2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA heater controls
[x] Cancel search: heater controlsPage 730 of 2643

1F – 484IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0420
CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR LOW EFFICIENCY
Circuit Description
In order to control exhaust emissions of Hydrocarbons
(HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Nitrogen Oxide (NOx),
a Three–Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) is used. The cat-
alyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction
which oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas,
converting them into harmless water vapor and carbon
dioxide, it also reduces NOx, converting it into nitrogen.
The catalytic converter also has the ability to store oxygen.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the capability to
monitor this process using a Heated
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2) located in the ex-
haust stream past the TWC. The HO2S2 produces an out-
put signal which indicates the oxygen storage capacity of
the catalyst; this in turn indicates the catalyst’s ability to
convert exhaust emissions effectively. The ECM monitors
the catalyst efficiency by first allowing the catalyst to heat
up, waiting for a stabilization period while the engine is id-
ling, and then adding and removing fuel while monitoring
the reaction of the HO2S2. When the catalyst is function-
ing properly, the HO2S2 response to the extra fuel is slow
compared to the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1).
When the HO2S2 response is close to that of the HO2S1,
the Oxygen storage capability or efficiency of the catalyst
is considered to be bad, and the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Oxygen storage capacity index time is less than 0.3
seconds.
S Before idle test, the vehicle needs to be driven for
at least:
S 15 seconds at airflow is greater than 9.2 g/sec.
for manual transaxle.
S 11 seconds at airflow is greater than 12 g/sec
for automatic transaxle.
S Oxygen Sensor Capacity test condition:
S Closed loop stoichiometry.
S Purge concentration learned.
S Engine is running more than 330 seconds.
S Airflow is between 2.5 and 7.25 g/sec.
S Throttle Position (TP) sensor is less than 1.5%.
S Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is between –7°C
(19.4°F) and 105°C (221°F).
S Barometric pressure (BARO) is greater than 72 kPa
(10.4 psi).
S Catalyst temperature is between 500°C (932°F)
and 850°C (1562°F) for automatic transaxle.
S Catalyst temperature is between 450°C (842°F)
and 850°C (1562°F) for automatic transaxle.
S Closed Loop integrator change is less than 0.03.
S Idle time is less than 1 minute.
S Vehicle speed is less than 3 km/h (1.9 mph).S Block Learn Mode is learned.
S Above condition is stabilized for 5 seconds.
Note : Test is aborted for this idle if:
S Change in engine speed is greater than 80 rpm.
S A/C status changed.
S Cooling fan status changed.
S Insufficient air/fuel shift.
S DTC(s) P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0133, P1133,
P0134, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141,
P1167, P1171, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0341,
P0342, P0351, P0352, P0402, P0404, P1404,
P0405, P0406, P0443, P0502, P0506, P0507, and
P0562 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
The catalyst test may abort due to a change in the engine
load. Do not change the engine load (i.e. A/C, coolant fan,
heater motor) while a catalyst test is in progress.
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent
complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions:
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
Page 879 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 633
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Failed This Ig. (Failed This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the diagnostic test
has failed at least once during the current ignition cycle.
This message will clear when DTCs are cleared or the igni-
tion is cycled.
History
This message display indicates that the DTC has been
stored in memory as a valid fault. A DTC displayed as a
History fault may not mean that the fault is no longer pres-
ent. The history description means that all the conditions
necessary for reporting a fault have been met (maybe
even currently), and the information was stored in the con-
trol module memory.
MIL Requested
This message display indicates that the DTC is currently
causing the MIL to be turned ON. Remember that only
type A and type B DTCs can request the MIL. The MIL re-
quest cannot be used to determine if the DTC fault condi-
tions are currently being experienced. This is because the
diagnostic executive will require up to three trips during
which the diagnostic test passes to turn OFF the MIL.
Not Run Since CI (Not Run Since Cleared)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run since the last time DTCs were cleared.
Therefore, the diagnostic test status (passing or failing) is
unknown. After DTCs are cleared, this message will con-
tinue to be displayed until the diagnostic test runs.
Not Run This Ig. (Not Run This Ignition)
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has not run during this ignition cycle.
Test Ran and Passed
This message display indicates that the selected diagnos-
tic test has done the following:
S Passed the last test.
S Run and passed during this ignition cycle.
S Run and passed since DTCs were last cleared.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Test Ran and
Passed” after a repair verification, the vehicle is ready to
be released to the customer.
If the indicated status of the vehicle is ”Failed This Ignition”
after a repair verification, then the repair is incomplete and
further diagnosis is required.
Prior to repairing a vehicle, status information can be used
to evaluate the state of the diagnostic test, and to help
identify an intermittent problem. The technician can con-
clude that although the MIL is illuminated, the fault condi-
tion that caused the code to set is not present. An intermit-
tent condition must be the cause.
PRIMARY SYSTEM – BASED
DIAGNOSTICS
There are primary system–based diagnostics which eval-
uate system operation and its effect on vehicle emissions.
The primary system–based diagnostics are listed below
with a brief description of the diagnostic function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) is
diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Slow response.
S Response time (time to switch R/L or L/R).
S Inactive signal (output steady at bias voltage
approx. 450 mv).
S Signal fixed high.
S Signal fixed low.
The catalyst monitor Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) is diagnosed for the following conditions:
S Heater performance (time to activity on cold start).
S Signal fixed low during steady state conditions or
power enrichment (hard acceleration when a rich-
mixture should be indicated).
S Signal fixed high during steady state conditions or
deceleration mode (deceleration when a lean mix-
ture should be indicated).
S Inactive sensor (output steady at approximately 438
mv).
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must be
replaced. Do not attempt to repair the wiring, connector or
terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, it
must have clean reference air provided to it. This clean air
reference is obtained by way of the oxygen sensor wire(s).
Any attempt to repair the wires, connector or terminals
could result in the obstruction of the reference air and de-
grade oxygen sensor performance.
Misfire Monitor Diagnostic Operation
The misfire monitor diagnostic is based on crankshaft
rotational velocity (reference period) variations. The en-
gine control module (ECM) determines crankshaft rota-
tional velocity using the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
and the Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor. When a cylinder
misfires, the crankshaft slows down momentarily. By mon-
itoring the CKP and CMP sensor signals, the ECM can cal-
culate when a misfire occurs.
For a non–catalyst damaging misfire, the diagnostic will be
required to monitor a misfire present for between
1000–3200 engine revolutions.
For catalyst–damaging misfire, the diagnostic will respond
to misfire within 200 engine revolutions.
Rough roads may cause false misfire detection. A rough
road will cause torque to be applied to the drive wheels and
drive train. This torque can intermittently decrease the
crankshaft rotational velocity. This may be falsely de-
tected as a misfire.
Page 1975 of 2643
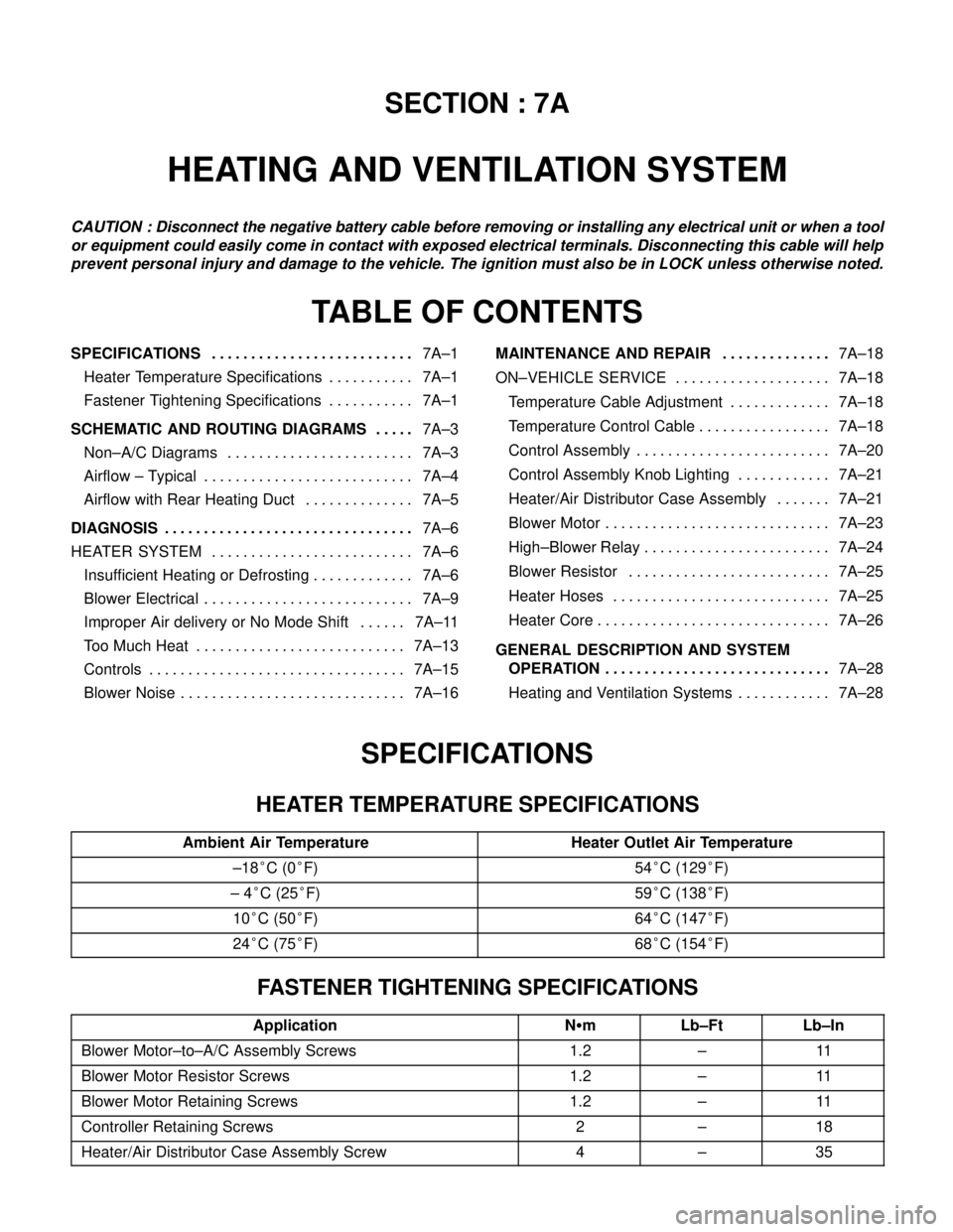
SECTION : 7A
HEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM
CAUTION : Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a tool
or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help
prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS7A–1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Heater Temperature Specifications 7A–1. . . . . . . . . . .
Fastener Tightening Specifications 7A–1. . . . . . . . . . .
SCHEMATIC AND ROUTING DIAGRAMS7A–3 . . . . .
Non–A/C Diagrams 7A–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Airflow – Typical 7A–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Airflow with Rear Heating Duct 7A–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DIAGNOSIS7A–6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HEATER SYSTEM 7A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Insufficient Heating or Defrosting 7A–6. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Blower Electrical 7A–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Improper Air delivery or No Mode Shift 7A–11. . . . . .
Too Much Heat 7A–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Controls 7A–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Blower Noise 7A–16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR7A–18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ON–VEHICLE SERVICE 7A–18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Temperature Cable Adjustment 7A–18. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Temperature Control Cable 7A–18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Assembly 7A–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Assembly Knob Lighting 7A–21. . . . . . . . . . . .
Heater/Air Distributor Case Assembly 7A–21. . . . . . .
Blower Motor 7A–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
High–Blower Relay 7A–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Blower Resistor 7A–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Heater Hoses 7A–25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Heater Core 7A–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION7A–28 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Heating and Ventilation Systems 7A–28. . . . . . . . . . . .
SPECIFICATIONS
HEATER TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS
Ambient Air TemperatureHeater Outlet Air Temperature
–18°C (0°F)54°C (129°F)
– 4°C (25°F)59°C (138°F)
10°C (50°F)64°C (147°F)
24°C (75°F)68°C (154°F)
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Blower Motor–to–A/C Assembly Screws1.2–11
Blower Motor Resistor Screws1.2–11
Blower Motor Retaining Screws1.2–11
Controller Retaining Screws2–18
Heater/Air Distributor Case Assembly Screw4–35
Page 1981 of 2643
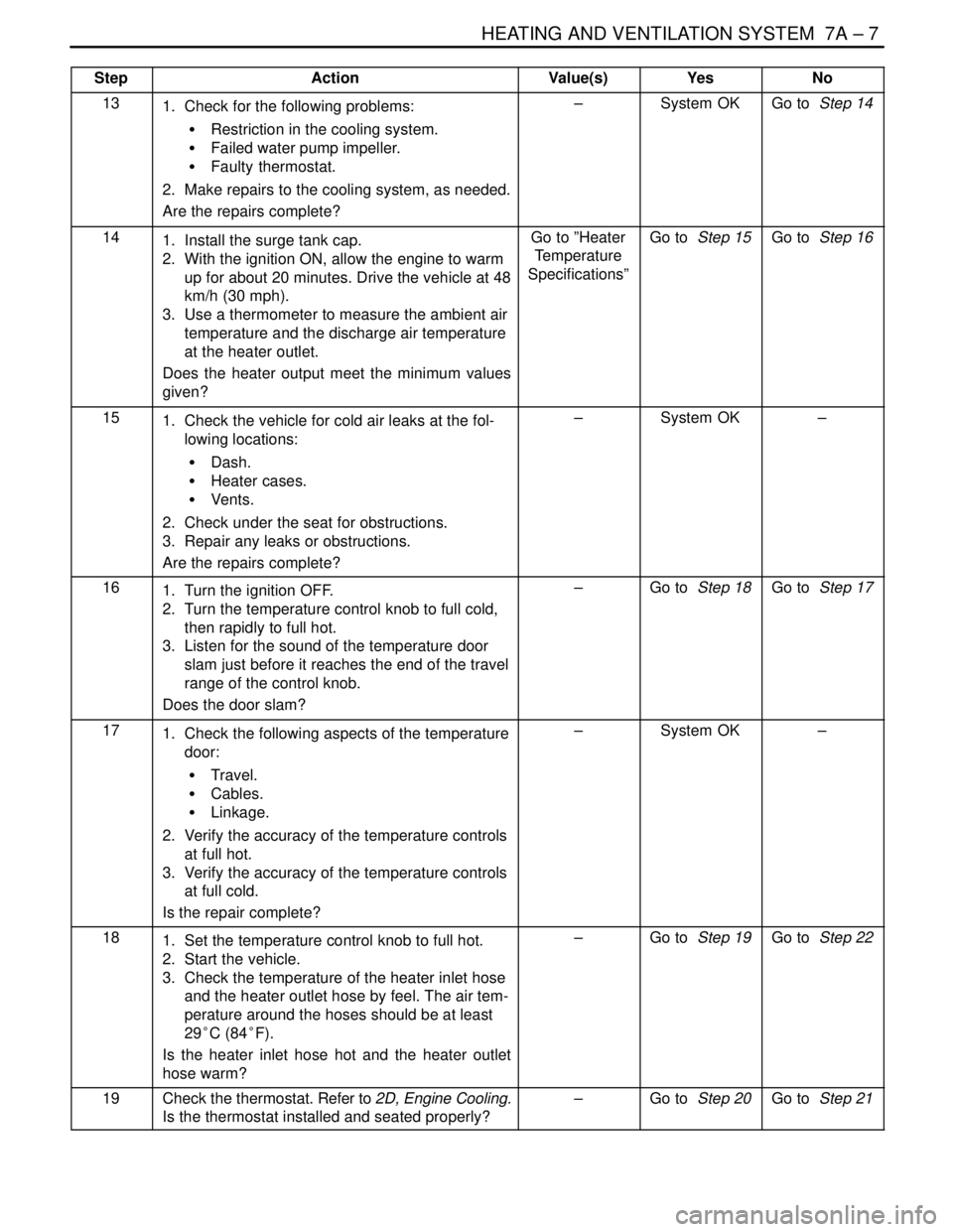
HEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM 7A – 7
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
131. Check for the following problems:
S Restriction in the cooling system.
S Failed water pump impeller.
S Faulty thermostat.
2. Make repairs to the cooling system, as needed.
Are the repairs complete?–System OKGo to Step 14
141. Install the surge tank cap.
2. With the ignition ON, allow the engine to warm
up for about 20 minutes. Drive the vehicle at 48
km/h (30 mph).
3. Use a thermometer to measure the ambient air
temperature and the discharge air temperature
at the heater outlet.
Does the heater output meet the minimum values
given?Go to ”Heater
Temperature
Specifications”Go to Step 15Go to Step 16
151. Check the vehicle for cold air leaks at the fol-
lowing locations:
S Dash.
S Heater cases.
S Vents.
2. Check under the seat for obstructions.
3. Repair any leaks or obstructions.
Are the repairs complete?–System OK–
161. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Turn the temperature control knob to full cold,
then rapidly to full hot.
3. Listen for the sound of the temperature door
slam just before it reaches the end of the travel
range of the control knob.
Does the door slam?–Go to Step 18Go to Step 17
171. Check the following aspects of the temperature
door:
S Travel.
S Cables.
S Linkage.
2. Verify the accuracy of the temperature controls
at full hot.
3. Verify the accuracy of the temperature controls
at full cold.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
181. Set the temperature control knob to full hot.
2. Start the vehicle.
3. Check the temperature of the heater inlet hose
and the heater outlet hose by feel. The air tem-
perature around the hoses should be at least
29°C (84°F).
Is the heater inlet hose hot and the heater outlet
hose warm?–Go to Step 19Go to Step 22
19Check the thermostat. Refer to 2D, Engine Cooling.
Is the thermostat installed and seated properly?–Go to Step 20Go to Step 21
Page 1997 of 2643

HEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM 7A – 23
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Tighten
Tighten the heater/air distributor case assembly
screws to 4 NSm (35 lb–in).
5. Install the heater/air distributor case assembly
screws at the side of the heater core pipes through
the firewall from the engine compartment side.
Tighten
Tighten the heater/air distributor case assembly
screw to 4 NSm (35 lb–in).
6. Install the two heater hoses.
7. Slide the heater hose clamps into position.
8. Connect the rear duct connector.
9. Install the instrument panel and tie–bar. Refer to
Section 9E, Instrumentation/Driver Information.
10. Fill the cooling system. Refer to Section 1D, Engine
Cooling.
11. Connect the negative battery cable.
12. Operate the controls to verify the proper function of
the heating and ventilation systems.
BLOWER MOTOR
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the glove box. Refer to Section 9E, Instru-
mentation/Driver Information.
3. Put the floor carpet aside for preventing stain.
4. Disconnect the blower motor electrical connector
and resistor connector.
5. Remove the screws that secure the motor to the
heater/air distributor case.
Page 2002 of 2643

7A – 28IHEATING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
HEATING AND VENTILATION
SYSTEMS
The base heater system is designed to provide heating,
ventilation, windshield defrosting, side window defogging,
and on some vehicles, heating directly to the rear seat
area.
The heater and fan assembly blower regulates the airflow
from the air inlet for further processing and distribution.
The heater core transfers the heat from the engine coolant
to the inlet air.
The temperature door regulates the amount of the air that
passes through the heater core. The temperature door
also controls the temperature of the air by controlling the
mix of the heated air and the ambient air.
The mode door regulates the flow and the distribution of
the processed air to the heater ducts and to the defroster
ducts.
This console–mounted heating and ventilation panel con-
tains the following:
The Rotary Temperature Control Knob
1. The Rotary Temperature Control Knob
S Actuates by cable.
S Raises the temperature of the air entering the
vehicle by rotation toward the right, or the red
portion of the knob.
2. The Rotary Blower Control Knob
S Turns ON to operate the blower motor at four
speeds.
S Turns OFF to stop the blower.
S Operates completely independently both from
the mode control that regulates the defroster
door and from the temperature control knob.S Changes the fan speed in any mode and at any
temperature setting.
3. The Rotary Mode Control Knob
S Actuates by cable.
S Regulates the air distribution between the wind-
shield, the instrument panel, and the floor vents.
Two Push Knobs
1. The Rear Window Defogger Push Knob
S Controls the rear window defogger.
S Turns ON the rear window defogger when the
push knob is pressed and the indicator lamp is
illuminated.
2. The A/C Push Knob (if the vehicle is equipped with
air conditioning)
S Controls the A/C.
S Turns the A/C ON when the push knob is down.
However, if the blower control knob is OFF, the
A/C system is OFF, regardless of the position of
the A/C knob.
Fresh Air Control Level Or Push Knob
1. The Fresh Air Control Level
S Operates by cable.
S Switches between recirculating passenger
compartment air and bringing outside air into the
passenger compartment.
S Draws in outside air when the lever is moved to
the right.
S Recirculates inside air when the lever is moved
to the left.
2. The Fresh Air Control Push Knob
S Operates by cable.
S Switches between recirculating passenger
compartment air and bringing outside air into the
passenger compartment.
S Draws in outside air when knob is off.
S Recirculates inside air when the knob is down
with the indicator lamp illuminated.
Page 2054 of 2643

7B – 52IMANUAL CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
SYSTEM COMPONENTS–CONTROL
Controller
The operation of the A/C system is controlled by the
switches and the lever on the control head. The compres-
sor clutch and the blower are connected electrically to the
control head by a wiring harness. The blower circuit is
open in the OFF mode. Airflow is provided by the four
blower speeds available in the remaining modes. Cooled
and dehumidified air is available in the MAX, NORMAL,
BI–LEVEL, and DEFROST modes.
The temperature is controlled by the position of the tem-
perature knob on the control head. A cable connects this
knob to the temperature door, which controls the airflow
through the heater core. As the temperature knob is
moved through its range of travel, a sliding clip on the
cable at the temperature valve connection should assume
a position ensuring that the temperature door will seat in
both extreme positions. The temperature door position is
independent of the mode control switch. The temperature
door on some models is controlled electrically, eliminating
the need for the temperature cable.
The electric engine cooling fan on some vehicles is not
part of the A/C control system; however, the fan is opera-
tional any time the A/C control is in the MAX, NORMAL,
or BI–LEVEL modes. Some models provide for engine
cooling fan operation when the controller is in the DE-
FROST mode. This added feature is part of the A/C con-
troller function and is aimed at preventing excessive com-
pressor head temperatures. It also allows the A/C system
to function more efficiently. On some models, the engine
cooling fan will be turned off during road speed conditions
above 56 km/h (35 mph), when the airflow though the con-
denser coil is adequate for efficient cooling. The operation
of the cooling fan is controlled by the powertrain control
module (PCM), or the engine control module (ECM),
through the cooling fan relay.
Pressure Transducer
The pressure transducer incorporates the functions of the
high–pressure and the low–pressure cutout switches
along with the fan cycling switch. The pressure transducer
is located in the high–side liquid refrigerant line near the
right front strut tower and the air filter assembly.
Wide–Open Throttle (WOT) Compressor
Cutoff
During full throttle acceleration on vehicles equipped with
multi–port injection (MPI), the throttle position sensor
(TPS) sends a signal to the PCM or the ECM, which then
controls the compressor clutch.
A/C Time Delay Relay
This relay on some vehicles controls the current to the en-
tire A/C system and provides a short delay of A/C opera-
tion upon start–up.
V5 COMPRESSOR–GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
Different vehicles with V5 compressors may exhibit differ-
ences in mounting and installation, but overhaul proce-
dures are similar.
Before removing the compressor or performing on–ve-
hicle repairs, clean the compressor connections and the
outside of the compressor.
Important : After removing a compressor from the vehicle
for servicing, drain the oil by removing the oil drain plug.
Also drain the oil from the suction and the discharge ports
to insure complete draining. Measure the amount of oil
drained, and record that amount. Discard the used oil and
add the same amount of new polyalkaline glycol (PAG) re-
frigerant oil to the compressor.
The compressor has been removed from the vehicle un-
less otherwise indicated.
Clean tools and a clean work area are important for proper
servicing. Keep dirt and foreign material from getting on or
into the compressor parts. Parts that are to be reassem-
bled should be cleaned with trichloroethane, naphtha,
stoddard solvent, kerosene, or equivalent solvents. Dry
the cleaned parts with clean dry air. Use only lint–free
cloths to wipe the parts.
V5 COMPRESSOR–DESCRIPTION OF
OPERATION
The V5 is a variable displacement compressor that can
match the automotive air conditioning (A/C) demand un-
der all conditions without cycling. The basic compressor
mechanism is a variable angle wobble–plate with five ax-
ially oriented cylinders. The center of control of the com-
pressor displacement is a bellows–actuated control valve
located in the rear head of the compressor. The control
valve senses compressor suction pressure.
The wobble–plate angle and the compressor displace-
ment are controlled by the crankcase suction pressure dif-
ferential. When the A/C capacity demand is high, the suc-
tion pressure will be above the control point. The valve will
maintain a bleed from crankcase to suction. With no
crankcase suction pressure differential, the compressor
will have maximum displacement.
When the A/C capacity demand is lower and the suction
pressure reaches the control point, the valve will bleed dis-
charge gas into the crankcase and close off a passage
from the crankcase to the suction plenum. The angle of the
wobble–plate is controlled by a force balance on the five
pistons. A slight elevation of the crankcase suction pres-
sure differential creates total force on the pistons resulting
in a movement about the wobbleplate pivot pin that re-
duces the plate angle.
The compressor has a unique lubrication system. The
crankcase suction bleed is routed through the rotating
wobble–plate for lubrication of the wobble–plate bearing.
The rotation acts as an oil separator which removes some
Page 2095 of 2643

7D – 40IAUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL INFORMATION
THE V5 SYSTEM
Refer to Section 7B, Manual Control Heating, Ventilation,
and Air Conditioning System,for general information de-
tails for the following:
S System Components – Functional.
S The V5 A/C System.
S V5 Compressor – Description of Operation.
S V5 Compressor – General Description.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS–CONTROL
Controller
The operation of the A/C system is controlled by the
switches on the control head. This console–mounted
heating and ventilation system contains the following
knobs and display:
Temperature Control Push Knobs
1. Raise the temperature of the air entering the ve-
hicle by pressing the top switch, with the red arrow
pointing upward.
2. Lower the temperature by pressing the bottom
switch, with the blue arrow pointing downward.
3. Actuate the air mix door by an electric motor.
4. Vary the mix of the air passing through the heater
core with the air bypassing the core.
Each press of a switch changes the set temperature by in-
crements of 0.5°C (1°F). This is shown in the temperature
window on the function display.
The Function Display
This is an LCD display indicating the status of the control
settings selected. Starting from the left end of the display,
the sections are as follows:
1. Temperature setting – Indicates the temperature set
with the temperature control knob.
2. Auto status – Indicates whether the system is oper-
ating in the full auto mode or the manual mode.
3. Defroster icon – Indicates manual selection of full
defrost mode.
4. Mode – Indicated by icon, the mode chosen by the
system in auto (or by the operator in manual) is
shown by an illumination arrow indicating the air
path.
5. A/C – A snowflake icon indicating whether the A/C
is ON or OFF.
6. Fan speed – Indicates the fan speed by illuminating
a bar based on the segment at the front, for low
speed, and adding additional segments in order up
to the fifth, for high speed.Eight Additional Push Knobs
1. Full defrost – Causes the mode motors to direct all
air to the windshield and aide window outlets for
maximum defrosting.
2. Air intake – Switches between fresh air intake, the
default, and recirculating air. Airflow arrows on the
display indicate the mode in effect.
3. Full Auto Switch – Maintains the set temperature
automatically. In this mode, the fully automatic tem-
perature control (FATC) system controls the follow-
ing:
S The air mix door motor.
S The mode door motor.
S The blower motor speed.
S The inlet air door motor.
S A/C ON/OFF.
4. OFF Switch – Turns the automatic air conditioning
and fan control off.
5. Mode Switch – Allows manual selection of the air-
flow direction.
S Selection is shown on the function display.
S Each time the mode switch is pressed, the next
function is displayed.
6. A/C Switch – Allows manual selection and control
of the air conditioning function.
7. Fan Control Switch – Allows manual selection
among five fan speeds.
8. Defogger Switch – Turns on the electric defogging
heater in the rear window and the outside rearview
mirrors, if the vehicle is equipped with heated mir-
rors.
Pressure Transducer
Pressure transducer switching incorporates the functions
of the high–pressure and the low–pressure cutout
switches along with the fan cycling switch. The pressure
transducer is located in the high–side liquid refrigerant line
behind the right strut tower, between the right strut tower
and the fire wall. The output from this pressure transducer
goes to the electronic control module (ECM), which con-
trols the compressor function based on the pressure sig-
nal.
Wide–Open Throttle (WOT) Compressor
Cutoff
During full–throttle acceleration, the throttle position sen-
sor (TPS) sends a signal to the ECM, which then controls
the compressor clutch.
High RPM Cutoff
As engine rpm approaches the maximum limit, the ECM
will disengage the compressor clutch until the engine
slows to a lower rpm.