2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER fuel tank removal
[x] Cancel search: fuel tank removalPage 2507 of 2585

CABIN HEATER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CABIN HEATER
DESCRIPTION........................112
OPERATION
OPERATION - MANUAL TEMPERATURE
CONTROL SYSTEM...................112
OPERATION - AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE
CONTROL SYSTEM...................112
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIESEL
SUPPLEMENTAL CABIN HEATER........113
AIR INTAKE PIPE
REMOVAL............................113
INSTALLATION........................114
EXHAUST TUBE
REMOVAL............................114
INSTALLATION........................115FUEL DOSING PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................115
OPERATION..........................115
REMOVAL............................115
INSTALLATION........................116
FUEL LINE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLEANING.....117
REMOVAL............................117
INSTALLATION........................118
HEATER UNIT
REMOVAL............................118
INSTALLATION........................119
SUPPLEMENTAL DIESEL HEATER WIRING
REMOVAL............................119
INSTALLATION........................119
CABIN HEATER
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the diesel engine are also
equipped with a supplemental cabin heater. This
cabin heater is mounted under the vehicle and oper-
ates similar to an oil fired furnace. The heater burns
small amounts of fuel to provide additional heat to
the coolant. Coolant is routed from the engine, to the
supplemental cabin heater and then to the front
heater core. This provides additional heat to the pas-
senger compartment. The supplemental cabin heater
system is interfaced to the vehicles on-board com-
puter systems and DRBIIItdiagnostics.
The supplemental cabin heater has an electronic
control module that monitors the heat output of the
heater. The cabin heater operates at full load (5 kW),
half load or idle mode (no additional heat) depending
on engine coolant temperature.
OPERATION
OPERATION - MANUAL TEMPERATURE
CONTROL SYSTEM
The supplemental cabin heater is activated via the
temperature slide control or knob on the A/C-heater
control when equipped with the manual temperature
control (MTC) system. If the slide control or knob is
moved to or above the upper set point the cabin
heater is activated. The cabin heater can operate in a
full or partial load range as well as an idle mode alldependent on the engine coolant temperature. The
cabin heater will also turn off if the A/C-heater tem-
perature control is lowered to less than the lower set
point. The cabin heater can take up to three minutes
to completely shut down when either the heater tem-
perature is set below the lower set point or the vehi-
cle ignition is shut down.
NOTE: Do not apply a strong vacuum source such
as a garage ventilation system directly on the sup-
plemental cabin heater exhaust line. Too strong of a
vacuum can prevent the supplemental cabin heater
from starting. If required, place the vacuum source
at least 75 mm (3 in.) away from the exhaust line.
The supplemental cabin heater only operates when
the engine is running, the mileage exceeds 8 kilome-
ter (5 mph) and the fuel tank volume exceeds 1/8 of a
tank. The supplemental heater control module moni-
tors blower speed and combustion during its start-up.
The cabin heater should operate if the coolant tem-
perature is below 40É C (104É F).
OPERATION - AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE
CONTROL SYSTEM
The automatic temperature control (ATC) system
will activate the supplemental cabin heater based on
engine coolant temperature and interior component
settings. The cabin heater can operate in a full or
partial load range as well as an idle mode all depen-
dent on the engine coolant temperature. The cabin
heater will also turn off if the A/C-heater tempera-
ture control is lowered to less than the lower set
24 - 112 CABIN HEATERRS
Page 2508 of 2585
point. The cabin heater can take up to three minutes
to completely shut down when either the heater tem-
perature is set below the lower set point or the vehi-
cle ignition is shut down.
NOTE: Do not apply a strong vacuum source such
as a garage ventilation system directly on the sup-
plemental cabin heater exhaust line. Too strong of a
vacuum can prevent the supplemental cabin heater
from starting. If required, place the vacuum source
at least 75 mm (3 in.) away from the exhaust line.
The supplemental cabin heater only operates when
the engine is running, the mileage exceeds 8 kilome-ter (5 mph) and the fuel tank volume exceeds 1/8 of a
tank. The supplemental heater control module moni-
tors blower speed and combustion during its start-up.
The cabin heater should operate if the coolant tem-
perature is below 40É C (104É F).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIESEL
SUPPLEMENTAL CABIN HEATER
Refer to the Symptoms Diagnosis table for basic
checks of the diesel fueled supplemental cabin heater.
SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS
Symptom Possible Causes
Smell of diesel fuel. Check cabin heater system integration in vehicle's fuel system. Check
fuel lines for leakage, kinks or obstructions. If OK, Inspect the inlet
muffler, drain as necessary. Re-test the cabin heater and re-inspect.
Inspect the exhaust tube and cabin heater for the presence of external
fuel. If presence of external fuel is observed on the heater unit or in the
exhaust tube or after draining and testing. Remove the cabin heater
from vehicle and repair or replace components as required.
Heater does not achieve full load
operation.Check cabin heater operation with DRBIIITscan tool and replace
components as required.
Continuous white smoke from heater
exhaust during combustion operation.Check cabin heater operation with DRBIIITscan tool and replace
components as required. White smoke is typical in extreme weather
conditions.
Heater can not be switched off. Check cabin heater operation with DRBIIITscan tool and replace
components as required.
Heater does not operate. Diagnosis cabin heater control module using the DRBIIITscan tool and
the procedures listed in Vehicle Performance under Cabin Heater
Diagnosis in Group 18.
Loss of coolant (Leakage) or heater
develops smoke during combustion
operation and exhaust has an
extremely sweet smell.Inspect coolant hoses for leakage, kinks or loose hose connection.
Inspect the exhaust tube assembly for continuous flow, if OK there is an
internal heater leak and cabin heater should be inspected and
components should be replaced as required.
Loss of fuel (dripping). Check cabin heater system integration in vehicles fuel system. Check
fuel line connection for leakage. If OK there is an internal leak and
cabin heater should be inspected and replaced as required.
AIR INTAKE PIPE
REMOVAL
NOTE: The air intake tube for the supplemental
cabin heater is part of an assembly that includes
the heater cooling intake and return pipes. If the
cabin heater air intake tube requires removal or
replacement the entire cabin heater assembly will
require removal or replacement.(1) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(2) Remove clamps from the cabin heater tubes at
the lower heater port and the lower EGR connector
which are located under the hood.
(3) Remove the retaining clamp at the cabin
heater air intake muffler connection (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CABIN HEAT-
ER/INLET MUFFLER - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the clamp at the flexible tube to steel
tube connection (Fig. 1).
RSCABIN HEATER24 - 113
CABIN HEATER (Continued)
Page 2510 of 2585
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the flexible exhaust pipe to the cabin
heater. Tighten the mounting clamp securely.
(2) Position the steel exhaust pipe to the flexible
exhaust. Tighten the mounting clamp securely.
(3) Loosely install the three exhaust pipe screws
and adjust pipe placement as required. Tighten the
screws securely.
(4) Install the clamp that secures the steel exhaust
pipe to the flexible exhaust pipe. Tighten the clamp
securely.
(5) Check exhaust end placement of the exhaust
pipe and make any final adjustments.
(6) Lower the vehicle.
FUEL DOSING PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The dosing pump is a combined delivery, dosing
and shut-off system for the fuel supply to the supple-
mental cabin heater from the vehicle fuel tank.
OPERATION
The dosing pump is an electrically operated pump
that receives its operation instructions from the sup-
plemental cabin heater control module. The pump
supplies diesel fuel from the vehicle fuel tank to the
cabin heater.
REMOVAL
NOTE: The dosing pump is serviceable without
removing the component from the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect the rubber hose at the fuel line to
heater fuel pump. Leave the rubber hose on the fuel
line (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CABIN HEATER/FUEL LINE - REMOVAL)
(Fig. 4).
(2) Disconnect the fuel line between the dosing
pump and the cabin heater unit.
NOTE: Position and retain the heater fuel line to
prevent fuel leakage while servicing the dosing
pump.
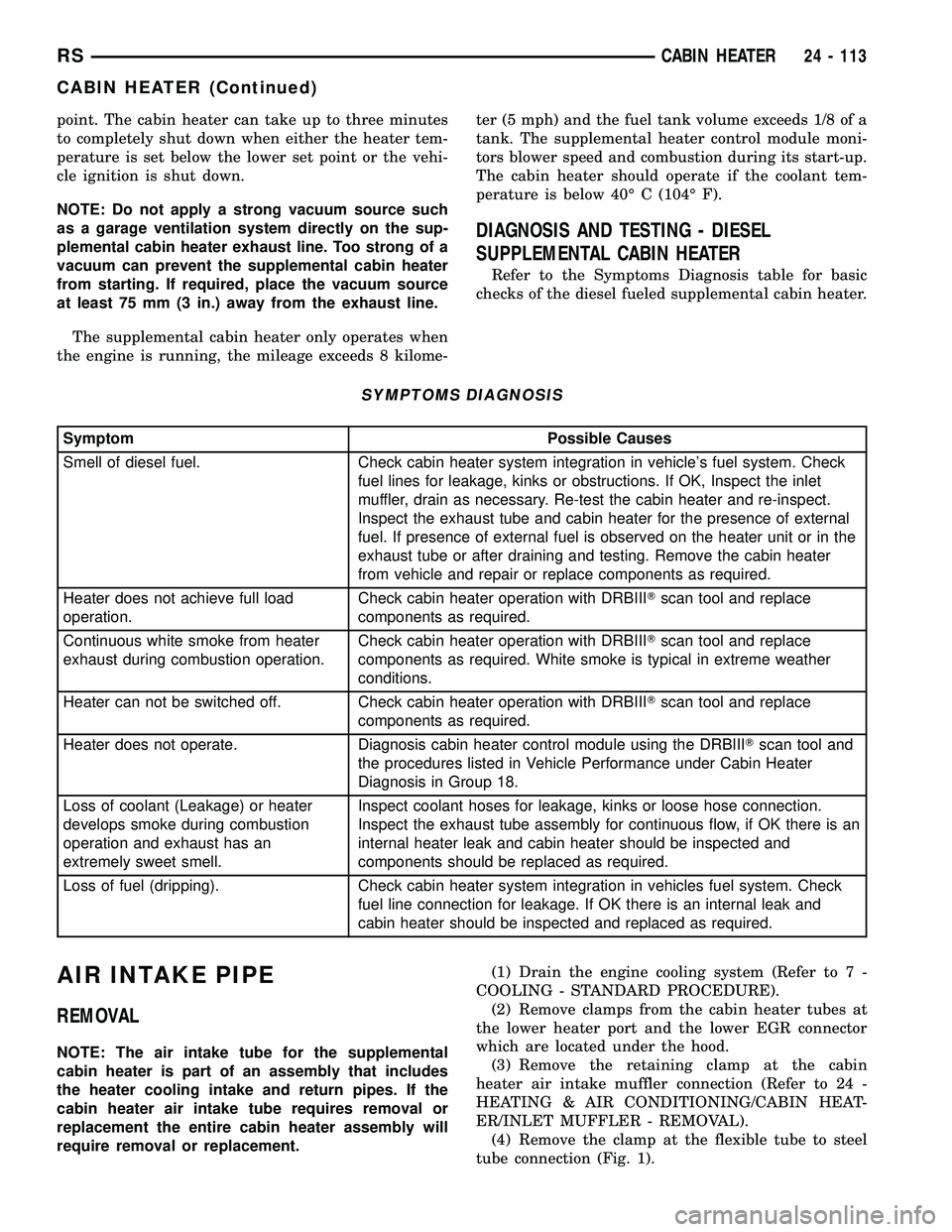
Fig. 3 Cabin Heater Exhaust System
1 - MOUNTING SCREWS (3)
2 - STEEL HEATER EXHAUST PIPE
3 - EXHAUST CLAMP (2)4 - FLEXIBLE HEATER EXHAUST PIPE
5 - CABIN HEATER AND SHIELD
6 - EXHAUST PIPE MOUNTING CLIPS (3) (IF EQUIPPED)
RSCABIN HEATER24 - 115
EXHAUST TUBE (Continued)
Page 2512 of 2585
FUEL LINE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLEANING
(1) Remove the cabin heater fuel line (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CABIN HEAT-
ER/FUEL LINE - REMOVAL).
(2) With the cabin heater fuel line removed from
the vehicle, place a shop cloth on the fuel tank end of
the fuel line to catch any residue, then apply a small
amount of air pressure to the other end of the fuel
line.
(3) Check to see if air pressure is coming from the
tank end of the line. If pressure is flowing unre-
stricted the line is clean.
(4) If the fuel line shows any signs of being
restricted after air pressure is applied, the fuel line
should be replaced.
(5) Install the cabin heater fuel line (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CABIN HEAT-
ER/FUEL LINE - INSTALLATION).
(6) Verify function of the cabin heater.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle. Take note of the
location of the flexible section of the cabin heater
exhaust tube.NOTE: Have an approved fuel holding device ready
to capture any diesel fuel that drains from the fuel
line or cabin heater unit.
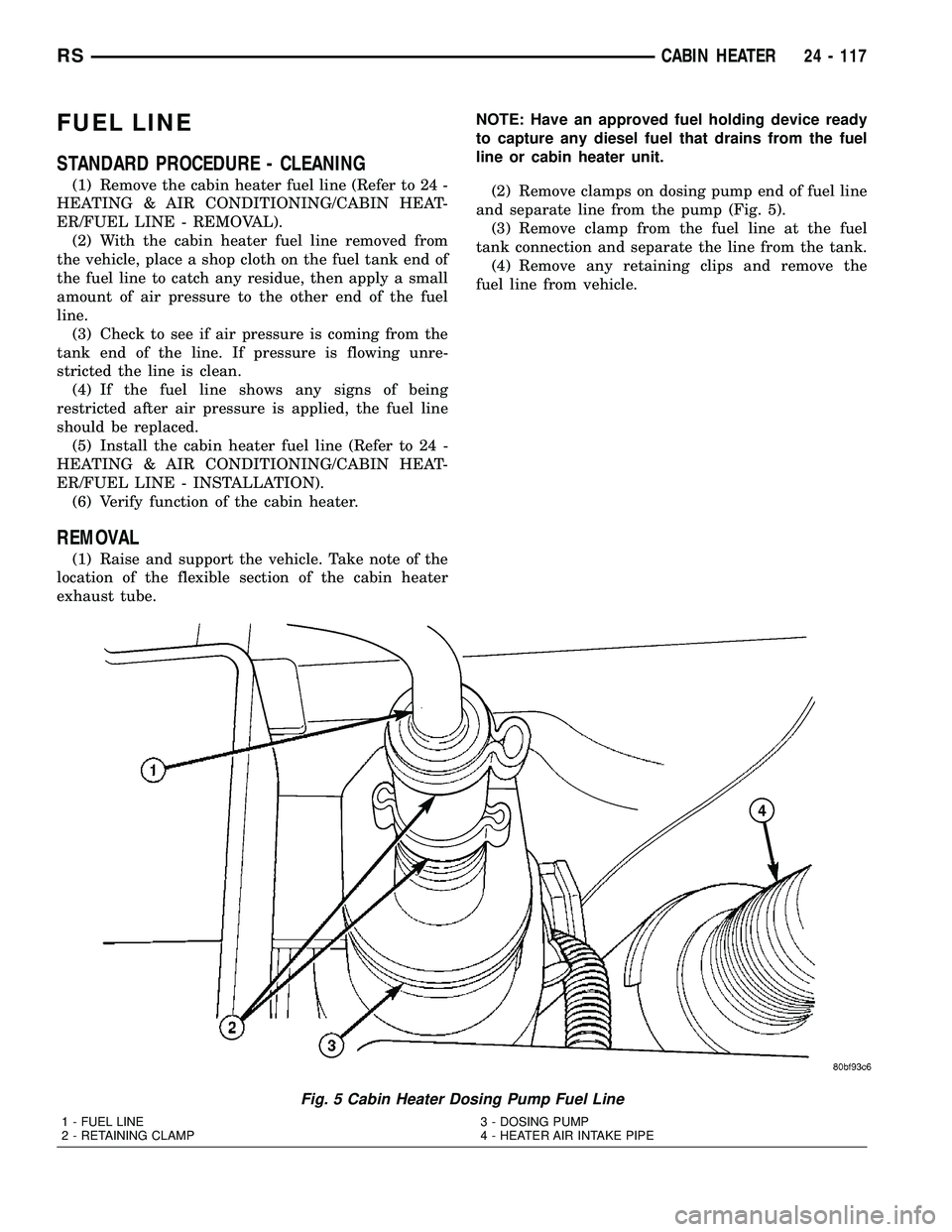
(2) Remove clamps on dosing pump end of fuel line
and separate line from the pump (Fig. 5).
(3) Remove clamp from the fuel line at the fuel
tank connection and separate the line from the tank.
(4) Remove any retaining clips and remove the
fuel line from vehicle.
Fig. 5 Cabin Heater Dosing Pump Fuel Line
1 - FUEL LINE
2 - RETAINING CLAMP3 - DOSING PUMP
4 - HEATER AIR INTAKE PIPE
RSCABIN HEATER24 - 117
Page 2513 of 2585

INSTALLATION
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE THE DIESEL SUP-
PLEMENTAL CABIN HEATER IN AN ENCLOSED
AREA SUCH AS A GARAGE THAT DOES NOT HAVE
EXHAUST VENTILATION FACILITIES. ALWAYS VENT
THE CABIN HEATER EXHAUST WHEN OPERATING
THE CABIN HEATER. ALLOW THE DIESEL SUPPLE-
MENTAL CABIN HEATER TO COOL BEFORE PER-
FORMING ANY SERVICE PROCEDURES TO THE
CABIN HEATER. VERIFY THAT ALL DIESEL SUP-
PLEMENTAL CABIN HEATER FUEL LINES ARE
SECURELY FASTENED TO THEIR RESPECTIVE
COMPONENTS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY SER-
VICE PROCEDURES TO THE CABIN HEATER. FAIL-
URE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTION MAY
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
NOTE: Verify that there is more than 1/8 of a tank of
fuel in the vehicle's fuel tank before performing this
procedure. Add fuel, if necessary.
(1) Install the cabin heater fuel supply line into
vehicle and fuel line retainers.
(2) Install the fuel line connection at the fuel tank
and tighten the connection securely.
(3) Install the fuel line at the dosing pump and
tighten the connection securely.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
NOTE: Failure to prime the dosing pump after drain-
ing the supplemental cabin fuel line will prevent
cabin heater activation during the first attempt to
start the cabin heater. This will also set a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC) in the cabin heater control's
memory. Do not perform the Dosing Pump Priming
procedure if an attempt was made to start the cabin
heater without priming the dosing pump first. This
will put excess fuel in the cabin heater and cause
smoke to emit from the cabin heater exhaust pipe
when cabin heater activation occurs.
(5) Connect the DRBIIItscan tool to the diagnos-
tic link connector.
(6) Turn the ignition to the ON position.
NOTE: Do not activate the dosing pump prime more
than one time. This will put excess fuel in the sup-
plemental cabin heater and cause smoke to emit
from the cabin heater exhaust pipe when cabin
heater activation occurs.
NOTE: A clicking noise heard coming from the dos-
ing pump indicates that the pump is operational.(7) With the DRBIIItscan tool in Cabin Heater,
select System Tests and Dosing Pump Prime. Allow
the dosing pump to run for the full 45 second cycle
time. When the 45 second cycle is complete, press
Page Back on the DRBIIItscan tool key pad to exit
the Dosing Pump Prime. The Dosing Pump Priming
procedure is now complete.
HEATER UNIT
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE THE DIESEL SUP-
PLEMENTAL CABIN HEATER IN AN ENCLOSED
AREA SUCH AS A GARAGE THAT DOES NOT HAVE
EXHAUST VENTILATION FACILITIES. ALWAYS VENT
THE CABIN HEATER EXHAUST WHEN OPERATING
THE CABIN HEATER. ALLOW THE DIESEL SUPPLE-
MENTAL CABIN HEATER TO COOL BEFORE PER-
FORMING ANY SERVICE PROCEDURES TO THE
CABIN HEATER. VERIFY THAT ALL DIESEL SUP-
PLEMENTAL CABIN HEATER FUEL LINES ARE
SECURELY FASTENED TO THEIR RESPECTIVE
COMPONENTS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY SER-
VICE PROCEDURES TO THE CABIN HEATER. FAIL-
URE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTION MAY
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle. Take note of the
location of the flexible section of the cabin heater
exhaust tube.
(2) Drain the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Carefully open one hose to the underbody tube
assembly and drain the remaining coolant. A salvage
hose is a good idea to control the residual coolant, as
flow will occur from both the cabin heater and the
hose and tube assemblies.
(4) Remove the second hose from the underbody
hose and tube assembly.
(5) Loosen the hose and tube assembly from the
toe-board crossmember at two locations.
(6) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
body harness near the toe-board crossmember and
rail.
(7) Remove the wiring harness from the toe-board
crossmember (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/CABIN HEATER/HEATER UNIT -
REMOVAL).
(8) Open the fuel filler cap. Disconnect the rubber
fuel hose between the body tube assembly and the
fuel pump nipple at the body tube joint. A minimal
amount of fuel may flow from the open port.
NOTE: Utilize an approved fuel storage container to
catch any residual fuel.
24 - 118 CABIN HEATERRS
FUEL LINE (Continued)
Page 2525 of 2585

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
OPERATION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................10
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................11
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
NATURAL VAC LEAK DETECTION ASSY
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13ORVR
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VEHICLE DOES
NOT FILL............................16
P C V VA LV E
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV SYSTEM . . . 17
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................18
REMOVAL
REMOVAL...........................18
REMOVAL - WITH NVLD................19
REMOVAL - REAR EVAP CANISTER.......19
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................19
INSTALLATION - WITH NVLD............20
INSTALLATION - REAR EVAP CANISTER . . . 20
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
OPERATION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through vent hoses or tubes to an activated carbon
filled evaporative canister. The canister temporarily
holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum to draw
vapors into the combustion chambers during certain
operating conditions (Fig. 1).All engines use a proportional purge solenoid sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
purge solenoid. Refer to Proportional Purge Solenoid
in this section.
NOTE: The evaporative system uses specially man-
ufactured hoses. If they need replacement, only use
fuel resistant hose. Also the hoses must be able to
pass an Ozone compliance test.
NOTE: For more information on Onboard Refueling
Vapor Recovery (ORVR), refer to the Fuel Delivery
section.
25 - 10 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSRS
Page 2527 of 2585
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles use a proportional purge solenoid (Fig.
2). The solenoid regulates the rate of vapor flow from
the EVAP canister to the throttle body. The PCM
operates the solenoid.
OPERATION
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The proportional purge solenoid operates at a fre-
quency of 200 hz and is controlled by an engine con-
troller circuit that senses the current being applied
to the proportional purge solenoid and then adjusts
that current to achieve the desired purge flow. The
proportional purge solenoid controls the purge rate of
fuel vapors from the vapor canister and fuel tank to
the engine intake manifold.
REMOVAL
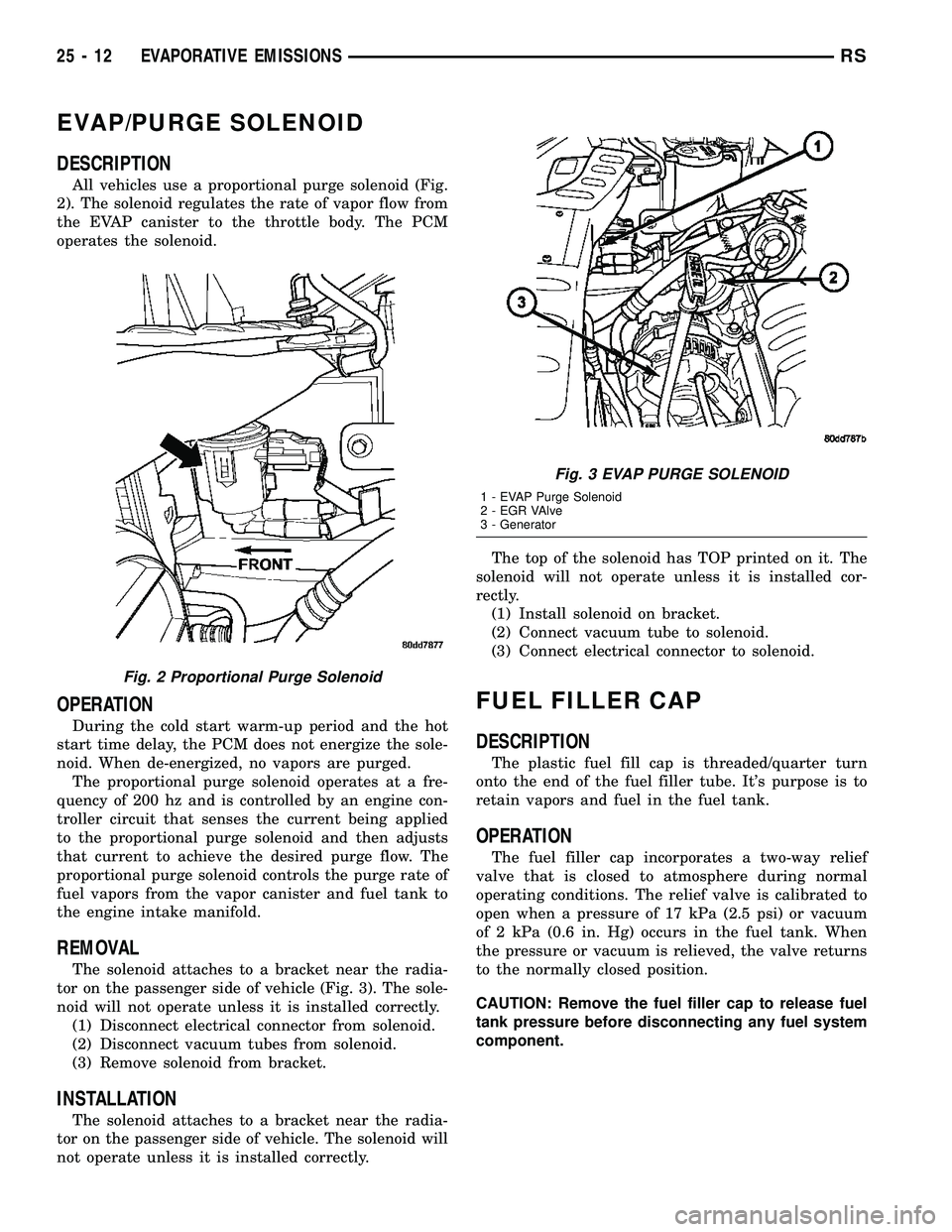
The solenoid attaches to a bracket near the radia-
tor on the passenger side of vehicle (Fig. 3). The sole-
noid will not operate unless it is installed correctly.
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from solenoid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum tubes from solenoid.
(3) Remove solenoid from bracket.
INSTALLATION
The solenoid attaches to a bracket near the radia-
tor on the passenger side of vehicle. The solenoid will
not operate unless it is installed correctly.The top of the solenoid has TOP printed on it. The
solenoid will not operate unless it is installed cor-
rectly.
(1) Install solenoid on bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum tube to solenoid.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel fill cap is threaded/quarter turn
onto the end of the fuel filler tube. It's purpose is to
retain vapors and fuel in the fuel tank.
OPERATION
The fuel filler cap incorporates a two-way relief
valve that is closed to atmosphere during normal
operating conditions. The relief valve is calibrated to
open when a pressure of 17 kPa (2.5 psi) or vacuum
of 2 kPa (0.6 in. Hg) occurs in the fuel tank. When
the pressure or vacuum is relieved, the valve returns
to the normally closed position.
CAUTION: Remove the fuel filler cap to release fuel
tank pressure before disconnecting any fuel system
component.
Fig. 2 Proportional Purge Solenoid
Fig. 3 EVAP PURGE SOLENOID
1 - EVAP Purge Solenoid
2 - EGR VAlve
3 - Generator
25 - 12 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSRS
Page 2529 of 2585
ORVR
OPERATION
The emission control principle used in the ORVR
system is that the fuel flowing into the filler tube
(appx. 1º I.D.) creates an aspiration effect which
draws air into the fill tube (Fig. 9). During refueling,
the fuel tank is vented to the vapor canister to cap-
ture escaping vapors. With air flowing into the filler
tube, there are no fuel vapors escaping to the atmo-
sphere. Once the refueling vapors are captured by
the canister, the vehicle's computer controlled purge
system draws vapor out of the canister for the engine
to burn. The vapors flow is metered by the purge
solenoid so that there is no or minimal impact on
driveability or tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fill tube, it opens
the normally closed check valve and enters the fuel
tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank through
the control valve to the vapor canister. Vapor is
absorbed in the canister until vapor flow in the lines
stops, either following shut-off or by having the fuel
level in the tank rise high enough to close the control
valve. The control valve(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL TANK - OPERATION)
contains a float that rises to seal the large diameter
vent path to the canister. At this point in the fueling
of the vehicle, the tank pressure increases, the check
valve closes (preventing tank fuel from spitting back
at the operator), and fuel then rises up the filler tube
to shut-off the dispensing nozzle.
If the engine is shut-off while the On-Board diag-
nostics test is running, low level tank pressure can
be trapped in the fuel tank and fuel can not be added
to the tank until the pressure is relieved. This is due
to the leak detection pump closing the vapor outlet
from the top of the tank and the one-way check valve
not allowing the tank to vent through the fill tube to
atmosphere. Therefore, when fuel is added, it will
back-up in the fill tube and shut off the dispensing
nozzle. The pressure can be eliminated in two ways:
1. Vehicle purge must be activated and for a long
enough period to eliminate the pressure. 2. Removing
the fuel cap and allowing enough time for the system
to vent thru the recirulation tube.
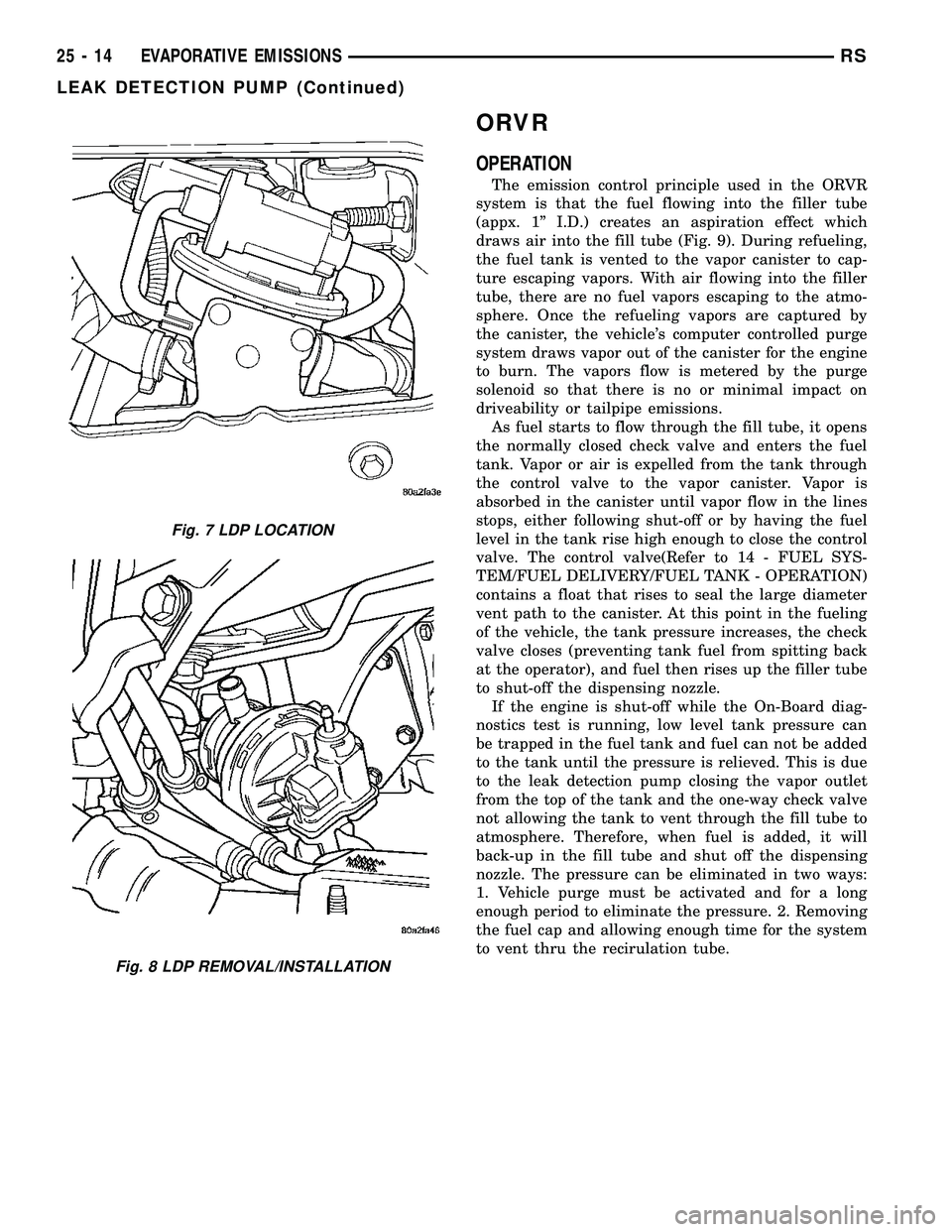
Fig. 7 LDP LOCATION
Fig. 8 LDP REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
25 - 14 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSRS
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)