2004 FORD E SERIES tires
[x] Cancel search: tiresPage 2 of 240

Seating and Safety Restraints 73
Seating 73
Safety restraints 79
Air bags 89
Child restraints 93
Driving 108
Starting 108
Brakes 111
Transmission operation 115
Vehicle loading 120
Trailer towing 123
Recreational towing 131
Roadside Emergencies 132
Getting roadside assistance 132
Hazard flasher switch 133
Fuel pump shut-off switch 133
Fuses and relays 135
Changing tires 143
Jump starting 151
Wrecker towing 156
Customer Assistance 157
Reporting safety defects (U.S. only) 165
Cleaning 166
Underbody preservation 170
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Table of Contents
2
Page 105 of 240

3. Clip the tether strap hook to the
tether bracket mounted under rear
rail of seat cushion frame.
4. Install the child safety seat tightly using the LATCH anchors or safety
belts. Follow the instructions in this chapter.
5. Tighten the child safety seat tether strap according to the
manufacturer’s instructions.
For additional important safety information on the proper use of seat
belts, child seats and infant seats, please read the entireSeating and
Safety Restraintschapter in this Owner’s Guide.
Attaching safety seats with LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for
Children) attachments for child seat anchors
Some child safety seats have two rigid or webbing mounted attachments
that connect to two anchors at certain seating positions in your vehicle.
This type of child seat eliminates the need to use seat belts to attach the
child seat. For forward-facing child seats, the tether strap must also be
attached to the proper tether anchor. SeeAttaching safety seats with
tether strapsin this chapter.
Your vehicle may be equipped with LATCH anchors for child seat
installation at the seating positions marked with the child seat symbol:
•Five passenger crew van
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
105
Page 114 of 240

In a rollover crash, an unbelted person is significantly more likely
to die than a person wearing a safety belt.
Your vehicle has larger tires and increased ground clearance, giving the
vehicle a higher center of gravity than a passenger car.
Vehicles with a higher center of gravity such as utility and
four-wheel drive vehicles handle differently than vehicles with a
lower center of gravity. Utility and four-wheel drive vehicles arenot
designed for cornering at speeds as high as passenger cars any more than
low-slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under off-road
conditions. Avoid sharp turns, excessive speed and abrupt maneuvers in
these vehicles. Failure to drive cautiously could result in an increased risk
of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death.
Loaded vehicles, with a higher center of gravity, may handle
differently than unloaded vehicles. Extra precautions, such as
slower speeds and increased stopping distance, should be taken when
driving a heavily loaded vehicle.
VEHICLE STABILITY AND HANDLING
The risk of a rollover crash increases as the number of people and load in
the vehicle increase. This increased risk occurs because the passenger
weight and load raises the vehicle’s center of gravity and causes it to shift
rearward. As a result, the van has less resistance to rollover and handles
differently from other commonly driven passenger vehicles, making it more
difficult to control in an emergency situation. Placing any load on the roof
also raises the center of gravity and increases the potential for rollover.
The van should be operated by an experienced driver. An organization that
owns a 15–passenger van should select one or two experienced drivers to
drive the van on a regular basis. These drivers will gain valuable experience
handling the van. This experience will help make each trip safer.
The van should be operated at a safe speed which, in some conditions,
may be less than the posted speed limit.
Further, all occupants should be properly restrained. Most people killed
in rollover crashes were unbelted. Occupants can dramatically reduce
their risk of being killed or seriously injured in a rollover crash by simply
using their seat belts. Organizations that own 15–passenger vans should
have a written seat belt use policy. Drivers should be responsible for
enforcing the policy.
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Driving
114
Page 119 of 240

If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow, it may be rocked out by
shifting from forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts in a
steady pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating
temperature or damage to the transmission may occur.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a minute or damage to the
transmission and tires may occur, or the engine may overheat.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly especially if the depth is not known. Never drive through water
that is higher than the bottom of the hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of
the wheel rims (for cars). Traction or brake capability may be limited
and your vehicle may stall. Water may also enter your engine’s air intake
and severely damage your engine.
Once through the water, always dry the brakes by moving your vehicle
slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Wet brakes do
not stop the vehicle as quickly as dry brakes.Driving through deep
water where the transmission vent tube is submerged may allow
water into the transmission and cause internal transmission
damage.
EMERGENCY MANEUVERS
•In an unavoidable emergency situation where a sudden sharp turn
must be made, remember to avoid“over-driving”your vehicle, i.e.,
turn the steering wheel only as rapidly and as far as required to avoid
the emergency. Excessive steering will result in less vehicle control,
not more. Additionally, smooth variations of the accelerator and/or
brake pedal pressure should be utilized if changes in vehicle speed are
called for. Avoid abrupt steering, acceleration or braking which could
result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover
and/or personal injury. Use all available road surface to return the
vehicle to a safe direction of travel.
•In the event of an emergency stop, avoid skidding the tires and do not
attempt any sharp steering wheel movements.
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Driving
119
Page 123 of 240

Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities
than the originals because they may lower the vehicle’s GVWR
and GAWR limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the
originals do not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
Exceeding any vehicle weight rating limitation could result in
serious damage to the vehicle and/or personal injury.
Special loading instructions for owners of pickup trucks and
utility-type vehicles
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, see thePreparing to drive your vehiclesection in
this chapter.
Loaded vehicles may handle differently than unloaded vehicles.
Extra precautions, such as slower speeds and increased stopping
distance, should be taken when driving a heavily loaded vehicle.
Your vehicle can haul more cargo and people than most passenger cars.
Depending upon the type and placement of the load, hauling cargo and
people may raise the center of gravity of the vehicle.
Calculating the load your vehicle can carry/tow
1. Use the appropriate maximum GCWR chart (in theTrailer Towing
section in this chapter) for your type of engine and rear axle ratio.
2. Weigh your vehicle without cargo. To obtain correct weights, take your
vehicle to a shipping company or an inspection station for trucks.
3. Subtract your loaded weight from the maximum GCWR in the chart.
This is the maximum trailer weight your vehicle can tow. It must be
below the maximum trailer weight shown in the chart.
TRAILER TOWING
Your vehicle may tow a class I, II or III trailer, provided the maximum
trailer weight is less than or equal to the maximum trailer weight listed
for your engine and rear axle ratio on the following charts.
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Driving
123
Page 128 of 240
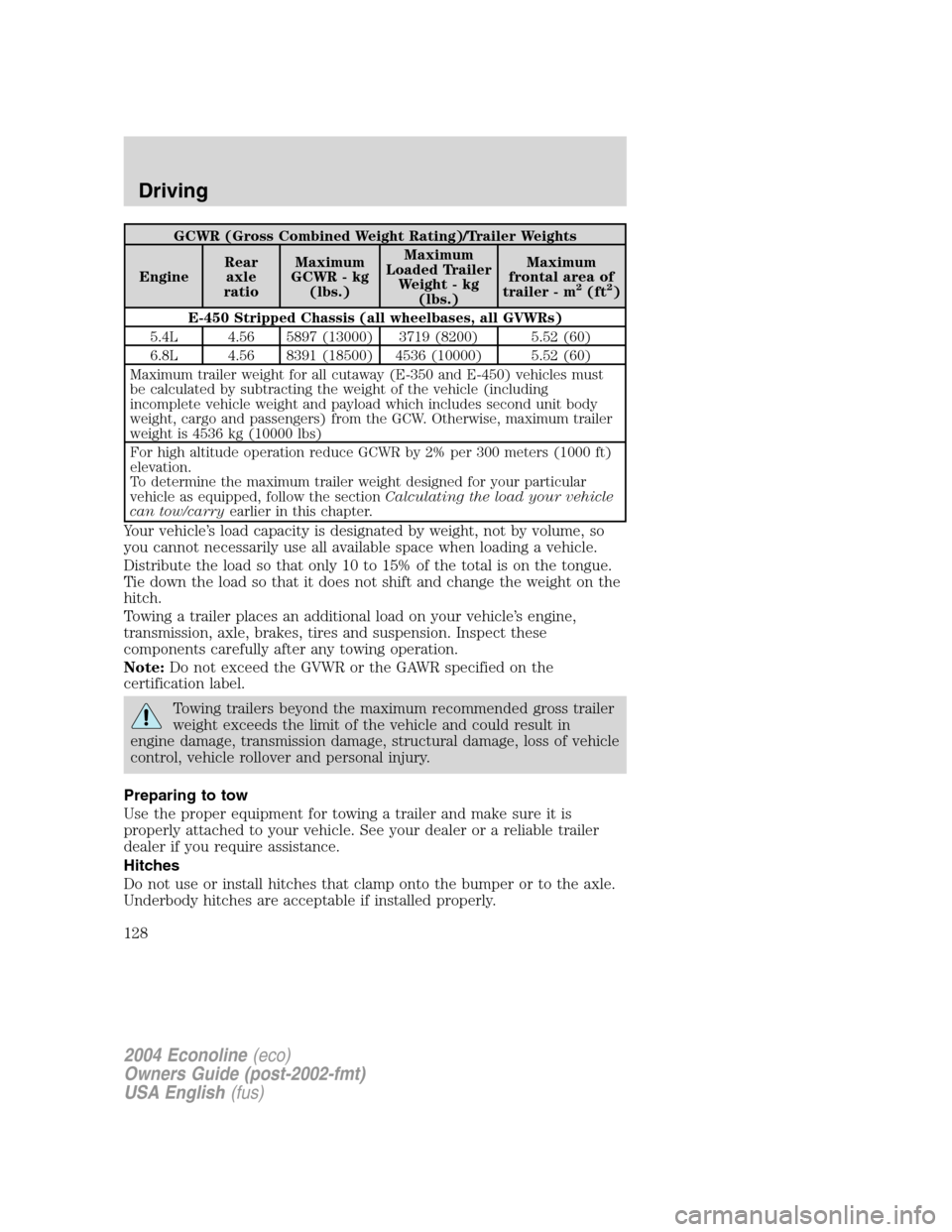
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer Weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
Loaded Trailer
Weight - kg
(lbs.)Maximum
frontal area of
trailer - m
2(ft2)
E-450 Stripped Chassis (all wheelbases, all GVWRs)
5.4L 4.56 5897 (13000) 3719 (8200) 5.52 (60)
6.8L 4.56 8391 (18500) 4536 (10000) 5.52 (60)
Maximum trailer weight for all cutaway (E-350 and E-450) vehicles must
be calculated by subtracting the weight of the vehicle (including
incomplete vehicle weight and payload which includes second unit body
weight, cargo and passengers) from the GCW. Otherwise, maximum trailer
weight is 4536 kg (10000 lbs)
For high altitude operation reduce GCWR by 2% per 300 meters (1000 ft)
elevation.
To determine the maximum trailer weight designed for your particular
vehicle as equipped, follow the sectionCalculating the load your vehicle
can tow/carryearlier in this chapter.
Your vehicle’s load capacity is designated by weight, not by volume, so
you cannot necessarily use all available space when loading a vehicle.
Distribute the load so that only 10 to 15% of the total is on the tongue.
Tie down the load so that it does not shift and change the weight on the
hitch.
Towing a trailer places an additional load on your vehicle’s engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires and suspension. Inspect these
components carefully after any towing operation.
Note:Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer
weight exceeds the limit of the vehicle and could result in
engine damage, transmission damage, structural damage, loss of vehicle
control, vehicle rollover and personal injury.
Preparing to tow
Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer and make sure it is
properly attached to your vehicle. See your dealer or a reliable trailer
dealer if you require assistance.
Hitches
Do not use or install hitches that clamp onto the bumper or to the axle.
Underbody hitches are acceptable if installed properly.
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Driving
128
Page 143 of 240

•Diesel engine: passenger side of the engine compartment behind the
power distribution box.
Have a certified technician or your dealer service this module, if
required.
The relays are coded as follows:
Relay location Description
1 Trailer tow left turn
2 A/C control
3 PCM back-up lamp
4 Trailer tow right turn
CHANGING A FLAT TIRE
If you get a flat tire while driving:
•do not brake heavily.
•gradually decrease the vehicle’s speed.
•hold the steering wheel firmly.
•slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
The use of tire sealants may damage your tires.
Spare tire information
The spare tire for your vehicle is stowed under the rear of your vehicle
(except cutaway and stripped chassis models or if equipped on E-350
Chassis Cab vehicles).
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
143
Page 196 of 240

•Warming up a vehicle on cold mornings is not required and may
reduce fuel economy.
•Resting your foot on the brake pedal while driving may reduce fuel
economy.
•Combine errands and minimize stop-and-go driving.
Maintenance
•Keep tires properly inflated and use only recommended size.
•Operating a vehicle with the wheels out of alignment will reduce fuel
economy.
•Use recommended engine oil. Refer toLubricant specificationsin
this chapter.
•Perform all regularly scheduled maintenance items. Follow the
recommended maintenance schedule and owner maintenance checks
found in your vehicle scheduled maintenance guide.
Conditions
•Heavily loading a vehicle or towing a trailer may reduce fuel economy
at any speed.
•Carrying unnecessary weight may reduce fuel economy (approximately
0.4 km/L [1 mpg] is lost for every 180 kg [400 lb] of weight carried).
•Adding certain accessories to your vehicle (for example bug
deflectors, rollbars/light bars, running boards, ski/luggage racks) may
reduce fuel economy.
•Using fuel blended with alcohol may lower fuel economy.
•Fuel economy may decrease with lower temperatures during the first
12–16 km (8–10 miles) of driving.
•Driving on flat terrain offers improved fuel economy as compared to
driving on hilly terrain.
•Transmissions give their best fuel economy when operated in the top
cruise gear and with steady pressure on the gas pedal.
•Close windows for high speed driving.
EPA window sticker
Every new vehicle should have the EPA window sticker. Contact your
dealer if the window sticker is not supplied with your vehicle. The EPA
window sticker should be your guide for the fuel economy comparisons
with other vehicles.
2004 Econoline(eco)
Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt)
USA English(fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
196