Kilometers 149 000 154 000 158 000 160 000 163 000 168 000
(Miles) (93,000) (96,000) (99,000) (100,000) (102,000) (105,000)
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXX X X
Rotate Tires X X
Inspect the brake linings. X
Inspect the engine air cleaner
filter, replace if necessary. *XXXXX
Replace theengine air
cleaner filter*X
Inspect and adjust the power
steering pump belt tension on
2.4 liter engines.X
Inspect the generator belt on
2.4 liter engines, replace if
necessary.X
Inspect engine accessory
drive belts on 3.3 liter
engines, replace if necessary.
³X
Change the manual
transmission fluid.X
Change the All Wheel Drive
(AWD) power transfer unit,
overrunning clutch and rear
carrier fluid. (See note at the
end of this chart)X
Flush and replace the engine
coolant at 60 months or
100,000 miles.X
Replace the air conditioning
filter.X
Kilometers 173 000 178 000 182 000 187 000 192 000
(Miles) (108,000) (111,000) (114,000) (117,000) (120,000)
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Rotate Tires X X X
Inspect the brake linings. X X
Inspect the engine air cleaner filter, replace
if necessary. *XXXX
Replace theengine air cleaner filter.X
Replace thespark plugson 2.4 liter
engines.X
Replace theignition cableson 2.4 liter
engines.X
Inspect and adjust the power steering pump
belt tension on 2.4 liter engines.X
0 - 20 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCERS
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 364 of 2339

IGNITION CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION - IGNITION SYSTEM..........1
OPERATION - IGNITION SYSTEM...........1
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE.............................2
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE........2
SPARK PLUG.........................2
FIRING ORDER........................3
AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L.......................5
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L....................5
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L...................6
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L.................6
IGNITION COIL
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L.......................7REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L....................7
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L...................7
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L.................8
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................8
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L.......................8
REMOVAL - 3.8L.......................8
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L...................8
INSTALLATION - 3.8L...................8
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD 4 CYLINDER . . . 9
DESCRIPTION - PLATINUM PLUGS........9
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
SPARK PLUG CABLE
DESCRIPTION.........................10
REMOVAL - 2.0/2.4L.....................10
INSTALLATION - 2.0/2.4L.................10
IGNITION CONTROL
DESCRIPTION - IGNITION SYSTEM
NOTE: All engines use a fixed ignition timing sys-
tem. Basic ignition timing is not adjustable. All
spark advance is determined by the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM).
The ignition system used on these engines is
referred to as the Direct Ignition System (DIS). The
system's three main components are the coils, crank-
shaft position sensor, and camshaft position sensor. If
equipped with the coil on plug ignition system it uti-
lizes an ignition coil for every cylinder, it is mounted
directly over the each spark plug.
OPERATION - IGNITION SYSTEM
The crankshaft position sensor and camshaft posi-
tion sensor are hall effect devices. The camshaft posi-
tion sensor and crankshaft position sensor generate
pulses that are inputs to the PCM. The PCM deter-
mines engine position from these sensors. The PCM
calculates injector sequence and ignition timing from
crankshaft & camshaft position. For a description of
both sensors, refer to Camshaft Position Sensor and
Crankshaft Position Sensor.
RSIGNITION CONTROL8I-1
Page 365 of 2339

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
2.4L Target Magnet Screw 3 30
2.4L Camshaft Sensor
Screw12.9 115
3.3/3.8L Camshaft Sensor
Screw14.1 125
2.4L Ignition coil bolts 11.8 105
3.3/3.8LIgnition coil bolts 11.8 105
Spark Plugs 17.5 13
Knock Sensor 10 7
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
2.4L
CABLE Maximum Resistance
1, 2, 3, & 4 10.8K ohms
3.3/3.8L
CABLE Maximum Resistance
#1 22.5K ohms
#2 22.8K ohms
#3 19.3K ohms
#4 19.3K ohms
#5 13.6K ohms
#6 16.4K ohms
SPARK PLUG
Engine Spark Plug Gap Thread Size
2.4L RE14MCC5 0.048 TO 0.053 14mm (1 in.) reach
Engine Spark Plug Gap Thread Size
3.3L RE14PLP5 0.048 TO 0.053 14mm (1 in.) reach
3.8L RE14PLP5 0.048 TO 0.053 14mm (1 in. ) reach
8I - 2 IGNITION CONTROLRS
IGNITION CONTROL (Continued)
Page 369 of 2339

(6) Pull sensor up out of the chain case cover.Do
not pull on the sensor wiring.There is an O-ring
on the body of the sensor. The O-ring may make
removal difficult. A light tap to top of sensor prior to
removal may reduce force needed for removal.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The target magnet has locating dowels that fit into
machined locating holes in the end of the camshaft
(Fig. 7).
(1) Install target magnet in end of camshaft.
Tighten mounting screw to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.) torque.
Over torqueing could cause cracks in magnet. If mag-
net cracks replace it.
(2) Install camshaft position sensor. Tighten sensor
mounting screws to 12.9 N´m (115 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Carefully attach electrical connector to cam-
shaft position sensor.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
If the removed sensor is reinstalled, clean off
the old spacer on the sensor face. A NEW
SPACER must be attached to the face before
installation.Inspect O-ring for damage, replace if
necessary. If the sensor is being replaced, confirm
that the paper spacer is attached to the face and
O-ring is positioned in groove of the new sensor (Fig.
8).
(1) Apply a couple drops of clean engine oil to the
O-ring prior to installation.
(2) Install sensor in the chain case cover and
rotate into position.(3) Push sensor down until contact is made with
the camshaft gear. While holding the sensor in this
position, install and tighten the retaining bolt 14
N´m (125 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect camshaft position sensor electrical
connector to harness connector.
(5) Install the air box cover and inlet hose (Fig. 5).
(6) Connect the negative battery cable.
IGNITION COIL
DESCRIPTION
The ignition coil assembly consists of 2 or 3 inde-
pendent coils molded together (Fig. 9) or (Fig. 10).
The coil assembly for the 3.3/3.8L is mounted on the
intake manifold. The coil assembly for the 2.4L is
mounted on the cylinder head cover. Spark plug
cables route to each cylinder from the coil.
OPERATION
The coil fires two spark plugs every power stroke.
One plug is the cylinder under compression, the
other cylinder fires on the exhaust stroke. The Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM) determines which of
the coils to charge and fire at the correct time.
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the magnetic energy in
the coil transfers to the secondary causing the spark.
The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it does
not receive the crankshaft position sensor and cam-
shaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shutdown
(ASD) RelayÐPCM Output, in this section for relay
operation.
Fig. 7 Target Magnet Installation
1 - LOCATING DOWELS
2 - LOCATING HOLES (2)
Fig. 8 Camshaft Position Sensor and Spacer
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - PAPER SPACER
8I - 6 IGNITION CONTROLRS
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 372 of 2339

(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative cable.
SPARK PLUG
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD 4 CYLINDER
All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
Refer to the Specifications section for gap and type
of spark plug.
DESCRIPTION - PLATINUM PLUGS
The V6 engines use platinum resistor spark plugs.
They have resistance values of 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt tester. For
spark plug identification and specifications, Refer to
the Specifications section.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.When the spark plugs use a single or double plat-
inum tips and they have a recommended service life
of 100,000 miles for normal driving conditions per
schedule A in this manual. The spark plugs have a
recommended service life of 75,000 miles for severe
driving conditions per schedule B in this manual. A
thin platinum pad is welded to both or just the cen-
ter electrode end(s) as shown in (Fig. 13). Extreme
care must be used to prevent spark plug cross
threading, mis-gapping (Fig. 14) and ceramic insula-
tor damage during plug removal and installation.
CAUTION: Cleaning of the platinum plug may dam-
age the platinum tip.
Fig. 12 Knock Sensor
1 - GENERATOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - KNOCK SENSOR
4-STARTER
Fig. 13 Platinum Pads
1 - APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND HERE ONLY
2 - PLATINUM SPARK SURFACE
Fig. 14 Setting Spark Plug Electrode Gap
1 - TAPER GAUGE
RSIGNITION CONTROL8I-9
KNOCK SENSOR (Continued)
Page 373 of 2339

REMOVAL
When replacing the spark plugs and spark plug
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise, cross ignition of the spark plugs orshort cir-
cuit the cables to ground.
Always remove cables by grasping at the boot,
rotating the boot 1/2 turn, and pulling straight back
in a steady motion.
(1) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug.
(2) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a foam insert.
(3) Inspect the spark plug condition.
INSTALLATION
When replacing the spark plugs and spark plug
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise, cross ignition of the spark plugs orshort cir-
cuit the cables to ground.
(1) Coat threads of spark plug with anti-seize. Be
sure not to get anti-seizeANYWHERE BUT ON
THE THREADS OF THE SPARK PLUG as
shown in (Fig. 13).
(2) To avoid cross threading, start the spark plug
into the cylinder head by hand.
(3) Tighten spark plugs to 17.5 N´m (13 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs. A
click will be heard and felt when the cable properly
attaches to the spark plug.
SPARK PLUG CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Spark Plug cables are sometimes referred to as
secondary ignition wires. The wires transfer electri-
cal current from the ignition coil pack to individualspark plugs at each cylinder. The resistive spark plug
cables are of nonmetallic construction. The cables
provide suppression of radio frequency emissions
from the ignition system.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil, and spark plugs. Terminals should
be fully seated. The insulators should be in good con-
dition and should fit tightly on the coil, and spark
plugs. Spark plug cables with insulators that are
cracked or torn must be replaced.
Clean Spark Plug cables with a cloth moistened
with a non-flammable solvent. Wipe the cables dry.
Check for brittle or cracked insulation. The spark
plug cables and spark plug boots are made from high
temperature materials.
REMOVAL - 2.0/2.4L
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
Remove spark plug cable from coil first.
Always remove the spark plug cable by grasping
the top of the spark plug insulator, turning the boot
1/2 turn and pulling straight up in a steady motion.
INSTALLATION - 2.0/2.4L
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
Install spark plug insulators over spark plugs.
Ensure the top of the spark plug insulator covers the
upper end of the spark plug tube, then connect the
other end to coil pack.
8I - 10 IGNITION CONTROLRS
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 1182 of 2339
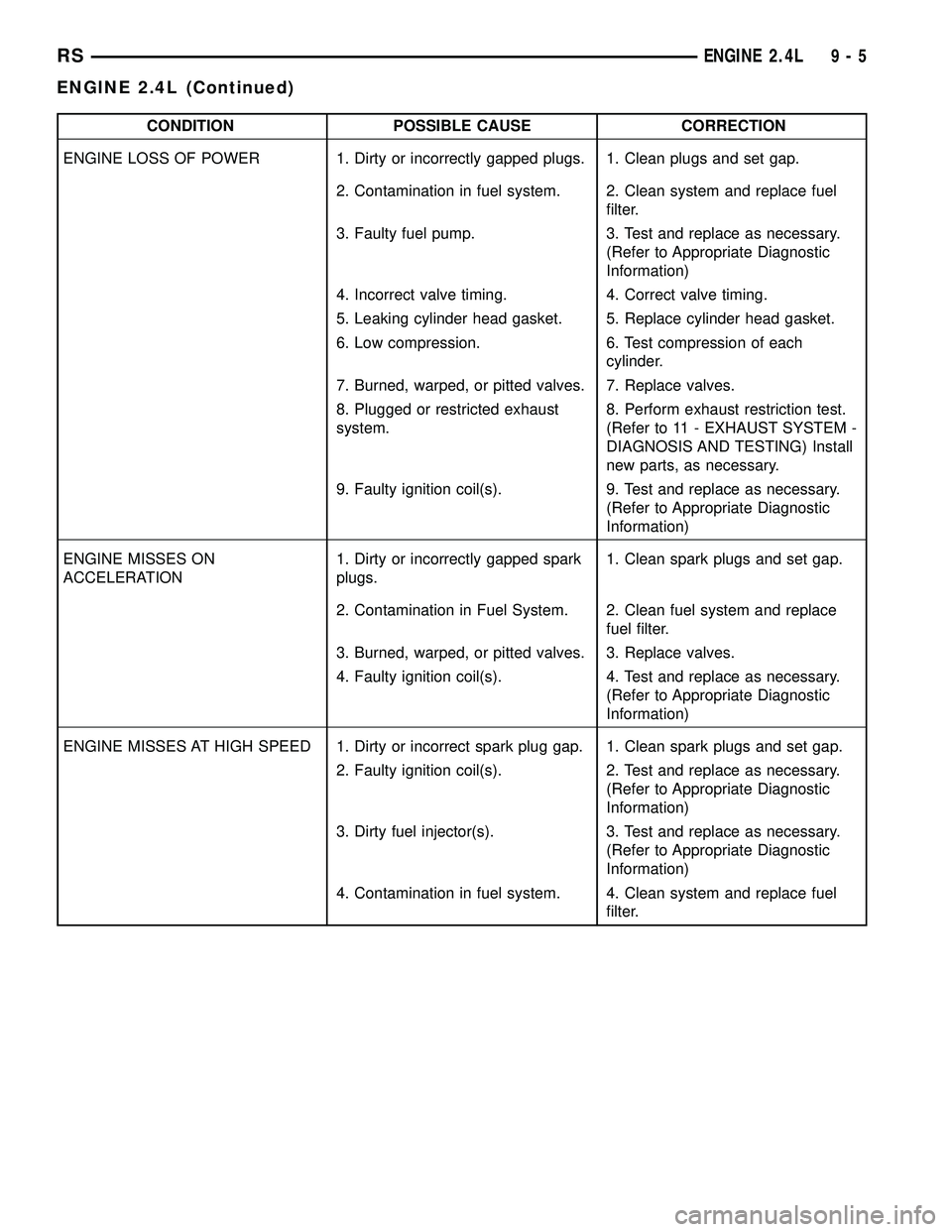
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs. 1. Clean plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Incorrect valve timing. 4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket. 5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression. 6. Test compression of each
cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.8. Perform exhaust restriction test.
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) Install
new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition coil(s). 9. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace
fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Faulty ignition coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). 3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-5
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1185 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL CONSUMPTION OR SPARK
PLUGS FOULED1. PCV system malfunction. 1. Check system and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 25 -
EMISSIONS CONTROL/
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/PCV
VALVE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
2. Worn, scuffed or broken rings. 2. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings.
3. Carbon in oil ring slots. 3. Install new rings.
4. Rings fitted too tightly in grooves. 4. Remove rings and check
grooves. If groove is not proper
width, replace piston.
5. Worn valve guide(s). 5. Replace cylinder head assembly.
6. Valve stem seal(s) worn or
damaged.6. Replace seal(s).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair as necessary.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (make-up air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the outlet on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve outlet on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and fresh air hose (make-up air). Proceed
to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube
to block location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using MoparTStud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube
applications only), and for O-ring style tubes,
remove tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
9 - 8 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)