2005 CHRYSLER CARAVAN coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 1592 of 2339
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 307)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combina-
tion of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM
interprets this information and determines the
appropriate transaxle gear position and shift sched-
ule.
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 308)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
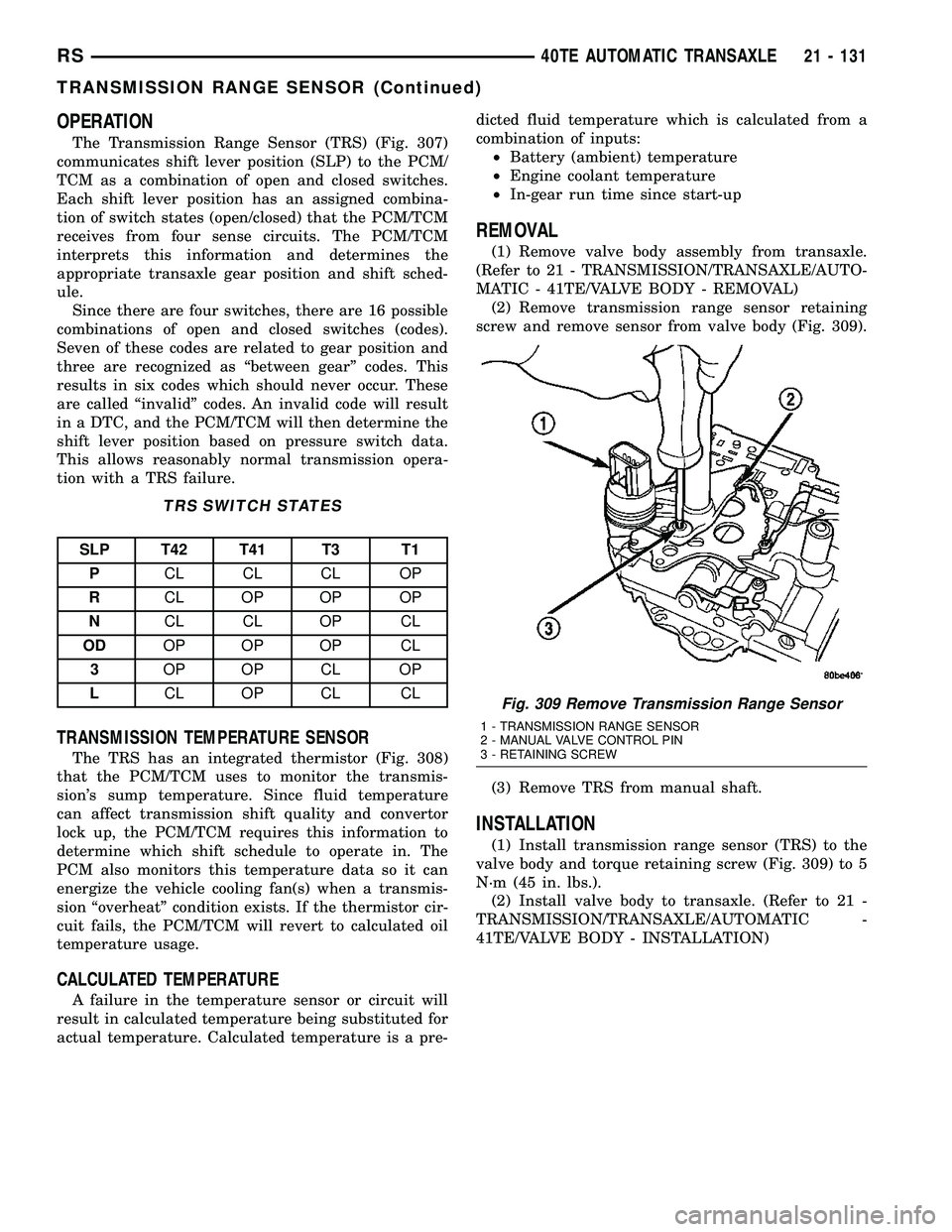
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 309).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 309) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 309 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 131
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1616 of 2339
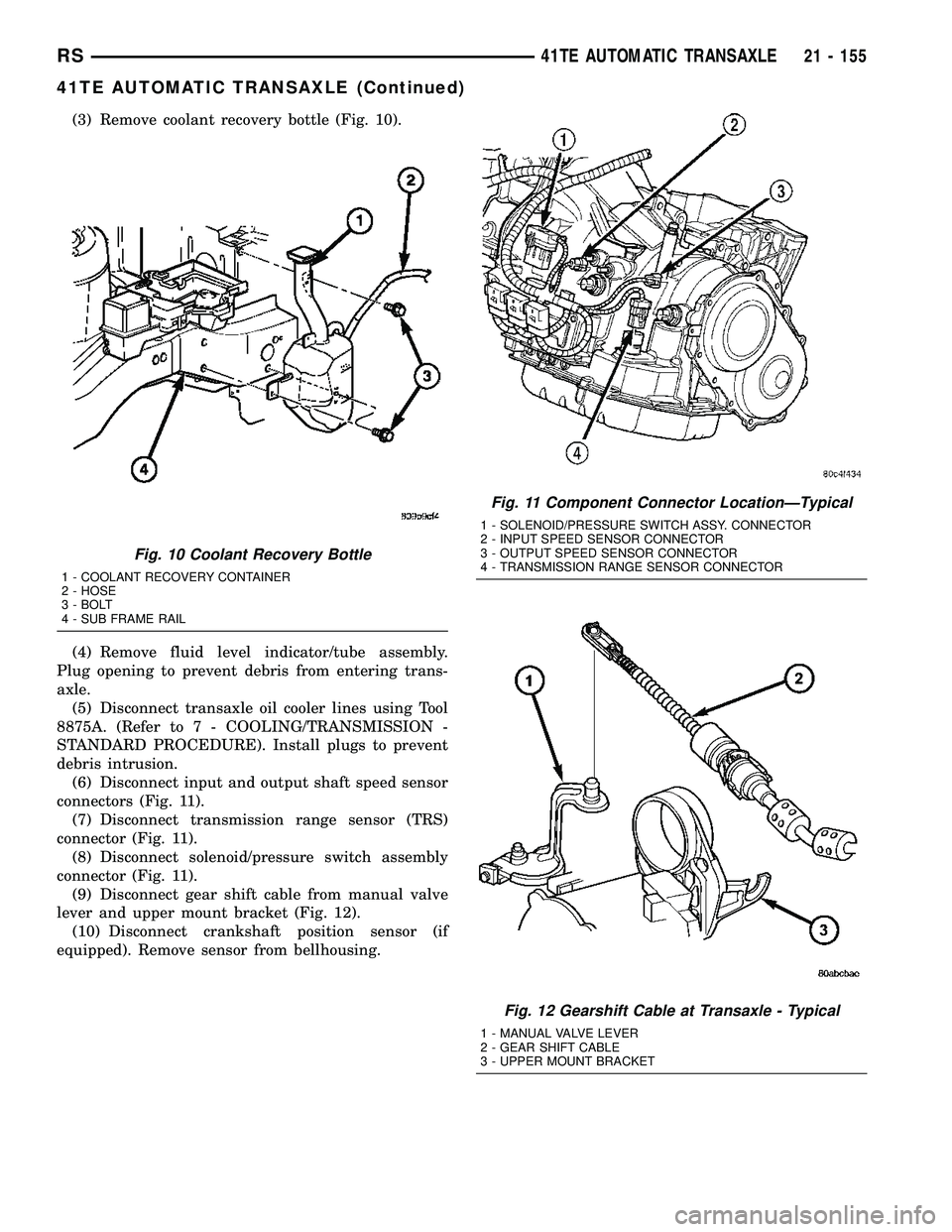
(3) Remove coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Disconnect transaxle oil cooler lines using Tool
8875A. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/TRANSMISSION -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Install plugs to prevent
debris intrusion.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 11).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 11).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 11).
(9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 12).
(10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped). Remove sensor from bellhousing.
Fig. 10 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
2 - HOSE
3 - BOLT
4 - SUB FRAME RAIL
Fig. 11 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 12 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 155
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1659 of 2339
(25) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 163). (26) Install battery shield.
(27) Connect battery cables.
(28) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 163 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
2 - HOSE
3 - BOLT
4 - SUB FRAME RAIL
21 - 198 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1741 of 2339
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
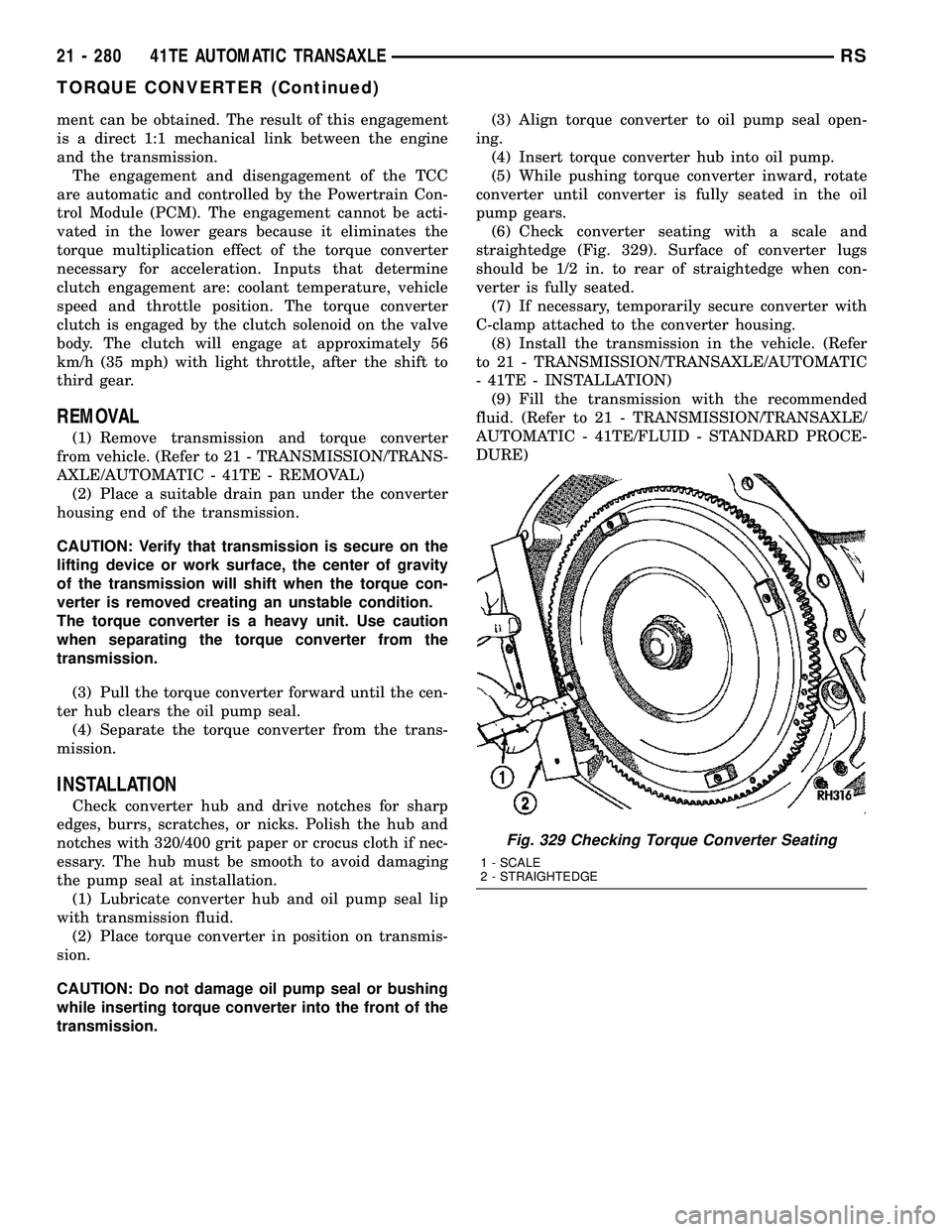
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 329). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
Fig. 329 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 280 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1743 of 2339
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 331)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combina-
tion of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM
interprets this information and determines the
appropriate transaxle gear position and shift sched-
ule.
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 332)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
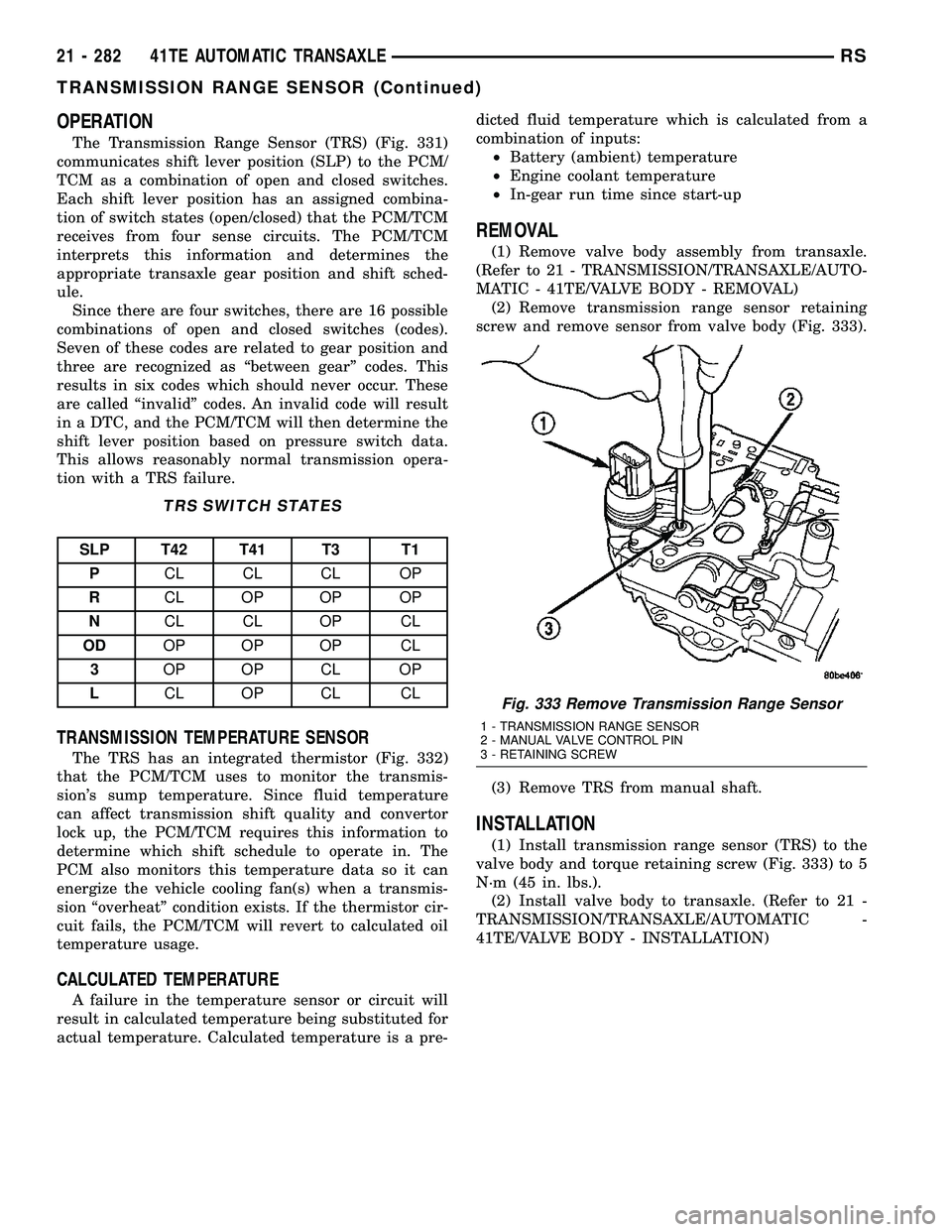
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 333).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 333) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 333 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
21 - 282 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1835 of 2339
UPPER RADIATOR
CROSSMEMBER
REMOVAL
(1) Release hood latch and open hood.
(2) Remove radiator sight shield.
(3) Remove engine air inlet resonator.
(4) Unclip hood cable from upper radiator cross-
member.
(5) Remove bolts attaching hood latch to cross-
member and position latch out of the way.
(6) Remove hood prop rod.
(7) Remove screw attaching coolant recovery bottle
to crossmember.
(8) Remove bolts attaching radiator isolators to
crossmember.
(9) Remove bolts attaching ends of crossmember to
radiator closure panel (Fig. 16).
(10) Lift crossmember upward and away from
radiator closure panel.
(11) Remove crossmember from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place radiator closure panel crossmember in
position on vehicle.
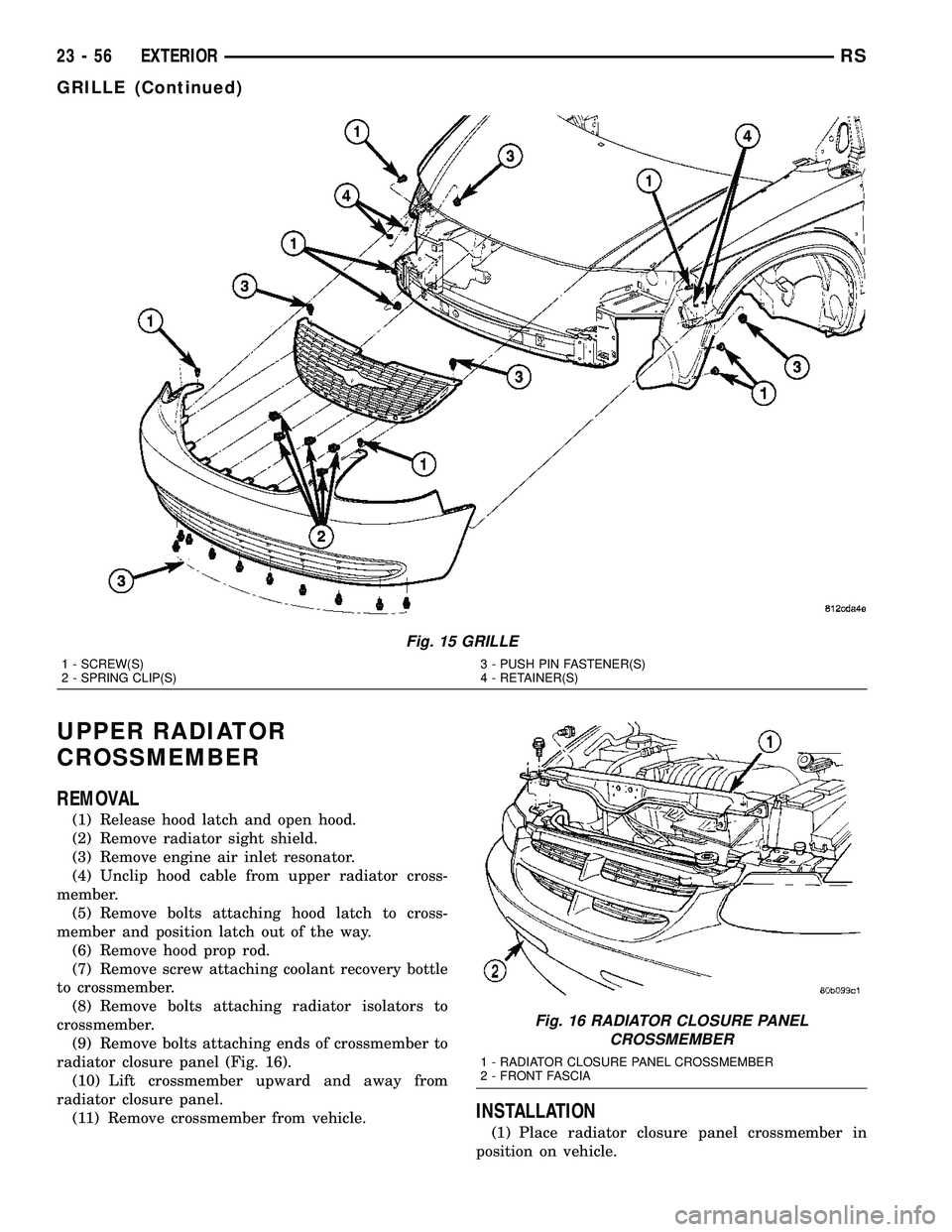
Fig. 15 GRILLE
1 - SCREW(S)
2 - SPRING CLIP(S)3 - PUSH PIN FASTENER(S)
4 - RETAINER(S)
Fig. 16 RADIATOR CLOSURE PANEL
CROSSMEMBER
1 - RADIATOR CLOSURE PANEL CROSSMEMBER
2 - FRONT FASCIA
23 - 56 EXTERIORRS
GRILLE (Continued)
Page 1836 of 2339
(2) Insert ends of crossmember between layered
metal sections of radiator closure panel at each side
of radiator.
(3) Align with paint breaks around bolt heads.
(4) Install bolts attaching ends of crossmember to
radiator closure panel (Fig. 16). Tighten bolts to 19
N´m (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install bolts attaching radiator isolators to
crossmember.
(6) Install screw attaching coolant recovery bottle
to crossmember.
(7) Install bolt attaching air cleaner housing to
crossmember.
(8) Install engine air inlet resonator.
(9) Install hood prop rod.
(10) Align hood latch by placing latch over net
pierce tabs. If alignment is required, flatten tabs.
(11) Install bolts attaching hood latch to cross-
member and clip cable. Tighten bolts to 13.5 N´m (10
ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Install radiator sight shield.
(13) Verify hood latch operation and hood align-
ment.
FRONT WHEELHOUSE
SPLASH SHIELD
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOIST-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove front wheel.
(3) Remove push pin fasteners attaching splash
shield to frame rail forward of suspension.
(4) Remove push pin fasteners attaching splash
shield to frame rail rearward of suspension.
(5) Remove screws attaching wheelhouse splash
shield to front fender and front bumper fascia.
(6) Remove splash shield from vehicle (Fig. 17).
INSTALLATION
(1) Place splash shield in position on vehicle (Fig.
17).
(2) Install push pin fasteners attaching splash
shield to frame rail forward of suspension.
(3) Install push pin fasteners attaching splash
shield to frame rail rearward of suspension.
(4) Install screws attaching wheelhouse splash
shield to front fender.
(5) Install front wheel.
(6) Lower vehicle.
LUGGAGE RACK RISER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove two fasteners from the front riser.
Gently pull up on the luggage rack side rail and
detach the riser snap to remove riser from the rail
(Fig. 18).
(2) Repeat for the opposite side, if necessary.
(3) Remove front riser(s) from vehicle (Fig. 19).
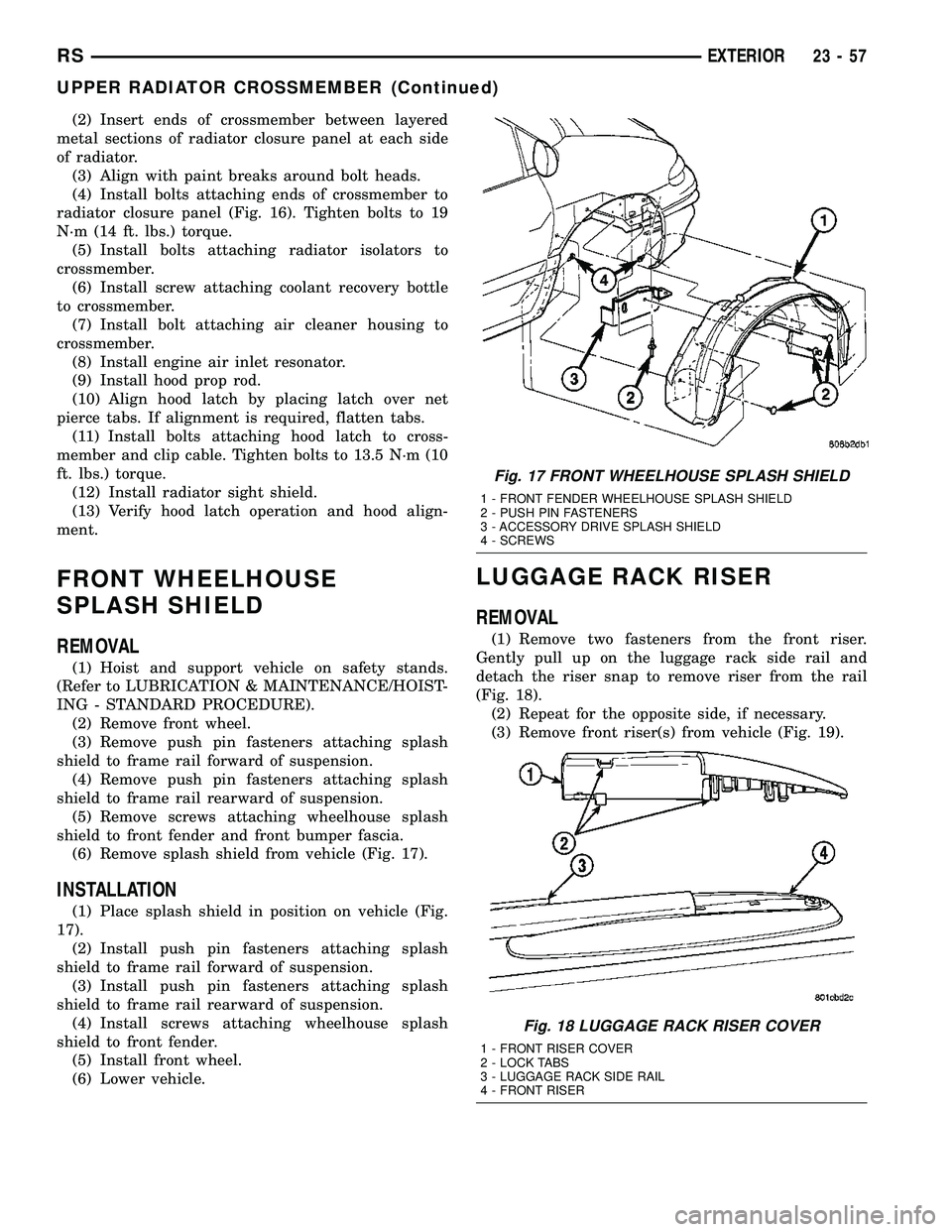
Fig. 17 FRONT WHEELHOUSE SPLASH SHIELD
1 - FRONT FENDER WHEELHOUSE SPLASH SHIELD
2 - PUSH PIN FASTENERS
3 - ACCESSORY DRIVE SPLASH SHIELD
4 - SCREWS
Fig. 18 LUGGAGE RACK RISER COVER
1 - FRONT RISER COVER
2 - LOCK TABS
3 - LUGGAGE RACK SIDE RAIL
4 - FRONT RISER
RSEXTERIOR23-57
UPPER RADIATOR CROSSMEMBER (Continued)
Page 2152 of 2339
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS.......................1
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER..........1
MANUAL SINGLE ZONE.................2
MANUAL DUAL ZONE...................2
MANUAL THREE ZONE..................2
AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL....3
OPERATION
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER..........4
MANUAL SINGLE ZONE.................4
MANUAL DUAL ZONE...................5
MANUAL THREE ZONE..................5AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL....5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/C COOL DOWN TEST.................6
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST...............7
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST..........10
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C SYSTEM.........................11
CONTROLS - FRONT.....................13
CONTROLS - REAR......................33
DISTRIBUTION - FRONT...................42
DISTRIBUTION - REAR....................56
PLUMBING - FRONT.....................64
PLUMBING - REAR......................98
CABIN HEATER........................113
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the heating,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system, the
engine cooling system must be properly maintained.
The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any
obstructions in front of the radiator or condenser will
reduce the performance of the air conditioning and
engine cooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the radiator,
thermostat, radiator hoses and the engine coolant
pump. Refer to Cooling for more information before
opening or attempting any service to the engine cool-
ing system.
HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
A manually controlled single zone type heating-air
conditioning system, manually controlled dual zone
type heating-air conditioning system, manually con-
trolled three zone type heating-air conditioning sys-
tem or an automatic controlled three zone type
heating-air conditioning system is available on this
model.
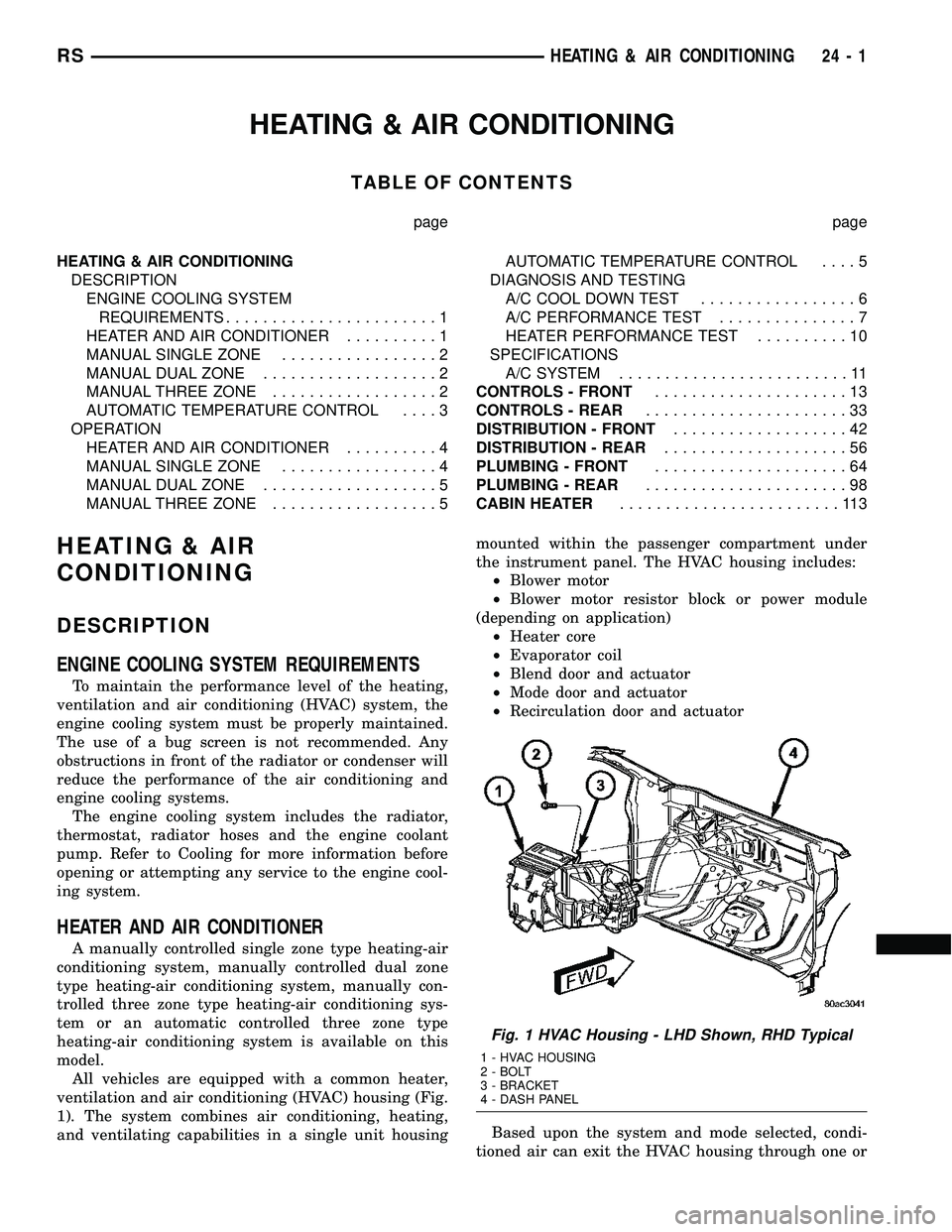
All vehicles are equipped with a common heater,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) housing (Fig.
1). The system combines air conditioning, heating,
and ventilating capabilities in a single unit housingmounted within the passenger compartment under
the instrument panel. The HVAC housing includes:
²Blower motor
²Blower motor resistor block or power module
(depending on application)
²Heater core
²Evaporator coil
²Blend door and actuator
²Mode door and actuator
²Recirculation door and actuator
Based upon the system and mode selected, condi-
tioned air can exit the HVAC housing through one or
Fig. 1 HVAC Housing - LHD Shown, RHD Typical
1 - HVAC HOUSING
2 - BOLT
3 - BRACKET
4 - DASH PANEL
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-1