2003 Oldsmobile Alero tires
[x] Cancel search: tiresPage 191 of 354

Driving too fast through large water puddles or even
going through some car washes can cause problems,
too. The water may affect your brakes. Try to avoid
puddles. But
if you can't, try to slow down before you
hit them. -Yet
bl_.__ es can cause
acJents. They wc.. t
work as well in a quick stop and may cause
pulling to one side. You could lose control
of
the vehicle.
After driving through a large puddle
of water
or a car wash, apply your brake pedal lightly
until your brakes work normally.
Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning is dangerous. So much water can build up
under your tires that they can actually ride on the
water. This can happen
if the road is wet enough and
you're going fast enough. When your vehicle is
hydroplaning,
it has little or no contact with the road.
4-1 8
Page 192 of 354

Hydroplaning doesn’t happen often. But it can if your Driving Through Flowing Water
tires do not have much tread or if the pressure in one or
more is low. It can happen
if a lot of water is standing
on the road.
If you can see reflections from trees,
telephone poles or other vehicles, and raindrops
“dimple” the water’s surface, there could be
hydroplaning.
Hydroplaning usually happens at higher speeds. There
just isn’t a hard and fast rule about hydroplaning.
The best advice is to slow down when
it is raining.
Driving Through Deep Standing Water
Notice: If you drive too quickly through deep
puddles or standing water, water can come in
through your engine’s air intake and badly damage
your engine. Never drive through water that
is
slightly lower than the underbody of your vehicle. If
you can’t avoid deep puddles or standing water,
drive through them very slowly. Fla
ng or rushi - ater creates strong
forces. If you try to drive through flowing
water, as you might at a low water crossing,
your vehicle can be carried away.
As little as
six inches
of flowing water can carry away a
smaller vehicle. If this happens, you and other
vehicle occupants could drown. Don’t ignore
police warning signs, and otherwise be
very cautious about trying to drive through
flowing water.
Some Other Rainy Weather Tips
e Besides slowing down, allow some extra following
distance. And be especially careful when you
pass another vehicle. Allow yourself more clear
room ahead, and be prepared to have your
view restricted by road spray.
Have good tires with proper tread depth. See Tires
on page 5-53.
4-1 9
Page 195 of 354

The exit ramp can be curved, sometimes quite sharply.
The exit speed
is usually posted. Reduce your speed
according
to your speedometer, not to your sense
of motion. After driving for any distance at higher
speeds, you may tend
to think you are going slower
than you actually are.
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
Make sure you’re ready. Try to be well rested. If you
must start when you’re not fresh
- such as after a day’s
work
- don’t plan to make too many miles that first
part of the journey. Wear comfortable clothing and shoes
you can easily drive in.
Is your vehicle ready for a long trip?
If you keep it
serviced and maintained, it’s ready
to go. If it needs
service, have it done before starting out. Of course,
you’ll find experienced and able service experts
in dealerships all across North America. They’ll be
ready and willing
to help if you need it.
Here are some things you can check before a trip:
Windshield Washer Fluid: Is the reservior full? Are
all windows clean inside and outside?
Wiper Blades: Are they in good shape?
Lamps: Are they all working? Are the lenses clean?
Tires: They are vitally important to a safe,
trouble-free trip. Is the tread good enough for
long-distance driving? Are the tires all inflated to the
recommended pressure?
Weather Forecasts: What’s the weather outlook
along your route? Should you delay your trip a
short time
to avoid a major storm system?
Maps: Do you have up-to-date maps?
Highway Hypnosis
Is there actually such a condition as “highway
hypnosis”? Or is it just plain falling asleep at the wheel?
Call it highway hypnosis, lack of awareness, or
whatever.
There is something about an easy stretch of road with
the same scenery, along with the hum of the tires on the
road, the drone of the engine, and the rush of the
wind against the vehicle that can make you sleepy. Don’t
let it happen to you!
If it does, your vehicle can leave
the road in
less than a second, and you could crash and
be injured.
Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids: Have you checked
all levels?
4-22
Page 197 of 354

If you drive regularly in steep country, or if you’re
planning to visit there, here are some tips that can make
your trips safer and more enjoyable.
Keep your vehicle in good shape. Check all fluid
levels and also the brakes, tires, cooling system
and transaxle. These parts can work hard on
mountain roads.
Know how to go down hills. The most important
thing to know is this: let your engine do some of
the slowing down. Shift to a lower gear when you go
down a steep or long hill.
I ou don’l down, 1 ir brakes cou.-. get
so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You would
then have poor braking or even none going down a
hill. You could crash. Shift down to let
your engine assist your brakes on a steep downhill slope. Coasting downhill in
NEUTRAL
(N) or with the
ignition
off is dangerous. Your brakes will have
to do all the work
of slowing down. They could
get
so hot that they wouldn’t work well. You
would then have poor braking or even none
going down a
hill. You could crash. Always
have your engine running and your vehicle in
gear when you go downhill.
e
e
e
e
Know how to go uphill. Drive in the highest gear
possible.
Stay in your own lane when driving on two-lane
roads in hills or mountains. Don’t swing wide or
cut across the center of the road. Drive at speeds
that let you stay in your own lane.
As you go over the top of a hill, be alert. There
could be something in your lane, like
a stalled car or
an accident.
You may see highway signs on mountains that
warn of special problems. Examples are long
grades, passing or no-passing zones, a falling rocks
area or winding roads. Be alert to these and take
appropriate action.
4-24
Page 199 of 354

Driving on Snow or Ice
Most of the time, those places where your tires meet
the road probably have good traction.
However,
if there is snow or ice between your tires and
the road, you can have a very slippery situation.
You’ll have a
lot less traction or “grip” and will need to
be very careful. What’s
the worst time for this? “Wet ice.” Very cold
snow or ice can be slick and hard to drive on. But wet
ice can be even more trouble because it may offer
the least traction of all. You can get wet ice when it’s
about freezing
(32°F; OOC) and freezing rain begins
to fall. Try to avoid driving on wet ice until salt and sand
crews can get there.
Whatever the condition
- smooth ice, packed, blowing
or loose snow
- drive with caution.
Keep your Enhanced Traction System on.
It will improve
your ability to accelerate when driving on a slippery
road. Even though your vehicle has this system, you’ll
want
to slow down and adjust your driving to the
road conditions. See
Enhanced Traction System (ETS)
on page 4-9.
Unless you have the anti-lock braking system, you’ll
want to brake very gently,
too. (If you do have anti-lock,
see
Braking on page 4-6. This system improves your
vehicle’s stability when you make a hard stop on a
slippery road.) Whether you have the anti-lock braking
system or not, you’ll want to begin stopping sooner than
you would on dry pavement. Without anti-lock brakes,
if you feel your vehicle begin to slide, let up on the
brakes a little. Push the brake pedal down steadily to
get the most traction you can.
4-26
Page 202 of 354

Run your engine only as long as you must. This saves If You Are Stuck: In Sand, Mud,
fuel. When you run the engine, make it go a iiliie
faster than iust idle. That is, push the accelerator Ice or Snow
slightly. This uses less fuel for the heat that you get and
it keeps the battery charged. You will need a
well-charged battery to restart the vehicle, and possibly need to spin the wheels, but you don’t want to spin your
for signaling later
on with your headlamps. Let the
heater run for a while. In
order to free your vehicle when it is stuck, you will
wheels too fast. The method known as “rocking” can
help you get out when you’re stuck, but you must
use caution.
Then, shut the engine
off and close the window almost all
the way to preserve the heat. Start the engine again and
repeat this only when you feel really uncomfortable from
the cold. But do it as little as possible. Preserve the fuel
as long as you can. To help keep warm, you can get out
of the vehicle and do some fairly vigorous exercises
every half hour or
so until help comes. _~OU let your tires spin __ -..gh speed, they
injured. And, the transaxle or other parts
of the
vehicle can overheat. That could cause an
engine compartment fire or other damage.
When you’re stuck, spin the wheels as little as
possible. Don’t spin the wheels above 35 mph
f55 km/h) as shown on the speedometer.
can expbde, and you or others could be
4-29
Page 203 of 354

Notice: Spinning your wheels can destroy parts of
your vehicle as well as the tires.
If you spin the
wheels
too fast while shifting your transaxle back
and forth, you can destroy your transaxle. See
“Rocking Your Vehicle
To Get It Out.”
For information about using tire chains on your vehicle,
see Tire
Chains on page 5-60.
Rocking Your Vehicle To Get It Out
First, turn your steering wheel left and right. That will
clear the area around your front wheels. Then shift back
and forth between REVERSE
(R) and a forward gear
(or with a manual transaxle, between FIRST
(1) or
SECOND
(2) and REVERSE (R)), spinning the wheels
as little as possible. Release the accelerator pedal
while you shift, and press lightly on the accelerator pedal
when the transaxle is in gear. By slowly spinning your
wheels in the forward and reverse directions, you
will cause a rocking motion that may free your vehicle.
H
that doesn’t get you out after a few tries, you may
need to be towed out. If you do need to be towed
out
see “Towing Your Vehicle’’ following.
4-30
Page 207 of 354
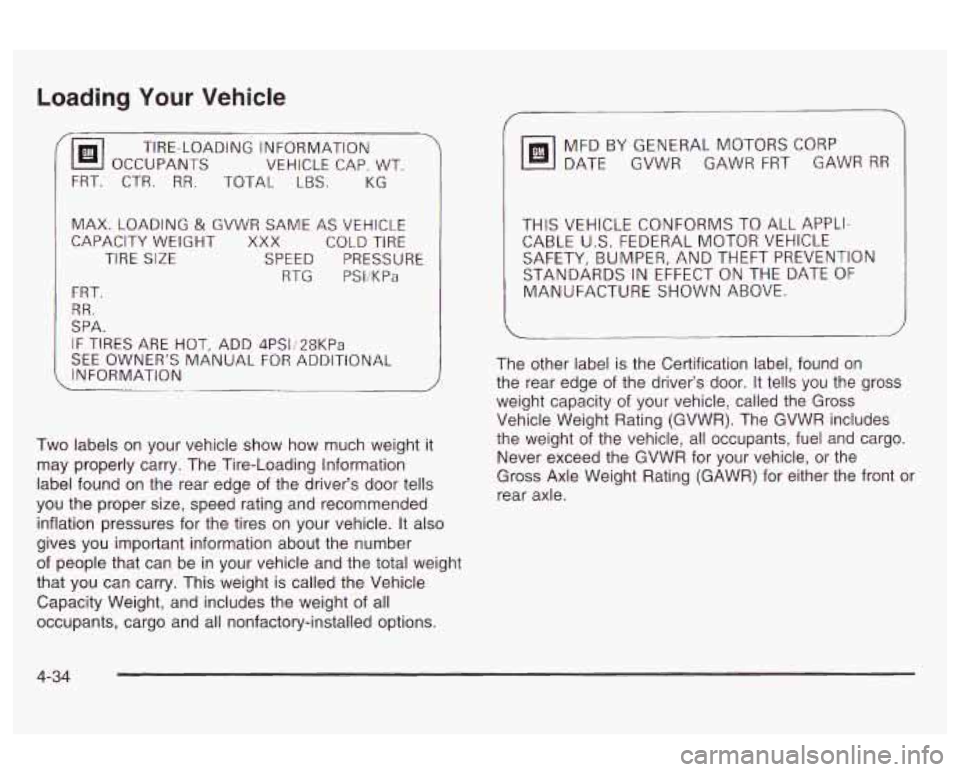
Loading Your Vehicle
(@I OCCUPANTS VEHICLE CAP. WT.
TIRE-LOADING
INFORMATION
TOTAL
LBS. KG
MAX. LOADING & GVWR SAME AS VEHICLE
CAPACITY WEIGHT XXX COLD TIRE
TIRE
SIZE SPEED PRESSURE
RTG PSliKPa
FRT.
RR.
SPA.
IF TIRES ARE HOT, ADD 4PS1;28KPa
SEE OWNER’S MANUAL FOR ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION
~ ~~~~ ~-
Two labels on your vehicle show how much weight it
may properly carry. The Tire-Loading Information
label found on the rear edge of the driver’s door tells
you the proper size, speed rating and recommended
inflation pressures for the tires on your vehicle. It also
gives you important information about the number
of people that can be in your vehicle and the total weight
that you can carry. This weight is called the Vehicle
Capacity Weight, and includes the weight of all
occupants, cargo and all nonfactory-installed options. MFDBYGENERALMOTORSCORP
DATE GVWR GAWR FRT GAWR
RR
THIS VEHICLE CONFORMS TO ALL APPLI-
CABLE U.S. FEDERAL MOTOR VEHICLE
SAFETY, BUMPER, AND THEFT PREVENTION
STANDARDS
IN EFFECT ON THE DATE OF
MANUFACTURE SHOWN ABOVE.
The other label is the Certification label, found on
the rear edge of the driver’s door. It tells you the gross
weight capacity of your vehicle, called the Gross
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). The GVWR includes
the weight of the vehicle, all occupants, fuel and cargo.
Never exceed the GVWR for your vehicle, or the
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) for either the front or
rear axle.
4-34