2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA display
[x] Cancel search: displayPage 1104 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 23
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F05
Left Front
Wheel Speed
Sensor
EBCM
LH BLU BRN1
2
76
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0035
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it moves
past the sensor. Each tooth–gap–tooth series on the
wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake control
module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these pulses to de-
termine the wheel speed. The voltage generated depends
on the air gap between the sensor and the toothed wheel,
and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or a
contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
S The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon-
nected.
S There is a problem in the wiring.
S There is a problem with a connector.
S There is a problem in the toothed ring.
S Wrong installed WSS.
S Wrong sensor signal.
S Signal noise via WSS.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is ON.
EBD is enabled. (Refer to the EBD failure matrix in this
section).
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed and
retained. This will help to prevent false signals due to the
pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the wiring
and the connectors carefully and completely may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the reap-
pearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during
a road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings is unusual, such
as one sensor varying in speed from the other three, a sig-
nal going intermittently high or low, etc. If this does not
identify the intermittent, wet the speed sensor harness on
the underside of the vehicle and perform a road test, moni-
toring the wheel speeds with the scan tool.
Important : If the WSS signal fault input to the EBCM, the
ABS warning lamp turns on. As if a sensor signal fault can
be removed by the scan tool, the ABS warning lamp
doesn’t turn off. In order to turn ABS warning lamp off, you
should driver a car up to 12 km/h.
Page 1107 of 2643

4F – 26IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F06
Right Front
Wheel Speed
Sensor
EBCM
PPL
GRYYEL
C111
WHT 1
12
2
4 5
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0040
RIGHT FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it moves
past the sensor. Each tooth–gap–tooth series on the
wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake control
module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these pulses to de-
termine the wheel speed. The voltage generated depends
on the air gap between the sensor and the toothed wheel,
and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or a
contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
S The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon-
nected.
S There is a problem in the wiring.
S There is a problem with a connector.
S There is a problem in the toothed ring.
S Wrong installed WSS.
S Wrong sensor signal.
S Signal noise via WSS.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is ON.
EBD is enabled. (Refer to the EBD failure matrix in this
section)
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or high resistance in the
wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed and
retained. This will help to prevent false signals due to the
pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the wiring
and the connectors carefully and completely may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the reap-
pearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during
a road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings is unusual, such
as one sensor varying in speed from the other three, a sig-
nal going intermittently high or low, etc. If this does not
identify the intermittent, wet the speed sensor harness on
the underside of the vehicle and perform a road test, moni-
toring the wheel speeds with the scan tool.
Important : If the WSS signal fault input to the EBCM, the
ABS warning lamp turns on. As if a sensor signal fault can
be removed by the scan tool, the ABS warning lamp
doesn’t turn off. In order to turn ABS warning lamp off, you
should drive a car up to 12 km/h.
Page 1110 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 29
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F07
Left Rear
Wheel Speed
Sensor EBCM
RED
DK BLUBLK
GRYBLK
C302 C110
WHT5 8
14 9
43
2
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0045
LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it moves
past the sensor. Each tooth–gap–tooth series on the
wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake control
module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these pulses to de-
termine the wheel speed. The voltage generated depends
on the air gap between the sensor and the toothed wheel,
and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or a
contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
S The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon-
nected.
S There is a problem in the wiring.
S There is a problem with a connector.
S There is a problem in the toothed ring.
S Wrong installed WSS.
S Wrong sensor signal.
S Signal noise via WSS.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is ON.
EBD is enabled. (Refer to the EBD failure matrix in this
section)
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or a high resistance in
the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed and
retained. This will help to prevent false signals due to the
pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the wiring
and the connectors carefully and completely may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the reap-
pearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during
a road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings is unusual, such
as one sensor varying in speed from the other three, a sig-
nal going intermittently high or low, etc. If this does not
identify the intermittent, wet the speed sensor harness on
the underside of the vehicle and perform a road test, moni-
toring wheel speeds with the scan tool.
Important : If the WSS signal fault input to the EBCM, the
ABS warning lamp turns on. As if a sensor signal fault can
be removed by the scan tool, the ABS warning lamp
doesn’t turn off. In order to turn ABS warning lamp off, you
should drive a car up to 12 km/h.
Page 1113 of 2643

4F – 32IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F08
Right Rear
Wheel Speed
Sensor EBCM
BRN
BRN
GRYC302 C110
WHT WHT
WHT1
110
1 3
3
2
2
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0050
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
Circuit Description
The toothed wheel generates a voltage pulse as it moves
past the sensor. Each tooth–gap–tooth series on the
wheel generates the pulses. The electronic brake control
module (EBCM) uses the frequency of these pulses to de-
termine the wheel speed. The voltage generated depends
on the air gap between the sensor and the toothed wheel,
and on the wheel speed.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks for a malfunctioning wheel speed
sensor, a short to ground or to voltage in the wiring, or a
contact problem in a connector.
Cause(s)
S The wheel speed sensor is defective or discon-
nected.
S There is a problem in the wiring.
S There is a problem with a connector.
S There is a problem in the toothed ring.
S Wrong installed WSS.
S Wrong sensor signal.
S Signal noise via WSS.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is ON.
EBD is enabled. (Refer to the EBD failure matrix in this
section)
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.1. This step begins an examination for a defective
wheel speed sensor.
6. This step tests the wiring for a short to voltage.
8. This step tests the wiring for a short to ground.
10. This step tests for an open or high resistance in the
wiring.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure that the speed sensor wiring is properly routed and
retained. This will help to prevent false signals due to the
pickup of electrical noise.
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the wiring
and the connectors carefully and completely may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the reap-
pearance of the malfunction.
You can use the scan tool to monitor wheel speeds during
a road test. Watch the wheel speeds being displayed on
the scan tool to see if any of the readings is unusual, such
as one sensor varying in speed from the other three, a sig-
nal going intermittently high or low, etc. If this does not
identify the intermittent, wet the speed sensor harness on
the underside of the vehicle and perform a road test, moni-
toring wheel speeds with the scan tool.
Important : If the WSS signal fault input to the EBCM, the
ABS warning lamp turns on. As if a sensor signal fault can
be removed by the scan tool, the ABS warning lamp
doesn’t turn off. In order to turn ABS warning lamp off, you
should drive a car up to 12 km/h.
Page 1398 of 2643

ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 49
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Functional Check Procedure
Inspect
1. Install a tachometer or scan tool.
2. Operate the vehicle unit proper operating tempera-
ture is reached.
3. Drive the vehicle at 80 to 88km/h (50 to 55 mph)
with light throttle(road load).
4. Maintaining throttle position, lightly touch the brake
pedal and check for release of the TCC and a slight
increase in engine speed(rpm).
5. Release the brake slowly accelerate and check for
a reapply of the Lock up clutch and a slight de-
crease in engine speed(rpm).
Torque Converter Evaluation
Torque Converter Stator
The torque converter stator roller clutch can have one of
two different type malfunctions :
A. Stator assembly freewheels in both directions.
B. Stator assembly remains Locked up at all times.
Condition A – Poor Acceleration Low
Speed
The car tends to have poor acceleration from a stand still.
At speeds above 50 to 55km/h(30 to 35mph), the car may
act normal. If poor acceleration is noted, it should first be
determined that the exhaust system is not blocked, and
the transaxle is in 1st(First) gear when starting out.
If the engine freely accelerates to high rpm in N(Neutral),
it can be assumed that the engine and exhaust system are
normal. Checking for poor performance in ”Drive” and ”Re-
verse” will help determine if the stator is freewheeling at all
times.
Condition B – Poor Acceleration High
Speed
Engine rpm and car speed limited or restricted at high
speeds. Performance when accelerating from a standstill
is normal. Engine may overheat. Visual examination of the
converter may reveal a blue color from overheating.
If the converter has been removed, the stator roller clutch
can be checked by inserting two fingers into the splined in-
ner race of the roller clutch and trying to turn freely clock-
wise, but not turn or be very difficult to turn counter clock-
wise.
Noise
Torque converter whine is usually noticed when the ve-
hicle is stopped and the transaxle is in ”Drive” or ”Re-
verse”. The noise will increase when engine rpm is in-
creased. The noise will stop when the vehicle is moving or
when the torque converter clutch is applied because both
halves of the converter are turning at the same speed.
Perform a stall test to make sure the noise is actually com-
ing from the converter :1. Place foot on brake.
2. Put gear selector in ”Drive”.
3. Depress accelerator to approximately 1200rpm for
no more than six seconds.
Notice : If the accelerator is depressed for more than six
seconds, damage to the transaxle may occur.
A torque converter noise will increase under this load.
Important : This noise should not be confused with pump
whine noise which is usually noticeable in P (Park), N
(Neutral) and all other gear ranges. Pump whine will vary
with pressure ranges.
The torque converter should be replaced under any of the
following conditions:
S External leaks in the hub weld area.
S Converter hub is scored or damaged.
S Converter pilot is broken, damaged or fits poorly
into crankshaft.
S Steel particles are found after flushing the cooler
and cooler lines.
S Pump is damaged or steel particles are found in the
converter.
S Vehicle has TCC shudder and/or no TCC apply.
Replace only after all hydraulic and electrical diag-
noses have been made.(Lock up clutch material
may be glazed.)
S Converter has an imbalance which cannot be cor–
rected. (Refer To Converter Vibration Test Proce-
dure.)
S Converter is contaminated with engine coolant con-
taining antifreeze.
S Internal failure of stator roller clutch.
S Excess end play.
S Heavy clutch debris due to overheating (blue con-
verter).
S Steel particles or clutch lining material found in fluid
filter or on magnet when no internal parts in unit are
worn or damaged(indicates that lining material
came from converter).
The torque converter should not be replace if :
S The oil has an odor, is discolored, and there is no
evidence of metal or clutch facing particles.
S The threads in one or more of the converter bolt
holes are damaged.
–correct with thread insert.
S Transaxle failure did not display evidence of dam-
age or worn internal parts, steel particles or clutch
plate lining material in unit and inside the fluid filter.
S Vehicle has been exposed to high mileage(only).
The exception may be where the Lock up clutch
damper plate lining has seen excess wear by ve-
hicles operated in heavy and/or constant traffic,
such as taxi, delivery or police use.
Lock–Up Clutch Shudder Diagnosis
The key to diagnosing lock–up clutch(TCC) shudder is to
note when it happens and under what conditions.
Page 1424 of 2643
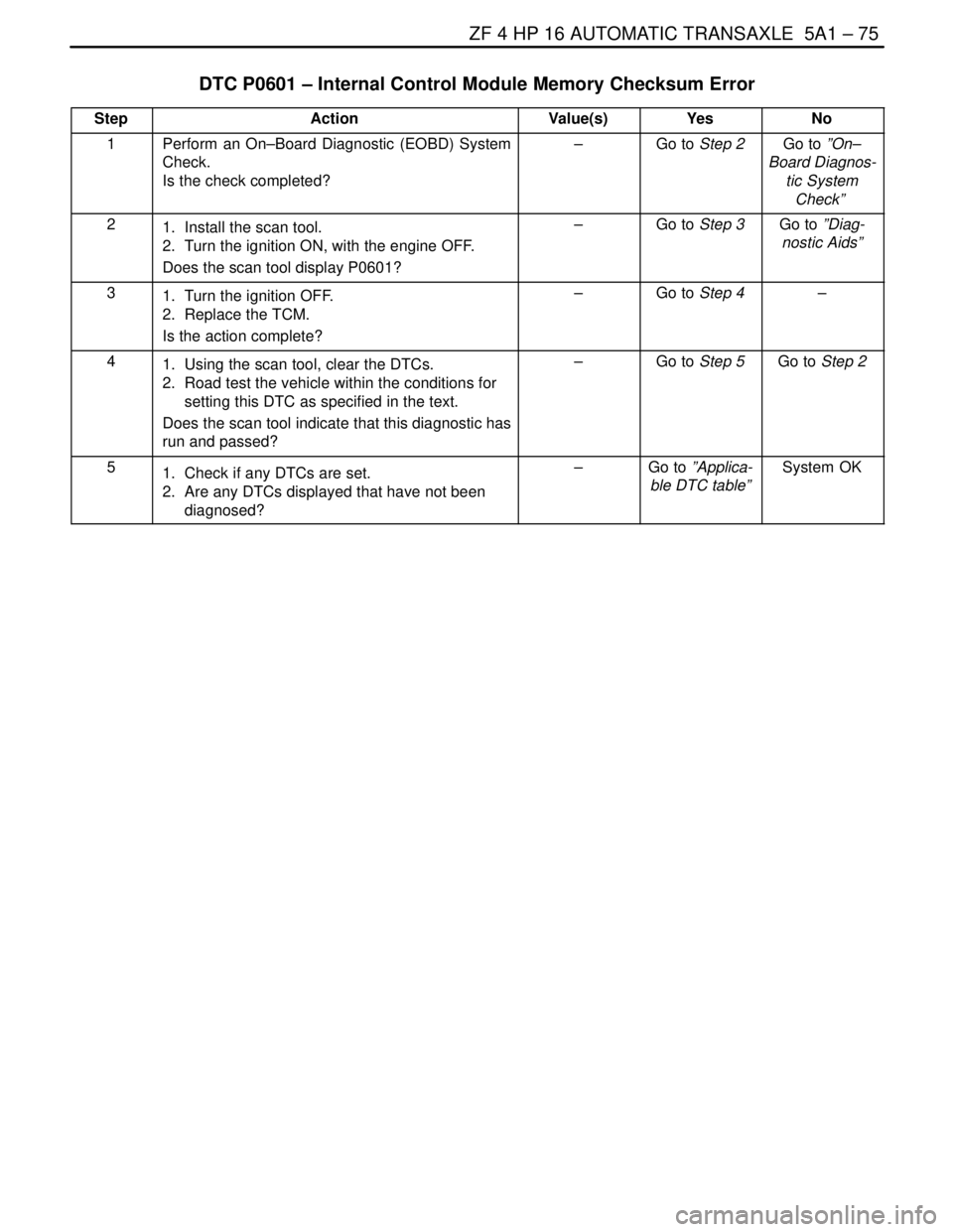
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 75
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0601 – Internal Control Module Memory Checksum Error
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the check completed?–Go to Step 2Go to ”On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
21. Install the scan tool.
2. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
Does the scan tool display P0601?–Go to Step 3Go to ”Diag-
nostic Aids”
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the TCM.
Is the action complete?–Go to Step 4–
41. Using the scan tool, clear the DTCs.
2. Road test the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 2
51. Check if any DTCs are set.
2. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been
diagnosed?–Go to ”Applica-
ble DTC table”System OK
Page 1426 of 2643
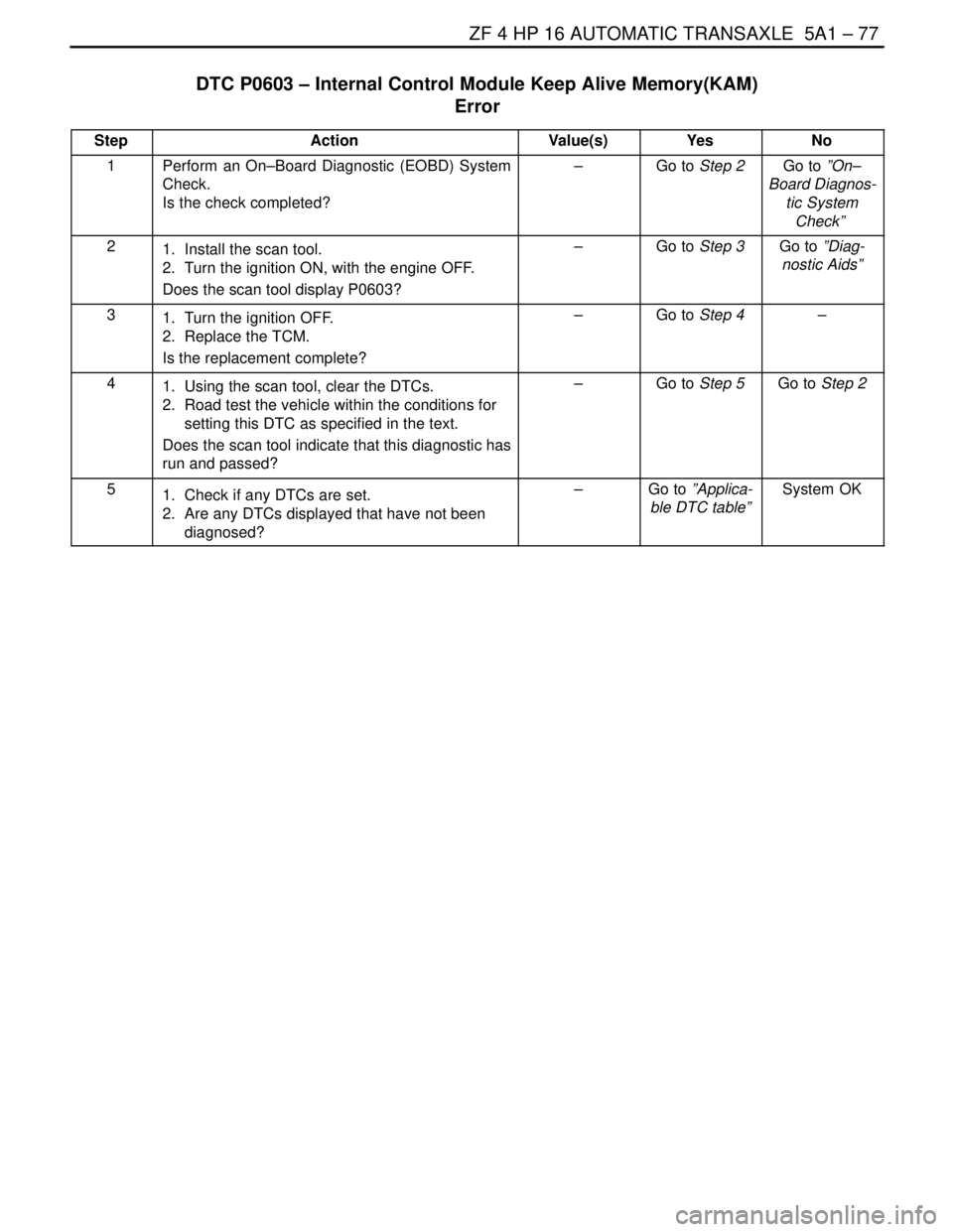
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 77
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0603 – Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory(KAM)
Error
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the check completed?–Go to Step 2Go to ”On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
21. Install the scan tool.
2. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
Does the scan tool display P0603?–Go to Step 3Go to ”Diag-
nostic Aids”
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the TCM.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 4–
41. Using the scan tool, clear the DTCs.
2. Road test the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 2
51. Check if any DTCs are set.
2. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been
diagnosed?–Go to ”Applica-
ble DTC table”System OK
Page 1428 of 2643
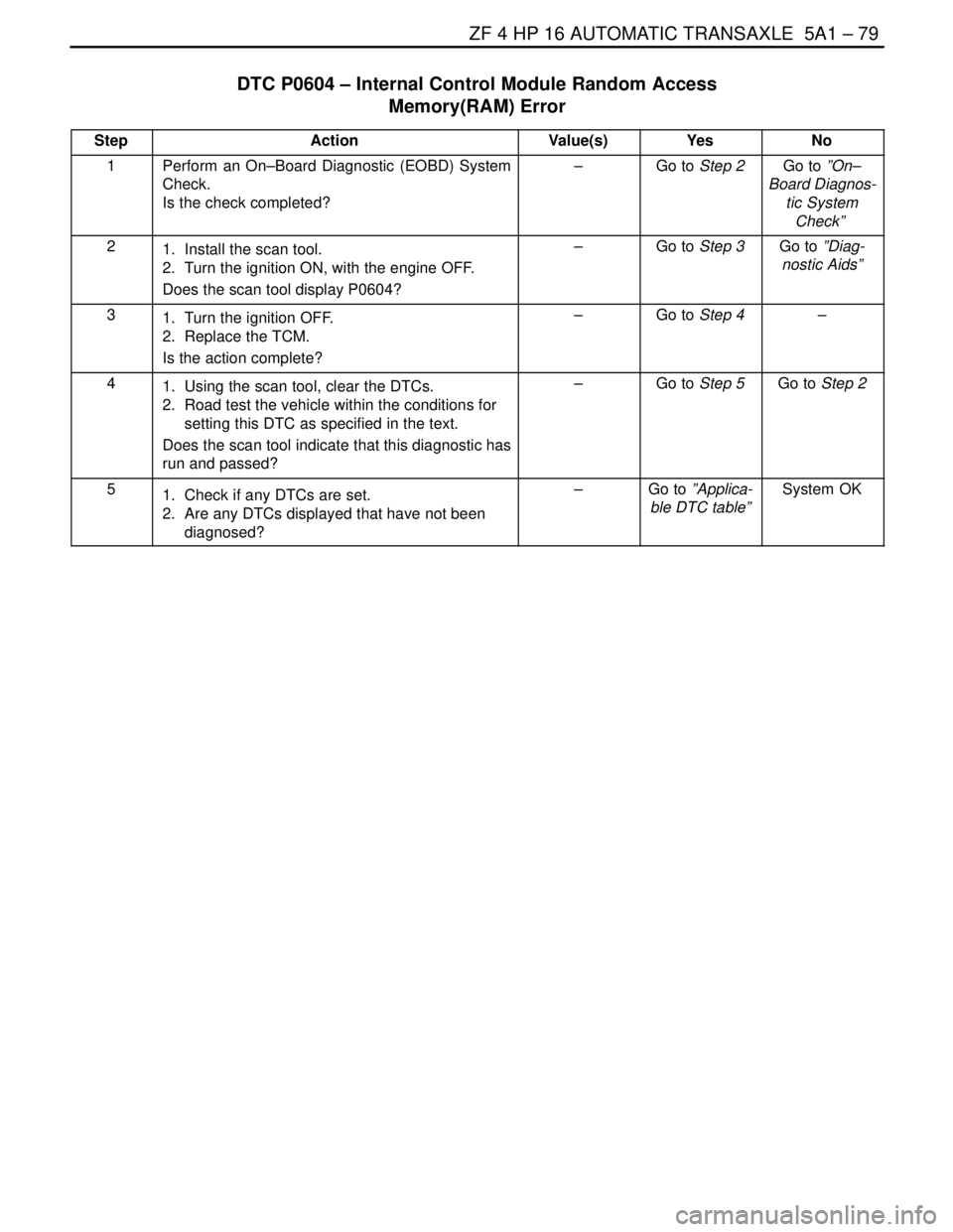
ZF 4 HP 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE 5A1 – 79
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0604 – Internal Control Module Random Access
Memory(RAM) Error
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the check completed?–Go to Step 2Go to ”On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
21. Install the scan tool.
2. Turn the ignition ON, with the engine OFF.
Does the scan tool display P0604?–Go to Step 3Go to ”Diag-
nostic Aids”
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the TCM.
Is the action complete?–Go to Step 4–
41. Using the scan tool, clear the DTCs.
2. Road test the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 2
51. Check if any DTCs are set.
2. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been
diagnosed?–Go to ”Applica-
ble DTC table”System OK