2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 1837 of 2585
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil (Fig.
310), an AC voltage is generated and sent to the
PCM/TCM. The PCM/TCM interprets this informa-
tion as input shaft rpm.
The PCM/TCM compares the input speed signal
with output speed signal to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The PCM/TCM also compares the input speed sig-
nal and the engine speed signal to determine the fol-
lowing:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) If necessary, disconnect and cap off transmis-
sion oil cooler lines.
(3) Disconnect input speed sensor connector.
(4) Unscrew and remove input speed sensor (Fig.
311).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 312) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position.
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector.
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 310 Sensor Relation to Input Clutch Hub
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - TRANSAXLE CASE
3 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB
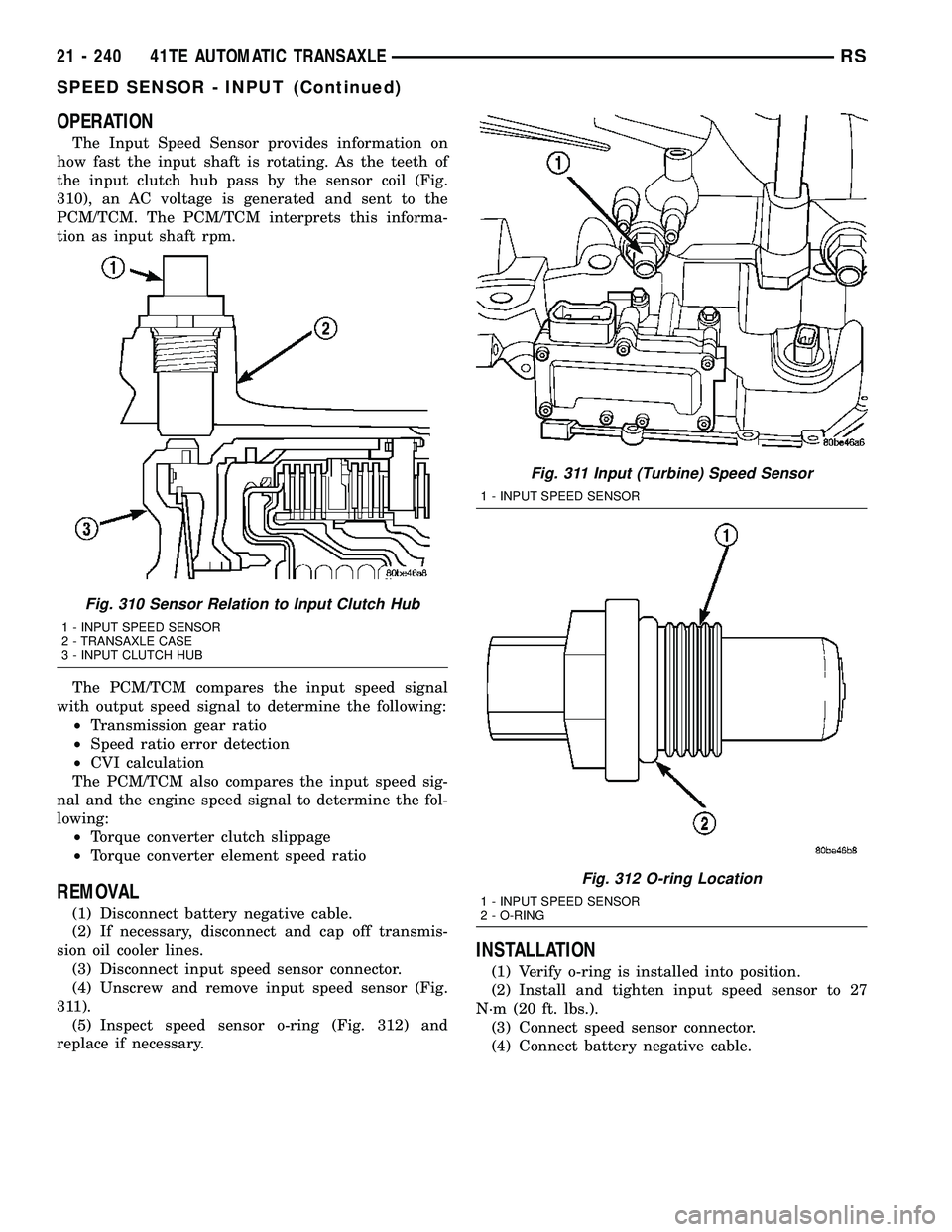
Fig. 311 Input (Turbine) Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
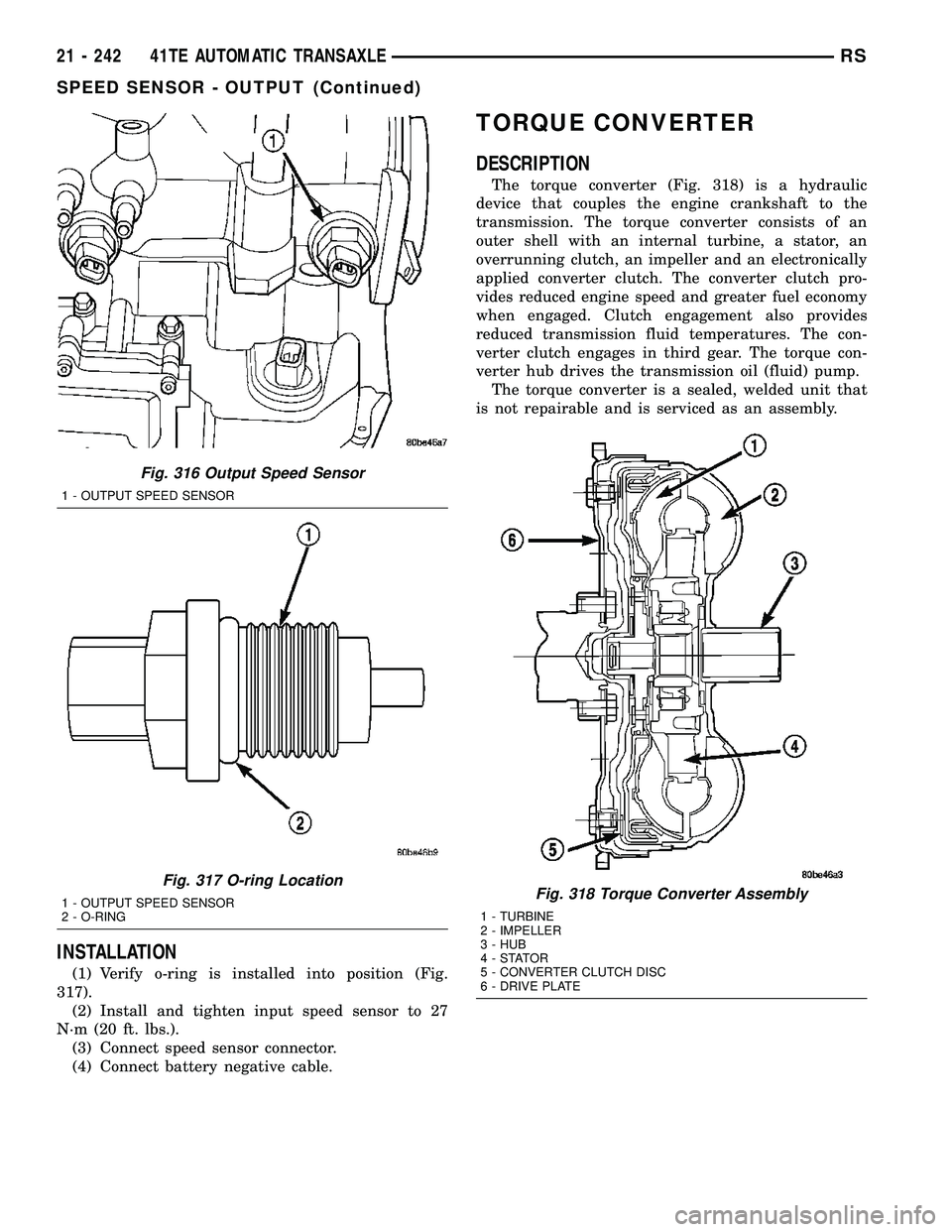
Fig. 312 O-ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
21 - 240 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT (Continued)
Page 1839 of 2585
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
317).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector.
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 318) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 316 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 317 O-ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RINGFig. 318 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
6 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 242 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT (Continued)
Page 1840 of 2585
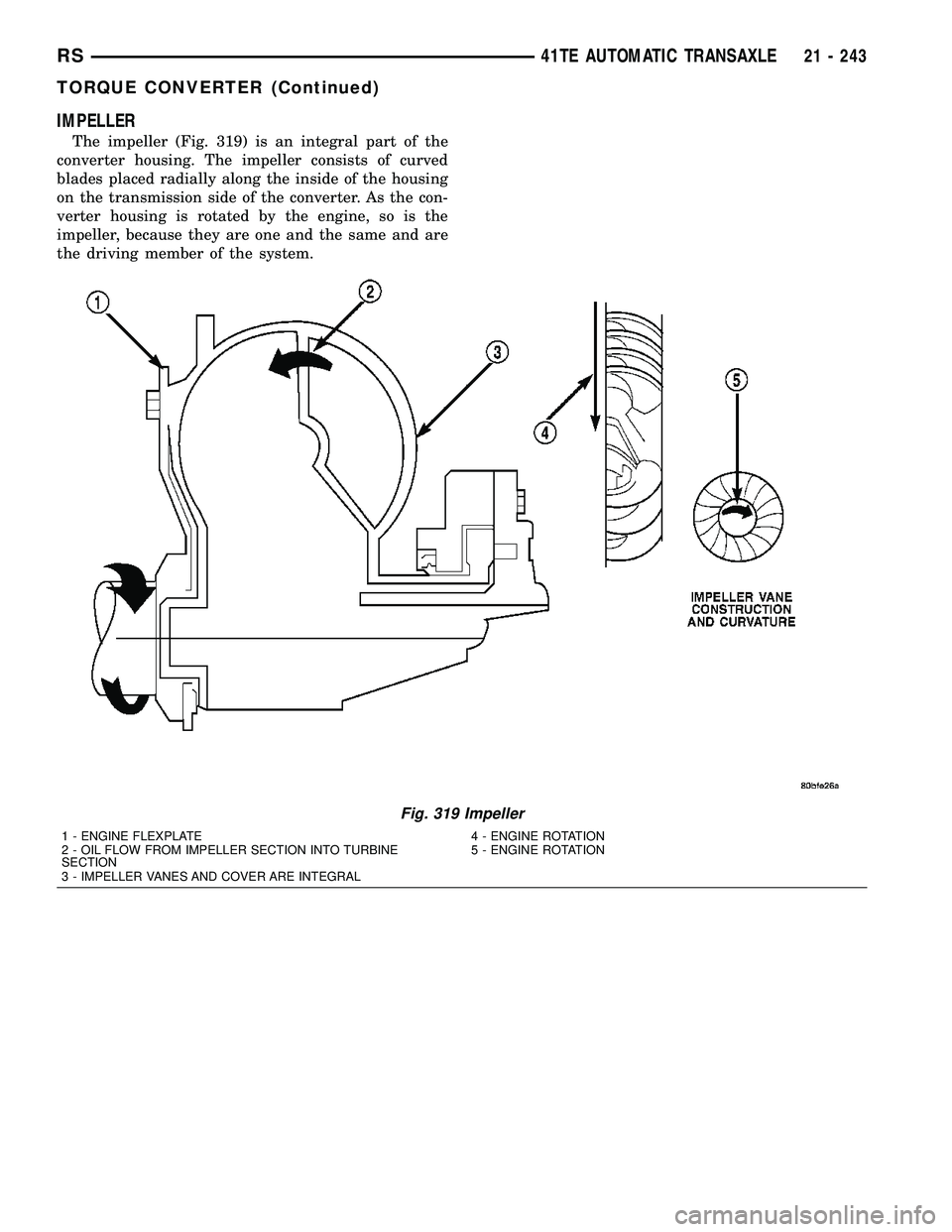
IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 319) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving member of the system.
Fig. 319 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 243
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1841 of 2585
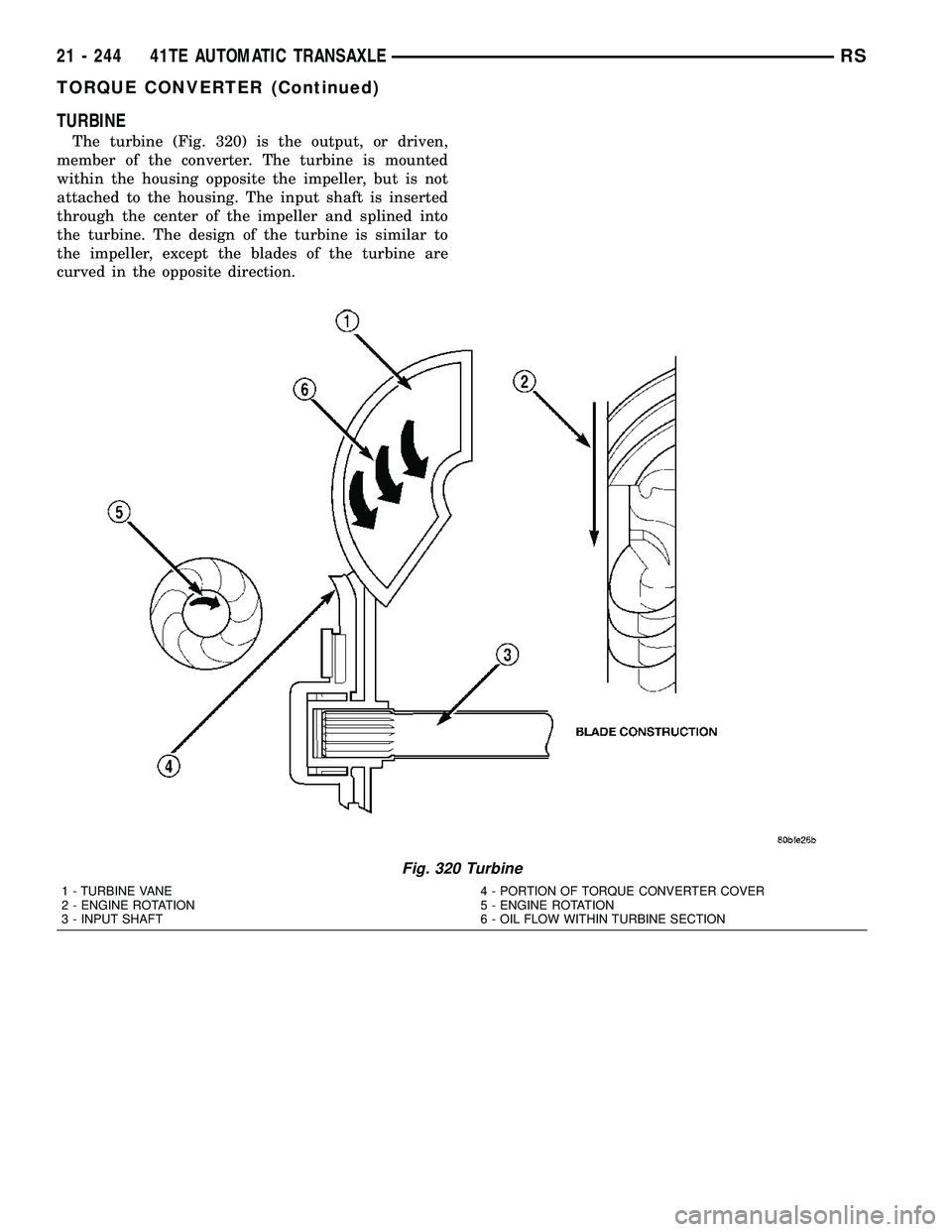
TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 320) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 320 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE
2 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
5 - ENGINE ROTATION
6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
21 - 244 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1842 of 2585
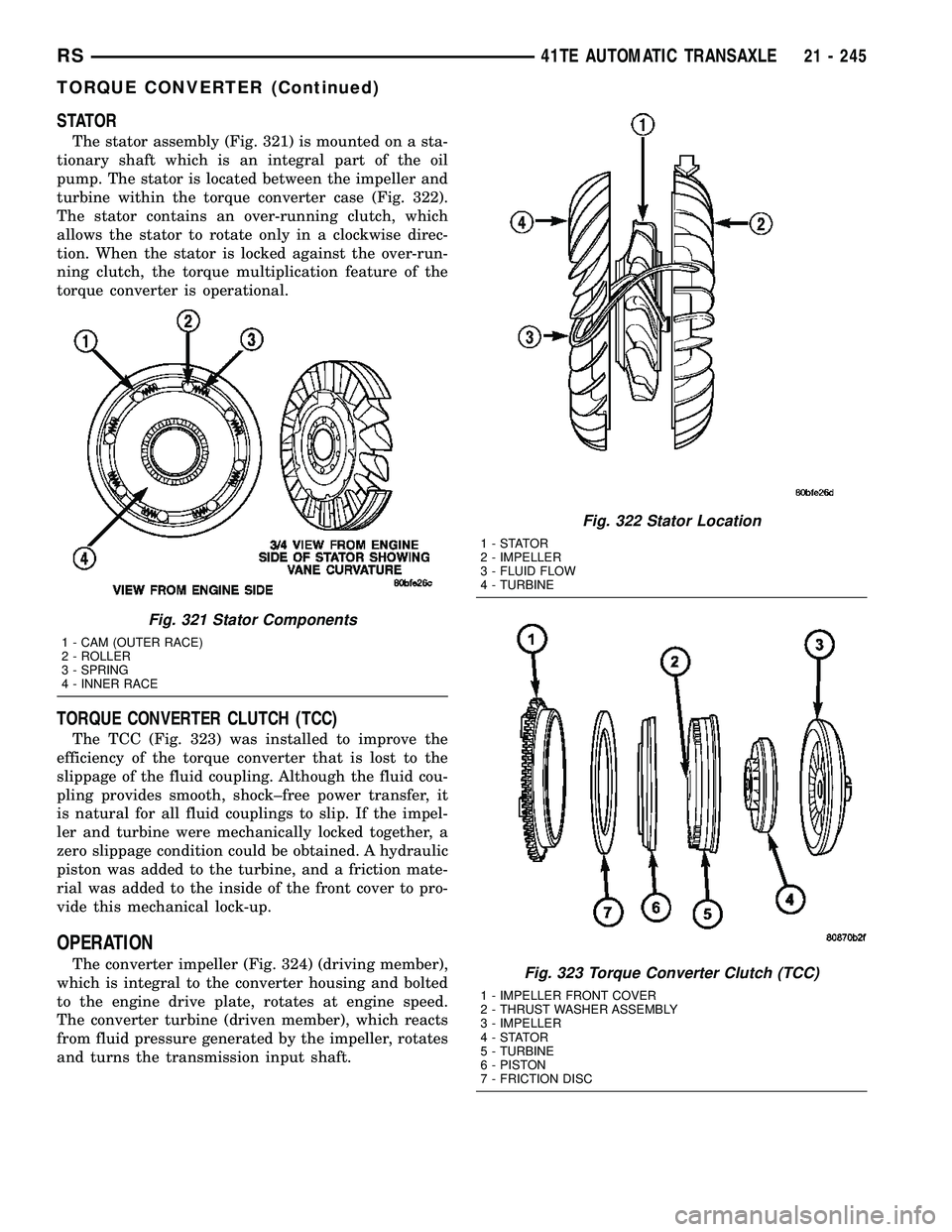
STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 321) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 322).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 323) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock±free power transfer, it
is natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impel-
ler and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston was added to the turbine, and a friction mate-
rial was added to the inside of the front cover to pro-
vide this mechanical lock-up.
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 324) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
Fig. 321 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 322 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 323 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 245
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1843 of 2585
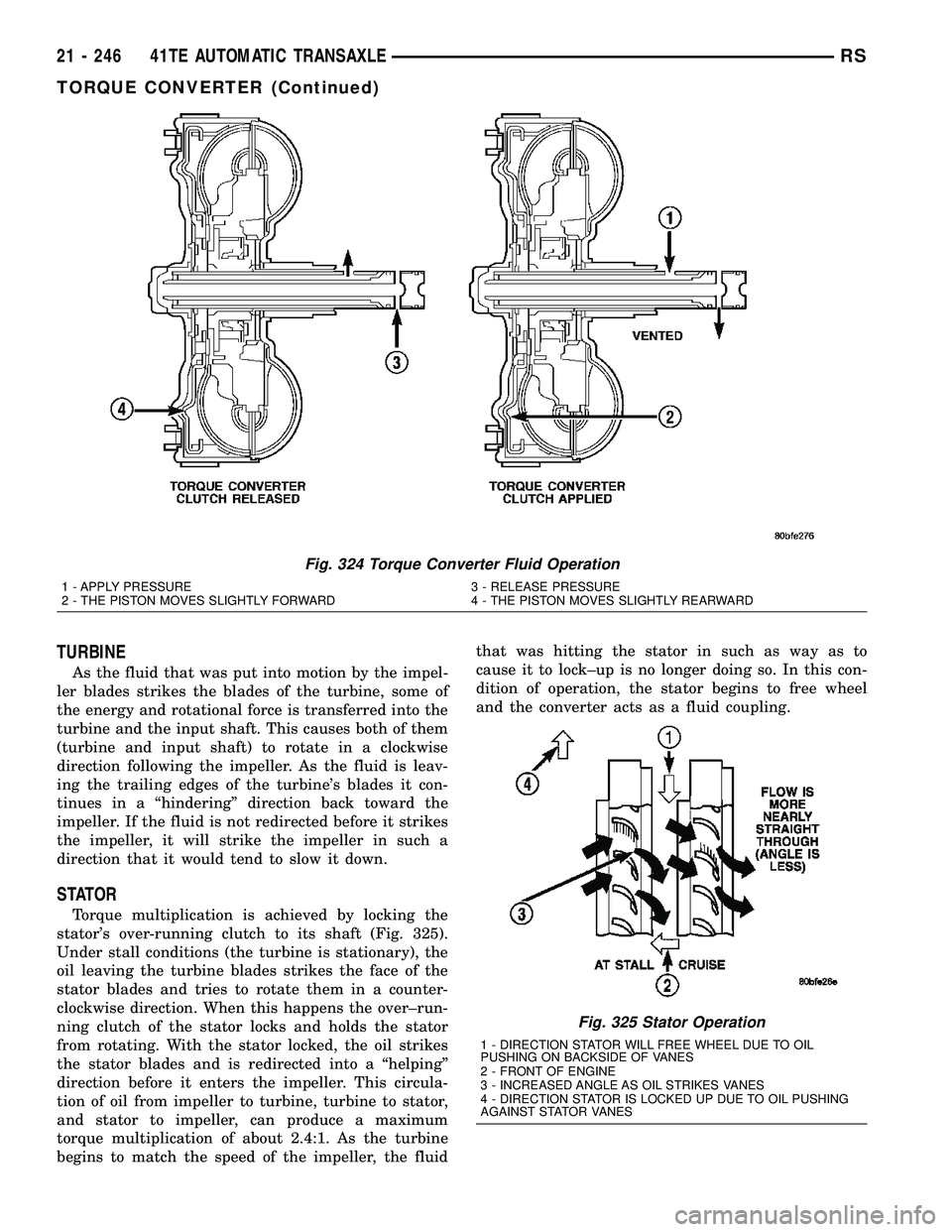
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 325).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluidthat was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
Fig. 324 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
Fig. 325 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
21 - 246 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1844 of 2585
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.
(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 326). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 327) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
Fig. 326 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 247
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1845 of 2585
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the PCM/TCM, and is used to supply power to the
solenoid pack when the transmission is in normal
operating mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is
supplied to the solenoid pack and the transmission is
in ªlimp-inº mode. After a controller reset (ignition
key turned to the ªrunº position or after cranking
engine), the PCM/TCM energizes the relay. Prior to
this, the PCM/TCM verifies that the contacts are
open by checking for no voltage at the switched bat-
tery terminals. After this is verified, the voltage at
the solenoid pack pressure switches is checked. After
the relay is energized, the PCM/TCM monitors the
terminals to verify that the voltage is greater than 3
volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle and
can only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 328).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 329).
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 328)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combination
of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM inter-
prets this information and determines the appropriate
transaxle gear position and shift schedule.
Fig. 327 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 328 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 329 Transmission Temperature Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - TEMPERATURE SENSOR
21 - 248 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY (Continued)