2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER battery location
[x] Cancel search: battery locationPage 2414 of 2585

COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
3.3L/3.8L - INSTALLATION).
(15) Lower the vehicle.
(16) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C-heater control to the A/C
Recirculation Mode, the blower motor switch in the
highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500
to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch relay (Fig. 7) is a Interna-
tional Standards Organization (ISO) micro-relay.
Relays conforming to the ISO specifications have
common physical dimensions, current capacities, ter-
minal patterns, and terminal functions. The ISO
micro-relay terminal functions are the same as a con-
ventional ISO relay. However, the ISO micro-relay
terminal pattern (or footprint) is different, the cur-
rent capacity is lower, and the physical dimensions
are smaller than those of the conventional ISO relay.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is located in the
Integrated Power Module (IPM) in the engine com-
partment. See the fuse and relay layout map molded
into the inner surface of the IPM cover for A/C com-
pressor clutch relay identification and location.The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the A/C compressor clutch relay. Five
male spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of
the base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical
system, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch relay is an electrome-
chanical switch that uses a low current input from
the powertrain control module (PCM) to control the
high current output to the compressor clutch electro-
magnetic coil. The movable common feed contact
point is held against the fixed normally closed con-
tact point by spring pressure. When the relay coil is
energized, an electromagnetic field is produced by the
coil windings. This electromagnetic field draws the
movable relay contact point away from the fixed nor-
mally closed contact point, and holds it against the
fixed normally open contact point. When the relay
coil is de-energized, spring pressure returns the mov-
able contact point back against the fixed normally
closed contact point. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and
helps to dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic
interference that can be generated as the electromag-
netic field of the relay coil collapses.
The compressor clutch relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the integrated power module (IPM). The
inputs and outputs of the A/C compressor clutch
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from a fuse in the IPM through a
fused B(+) circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input from the PCM through the compressor clutch
relay control circuit only when the PCM electroni-
cally pulls the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the PCM through a fused ignition
switch output (run-start) circuit only when the igni-
tion switch is in the On or Start positions.
Fig. 7 A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-19
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL (Continued)
Page 2415 of 2585

²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the compressor clutch coil
through the compressor clutch relay output circuit
only when the compressor clutch relay coil is ener-
gized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the compressor
clutch relay coil is de-energized.
The A/C compressor clutch relay cannot be
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced. Refer to the appropriate wiring information
for diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for
complete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the integrated power
module (IPM) (Fig. 8).
(3) Refer to the fuse and relay layout map on the
inner surface of the IPM cover for A/C compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Remove the A/C compressor clutch relay from
the IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) Refer to the fuse and relay layout map on the
inner surface of the integrated power module (IPM)cover for A/C compressor clutch relay identification
and location.
(2) Position the A/C compressor clutch relay into
the proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the A/C compressor clutch relay termi-
nals with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the A/C compressor clutch
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.
(6) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The A/C-heater control is located at the center of
the instrument panel and uses electrical controls.
These controls provide the vehicle operator with a
number of setting options to help control the climate
and comfort within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's
manual in the vehicle glove box for more information
on the suggested operation and use of these controls.
The A/C-heater control cannot be repaired. If faulty
or damaged, the entire unit must be replaced. The
control knobs and the illumination lamps are avail-
able for service replacement.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C-HEATER
CONTROL CALIBRATION
The A/C-heater control module must be recali-
brated each time an actuator motor or the control
module is replaced. If the vehicle is so equipped, the
calibration procedure also includes rear HVAC posi-
tions for each actuator motor.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
(2) If equipped with the manual temperature con-
trol (MTC) system, press and hold the Rear Wipe/
Wash and Recirculation buttoms for at least five
seconds. If equipped with the automatic temperature
control (ATC) systen, simultaneously press and hold
the Power and Recirculation buttons on the A/C-
heater control for at least five seconds. The MTC
A/C-heater control Rear Wipe/Wash Light Emitting
Diode (LED) and Recirculation LED, or the ATC A/C-
heater control Delay and Recirculation graphics will
begin to flash when the calibration procedure has
begun.
(3) The calibration procedure should take less than
two minutes to complete for the manual A/C-heater
control, and less than twenty seconds for the ATC
A/C-heater control. When the LEDs or graphics stop
flashing, the calibration procedure is complete.
(4) If the LEDs or graphics continue to flash
beyond the two minute (manual) or twenty second
(ATC) calibration time, it indicates that the A/C-
Fig. 8 Integrated Power Module (IPM)
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE (IPM)
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
24 - 20 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2419 of 2585
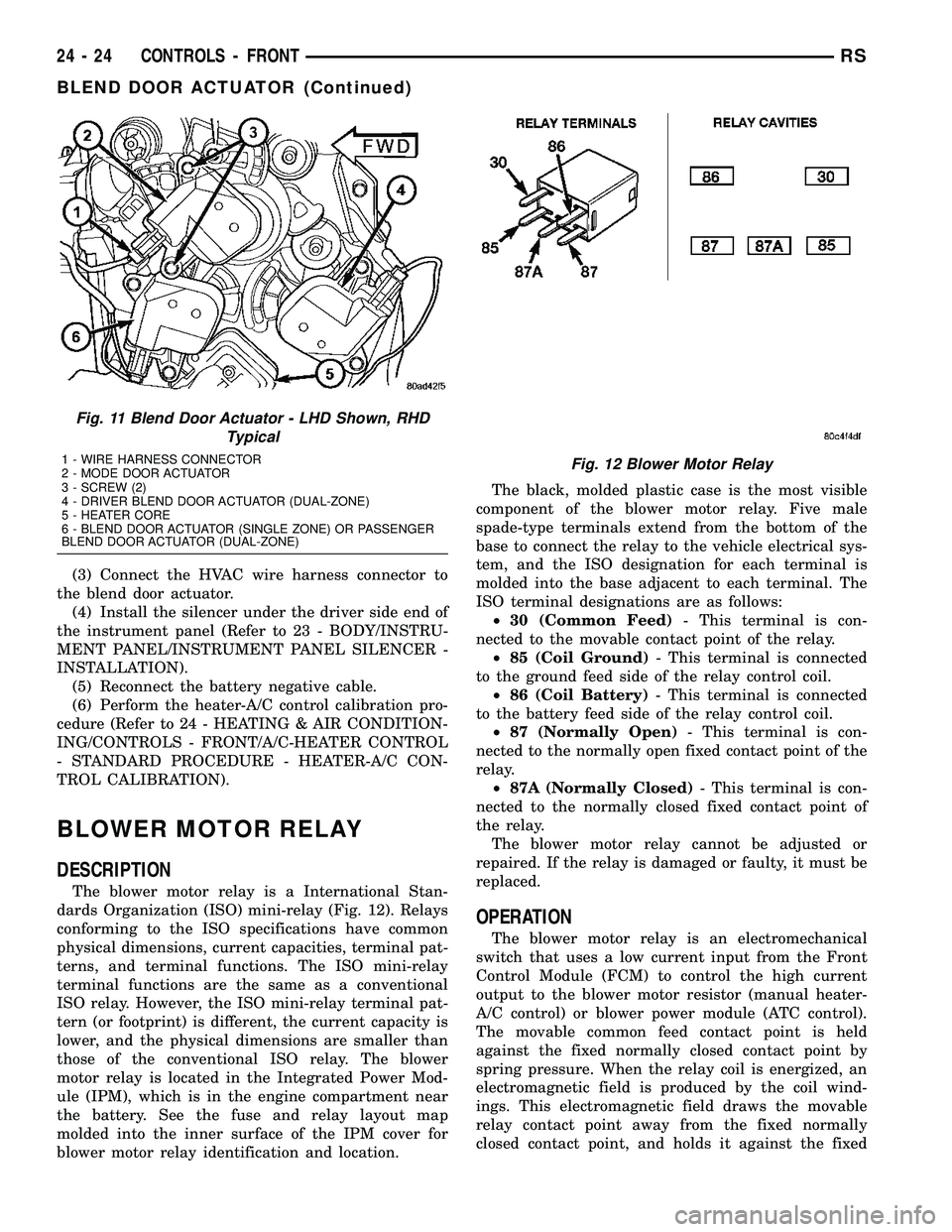
(3) Connect the HVAC wire harness connector to
the blend door actuator.
(4) Install the silencer under the driver side end of
the instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL SILENCER -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(6) Perform the heater-A/C control calibration pro-
cedure (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS - FRONT/A/C-HEATER CONTROL
- STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEATER-A/C CON-
TROL CALIBRATION).
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor relay is a International Stan-
dards Organization (ISO) mini-relay (Fig. 12). Relays
conforming to the ISO specifications have common
physical dimensions, current capacities, terminal pat-
terns, and terminal functions. The ISO mini-relay
terminal functions are the same as a conventional
ISO relay. However, the ISO mini-relay terminal pat-
tern (or footprint) is different, the current capacity is
lower, and the physical dimensions are smaller than
those of the conventional ISO relay. The blower
motor relay is located in the Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM), which is in the engine compartment near
the battery. See the fuse and relay layout map
molded into the inner surface of the IPM cover for
blower motor relay identification and location.The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the blower motor relay. Five male
spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of the
base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.
²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
The blower motor relay cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If the relay is damaged or faulty, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The blower motor relay is an electromechanical
switch that uses a low current input from the Front
Control Module (FCM) to control the high current
output to the blower motor resistor (manual heater-
A/C control) or blower power module (ATC control).
The movable common feed contact point is held
against the fixed normally closed contact point by
spring pressure. When the relay coil is energized, an
electromagnetic field is produced by the coil wind-
ings. This electromagnetic field draws the movable
relay contact point away from the fixed normally
closed contact point, and holds it against the fixed
Fig. 11 Blend Door Actuator - LHD Shown, RHD
Typical
1 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
2 - MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
3 - SCREW (2)
4 - DRIVER BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (DUAL-ZONE)
5 - HEATER CORE
6 - BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (SINGLE ZONE) OR PASSENGER
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (DUAL-ZONE)Fig. 12 Blower Motor Relay
24 - 24 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 2420 of 2585

normally open contact point. When the relay coil is
de-energized, spring pressure returns the movable
contact point back against the fixed normally closed
contact point. The resistor or diode is connected in
parallel with the relay coil in the relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes and electromagnetic interfer-
ence that can be generated as the electromagnetic
field of the relay coil collapses.
The blower motor relay terminals are connected to
the vehicle electrical system through a receptacle in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM). The inputs and
outputs of the blower motor relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from the battery through a B(+)
circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input through the front/rear blower motor relay con-
trol circuit only when the FCM electronically pulls
the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the battery through a B(+) circuit
at all times.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the blower motor resistor
(manual heater-A/C control) or blower power module
(automatic heater-A/C control) through a fuse in the
IPM on the fused front blower motor relay output cir-
cuit only when the blower motor relay coil is ener-
gized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the blower motor
relay coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and remove the cover from the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 13).
(3) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the IPM cover for front blower
motor relay identification and location.(4) Remove the front blower motor relay from the
IPM by pulling the relay straight up.
INSTALLATION
(1) Refer to the fuse and relay layout map on the
inner surface of the integrated power module (IPM)
cover for front blower motor relay identification and
location.
(2) Position the front blower motor relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the front blower motor relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(4) Push down firmly on the front blower motor
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.
(6) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
Fig. 13 Integrated Power Module - Typical
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
RSCONTROLS - FRONT24-25
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
Page 2421 of 2585

BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
A blower motor resistor is used on this model when
it is equipped with the manual heater-A/C system.
Models equipped with the optional Automatic Tem-
perature Control (ATC) system use a blower power
module, instead of the blower motor resistor block
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
CONTROLS/POWER MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
The blower motor resistor block is mounted to the
rear of the HVAC housing, directly behind the glove
box opening in the instrument panel. The resistor
block consists of a molded plastic mounting plate
with two integral connector receptacles. Concealed
behind the mounting plate are four coiled resistor
wires contained within a protective stamped steel
cage. The blower motor resistor block is accessed for
service by removing the glove box from the instru-
ment panel.
OPERATION
The blower motor resistor block is connected to the
vehicle electrical system through a dedicated take
out and connector of the instrument panel wire har-
ness. A second connector receptacle receives the pig-
tail wire connector from the blower motor. The
blower motor resistor has multiple resistor wires,
each of which will reduce the current flow through
the blower motor to change the blower motor speed.
The blower motor switch in the manual heater-A/C
system directs the ground path for the blower motor
through the correct resistor wire to obtain the
selected speed.
With the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, the ground path for the motor is applied
through all of the resistor wires. Each higher speed
selected with the blower motor switch applies the
blower motor ground path through fewer of the resis-
tor wires, increasing the blower motor speed.
The blower motor resistor cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER MOTOR
RESISTOR BLOCK
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the glove box from the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
GLOVE BOX - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the two wire harness connectors
from the blower motor resistor block.
(4) Check for continuity between each of the
blower motor switch input terminals of the resistor
and the resistor output terminal. In each case there
should be continuity. If OK, repair the wire harness
circuits between the blower motor switch and the
blower motor resistor, blower motor or blower motor
relay as required. If not OK, replace the faulty
blower motor resistor block.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: THE BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
BLOCK MAY GET VERY HOT DURING NORMAL
OPERATION. IF THE BLOWER MOTOR WAS
TURNED ON PRIOR TO SERVICING THE BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK, WAIT FIVE MINUTES
TO ALLOW THE BLOWER MOTOR RESISTORS TO
COOL BEFORE PERFORMING DIAGNOSIS OR SER-
VICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THIS PRECAUTION CAN
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
24 - 26 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
Page 2423 of 2585
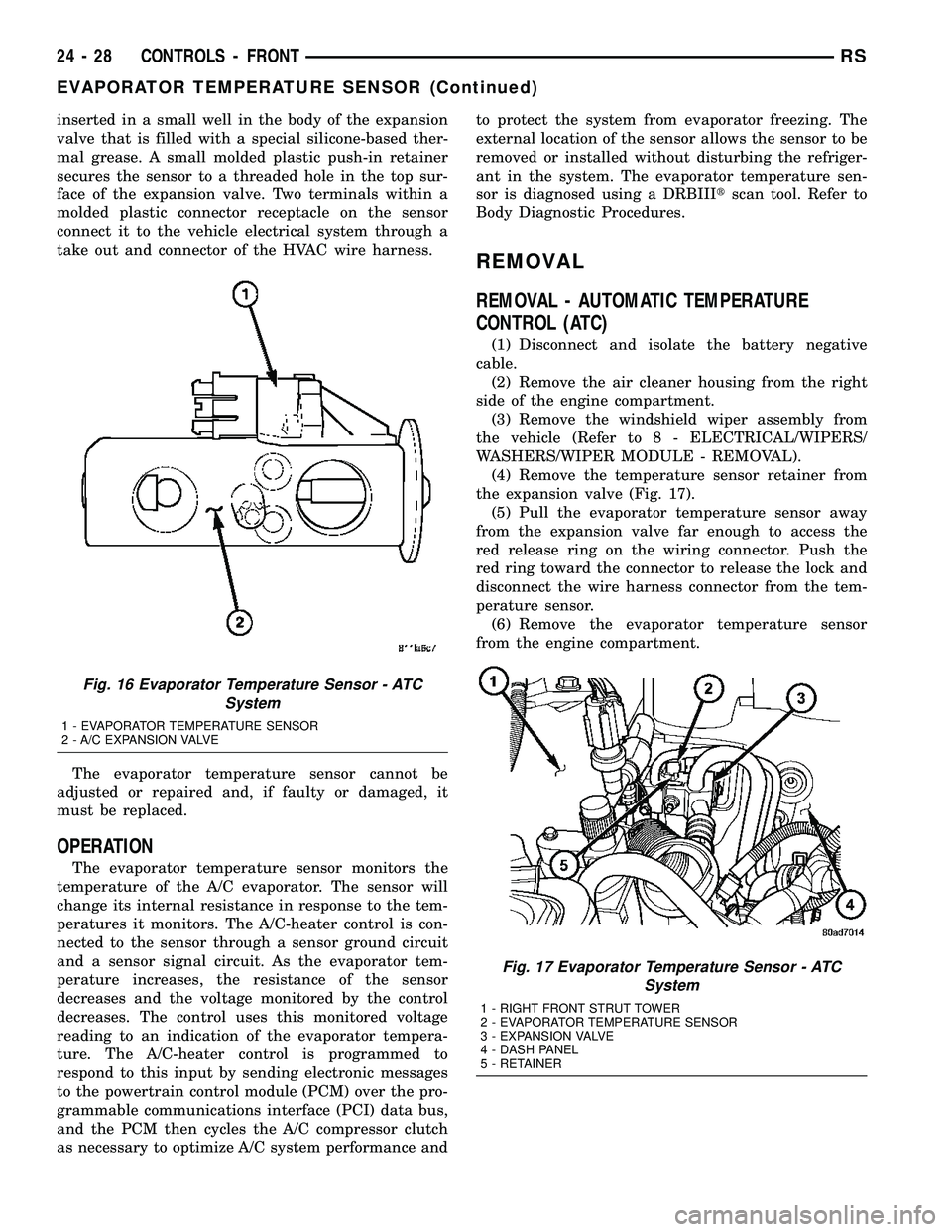
inserted in a small well in the body of the expansion
valve that is filled with a special silicone-based ther-
mal grease. A small molded plastic push-in retainer
secures the sensor to a threaded hole in the top sur-
face of the expansion valve. Two terminals within a
molded plastic connector receptacle on the sensor
connect it to the vehicle electrical system through a
take out and connector of the HVAC wire harness.
The evaporator temperature sensor cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The evaporator temperature sensor monitors the
temperature of the A/C evaporator. The sensor will
change its internal resistance in response to the tem-
peratures it monitors. The A/C-heater control is con-
nected to the sensor through a sensor ground circuit
and a sensor signal circuit. As the evaporator tem-
perature increases, the resistance of the sensor
decreases and the voltage monitored by the control
decreases. The control uses this monitored voltage
reading to an indication of the evaporator tempera-
ture. The A/C-heater control is programmed to
respond to this input by sending electronic messages
to the powertrain control module (PCM) over the pro-
grammable communications interface (PCI) data bus,
and the PCM then cycles the A/C compressor clutch
as necessary to optimize A/C system performance andto protect the system from evaporator freezing. The
external location of the sensor allows the sensor to be
removed or installed without disturbing the refriger-
ant in the system. The evaporator temperature sen-
sor is diagnosed using a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to
Body Diagnostic Procedures.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE
CONTROL (ATC)
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the air cleaner housing from the right
side of the engine compartment.
(3) Remove the windshield wiper assembly from
the vehicle (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/
WASHERS/WIPER MODULE - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the temperature sensor retainer from
the expansion valve (Fig. 17).
(5) Pull the evaporator temperature sensor away
from the expansion valve far enough to access the
red release ring on the wiring connector. Push the
red ring toward the connector to release the lock and
disconnect the wire harness connector from the tem-
perature sensor.
(6) Remove the evaporator temperature sensor
from the engine compartment.
Fig. 16 Evaporator Temperature Sensor - ATC
System
1 - EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - A/C EXPANSION VALVE
Fig. 17 Evaporator Temperature Sensor - ATC
System
1 - RIGHT FRONT STRUT TOWER
2 - EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - EXPANSION VALVE
4 - DASH PANEL
5 - RETAINER
24 - 28 CONTROLS - FRONTRS
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 2432 of 2585

BLOWER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The blower motor relay is a International Stan-
dards Organization (ISO) mini-relay (Fig. 4). Relays
conforming to the ISO specifications have common
physical dimensions, current capacities, terminal pat-
terns, and terminal functions. The ISO mini-relay
terminal functions are the same as a conventional
ISO relay. However, the ISO mini-relay terminal pat-
tern (or footprint) is different, the current capacity is
lower, and the physical dimensions are smaller than
those of the conventional ISO relay. The rear blower
motor relay is located in the Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM), which is in the engine compartment near
the battery. See the fuse and relay layout map
molded into the inner surface of the IPM cover for
rear blower motor relay identification and location.
The black, molded plastic case is the most visible
component of the blower motor relay. Five male
spade-type terminals extend from the bottom of the
base to connect the relay to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem, and the ISO designation for each terminal is
molded into the base adjacent to each terminal. The
ISO terminal designations are as follows:
²30 (Common Feed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the movable contact point of the relay.
²85 (Coil Ground)- This terminal is connected
to the ground feed side of the relay control coil.
²86 (Coil Battery)- This terminal is connected
to the battery feed side of the relay control coil.
²87 (Normally Open)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally open fixed contact point of the
relay.²87A (Normally Closed)- This terminal is con-
nected to the normally closed fixed contact point of
the relay.
The rear blower motor relay cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If the relay is damaged or faulty, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The rear blower motor relay is an electromechani-
cal switch that uses a low current input from the
Front Control Module (FCM) to control the high cur-
rent output to the rear blower motor resistor (man-
ual heater-A/C control) or rear blower motor power
module (ATC heater-A/C control). The movable com-
mon feed contact point is held against the fixed nor-
mally closed contact point by spring pressure. When
the relay coil is energized, an electromagnetic field is
produced by the coil windings. This electromagnetic
field draws the movable relay contact point away
from the fixed normally closed contact point, and
holds it against the fixed normally open contact
point. When the relay coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns the movable contact point back
against the fixed normally closed contact point. The
resistor or diode is connected in parallel with the
relay coil in the relay, and helps to dissipate voltage
spikes and electromagnetic interference that can be
generated as the electromagnetic field of the relay
coil collapses.
The rear blower motor relay terminals are con-
nected to the vehicle electrical system through a
receptacle in the Integrated Power Module (IPM).
The inputs and outputs of the rear blower motor
relay include:
²The common feed terminal (30) receives a bat-
tery current input from the battery through a B(+)
circuit at all times.
²The coil ground terminal (85) receives a ground
input through the front/rear blower motor relay con-
trol circuit only when the FCM electronically pulls
the control circuit to ground.
²The coil battery terminal (86) receives a battery
current input from the battery through a B(+) circuit
at all times.
²The normally open terminal (87) provides a bat-
tery current output to the blower motor resistor
(manual heater-A/C control) or blower power module
(ATC heater-A/C control) through a fuse in the IPM
on the fused rear blower motor relay output circuit
only when the blower motor relay coil is energized.
²The normally closed terminal (87A) is not con-
nected to any circuit in this application, but provides
a battery current output only when the rear blower
motor relay coil is de-energized.
Fig. 4 Rear Blower Motor Relay
RSCONTROLS - REAR24-37
Page 2433 of 2585
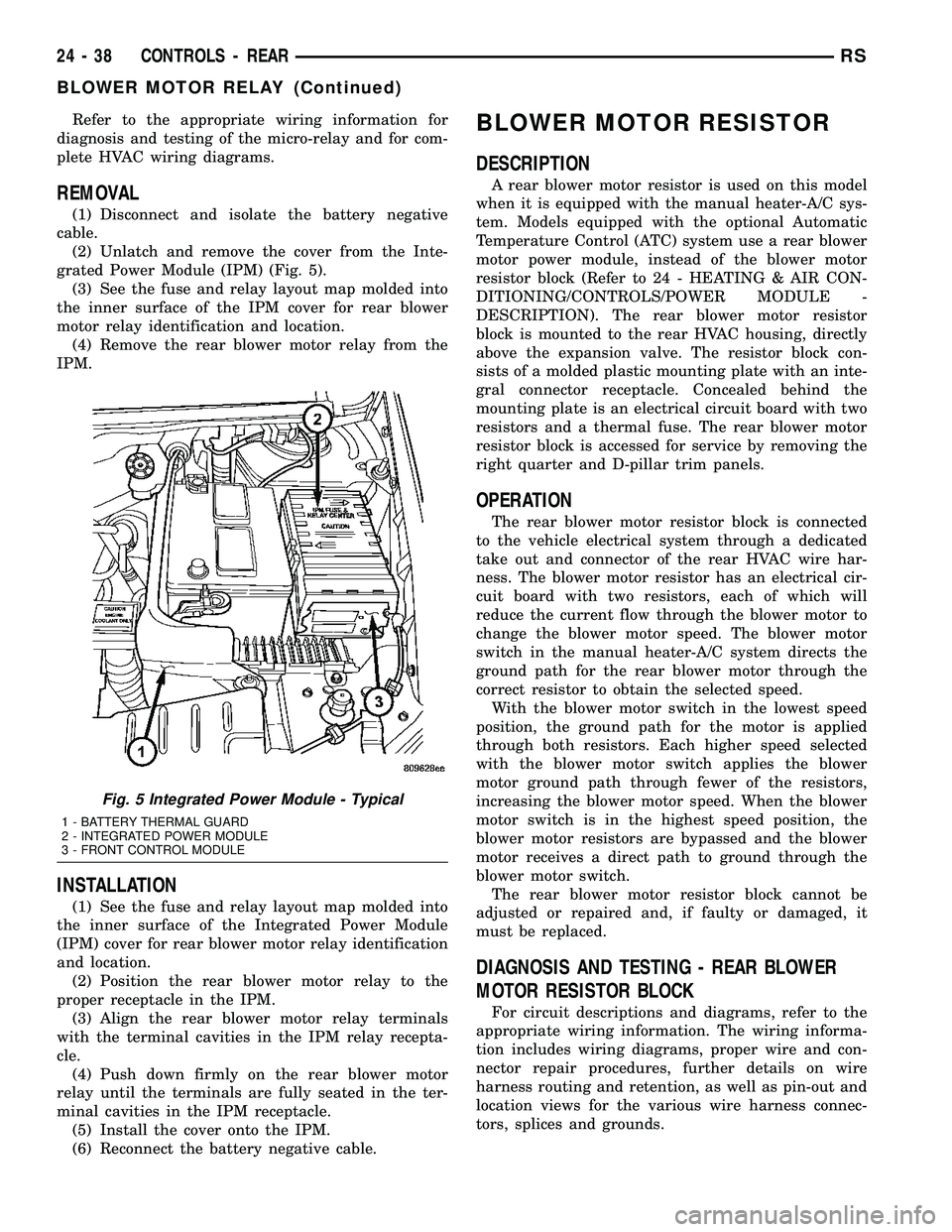
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the micro-relay and for com-
plete HVAC wiring diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unlatch and remove the cover from the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM) (Fig. 5).
(3) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the IPM cover for rear blower
motor relay identification and location.
(4) Remove the rear blower motor relay from the
IPM.
INSTALLATION
(1) See the fuse and relay layout map molded into
the inner surface of the Integrated Power Module
(IPM) cover for rear blower motor relay identification
and location.
(2) Position the rear blower motor relay to the
proper receptacle in the IPM.
(3) Align the rear blower motor relay terminals
with the terminal cavities in the IPM relay recepta-
cle.
(4) Push down firmly on the rear blower motor
relay until the terminals are fully seated in the ter-
minal cavities in the IPM receptacle.
(5) Install the cover onto the IPM.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR
DESCRIPTION
A rear blower motor resistor is used on this model
when it is equipped with the manual heater-A/C sys-
tem. Models equipped with the optional Automatic
Temperature Control (ATC) system use a rear blower
motor power module, instead of the blower motor
resistor block (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING/CONTROLS/POWER MODULE -
DESCRIPTION). The rear blower motor resistor
block is mounted to the rear HVAC housing, directly
above the expansion valve. The resistor block con-
sists of a molded plastic mounting plate with an inte-
gral connector receptacle. Concealed behind the
mounting plate is an electrical circuit board with two
resistors and a thermal fuse. The rear blower motor
resistor block is accessed for service by removing the
right quarter and D-pillar trim panels.
OPERATION
The rear blower motor resistor block is connected
to the vehicle electrical system through a dedicated
take out and connector of the rear HVAC wire har-
ness. The blower motor resistor has an electrical cir-
cuit board with two resistors, each of which will
reduce the current flow through the blower motor to
change the blower motor speed. The blower motor
switch in the manual heater-A/C system directs the
ground path for the rear blower motor through the
correct resistor to obtain the selected speed.
With the blower motor switch in the lowest speed
position, the ground path for the motor is applied
through both resistors. Each higher speed selected
with the blower motor switch applies the blower
motor ground path through fewer of the resistors,
increasing the blower motor speed. When the blower
motor switch is in the highest speed position, the
blower motor resistors are bypassed and the blower
motor receives a direct path to ground through the
blower motor switch.
The rear blower motor resistor block cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it
must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 5 Integrated Power Module - Typical
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
24 - 38 CONTROLS - REARRS
BLOWER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)