2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA engine e
[x] Cancel search: engine ePage 1129 of 2643
4F – 48IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
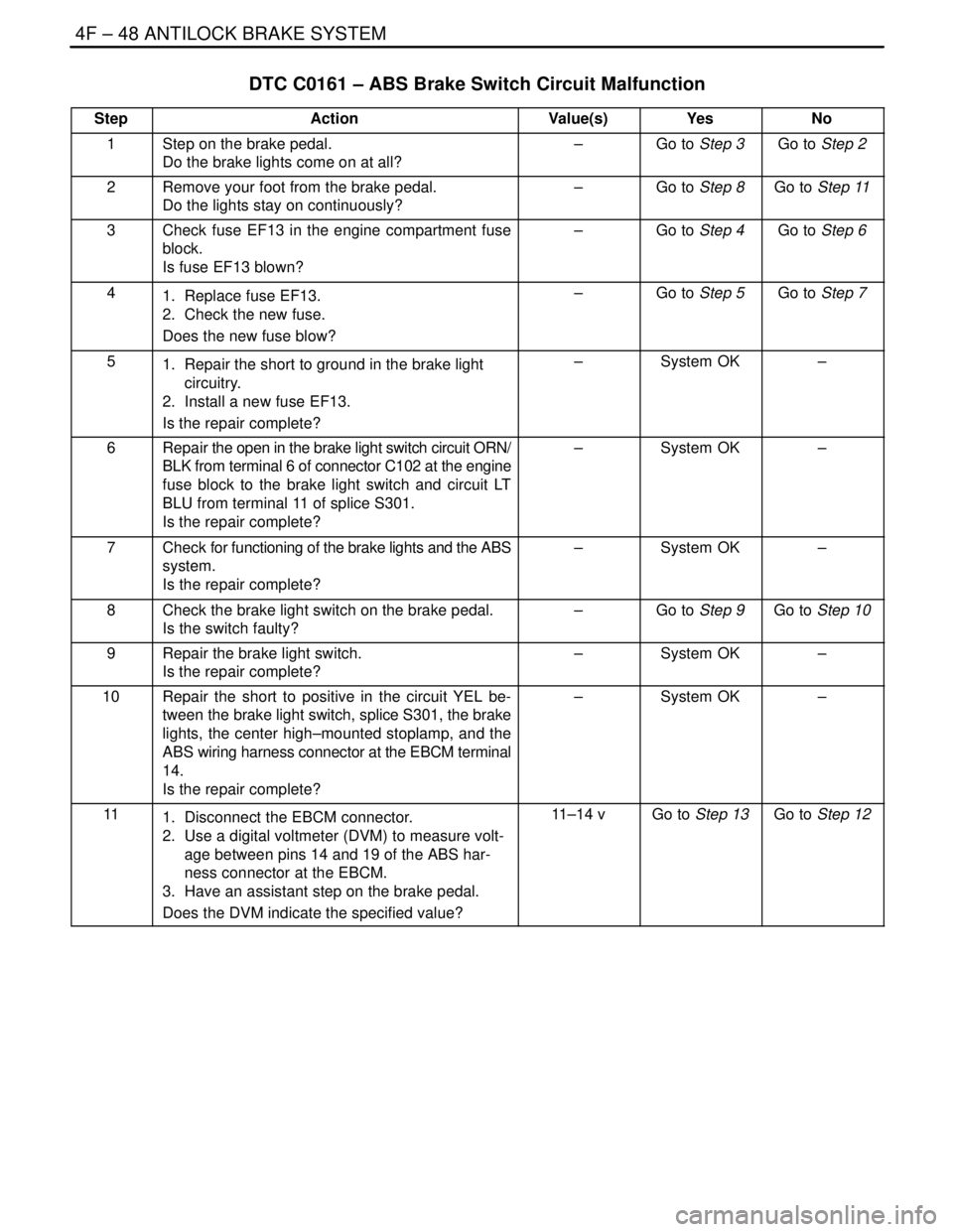
DTC C0161 – ABS Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Step on the brake pedal.
Do the brake lights come on at all?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 2
2Remove your foot from the brake pedal.
Do the lights stay on continuously?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 11
3Check fuse EF13 in the engine compartment fuse
block.
Is fuse EF13 blown?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
41. Replace fuse EF13.
2. Check the new fuse.
Does the new fuse blow?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 7
51. Repair the short to ground in the brake light
circuitry.
2. Install a new fuse EF13.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
6Repair the open in the brake light switch circuit ORN/
BLK from terminal 6 of connector C102 at the engine
fuse block to the brake light switch and circuit LT
BLU from terminal 11 of splice S301.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
7Check for functioning of the brake lights and the ABS
system.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
8Check the brake light switch on the brake pedal.
Is the switch faulty?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
9Repair the brake light switch.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
10Repair the short to positive in the circuit YEL be-
tween the brake light switch, splice S301, the brake
lights, the center high–mounted stoplamp, and the
ABS wiring harness connector at the EBCM terminal
14.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
111. Disconnect the EBCM connector.
2. Use a digital voltmeter (DVM) to measure volt-
age between pins 14 and 19 of the ABS har-
ness connector at the EBCM.
3. Have an assistant step on the brake pedal.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 13Go to Step 12
Page 1132 of 2643
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 51
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Diagnostic Aids
DTC C0245 may be set by running the scan tool auto test
if the throttle angle readings are not updating while in the
data list mode. If this is the case, clear the DTCs, discon-
nect the scan tool, and road test the vehicle to at least 12
km/h (7 mph) to see if the DTC resets.
Check the toothed wheels for any large grooves, gouges,
marks, etc. that might influence the tooth’s signal at the
wheel speed sensor. Also check for a buildup of foreignmaterial in the gaps between teeth in the toothed wheel,
this material may cause this malfunction.
A badly worn hub/bearing assembly may cause this mal-
function. The wheel speed sensor–to–toothed wheel air
gap may change excessively due to bearing play.
If an improper rear hub assembly or front outer constant
velocity joint is installed, one with a toothed wheel contain-
ing the incorrect number of teeth, this DTC can set. Be
sure that the front and the rear toothed wheel have 47 and
29 teeth.
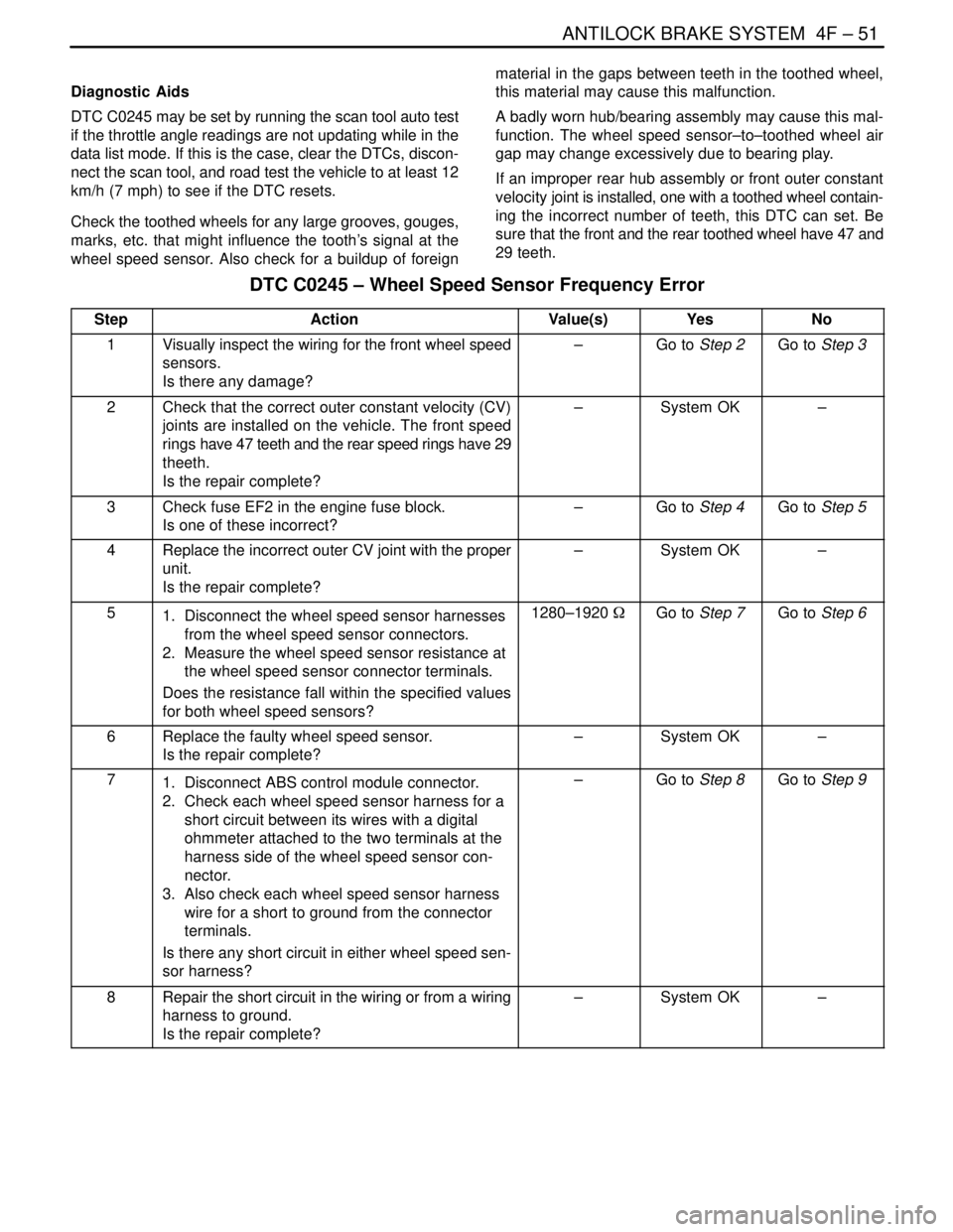
DTC C0245 – Wheel Speed Sensor Frequency Error
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Visually inspect the wiring for the front wheel speed
sensors.
Is there any damage?–Go to Step 2Go to Step 3
2Check that the correct outer constant velocity (CV)
joints are installed on the vehicle. The front speed
rings have 47 teeth and the rear speed rings have 29
theeth.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
3Check fuse EF2 in the engine fuse block.
Is one of these incorrect?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Replace the incorrect outer CV joint with the proper
unit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
51. Disconnect the wheel speed sensor harnesses
from the wheel speed sensor connectors.
2. Measure the wheel speed sensor resistance at
the wheel speed sensor connector terminals.
Does the resistance fall within the specified values
for both wheel speed sensors?1280–1920 WGo to Step 7Go to Step 6
6Replace the faulty wheel speed sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
71. Disconnect ABS control module connector.
2. Check each wheel speed sensor harness for a
short circuit between its wires with a digital
ohmmeter attached to the two terminals at the
harness side of the wheel speed sensor con-
nector.
3. Also check each wheel speed sensor harness
wire for a short to ground from the connector
terminals.
Is there any short circuit in either wheel speed sen-
sor harness?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
8Repair the short circuit in the wiring or from a wiring
harness to ground.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 1138 of 2643
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 57
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
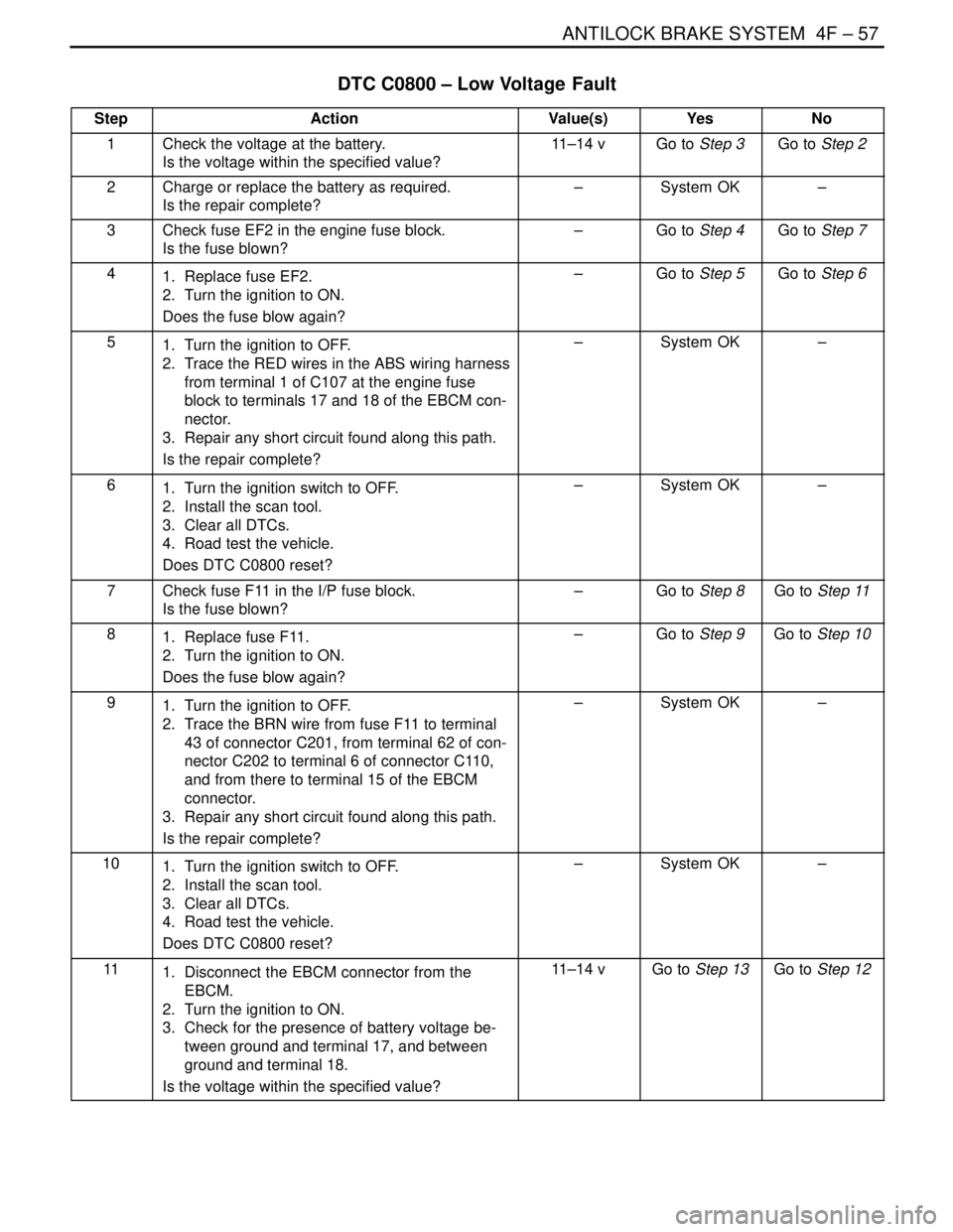
DTC C0800 – Low Voltage Fault
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Check the voltage at the battery.
Is the voltage within the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 3Go to Step 2
2Charge or replace the battery as required.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
3Check fuse EF2 in the engine fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 7
41. Replace fuse EF2.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
Does the fuse blow again?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
51. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Trace the RED wires in the ABS wiring harness
from terminal 1 of C107 at the engine fuse
block to terminals 17 and 18 of the EBCM con-
nector.
3. Repair any short circuit found along this path.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
61. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Install the scan tool.
3. Clear all DTCs.
4. Road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0800 reset?–System OK–
7Check fuse F11 in the I/P fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 11
81. Replace fuse F11.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
Does the fuse blow again?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
91. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Trace the BRN wire from fuse F11 to terminal
43 of connector C201, from terminal 62 of con-
nector C202 to terminal 6 of connector C110,
and from there to terminal 15 of the EBCM
connector.
3. Repair any short circuit found along this path.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
101. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Install the scan tool.
3. Clear all DTCs.
4. Road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0800 reset?–System OK–
111. Disconnect the EBCM connector from the
EBCM.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
3. Check for the presence of battery voltage be-
tween ground and terminal 17, and between
ground and terminal 18.
Is the voltage within the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 13Go to Step 12
Page 1139 of 2643
4F – 58IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
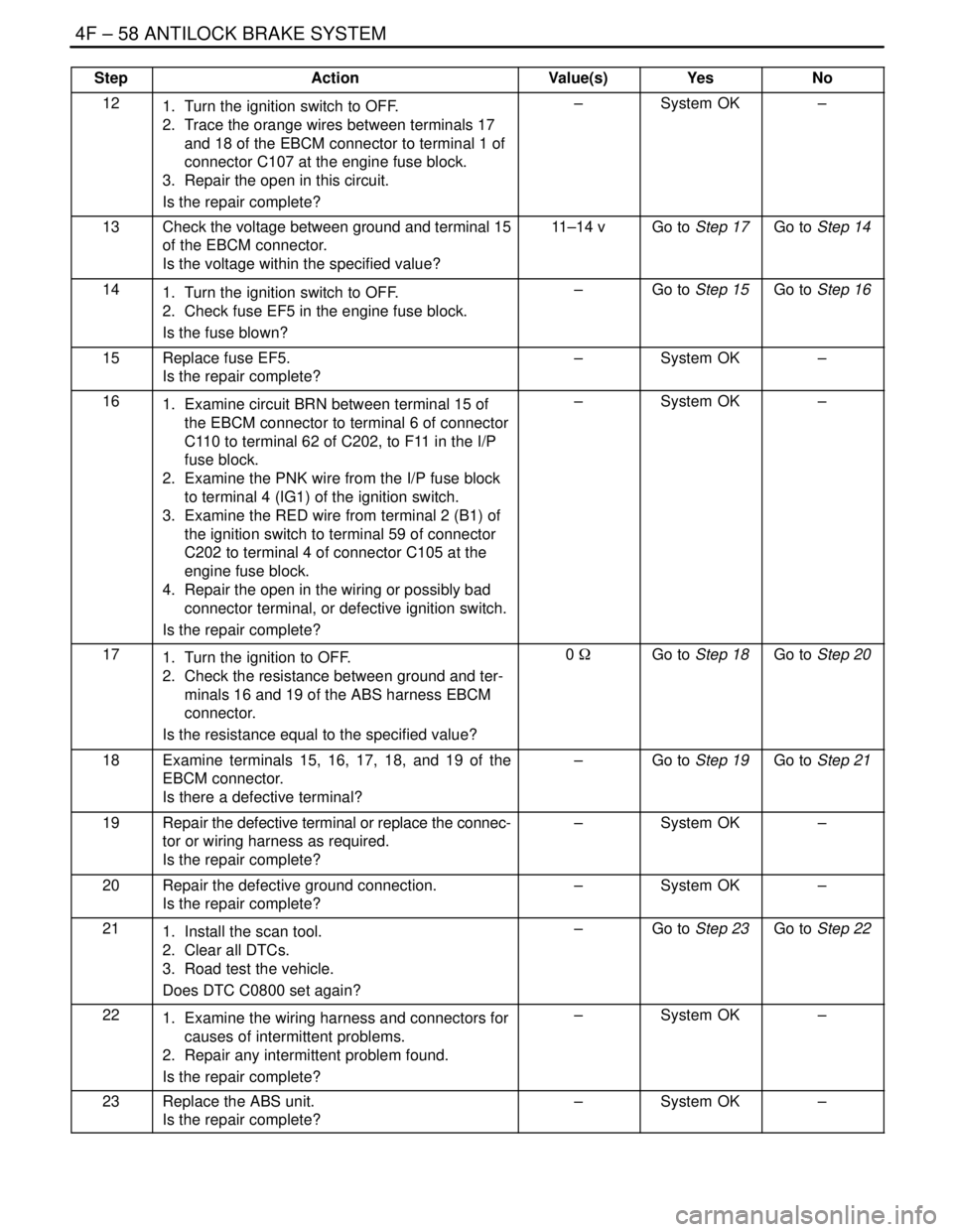
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
121. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Trace the orange wires between terminals 17
and 18 of the EBCM connector to terminal 1 of
connector C107 at the engine fuse block.
3. Repair the open in this circuit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
13Check the voltage between ground and terminal 15
of the EBCM connector.
Is the voltage within the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 17Go to Step 14
141. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Check fuse EF5 in the engine fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 16
15Replace fuse EF5.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
161. Examine circuit BRN between terminal 15 of
the EBCM connector to terminal 6 of connector
C110 to terminal 62 of C202, to F11 in the I/P
fuse block.
2. Examine the PNK wire from the I/P fuse block
to terminal 4 (IG1) of the ignition switch.
3. Examine the RED wire from terminal 2 (B1) of
the ignition switch to terminal 59 of connector
C202 to terminal 4 of connector C105 at the
engine fuse block.
4. Repair the open in the wiring or possibly bad
connector terminal, or defective ignition switch.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
171. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Check the resistance between ground and ter-
minals 16 and 19 of the ABS harness EBCM
connector.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?0 WGo to Step 18Go to Step 20
18Examine terminals 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19 of the
EBCM connector.
Is there a defective terminal?–Go to Step 19Go to Step 21
19Repair the defective terminal or replace the connec-
tor or wiring harness as required.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
20Repair the defective ground connection.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
211. Install the scan tool.
2. Clear all DTCs.
3. Road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0800 set again?–Go to Step 23Go to Step 22
221. Examine the wiring harness and connectors for
causes of intermittent problems.
2. Repair any intermittent problem found.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
23Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 1143 of 2643
4F – 62IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
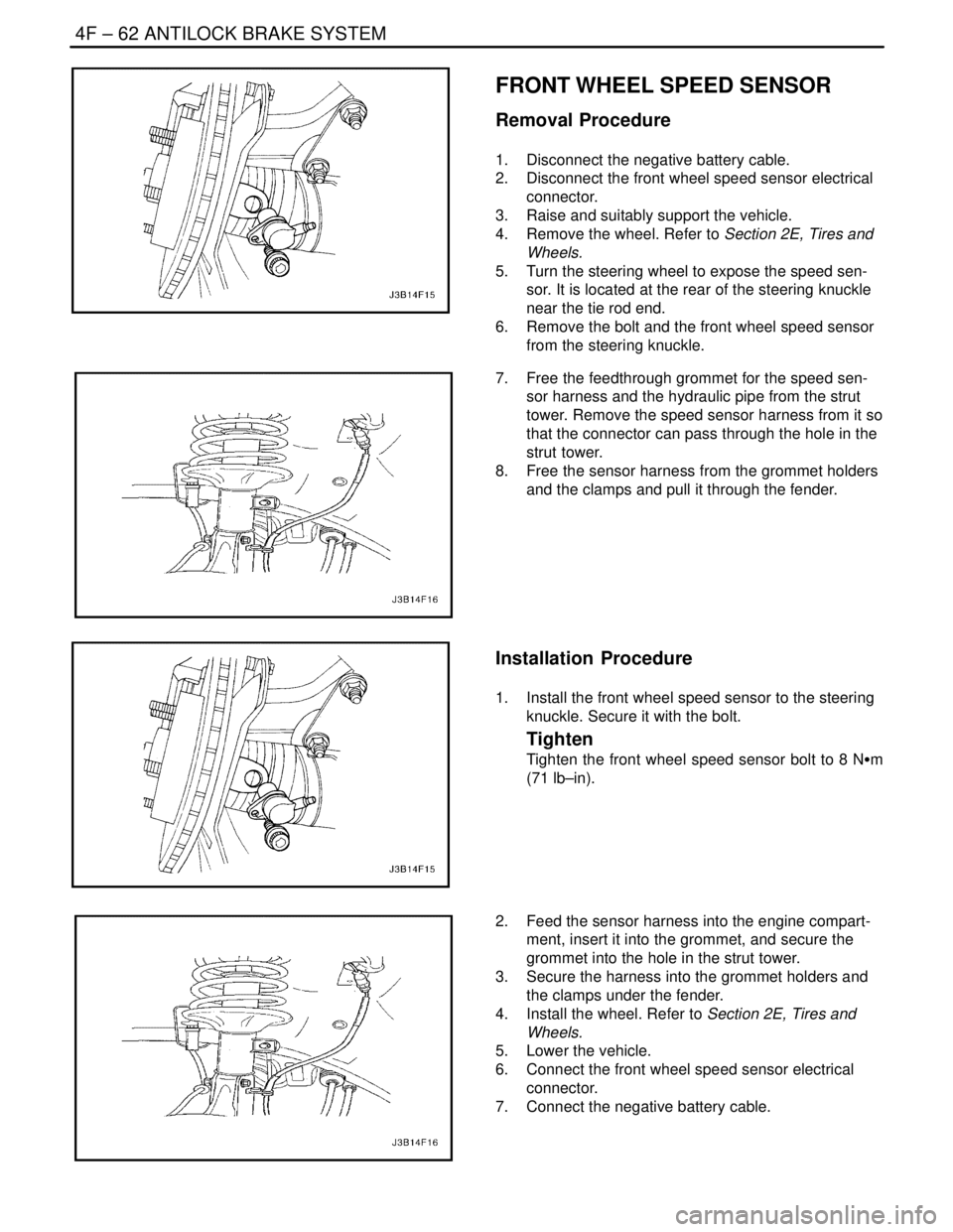
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the front wheel speed sensor electrical
connector.
3. Raise and suitably support the vehicle.
4. Remove the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
5. Turn the steering wheel to expose the speed sen-
sor. It is located at the rear of the steering knuckle
near the tie rod end.
6. Remove the bolt and the front wheel speed sensor
from the steering knuckle.
7. Free the feedthrough grommet for the speed sen-
sor harness and the hydraulic pipe from the strut
tower. Remove the speed sensor harness from it so
that the connector can pass through the hole in the
strut tower.
8. Free the sensor harness from the grommet holders
and the clamps and pull it through the fender.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the front wheel speed sensor to the steering
knuckle. Secure it with the bolt.
Tighten
Tighten the front wheel speed sensor bolt to 8 NSm
(71 lb–in).
2. Feed the sensor harness into the engine compart-
ment, insert it into the grommet, and secure the
grommet into the hole in the strut tower.
3. Secure the harness into the grommet holders and
the clamps under the fender.
4. Install the wheel. Refer to Section 2E, Tires and
Wheels.
5. Lower the vehicle.
6. Connect the front wheel speed sensor electrical
connector.
7. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 1152 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 71
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
TIRES AND ABS/EBD
Replacement Tires
Tire size is important for proper performance of the ABS
system. Replacement tires should be the same size, load
range, and construction as the original tires. Replace tires
in axle sets and only with tires of the same tire perfor-
mance criteria (TPC) specification number. Use of any
other size or type may seriously affect the ABS operation.
TIRES AND ABS/EBD
Notice : There is no serviceable or removable EEPROM.
The EBCM must be replaced as an assembly.
The EBCM is attached to the hydraulic unit in the engine
compartment. The controlling element of ABS 5.3 is a mi-
croprocessor–based EBCM. Inputs to the system include
the four wheel speed sensors, the stoplamp switch, the
ignition switch, and the unswitched battery voltage. There
is an output to a bi–directional serial data link, located in
pin K of Data Link Connector (DLC) for service diagnostic
tools and assembly plant testing.
The EBCM monitors the speed of each wheel. If any wheel
begins to approach lockup and the brake switch is closed
(brake pedal depressed), the EBCM controls the sole-
noids to reduce brake pressure to the wheel approaching
lockup. Once the wheel regains traction, brake pressure
is increased until the wheel again begins to approach lock-
up. This cycle repeats until either the vehicle comes to a
stop, the brake pedal is released, or no wheels approach
lockup.
Additionally, the EBCM monitors itself, each input (except
the serial data link), and each output for proper operation.
If it detects any system malfunction, the EBCM will store
a DTC in nonvolatile memory (EEPROM) (DTCs will not
disappear if the battery is disconnected). Refer to ”Self
Diagnostics” in this section for more detailed information.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
The front wheel speed sensors are of a variable reluctance
type. Each sensor is attached to the steering knuckle,
close to a toothed ring. The result, as teeth pass by the
sensor, is an AC voltage with a frequency proportional to
the speed of the wheel. The magnitude of the voltage and
frequency increase with increasing speed. The sensor is
not repairable, nor is the air gap adjustable.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
RINGS
The toothed ring mentioned above is pressed onto the
wheel–side (outer) constant velocity joint. Each ring con-
tains 47 equally spaced teeth. Exercise care during ser-
vice procedures to avoid prying or contacting this ring. Ex-cessive contact may cause damage to one or more teeth.
If the ring is damaged, the wheel–side constant velocity
joint must be replaced.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR AND
RINGS
The rear wheel speed sensors operate in the same man-
ner as the front wheel speed sensors. They incorporate a
length of flexible harness with the connector attached to
the end of the harness. The rear wheel speed rings are in-
corporated into the hub assemblies and cannot be re-
placed separately, but require replacement of the rear
hub/bearing assembly.
VALUE RELAY AND PUMP MOTOR
RELAY
The valve relay and the motor pump relay are located in-
side the electronic brake control module (EBCM) and are
not replaceable. If one should fail, replace the EBCM.
WIRING HARNESS
The wiring harness is the mechanism by which the elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM) is electrically con-
nected to power and to ground, to the wheel speed sen-
sors, the fuses, the switches, the indicators, and the serial
communications port. The components, considered part
of the wiring harness, are the wires that provide electrical
interconnection, and connectors (terminals, pins, con-
tacts, or lugs) that provide an electrical/mechanical inter-
face from the wire to a system component.
INDICATORS
The electronic brake control module (EBCM) continuously
monitors itself and the other ABS components. If the
EBCM detects a problem with the system, the amber ABS
indicator will light continuously to alert the driver to the
problem. An illuminated ABS indicator indicates that the
ABS system has detected a problem that affects the op-
eration of ABS. No antilock braking will be available. Nor-
mal, non–antilock brake performance will remain. In order
to regain ABS braking ability, the ABS must be serviced.
The red BRAKE indicator will be illuminated when the sys-
tem detects a low brake fluid level in the master cylinder
or when the parking brake switch is closed (the parking
brake is engaged) or EBD system is diabled.
WARNING : EBD INDICATOR LAMP WIRING IS CON-
NECTED TO THE PARKING BRAKE LAMP. IF THE
PARKING BRAKE LAMP IS TURNED ON WHEN YOU
DRIVING, CHECKING ON WHETHER THE PARKING
BRAKE LEVER IS ENAGED OR THE BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL IS LOW. IF THE SYSTEM HAS NO PROBLEM,
THE EBD SYSTEM IS WORKING IMPROPERLY. THE
EBD SYSTEM MUST BE SERVICED.
Page 1162 of 2643

SECTION 5
ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAMS
CONTENTS
1. STARTING & CHARGING SYSTEM5–8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) BATTERY, IGNITION SWITCH, STARTER MOTOR, GENERATOR & PNP SWITCH CIRCUIT 5–8. . . . . . . . . .
2. ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE) : MR–140 5–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) BATTERY POWER SUPPLY, GROUND, EI SYSTEM & CKP SENSOR CIRCUIT 5–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2) FUEL PUMP, INJECTOR & HEATED O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT 5–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3) IAC, SENSOR(MAP, ECT, TP, KNOCK, ACP & ROUGH ROAD) & LEGR CIRCUIT 5–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4) EVAP CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID, CMP SENSOR, CLUSTER & VSS CIRCUIT 5–16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5) CLUSTER, FUEL PUMP & TCM CIRCUIT 5–18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6) DLC, MIL LAMP & IMMOBILIZER CONTROL CIRCUIT 5–20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE) : HV–240 5–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) BATTERY POWER SUPPLY, GROUND, EI SYSTEM & CKP SENSOR CIRCUIT 5–22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2) FUEL PUMP, INJECTOR & O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT 5–24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3) IAC, SENSOR(MAP, ECT, TP, IAT, KNOCK & ACP) & EGR VALVE CIRCUIT 5–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4) EVAP CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID, CMP SENSOR, CLUSTER & VSS CIRCUIT 5–28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5) CLUSTER, FUEL PUMP & TCM CIRCUIT 5–30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6) DLC, MIL LAMP, IMMOBILIZER CONTROL & RON SWITCH CIRCUIT 5–32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 1163 of 2643

ELECTRICAL WIRING DIAGRAMSW5–3
4. ECM (ENGINE CONTROL MODULE) : SIRIUS D4 5–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) BATTERY POWER SUPPLY, GROUND, EI SYSTEM & CKP SENSOR CIRCUIT 5–34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2) FUEL PUMP, INJECTOR, FUEL CONNECTOR & CMP SENSOR CIRCUIT 5–36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3) MTIA, SENSOR(ECT, KNOCK, IAT, MAP, ACP & HO2S) & POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
CIRCUIT : EOBD5–38 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4) MTIA, SENSOR(ECT, KNOCK, IAT, MAP, ACP & O2) & POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
CIRCUIT : NON EOBD5–40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5) EEGR VALVE, VR SENSOR, CLUSTER & FUEL PUMP CIRCUIT : EOBD 5–42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6) EGR VALVE, CLUSTER & FUEL PUMP CIRCUIT: NON EOBD 5–44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7) EVAP CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID, VGIS, CLUSTER, VSS, TCM & RON SWITCH CIRCUIT 5–46. . . . . . .
8) DLC, MIL LAMP & IMMOBILIZER CONTROL CIRCUIT 5–48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5. TCM (TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE) : MR–140/HV–240 5–50. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) POWER SUPPLY, GROUND, PNP SWITCH, BRAKE SWITCH & SOLENOID VALVE CIRCUIT 5–50. . . . . . . .
2) SENSOR(INPUT SPEED,OUTPUT SPEED, TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMP.), CLUSTER, DLC, ECM &
HOLD MODE SWITCH CIRCUIT5–52 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3) PNP SWITCH & CLUSTER CIRCUIT 5–54. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6. TCM (TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE) : SIRIUS D4 5–56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) POWER SUPPLY, GROUND, PNP SWITCH, CLUSTER & ECM CIRCUIT : NOTCH BACK 5–56. . . . . . . . . . . .
2) POWER SUPPLY, GROUND, PNP SWITCH, CLUSTER & ECM CIRCUIT : HATCH BACK 5–58. . . . . . . . . . . .
3) BRAKE SWITCH, BTSI SOLENOID, ISS SENSOR & TRANSAXLE CIRCUIT 5–60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4) HOLD MODE SWITCH, VSS & DLC CIRCUIT 5–62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7. AIR CONDITIONER5–64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1) AIR CONDITIONER CONTROL SWITCH, BLOWER MOTOR RESISTER & BLOWER MOTOR
CIRCUIT5–64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2) AIR CONDITIONER CONTROL, INTAKE MOTOR SWITCH & AIR CONDITIONER COMPRESSOR
CIRCUIT5–66 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .