2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 903 of 2643

2A – 2ISUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Abnormal or Excessive Tire Wear
ChecksAction
Check the front–wheel and the rear–wheel alignment.Align the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for excessive toe on the front and the rear wheels.Adjust the toe on the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Inspect for out–of–balance tires.Balance the tires.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Check for a failure to rotate tires.Rotate the tires. Replace the tires as needed.
Check for an overloaded vehicle.Maintain the proper load weight.
Inspect for low tire inflation.Inflate the tires to the proper pressure.
Scuffed Tires
ChecksAction
Inspect for incorrect toe on the front and the rear wheels.Adjust the toe on the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for a twisted or a bent suspension arm.Replace the suspension arm.
Wheel Tramp
ChecksAction
Inspect for an out–of–balance tire or wheel.Balance the tire or the wheel.
Inspect for improper strut dampener action.Replace the strut dampeners.
Shimmy, Shake, or Vibration
ChecksAction
Inspect for an out–of–balance tire or wheel.Balance the tire or the wheel.
Inspect for excessive wheel hub runout.Measure the hub flange runout. Replace the hub as need-
ed.
Inspect for excessive brake drum or brake rotor imbal-
ance.Adjust the brakes. Replace the brake rotor or the brake
drum as needed.
Inspect for worn tie rod ends.Replace the outer tie rods.
Inspect for wheel trim imbalance.Balance the wheel.
Inspect for a worn lower ball joint.Replace the lower ball joint.
Inspect for excessive wheel runout.Measure the wheel runout. Replace the wheel as needed.
Inspect for excessive loaded radial runout on the tire and
wheel assembly.Match–mount the tire and wheel assembly.
Hard Steering
ChecksAction
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
Check the hydraulic system. Test the power steering sys-
tem pressure with a gauge.Replace the seals and the hoses as needed.
Inspect for binding or catching in the steering gear.Lubricate the steering gear. Repair or replace the steering
gear as needed.
Inspect for a loose steering gear mounting.Tighten the steering gear mounting bracket nuts.
Page 904 of 2643

SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS 2A – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Too Much Play in Steering
ChecksAction
Inspect for worn or loose wheel bearings.Tighten the drive axle nut. Replace the wheel bearings as
needed.
Inspect for a loose steering gear mounting.Tighten the steering gear mounting bracket nuts.
Inspect the joint from the column to the steering gear for
loose connections or wear.Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace the in-
termediate shaft as needed.
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
Poor Returnability
ChecksAction
Inspect for lack of lubrication of the ball joints and the tie
rod ends.Replace the ball joints and the outer tie rods.
Inspect for binding in the ball joints.Replace the ball joint.
Inspect for binding in the steering column.Lubricate the steering column. Replace the steering col-
umn as needed.
Check the front–wheel alignment.Align the front wheels.
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
Inspect for a sticking valve.Lubricate the pinion valve assembly. Replace the pinion
valve assembly as needed.
Inspect for binding in the intermediate shaft on the steering
gear.Replace the intermediate shaft.
Abnormal Noise, Front Suspension
ChecksAction
Inspect for a lack of lubrication of the ball joints and the tie
rod ends.Replace the ball joints and the outer tie rods.
Inspect for damaged suspension components.Replace the damaged suspension components.
Inspect for worn control arm bushings or tie rod ends.Replace the control arm bushings or the tie rods.
Inspect for a loose stabilizer shaft link.Tighten the stabilizer shaft link.
Inspect for loose wheel bolts.Tighten the wheel bolts.
Inspect for loose suspension bolts or nuts.Tighten the suspension bolts or the nuts.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners or strut mountings.Replace the strut dampeners. Tighten the strut mounting
bolts.
Inspect for an improperly positioned strut spring.Adjust the strut spring to the proper position.
Wander or Poor Steering Ability
ChecksAction
Inspect for mismatched or uneven tires.Replace the tires.
Inspect for lack of lubrication of the ball joints and the tie
rod ends.Replace the ball joints and the outer tie rods.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Inspect for a loose stabilizer shaft link.Tighten the stabilizer shaft link.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Page 905 of 2643
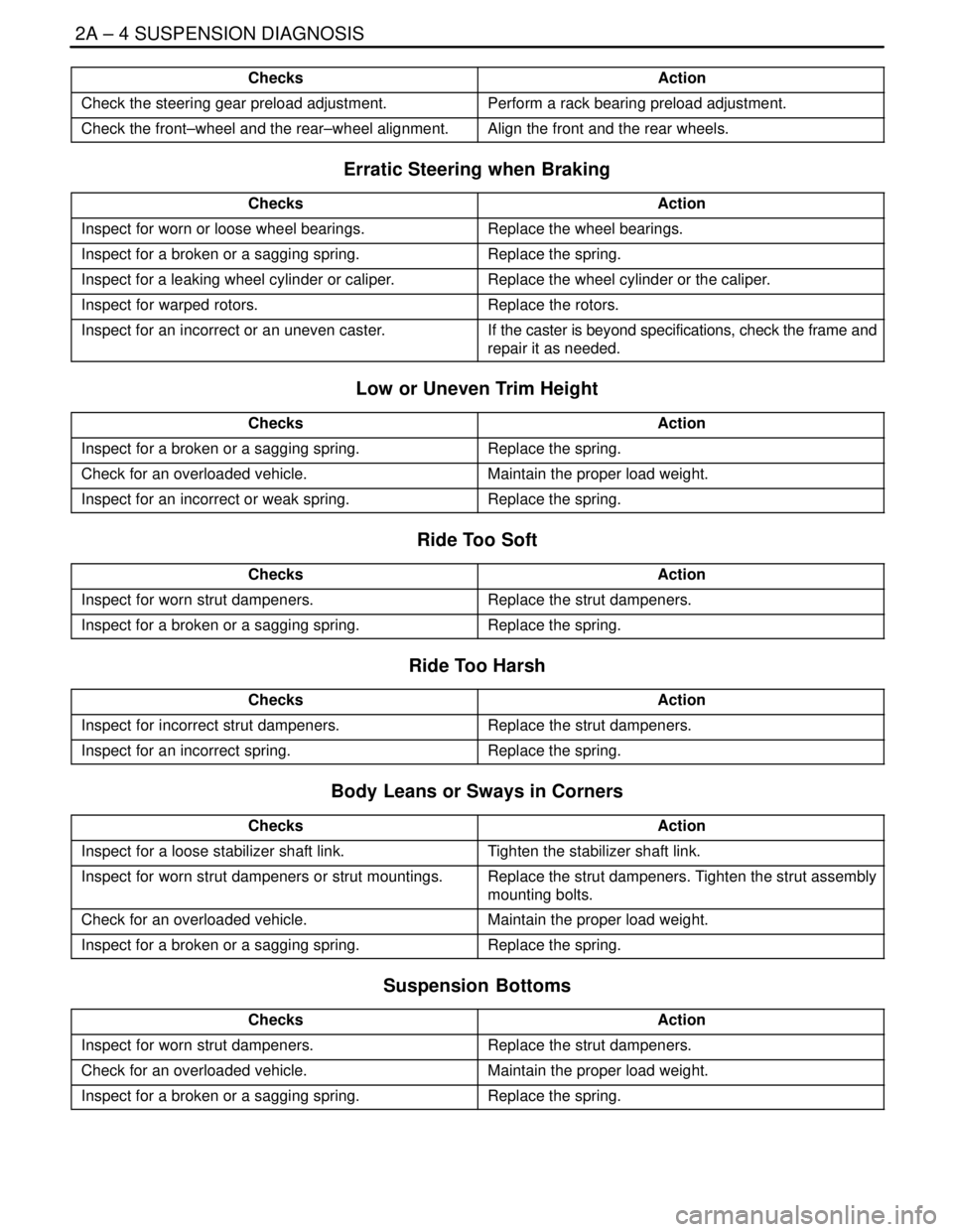
2A – 4ISUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Checks Action
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
Check the front–wheel and the rear–wheel alignment.Align the front and the rear wheels.
Erratic Steering when Braking
ChecksAction
Inspect for worn or loose wheel bearings.Replace the wheel bearings.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Inspect for a leaking wheel cylinder or caliper.Replace the wheel cylinder or the caliper.
Inspect for warped rotors.Replace the rotors.
Inspect for an incorrect or an uneven caster.If the caster is beyond specifications, check the frame and
repair it as needed.
Low or Uneven Trim Height
ChecksAction
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Check for an overloaded vehicle.Maintain the proper load weight.
Inspect for an incorrect or weak spring.Replace the spring.
Ride Too Soft
ChecksAction
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Ride Too Harsh
ChecksAction
Inspect for incorrect strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Inspect for an incorrect spring.Replace the spring.
Body Leans or Sways in Corners
ChecksAction
Inspect for a loose stabilizer shaft link.Tighten the stabilizer shaft link.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners or strut mountings.Replace the strut dampeners. Tighten the strut assembly
mounting bolts.
Check for an overloaded vehicle.Maintain the proper load weight.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Suspension Bottoms
ChecksAction
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Check for an overloaded vehicle.Maintain the proper load weight.
Inspect for a broken or a sagging spring.Replace the spring.
Page 906 of 2643

SUSPENSION DIAGNOSIS 2A – 5
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Steering Wheel Kickback
ChecksAction
Inspect for air in the power steering system.Purge the power steering system of air.
Inspect for a loose steering gear mounting.Tighten the steering gear mounting bracket nuts.
Inspect the joint from the column to the steering gear for
loose connections or wear.Tighten the intermediate shaft pinch bolts. Replace the in-
termediate shaft as needed.
Inspect for loose tie rod ends.Tighten the tie rod ends. Replace the outer tie rods as
needed.
Inspect for loose or worn wheel bearings.Tighten the drive axle nut. Replace the wheel bearings as
needed.
Steering Wheel Surges or Jerks
ChecksAction
Check the hydraulic system. Test the power steering sys-
tem pressure with a gauge.Replace the seals and the hoses as needed.
Inspect for a sluggish steering gear valve.Clean the pinion valve assembly. Replace the pinion valve
assembly as needed.
Inspect for a loose power steering pump serpentine belt.Adjust the power steering pump serpentine belt.
Cupped Tires
ChecksAction
Check the front–wheel and the rear–wheel alignment.Align the front and the rear wheels.
Inspect for worn strut dampeners.Replace the strut dampeners.
Inspect for worn or loose wheel bearings.Tighten the drive axle nut. Replace the wheel bearings as
needed.
Inspect for excessive tire or wheel runout.Match–mount the tires. Replace the tires as needed. Re-
place the wheels as needed.
Inspect for a worn ball joint.Replace the ball joint.
Check the steering gear preload adjustment.Perform a rack bearing preload adjustment.
TORQUE STEER
A degree of torque steer to the right may be experienced
during the use of heavy throttle on some front–wheel drive
cars with drive axles of unequal length. This torque steer
to the right results from the right drive axle being longer
than the left drive axle, which creates a difference in the
drive axle angle. Cars with intermediate shaft assemblies
have axles of almost equal length.
A difference in the drive axle lengths results in more torque
toe–in in the left front wheel. You will notice the torque toe–
in when the vehicle accelerates from a standing start or at
lower speeds.
Inspection Procedure
1. Place a small piece of tape at the top center of the
steering wheel.2. Note the inches of steering wheel deflection re-
quired to keep the vehicle straight during heavy ac-
celeration.
3. Compare this finding with similar cars.
Factors that may cause torque steer to be more apparent
on a particular vehicle include:
S Variations in the tire and wheel assemblies. This
has the most significant effect on torque steer. A
slightly smaller diameter on the right front tire will
increase a right torque lead.
S Large differences in the right and the left front tire
pressure.
S Looseness in the control arm bushings, the tie rod
assemblies, or the steering gear mounting. This
looseness permits a front wheel to pull forward and
toe–in under a torque greater than the wheel on the
opposite side. A loose suspension component may
result in an opposite lead upon deceleration.
Page 908 of 2643

SECTION : 2B
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS2B–1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wheel Alignment Specifications 2B–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 2B–1. . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSIS2B–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Tire Diagnosis 2B–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Radial Tire Lead/Pull 2B–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vibration Diagnosis 2B–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Preliminary Inspection 2B–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Toe Adjustment 2B–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Front Camber and Caster Check 2B–8. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Rear Camber Check 2B–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Rear Toe Adjustment 2B–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION2B–10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Four Wheel Alignment 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Toe 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Caster 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camber 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Steering Axis Inclination 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Included Angle 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Scrub Radius 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Setback 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Turning Angle 2B–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationFrontRear
Camber–0°20’ ± 45’–1°00’ ± 45’
Caster4°00’ ± 45’–
Toe–in (No person, full tank)0°00 ± 10’0°12’ ± 10’
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Rear Parallel Link–to–Crossmember Nut9066–
Page 910 of 2643

WHEEL ALIGNMENT 2B – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Install original tires one at a time to find the offend-
ing tire.
RADIAL TIRE LEAD/PULL
Lead/pull is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight pathon a level road with no pressure on the steering wheel.
Lead is usually caused by:
S Incorrect alignment.
S Uneven brake adjustment.
S Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead/pull in the
vehicle. Off–center belts on radial tires can cause the tire
to develop a side force while the vehicle rolls straight down
the road. If one side of the tire has even a little larger diam-
eter than the diameter of the other side, the tire will tend
to roll to one side. Unequal diameters will cause the tire to
develop a side force which can produce vehicle lead/pull.
The radial lead/pull diagnosis chart should be used to de-
termine whether the problem originates from an alignment
problem or from the tires. Part of the lead diagnosis proce-
dure calls for tire rotation that is different from the proper
tire rotation pattern. If a medium– to high–mileage tire is
moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to check for
ride roughness. Rear tires will not cause lead/pull.
Page 915 of 2643

2B – 8IWHEEL ALIGNMENT
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
PRELIMINARY INSPECTION
ChecksAction
Check the tires for proper inflation pressures and normal
tread wear.Inflate the tires to the proper tire pressure. Replace the
tires as needed.
Check the wheel bearings for looseness.Tighten the axle nut to the proper specification. Replace
the strut wheel bearing as needed.
Check for loose ball joints and tie rod ends.Tighten the ball joints and the tie rods.
Check the runout of the wheels and the tires.Measure and correct the tire runout.
Check the vehicle trim heights.Correct the trim heights. Make the correction before ad-
justing the toe.
Check for loose rack and pinion mounting.Tighten the mounting brackets for the rack and pinion as-
sembly.
Check for improperly operating struts.Replace the strut assembly.
Check for loose control arms.Tighten the control arm attachment bolts. Replace the con-
trol arm bushings as needed.
FRONT TOE ADJUSTMENT
1. Disconnect the outer tie rods from the knuckle as-
semblies. Refer to Section 6C, Power Steering
Gear.
2. Turn the right and the left outer tie rods and the ad-
juster nuts to align the toe to 0.0 ± 0.10 degree.
3. Reconnect the outer tie rods to the knuckle assem-
blies. Refer to Section 6C, Power Steering Gear.
Notice : In this adjustment, the right and the left tie rods
must be equal in length, or the tires will wear unevenly.FRONT CAMBER AND CASTER
CHECK
The front camber and caster are not adjustable. Refer to
”Wheel Alignment Specifications” in this section. Jounce
the bumper three times before measuring the camber or
the caster in order to prevent an incorrect reading. If the
front camber or caster measurements deviate from the
specifications, locate and replace or repair any damaged,
loose, bent, dented, or worn suspension part. If the prob-
lem is body related, repair the body.
REAR CAMBER CHECK
The rear camber is not adjustable. Refer to ”Wheel Align-
ment Specifications” in this section. If the rear camber
deviates from the specification, locate the cause and cor-
rect it. If damaged, loose, bent, dented, or worn suspen-
sion parts are found, they should be repaired or replaced.
If the problem is body related, repair the body.
Page 917 of 2643

2B – 10IWHEEL ALIGNMENT
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
FOUR WHEEL ALIGNMENT
The first responsibility of engineering is to design safe
steering and suspension systems. Each component must
be strong enough to withstand and absorb extreme pun-
ishment. Both the steering system and the front and the
rear suspension must function geometrically with the body
mass.
The steering and the suspension systems require that the
front wheels self–return and that the tire rolling effort and
the road friction be held to a negligible force in order to al-
low the customer to direct the vehicle with the least effort
and the most comfort.
A complete wheel alignment check should include mea-
surements of the rear toe and camber.
Four–wheel alignment assures that all four wheels will be
running in precisely the same direction.
When the vehicle is geometrically aligned, fuel economy
and tire life are at their peak, and steering and perfor-
mance are maximized.
TOE
Toe–in is the turning in of the tires, while toe–out is the
turning out of the tires from the geometric centerline or
thrust line. The toe ensures parallel rolling of the wheels.
The toe serves to offset the small deflections of the wheel
support system which occur when the vehicle is rolling for-
ward. The specified toe angle is the setting which achieves
0 degrees of toe when the vehicle is moving.
Incorrect toe–in or toe–out will cause tire wear and re-
duced fuel economy. As the individual steering and sus-
pension components wear from vehicle mileage, addition-
al toe will be needed to compensate for the wear.
Always correct the toe dimension last.
CASTER
Caster is the tilting of the uppermost point of the steering
axis either forward or backward from the vertical when
viewed from the side of the vehicle. A backward tilt is posi-
tive, and a forward tilt is negative. Caster influences direc-
tional control of the steering but does not affect tire wear.
Weak springs or overloading a vehicle will affect caster.
One wheel with more positive caster will pull toward the
center of the car. This condition will cause the car to move
or lean toward the side with the least amount of positive
caster. Caster is measured in degrees and is not adjust-
able.
CAMBER
Camber is the tilting of the top of the tire from the vertical
when viewed from the front of the vehicle. When the tires
tilt outward, the camber is positive. When the tires tilt in-
ward, the camber is negative. The camber angle is mea-
sured in degrees from the vertical. Camber influences
both directional control and tire wear.
If the vehicle has too much positive camber, the outside
shoulder of the tire will wear. If the vehicle has too much
negative camber, the inside shoulder of the tire will wear.
Camber is not adjustable.
STEERING AXIS INCLINATION
Steering Axis Inclination (SAI) is the tilt at the top of the
steering knuckle from the vertical. Measure the SAI angle
from the true vertical to a line through the center of the strut
and the lower ball joint as viewed from the front of the ve-
hicle.
SAI helps the vehicle track straight down the road and as-
sists the wheel back into the straight ahead position. SAI
on front wheel drive vehicles should be negative.
INCLUDED ANGLE
The included angle is the angle measured from the cam-
ber angle to the line through the center of the strut and the
lower ball joint as viewed from the front of the vehicle.
The included angle is calculated in degrees. Most align-
ment racks will not measure the included angle directly. To
determine the included angle, subtract the negative or add
the positive camber readings to the Steering Axis Inclina-
tion (SAI).
SCRUB RADIUS
The scrub radius is the distance between true vertical and
the line through the center of the strut and lower ball joint
to the road surface. Scrub radius is built into the design of
the vehicle. Scrub radius is not adjustable.
SETBACK
The setback is the distance in which one front hub and
bearing assembly may be rearward of the other front hub
and bearing assembly. Setback is primarily caused by a
road hazard or vehicle collision.
TURNING ANGLE
The turning angle is the angle of each front wheel to the
vertical when the vehicle is making a turn.