2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN catalytic converter
[x] Cancel search: catalytic converterPage 1340 of 2339
(5) Apply the park brake and start the engine.
(6) With transmission in Park or Neutral, raise
engine speed to 2000 RPM. Monitor the pressure
readings on the DRBIIIt. Back pressure should not
exceed specified limit. Refer to specification in table
below EXHAUST BACK PRESSURE LIMITS.
(7) If pressure exceeds maximum limits, inspect
exhaust system for restricted component. For further
catalytic converter inspection procedures, (Refer to 11
- EXHAUST SYSTEM/CATALYTIC CONVERTER -
INSPECTION). Replace component(s) as necessary.
EXHAUST BACK PRESSURE LIMITS
Exhaust Back Pressure Limit (Max)
Vehicle in Park/Neutral
(no load) @2000 RPM3.45 Kpa (0.5 psi)
INSPECTION
Inspect the exhaust pipes, catalytic converters,
muffler, and resonators for cracked joints, broken
welds and corrosion damage that would result in a
leaking exhaust system. Inspect the clamps, support
brackets, and insulators for cracks and corrosion
damage.
NOTE: Slip joint band clamps are spot welded to
exhaust system. If a band clamp must be replaced,
the spot weld must be ground off.
ADJUSTMENTS
A misaligned exhaust system is usually indicated
by a vibration, rattling noise, or binding of exhaust
system components. These noises are sometimes hard
to distinguish from other chassis noises. Inspect
exhaust system for broken, damaged or loose compo-
nents such as; clamps, heat shields, isolators, and
hanger brackets. Replace or tighten as necessary. It
is important that exhaust system clearances and
alignment be maintained.
Perform the following procedures to align the
exhaust system:
(1) Loosen band clamp at catalytic converter pipe
to muffler/resonator assembly.
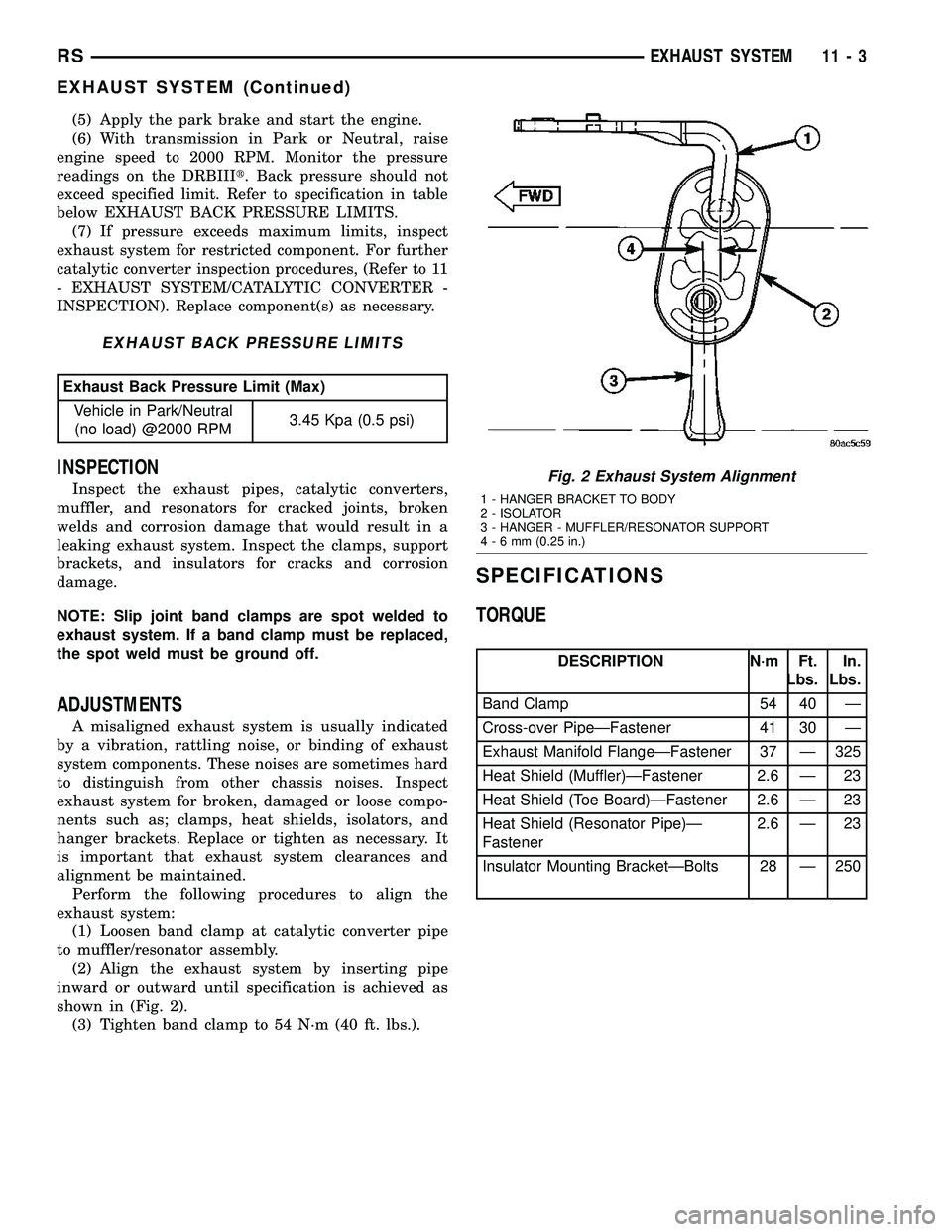
(2) Align the exhaust system by inserting pipe
inward or outward until specification is achieved as
shown in (Fig. 2).
(3) Tighten band clamp to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Band Clamp 54 40 Ð
Cross-over PipeÐFastener 41 30 Ð
Exhaust Manifold FlangeÐFastener 37 Ð 325
Heat Shield (Muffler)ÐFastener 2.6 Ð 23
Heat Shield (Toe Board)ÐFastener 2.6 Ð 23
Heat Shield (Resonator Pipe)Ð
Fastener2.6 Ð 23
Insulator Mounting BracketÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Fig. 2 Exhaust System Alignment
1 - HANGER BRACKET TO BODY
2 - ISOLATOR
3 - HANGER - MUFFLER/RESONATOR SUPPORT
4-6mm(0.25 in.)
RSEXHAUST SYSTEM11-3
EXHAUST SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1341 of 2339
SPECIAL TOOLS
EXHAUST SYSTEM
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The toe board three-way catalytic converter is con-
nected to the exhaust manifold by the use of flex
joint and a gasket. The outlet connects to the muffler
inlet pipe and is secured with a band type clamp
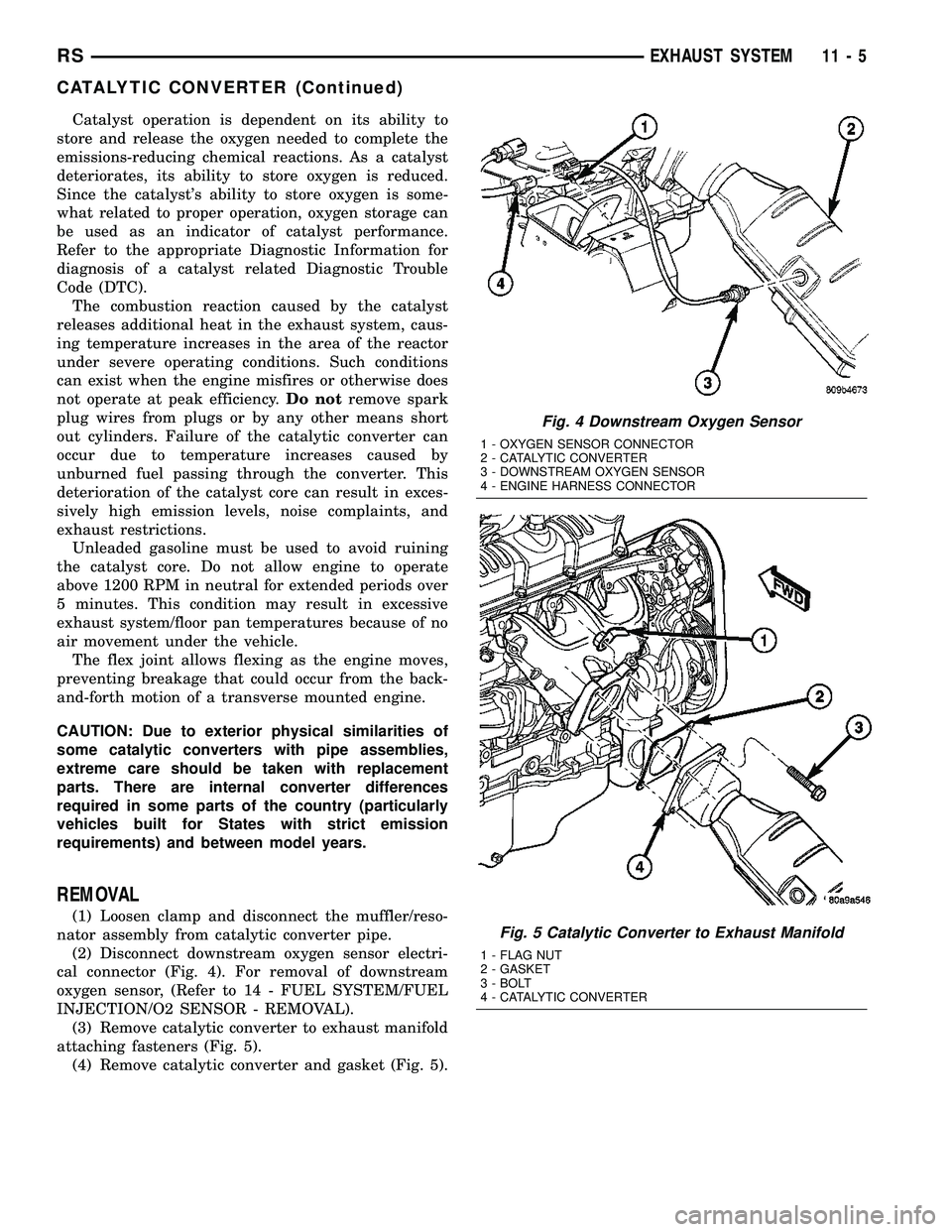
(Fig. 1).The exhaust flex-joint coupling (Fig. 3) is used to
secure the catalytic converter to the exhaust mani-
fold. The flex-joint has four bolts, four flag nuts and
a gasket that are separate parts from the exhaust
flex-joint. The flex-joint is welded to the catalytic
converter.
CAUTION: When servicing, care must be exercised
not to dent or bend the bellows or bellows cover of
the flex-joint. Should this occur, the flex-joint will
eventually fail and require the catalytic converter be
replaced.
OPERATION
The three-way catalytic converter simultaneously
converts three exhaust emissions into harmless
gases. Specifically, HC and CO emissions are con-
verted into water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) are converted into Nitrogen
(N) and Oxygen. The three-way catalyst is most effi-
cient in converting HC, CO and NOx at the stoichio-
metric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.
The oxygen content in a catalyst is important for
efficient conversion of exhaust gases. When a high
oxygen content (lean) air/fuel ratio is present for an
extended period, oxygen content in a catalyst can
reach a maximum. When a rich air/fuel ratio is
present for an extended period, the oxygen content in
the catalyst can become totally depleted. When this
occurs, the catalyst fails to convert the gases. This is
known as catalyst9punch through.9
Back Pressure Test Adapter - CH8519
Pressure Transducer CH7063
DRB III & PEP Module - OT-CH6010A
Fig. 3 Flex-joint
1 - FLANGE
2 - END CAPS
3 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
4 - FLEXIBLE BELLOWS
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMRS
EXHAUST SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1342 of 2339
Catalyst operation is dependent on its ability to
store and release the oxygen needed to complete the
emissions-reducing chemical reactions. As a catalyst
deteriorates, its ability to store oxygen is reduced.
Since the catalyst's ability to store oxygen is some-
what related to proper operation, oxygen storage can
be used as an indicator of catalyst performance.
Refer to the appropriate Diagnostic Information for
diagnosis of a catalyst related Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC).
The combustion reaction caused by the catalyst
releases additional heat in the exhaust system, caus-
ing temperature increases in the area of the reactor
under severe operating conditions. Such conditions
can exist when the engine misfires or otherwise does
not operate at peak efficiency.Do notremove spark
plug wires from plugs or by any other means short
out cylinders. Failure of the catalytic converter can
occur due to temperature increases caused by
unburned fuel passing through the converter. This
deterioration of the catalyst core can result in exces-
sively high emission levels, noise complaints, and
exhaust restrictions.
Unleaded gasoline must be used to avoid ruining
the catalyst core. Do not allow engine to operate
above 1200 RPM in neutral for extended periods over
5 minutes. This condition may result in excessive
exhaust system/floor pan temperatures because of no
air movement under the vehicle.
The flex joint allows flexing as the engine moves,
preventing breakage that could occur from the back-
and-forth motion of a transverse mounted engine.
CAUTION: Due to exterior physical similarities of
some catalytic converters with pipe assemblies,
extreme care should be taken with replacement
parts. There are internal converter differences
required in some parts of the country (particularly
vehicles built for States with strict emission
requirements) and between model years.
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen clamp and disconnect the muffler/reso-
nator assembly from catalytic converter pipe.
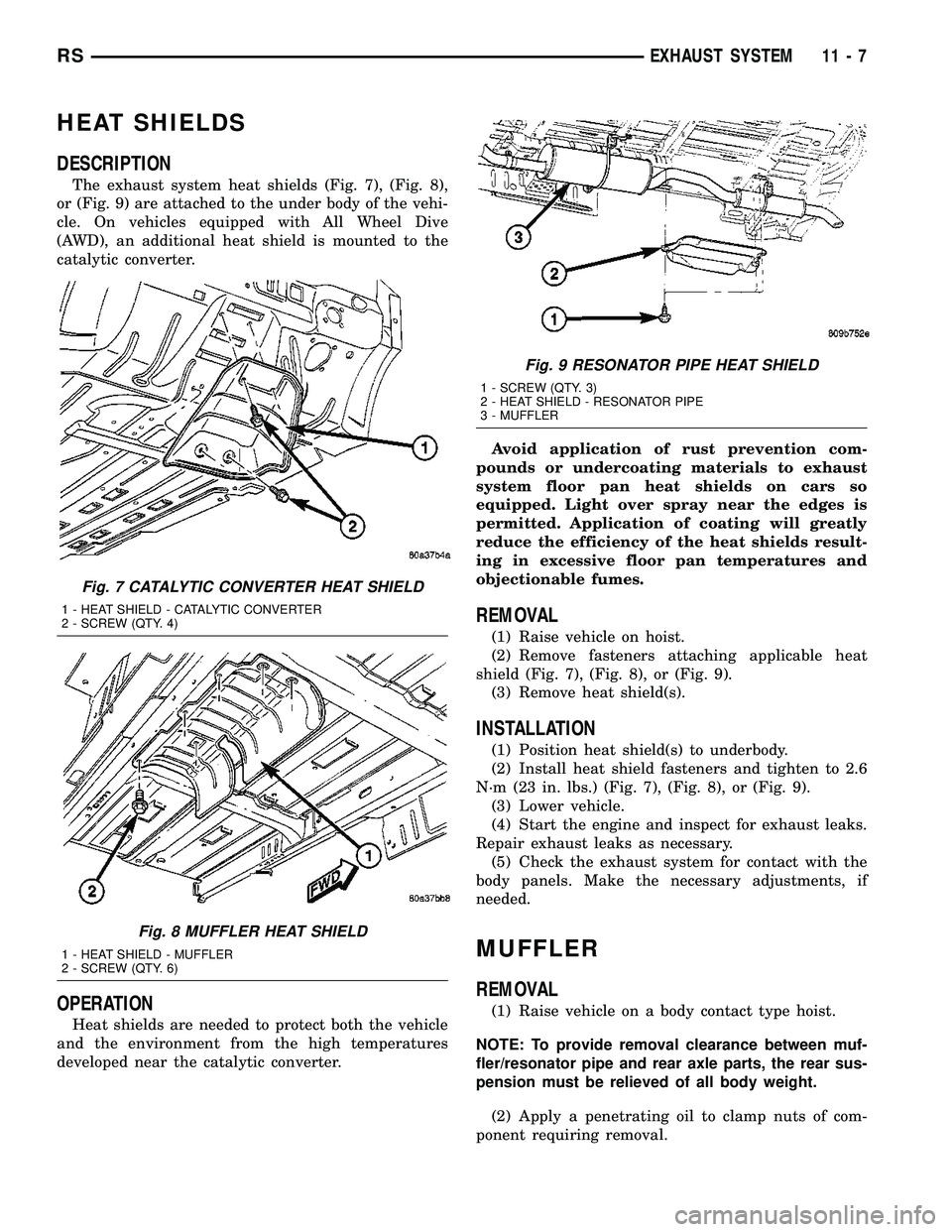
(2) Disconnect downstream oxygen sensor electri-
cal connector (Fig. 4). For removal of downstream
oxygen sensor, (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/O2 SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
attaching fasteners (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove catalytic converter and gasket (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 Downstream Oxygen Sensor
1 - OXYGEN SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
3 - DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
4 - ENGINE HARNESS CONNECTOR
Fig. 5 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
1 - FLAG NUT
2 - GASKET
3 - BOLT
4 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
RSEXHAUST SYSTEM11-5
CATALYTIC CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1343 of 2339

INSPECTION
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER ATTEMPT TO SERVICE ANY
PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM UNTIL IT IS
COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN
WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC CON-
VERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CONVERTER
RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT PERIOD
OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
Check catalytic converter for a flow restriction.
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) Exhaust System Restriction Check
for procedure.
Visually inspect the catalytic converter element by
using a borescope or equivalent. Remove oxygen sen-
sor(s) and insert borescope. If borescope is not avail-
able, remove converter and inspect element using a
flashlight. Inspect element for cracked or melted sub-
strate.
NOTE: Before replacing a catalytic converter, deter-
mine the root cause of failure. Most catalytic con-
verter failures are caused by air, fuel or ignition
problems. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Informa-
tion) for test procedures.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position new gasket onto the manifold flange
and install catalytic converter (Fig. 5). Tighten fas-
teners to 37 N´m (325 in. lbs.).
NOTE: Be careful not to twist or kink the oxygen
sensor wires.
(2) Install (if removed) and connect the down-
stream oxygen sensor (Fig. 4).
(3) Install the muffler/resonator assembly. (Refer
to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/MUFFLER - INSTALLA-
TION)
(4) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks.
Repair exhaust leaks as necessary.
(5) Check the exhaust system for contact with the
body panels. Make the necessary adjustments, if
needed.
CROSS-OVER PIPE - 3.3/3.8L
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the fasteners attaching the left bank
manifold connection to cross-over pipe (Fig. 6).
(3) Raise vehicle and remove the left front wheel.(4) Access the lower right bank pipe connection
fastener through the left front wheel opening using a
long ratchet extension. Loosen and remove the lower
fastener.
(5) Remove the upper right bank pipe connection
fastener by accessing though the catalytic converter
floor pan tunnel.
(6) Lower the vehicle.
(7) Remove the cross-over pipe (Fig. 6).
(8) Remove gaskets and discard (Fig. 6).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position cross-over pipe to the manifold connec-
tions (Fig. 6).
(2) Position new gasket on left bank (front) pipe
connection and loosely install fasteners (Fig. 6).
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Position new gasket on the right bank pipe con-
nection and install fasteners.
(5) Tighten right bank upper fastener to 41 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.).
(6) Tighten right bank lower fastener to 41 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.) using a long ratchet extension accessing
through the left wheel opening.
(7) Install the left front wheel and lower vehicle.
(8) Tighten the left bank pipe connection fasteners
to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 6).
(9) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks.
Repair exhaust leaks as necessary.
(10) Check the exhaust system for contact with the
body panels. Make the necessary adjustments, if
needed.
Fig. 6 CROSS-OVER PIPE
1 - CROSS-OVER PIPE
2 - BOLT
3 - GASKET
4 - FLAG NUT
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMRS
CATALYTIC CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1344 of 2339
HEAT SHIELDS
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust system heat shields (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8),
or (Fig. 9) are attached to the under body of the vehi-
cle. On vehicles equipped with All Wheel Dive
(AWD), an additional heat shield is mounted to the
catalytic converter.
OPERATION
Heat shields are needed to protect both the vehicle
and the environment from the high temperatures
developed near the catalytic converter.Avoid application of rust prevention com-
pounds or undercoating materials to exhaust
system floor pan heat shields on cars so
equipped. Light over spray near the edges is
permitted. Application of coating will greatly
reduce the efficiency of the heat shields result-
ing in excessive floor pan temperatures and
objectionable fumes.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove fasteners attaching applicable heat
shield (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8), or (Fig. 9).
(3) Remove heat shield(s).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position heat shield(s) to underbody.
(2) Install heat shield fasteners and tighten to 2.6
N´m (23 in. lbs.) (Fig. 7), (Fig. 8), or (Fig. 9).
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks.
Repair exhaust leaks as necessary.
(5) Check the exhaust system for contact with the
body panels. Make the necessary adjustments, if
needed.
MUFFLER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on a body contact type hoist.
NOTE: To provide removal clearance between muf-
fler/resonator pipe and rear axle parts, the rear sus-
pension must be relieved of all body weight.
(2) Apply a penetrating oil to clamp nuts of com-
ponent requiring removal.
Fig. 7 CATALYTIC CONVERTER HEAT SHIELD
1 - HEAT SHIELD - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 - SCREW (QTY. 4)
Fig. 8 MUFFLER HEAT SHIELD
1 - HEAT SHIELD - MUFFLER
2 - SCREW (QTY. 6)
Fig. 9 RESONATOR PIPE HEAT SHIELD
1 - SCREW (QTY. 3)
2 - HEAT SHIELD - RESONATOR PIPE
3 - MUFFLER
RSEXHAUST SYSTEM11-7
Page 1345 of 2339
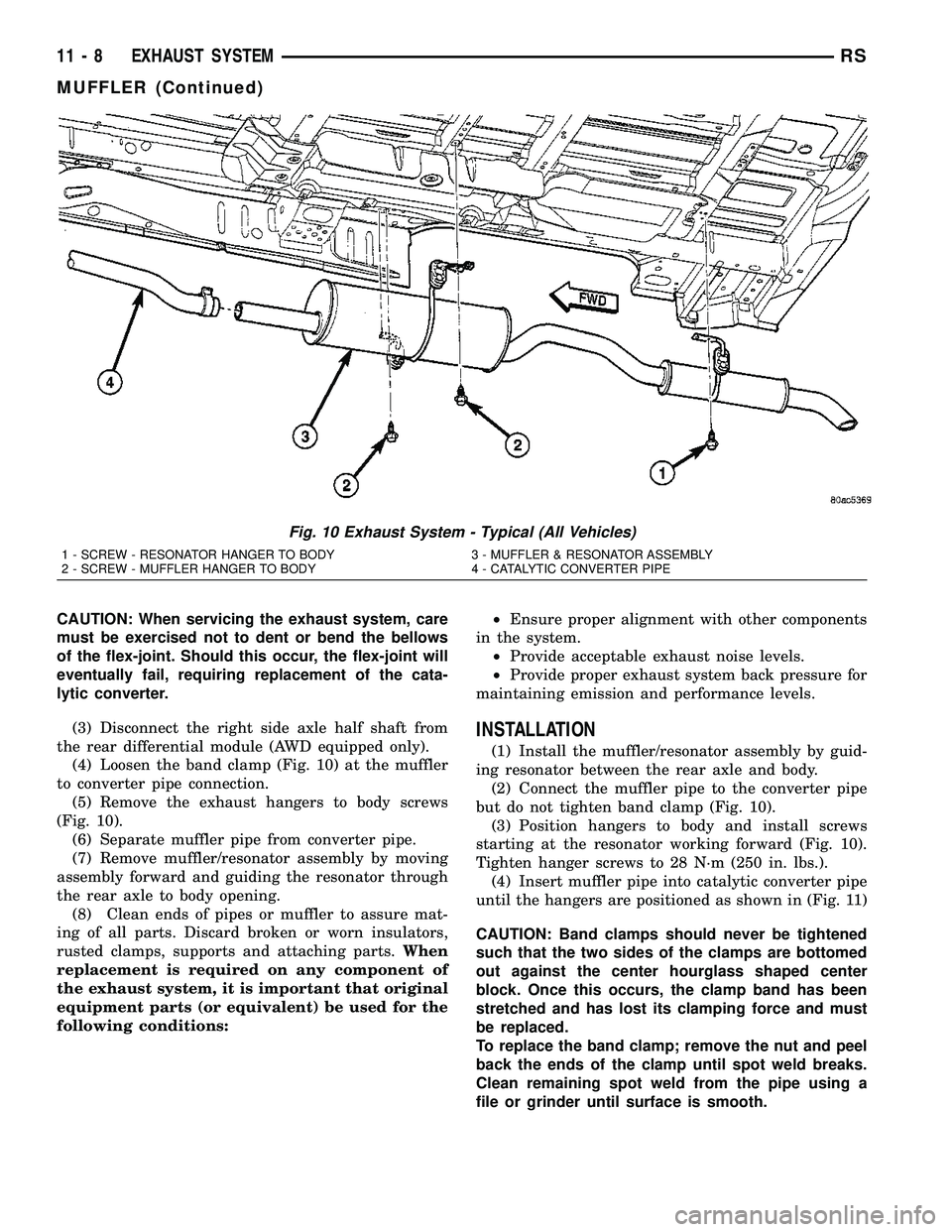
CAUTION: When servicing the exhaust system, care
must be exercised not to dent or bend the bellows
of the flex-joint. Should this occur, the flex-joint will
eventually fail, requiring replacement of the cata-
lytic converter.
(3) Disconnect the right side axle half shaft from
the rear differential module (AWD equipped only).
(4) Loosen the band clamp (Fig. 10) at the muffler
to converter pipe connection.
(5) Remove the exhaust hangers to body screws
(Fig. 10).
(6) Separate muffler pipe from converter pipe.
(7) Remove muffler/resonator assembly by moving
assembly forward and guiding the resonator through
the rear axle to body opening.
(8) Clean ends of pipes or muffler to assure mat-
ing of all parts. Discard broken or worn insulators,
rusted clamps, supports and attaching parts.When
replacement is required on any component of
the exhaust system, it is important that original
equipment parts (or equivalent) be used for the
following conditions:²Ensure proper alignment with other components
in the system.
²Provide acceptable exhaust noise levels.
²Provide proper exhaust system back pressure for
maintaining emission and performance levels.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the muffler/resonator assembly by guid-
ing resonator between the rear axle and body.
(2) Connect the muffler pipe to the converter pipe
but do not tighten band clamp (Fig. 10).
(3) Position hangers to body and install screws
starting at the resonator working forward (Fig. 10).
Tighten hanger screws to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(4) Insert muffler pipe into catalytic converter pipe
until the hangers are positioned as shown in (Fig. 11)
CAUTION: Band clamps should never be tightened
such that the two sides of the clamps are bottomed
out against the center hourglass shaped center
block. Once this occurs, the clamp band has been
stretched and has lost its clamping force and must
be replaced.
To replace the band clamp; remove the nut and peel
back the ends of the clamp until spot weld breaks.
Clean remaining spot weld from the pipe using a
file or grinder until surface is smooth.
Fig. 10 Exhaust System - Typical (All Vehicles)
1 - SCREW - RESONATOR HANGER TO BODY 3 - MUFFLER & RESONATOR ASSEMBLY
2 - SCREW - MUFFLER HANGER TO BODY 4 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER PIPE
11 - 8 EXHAUST SYSTEMRS
MUFFLER (Continued)
Page 1401 of 2339
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Install two screws and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector and vacuum
hose to the MAP sensor (Fig. 20).
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 21).
(2) Install screws and tighten toPLASTIC MAN-
IFOLD 1.7 N´m (15 in. lbs.) ALUMINUM MANI-
FOLD 3.3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
Install vacuum hose.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The upstream oxygen sensor threads into the out-
let flange of the exhaust manifold (Fig. 22) or (Fig.
23).
The downstream heated oxygen sensor threads into
the outlet pipe at the rear of the catalytic convertor
(Fig. 24).
OPERATION
A seperate upstream and downstream grounds are
used on the NGC vehicles (4 Cyl.).
As vehicles accumulate mileage, the catalytic con-
vertor deteriorates. The deterioration results in a
less efficient catalyst. To monitor catalytic convertordeterioration, the fuel injection system uses two
heated oxygen sensors. One sensor upstream of the
catalytic convertor, one downstream of the convertor.
The PCM compares the reading from the sensors to
calculate the catalytic convertor oxygen storage
capacity and converter efficiency. Also, the PCM uses
the upstream heated oxygen sensor input when
adjusting injector pulse width.
When the catalytic converter efficiency drops below
emission standards, the PCM stores a diagnostic
trouble code and illuminates the malfunction indica-
tor lamp (MIL).
The O2 sensors produce a constant 2.5 volts on
NGC vehicles, depending upon the oxygen content of
the exhaust gas. When a large amount of oxygen is
Fig. 22 O2 SENSOR UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L
Fig. 23 O2 SENSOR UPSTREAM 1/1 - 3.3/3.8L
Fig. 24 O2 SENSOR DOWNSTREAM 1/2 - 2.4/3.3/
3.8L
14 - 36 FUEL INJECTIONRS
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1403 of 2339
REMOVAL - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Remove battery, refer to the Battery section for
more information.
(2) Remove the battery tray, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(3) Disconnect the speed control vacuum harness
from servo.
(4) Disconnect the electrical connector from servo.
(5) Remove the speed control servo and bracket
and reposition.
(6) Use a socket such as the Snap-OntYA8875 or
equivalent to remove the sensor (Fig. 25).
(7) When the sensor is removed, the threads must
be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap. If using
the original sensor, coat the threads with Loctite
771±64 anti-seize compound or equivalent.
REMOVAL - DOWNSTREAM 1/2 - 2.4/3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Disconnect the electrical connector (Fig. 26).
(4) Use a socket such as the Snap-OntYA8875 or
equivalent to remove the sensor (Fig. 27).
(5) When the sensor is removed, the threads must
be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap. If using
the original sensor, coat the threads with Loctite
771±64 anti-seize compound or equivalent.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L
The engines uses two heated oxygen sensors.
(1) After removing the sensor, the exhaust mani-
fold threads must be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 +
6E tap. If reusing the original sensor, coat the sensor
threads with an anti-seize compound such as Loctite
771- 64 or equivalent. New sensors have compound
on the threads and do not require an additional coat-
ing.
Fig. 25 O2 SENSOR 1/1
Fig. 26 Downstream Oxygen Sensor (1/2)
1 - OXYGEN SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
3 - DOWNSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR
4 - ENGINE HARNESS CONNECTOR
Fig. 27 DOWNSTREAM 2/1 O2 SENSOR
14 - 38 FUEL INJECTIONRS
O2 SENSOR (Continued)