2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER Relays
[x] Cancel search: RelaysPage 1245 of 2585

SPLICE NUMBER LOCATION FIG.
S126 In Right Headlamp Leveling Assembly N/S
S127 (Diesel) In T/O for Engine Starter Motor N/S
S128 (Diesel) Near T/O for Engine Starter Motor N/S
S129 (Diesel) Near T/O for Battery (+) N/S
S130 (Diesel) Near T/O for Battery (+) N/S
S131 Near T/O for Transmission Control Module 11
S131 (3.3L/3.8L) Near T/O for C110 N/S
S132 (Diesel) Near T/O for Battery (+) N/S
S134 (Diesel) IN T/O for Engine Control Module N/S
S135 (Diesel) Near T/O for Glow Plug No.2 N/S
S136 (Diesel) In T/O for Radiator Fan Relays 2
S137 (Diesel) Above Starter 15
S138 (Diesel) Between T/O for Radiator Fan No.2 and T/O for G102 N/S
S139 (Diesel) Between T/O for Engine Starter Motor and T/O for
Engine Control Module C115, 16
S141 (2.4L) Near T/O for C110 11
S141 (Diesel) Near T/O for G100 N/S
S141 (3.3L/3.8L) Near T/O for Powertrain Control Module N/S
S142 (3.3L/3.8L) Near T/O for A/C Compressor Clutch 18
S144 (Diesel) Between T/O for Battery Temperature Sensor and T/O
for C103N/S
S148 (Diesel) Near T/O for Engine Starter Motor 5
S150 (Diesel) Between T/O for Battery Temperature Sensor and T/O
for C103N/S
S151 (Diesel) Near T/O for Radiator Fan Relays 2
S152 (Diesel) Near T/O for Radiator Fan No.1 N/S
S157 (Diesel) Near T/O for Glow Plug No.4 15
S177 In Right Headlamp Wiring Assembly N/S
S179 In Left Headlamp Wiring Assembly N/S
S187 (Diesel) In T/O for Engine Control Module C1 N/S
S188 (Diesel) Near T/O for Radiator Fan Relays 2
S201 In T/O to Instrument Panel Speaker 20, 26
S202 Near T/O for Instrument Panel Switch Bank 20, 26
S203 Near T/O for Instrument Panel Switch Bank 26
S204 Near T/O to Instrument Panel Speaker 20, 26
S205 Near T/O for C201 N/S
S206 Near T/O for Instrument Cluster 20
S207 Near T/O for A/C Heater Control 20, 26
S208 (RHD) Between T/O for Antenna Connector and T/O for Front
Cigar Lighter26
S209 Near T/O for Evaporator Temperature Sensor N/S
S210 (RHD) Near T/O for C203 26
S211 In Steering Column Wiring Assembly N/S
8W - 91 - 14 8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATIONRS
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1292 of 2585
8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........1
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
REMOVAL.............................2
INSTALLATION..........................3IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET . . 4
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
POWER DISTRIBUTION
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
This group covers the various standard and
optional power distribution components used on this
model. The power distribution system for this vehicle
consists of the following components:
²Integrated Power Module (IPM)
²Front Control Module (FCM)
²Power Outlets
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit sche-
matics.
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses
²Bus bars
²Cartridge fuses
²Circuit splice blocks
²Flashers
²Fusible links
²Relays
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the power distribution system. See the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features and use of all of the
power distribution system components.
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the many standard and optional facto-
ry-installed electrical and electronic powertrain,
chassis, safety, security, comfort and convenience sys-
tems. At the same time, the power distribution sys-
tem was designed to provide ready access to these
electrical distribution points for the vehicle techni-
cian to use when conducting diagnosis and repair of
faulty circuits. The power distribution system can
also prove useful for the sourcing of additional elec-
trical circuits that may be required to provide the
electrical current needed to operate many accessories
that the vehicle owner may choose to have installed
in the aftermarket.
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
Terminal Pick Kit 6680
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-1
Page 1293 of 2585
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
DESCRIPTION
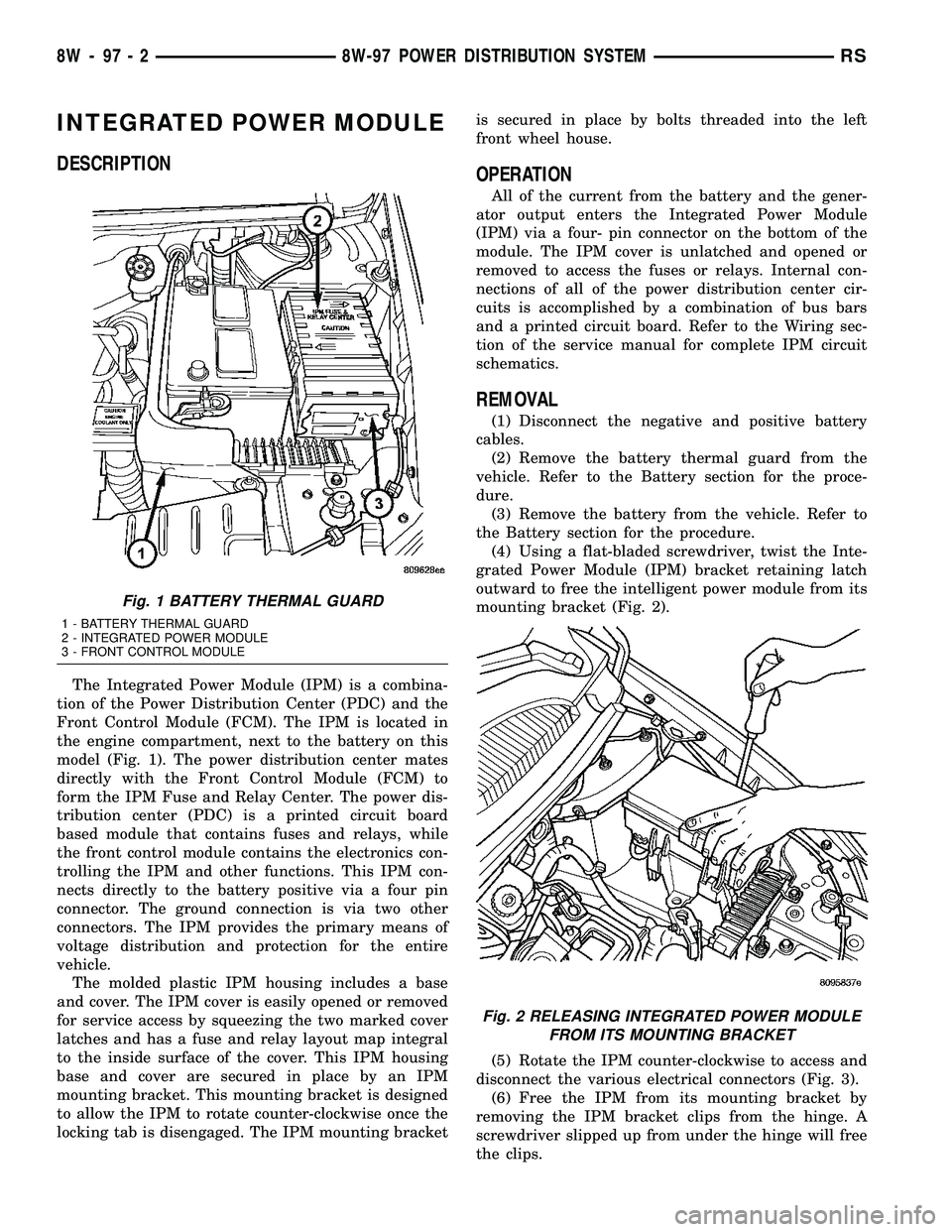
The Integrated Power Module (IPM) is a combina-
tion of the Power Distribution Center (PDC) and the
Front Control Module (FCM). The IPM is located in
the engine compartment, next to the battery on this
model (Fig. 1). The power distribution center mates
directly with the Front Control Module (FCM) to
form the IPM Fuse and Relay Center. The power dis-
tribution center (PDC) is a printed circuit board
based module that contains fuses and relays, while
the front control module contains the electronics con-
trolling the IPM and other functions. This IPM con-
nects directly to the battery positive via a four pin
connector. The ground connection is via two other
connectors. The IPM provides the primary means of
voltage distribution and protection for the entire
vehicle.
The molded plastic IPM housing includes a base
and cover. The IPM cover is easily opened or removed
for service access by squeezing the two marked cover
latches and has a fuse and relay layout map integral
to the inside surface of the cover. This IPM housing
base and cover are secured in place by an IPM
mounting bracket. This mounting bracket is designed
to allow the IPM to rotate counter-clockwise once the
locking tab is disengaged. The IPM mounting bracketis secured in place by bolts threaded into the left
front wheel house.
OPERATION
All of the current from the battery and the gener-
ator output enters the Integrated Power Module
(IPM) via a four- pin connector on the bottom of the
module. The IPM cover is unlatched and opened or
removed to access the fuses or relays. Internal con-
nections of all of the power distribution center cir-
cuits is accomplished by a combination of bus bars
and a printed circuit board. Refer to the Wiring sec-
tion of the service manual for complete IPM circuit
schematics.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative and positive battery
cables.
(2) Remove the battery thermal guard from the
vehicle. Refer to the Battery section for the proce-
dure.
(3) Remove the battery from the vehicle. Refer to
the Battery section for the procedure.
(4) Using a flat-bladed screwdriver, twist the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM) bracket retaining latch
outward to free the intelligent power module from its
mounting bracket (Fig. 2).
(5) Rotate the IPM counter-clockwise to access and
disconnect the various electrical connectors (Fig. 3).
(6) Free the IPM from its mounting bracket by
removing the IPM bracket clips from the hinge. A
screwdriver slipped up from under the hinge will free
the clips.
Fig. 1 BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
Fig. 2 RELEASING INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
FROM ITS MOUNTING BRACKET
8W - 97 - 2 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMRS
Page 1294 of 2585

INSTALLATION
(1) Snap the left side of the Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM) housing in its mounting bracket and con-
nect the various electrical connectors. Care must be
taken that the Connector Positive Assurance (CPA)
on the five-pin B+ connector is positively engaged to
prevent generating a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
NOTE: IPM electrical connectors are color coded to
ease location reference.
(2) Being certain no wires are stressed or pinched,
rotate the IPM clock-wise until secured in mounting
bracket. An audible click may be heard.
(3) Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to the
Battery section for the procedure.
(4) Install the battery thermal guard in the vehi-
cle. Refer to the Battery section for the procedure.
(5)
Connect the negative and positive battery cables.
(6) Using a diagnostic scan tool, check for any
stored diagnostic trouble codes and correct, check
that all vehicle options are operational before return-
ing the vehicle to service.
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse that is removed from its normal
cavity in the Integrated Power Module (IPM) whenthe vehicle is shipped from the factory. Dealer per-
sonnel are to remove the IOD fuse from the storage
location and install it into the IPM fuse cavity
marked IOD as part of the preparation procedures
performed just prior to new vehicle delivery.
The IPM has a molded plastic cover that can be
removed to provide service access to all of the fuses
and relays in the IPM. An integral latch and hinges
are molded into the IPM cover for easy removal. A
fuse layout map is integral to the underside of the
IPM cover to ensure proper fuse and relay identifica-
tion. The IOD fuse is a 20 ampere blade-type mini
fuse and, when removed, it is stored in a fuse cavity
adjacent to the washer fuse within the IPM.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal condi-
tion where power is being drained from the battery with
the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD fuse
feeds the memory and sleep mode functions for some of
the electronic modules in the vehicle as well as various
other accessories that require battery current when the
ignition switch is in the Off position, including the
clock. The only reason the IOD fuse is removed is to
reduce the normal IOD of the vehicle electrical system
during new vehicle transportation and pre-delivery stor-
age to reduce battery depletion, while still allowing
vehicle operation so that the vehicle can be loaded,
unloaded and moved as needed by both vehicle trans-
portation company and dealer personnel.
The IOD fuse is removed from the IPM fuse cavity
when the vehicle is shipped from the assembly plant.
Dealer personnel must install the IOD fuse when the
vehicle is being prepared for delivery in order to
restore full electrical system operation. Once the
vehicle is prepared for delivery, the IOD function of
this fuse becomes transparent and the fuse that has
been assigned the IOD designation becomes only
another Fused B(+) circuit fuse. The IOD fuse serves
no useful purpose to the dealer technician in the ser-
vice or diagnosis of any vehicle system or condition,
other than the same purpose as that of any other
standard circuit protection device.
The IOD fuse can be used by the vehicle owner as
a convenient means of reducing battery depletion
when a vehicle is to be stored for periods not to
exceed about thirty days. However, it must be
remembered that removing the IOD fuse will not
eliminate IOD, but only reduce this normal condition.
If a vehicle will be stored for more than about thirty
days, the battery negative cable should be discon-
nected to eliminate normal IOD; and, the battery
should be tested and recharged at regular intervals
during the vehicle storage period to prevent the bat-
tery from becoming discharged or damaged. Refer to
Battery Systemfor additional service information.
Fig. 3 DISCONNECTING IPM
1 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE FUSE & RELAY CENTER
RS8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM8W-97-3
INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (Continued)
Page 1525 of 2585

FUEL INJECTION
OPERATION
OPERATION - INJECTION SYSTEM
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are theprimaryinputs that determine
injector pulse width.
OPERATION - MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygensensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).
During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 15
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait 3
seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than 0.745
volts or less than 0.29 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
14 - 18 FUEL INJECTIONRS
Page 1526 of 2585

1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay when the engine is
not running. The following actions occur when the
starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
If the PCM does not receive both signals within
approximately one second, it will not energize the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel
pump relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil, (EGR solenoid and PCV
heater if equipped) and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes the injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within 64 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²MAP
²Engine RPM
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Engine coolant temperature
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch status
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²O2 sensors
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (O2 sensors)
²A/C switch status
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory, if 2nd trip with fault.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor (if equipped)
²Purge system monitor
²Catalyst efficiency monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range,
rationality.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-19
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 2414 of 2585

COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
3.3L/3.8L - INSTALLATION).
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C-heater control to the A/C
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 7) is a Interna-
tional Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay.
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is located in the
Integrated Power Module (IPM) in the engine com-
partment. See the fuse and relay layout map molded
into the inner surface of the IPM cover for A/C com-
pressor clutch relay identification and location.The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the A/C compressor clutch relay. Five
male spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the powertrain control module (PCM) to control the
high current output to the compressor clutch electro-
magnetic coil. The movable common feed contact
point is held against the fixed normally closed con-
tact point by spring pressure. When the relay coil is
energized, an electromagnetic field is produced by the
coil windings. This electromagnetic field draws the
movable relay contact point away from the fixed nor-
mally closed contact point, and holds it against the
fixed normally open contact point. When the relay
coil is de-energized, spring pressure returns the mov-
able contact point back against the fixed normally
closed contact point. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and
helps to dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic
interference that can be generated as the electromag-
netic field of the relay coil collapses.
The compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input from the PCM through the compressor clutch
relay control circuit only when the PCM electroni-
cally pulls the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the PCM through a fused ignition
switch output (run-start) circuit only when the igni-
tion switch is in the On or Start positions.
Fig. 7 A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-19
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2419 of 2585
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the blend door actuator.
(4) Install the silencer under the driver side end of
the instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL SILENCER -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(6) Perform the heater-A/C control calibration pro-
cedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CONTROL
- STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C CON-
TROL CALIBRATION).
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor relay is a International Stan-
dards Organization (ISO) mini-relay (Fig. 12). Relays
conforming to the ISO specifications have common
physical dimensions, current capacities, terminal pat-
terns, and terminal functions. The ISO mini-relay
terminal functions are the same as a conventional
ISO relay. However, the ISO mini-relay terminal pat-
tern (or footprint) is different, the current capacity is
lower, and the physical dimensions are smaller than
those of the conventional ISO relay. The blower
motor relay is located in the Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM), which is in the engine compartment near
the battery. See the fuse and relay layout map
molded into the inner surface of the IPM cover for
blower motor relay identification and location.The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the blower motor relay. Five male
spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of the
base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
The blower motor relay cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If the relay is damaged or faulty, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The blower motor relay is an electromechanical
switch that uses a low current input from the Front
Control Module (FCM) to control the high current
output to the blower motor resistor (manual heater-
A/C control) or blower power module (ATC control).
The movable common feed contact point is held
against the fixed normally closed contact point by
spring pressure. When the relay coil is energized, an
electromagnetic field is produced by the coil wind-
ings. This electromagnetic field draws the movable
relay contact point away from the fixed normally
closed contact point, and holds it against the fixed
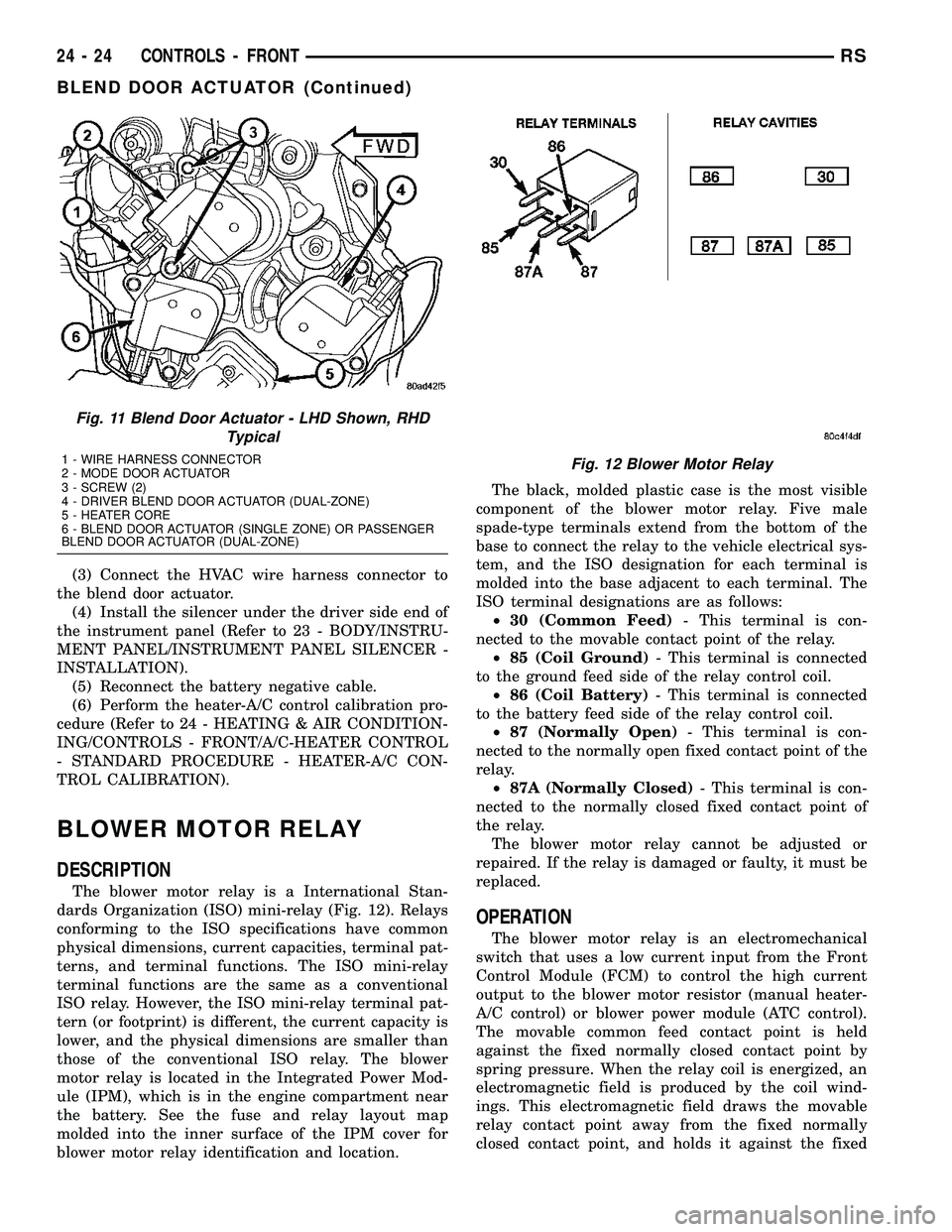
Fig. 11 Blend Door Actuator - LHD Shown, RHD
Typical
1 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - SCREW (2)
4 - DRIVER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (DUAL-ZONE)
5 - HEATER CORE
6 - BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (SINGLE ZONE) OR PASSENGER
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (DUAL-ZONE)Fig. 12 Blower Motor Relay
24 - 24 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)