2003 NISSAN ALMERA N16 Ac system
[x] Cancel search: Ac systemPage 28 of 3189

TESTING FOR “OPENS” IN THE CIRCUITNJGI0005S0302Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should
rough sketch a schematic of the system. This will help you to logi-
cally walk through the diagnoses process. Drawing the sketch will
also reinforce your working knowledge of the system.
SGI846
Continuity Check Method
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The
Digital Multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance function will indicate
an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol).
Make sure to always start with the DMM at the highest resistance
level.
To help in understanding the diagnoses of open circuits please
refer to the schematic above.
1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2) Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other
end. (At the fuse block in this example)
3) Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on
the load side.
4) Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1.
Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has
good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM
would indicate an over limit or infinite resistance condition.
(point A)
5) Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no
resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has good con-
tinuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would
indicate an over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point B)
6) Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little
or no resistance will indicate that portion of the circuit has good
continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would
indicate an over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the above
example.
Voltage Check Method
To help in understanding the diagnoses of open circuits please
refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically
checking the system for the presence of voltage. This is done by
switching the DMM to the voltage function.
1) Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
2) Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to
the other end.
3) With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
4) Close SW1 and probe at relay.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-26
Page 29 of 3189
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
5) Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the
above example.
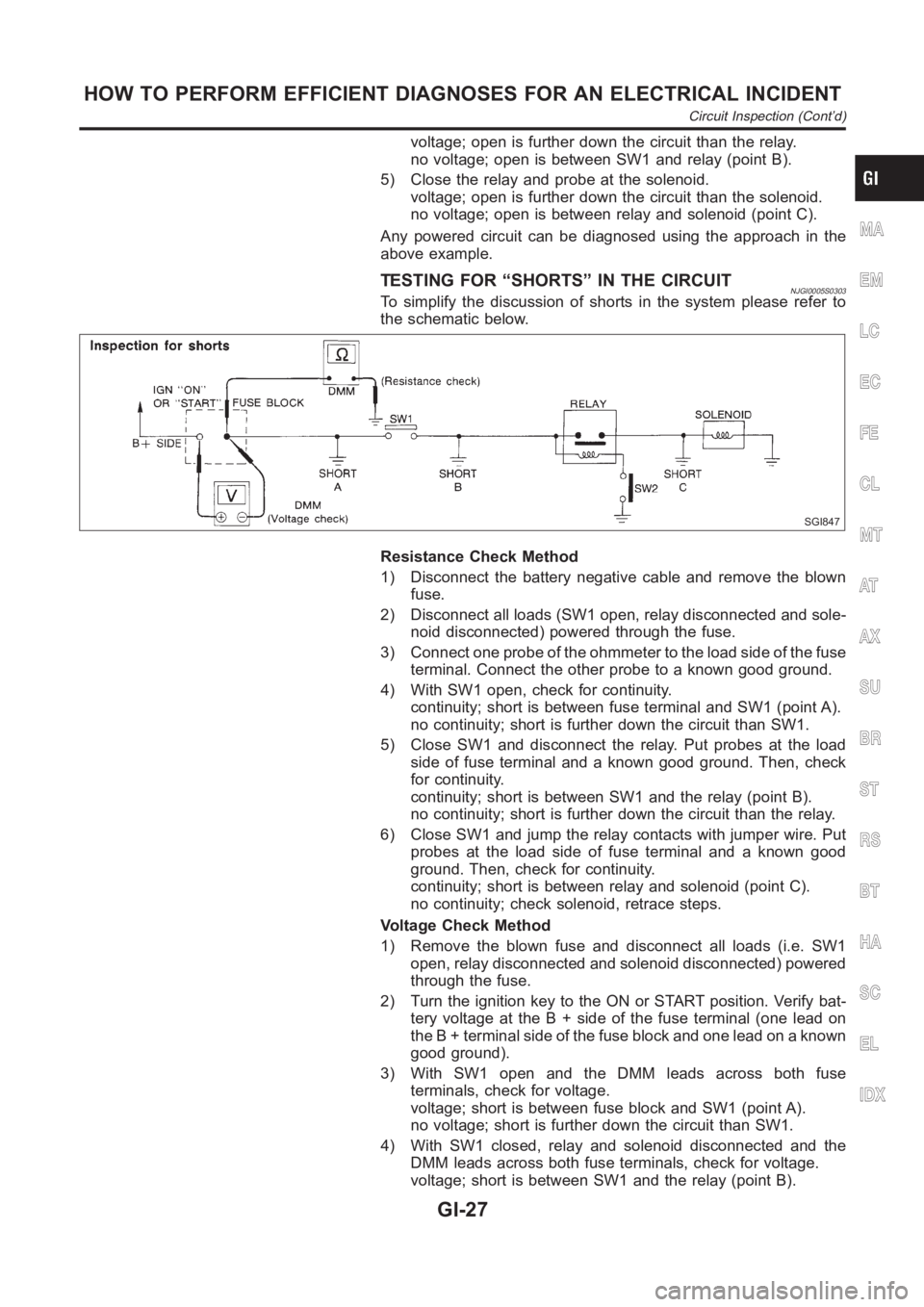
TESTING FOR “SHORTS” IN THE CIRCUITNJGI0005S0303To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system please refer to
the schematic below.
SGI847
Resistance Check Method
1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown
fuse.
2) Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and sole-
noid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
3) Connect one probe of the ohmmeter to the load side of the fuse
terminal. Connect the other probe to a known good ground.
4) With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
5) Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load
side of fuse terminal and a known good ground. Then, check
for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
6) Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put
probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
Voltage Check Method
1) Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1
open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered
through the fuse.
2) Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify bat-
tery voltage at the B + side of the fuse terminal (one lead on
the B + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known
good ground).
3) With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse
terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
4) With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the
DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-27
Page 31 of 3189
strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
Undersized wiring (single strand example)
Corrosion on switch contacts
Loose wire connections or splices.
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger
gauge.
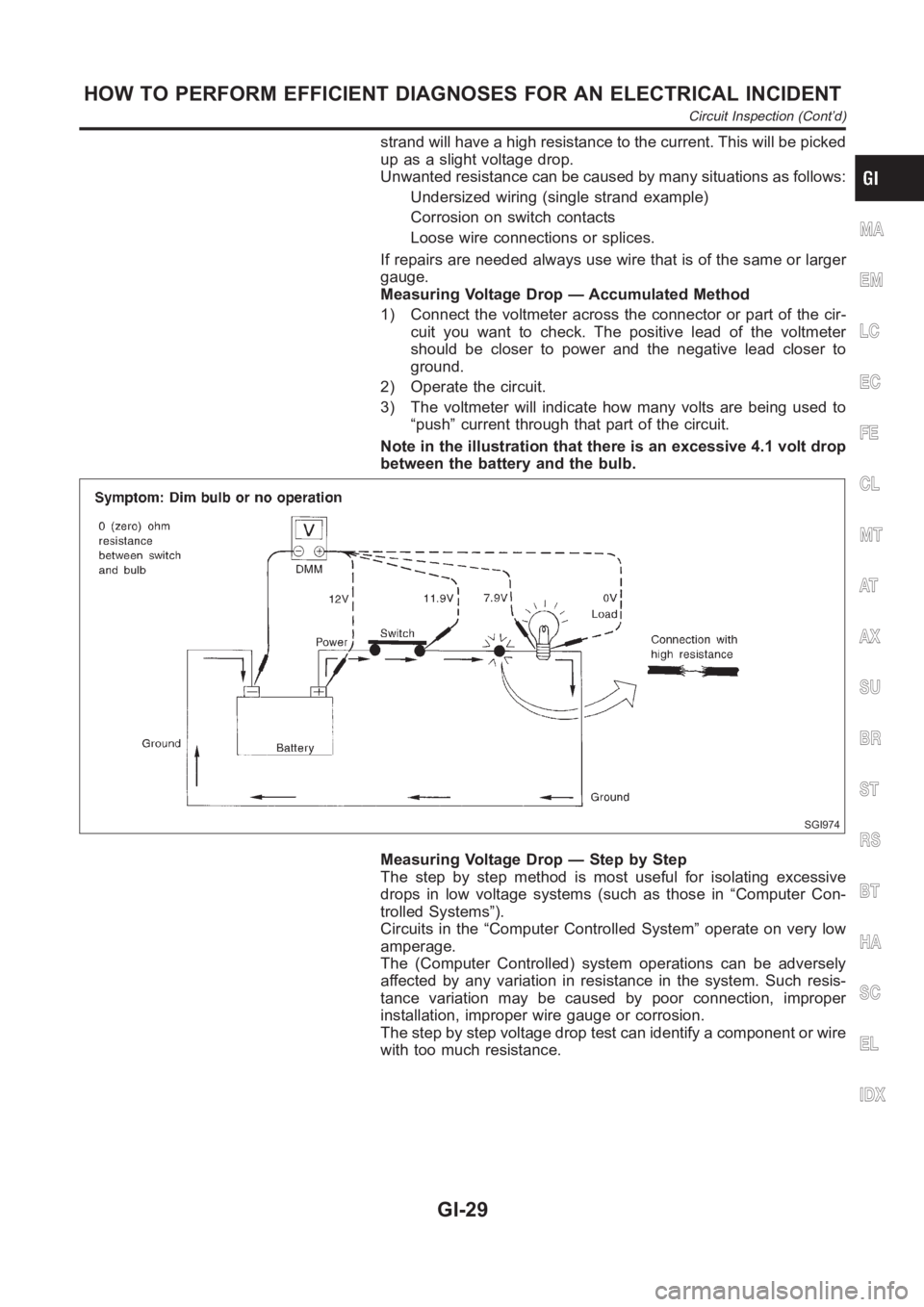
Measuring Voltage Drop — Accumulated Method
1) Connect the voltmeter across the connector or part of the cir-
cuit you want to check. The positive lead of the voltmeter
should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to
ground.
2) Operate the circuit.
3) The voltmeter will indicate how many volts are being used to
“push” current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop
between the battery and the bulb.
SGI974
Measuring Voltage Drop — Step by Step
The step by step method is most useful for isolating excessive
drops in low voltage systems (such as those in “Computer Con-
trolled Systems”).
Circuits in the “Computer Controlled System” operate on very low
amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely
affected by any variation in resistance in the system. Such resis-
tance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper
installation, improper wire gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire
with too much resistance.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-29
Page 32 of 3189
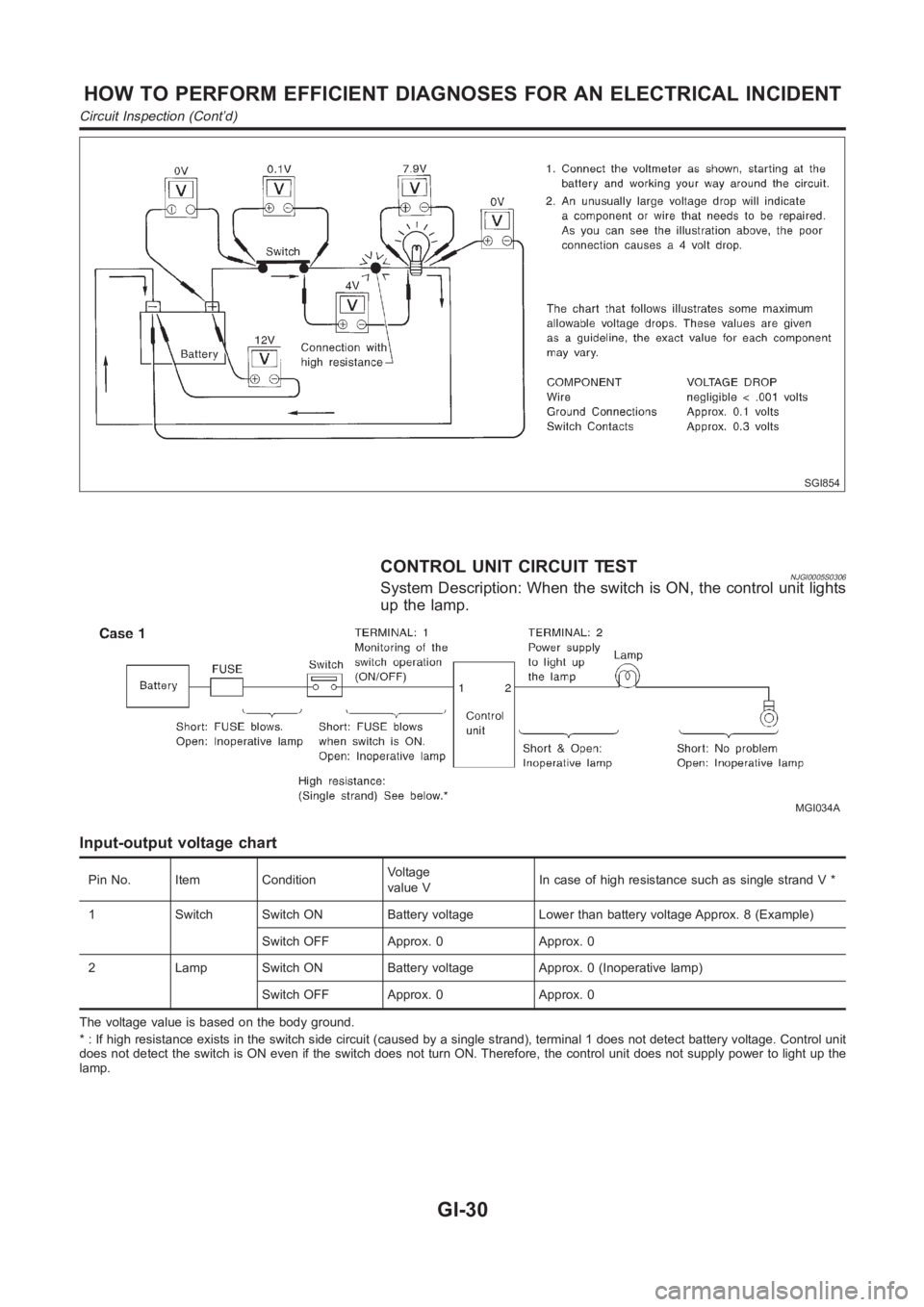
SGI854
CONTROL UNIT CIRCUIT TESTNJGI0005S0306System Description: When the switch is ON, the control unit lights
up the lamp.
MGI034A
Input-output voltage chart
Pin No. Item ConditionVoltage
value VIn case of high resistance such as single strand V *
1 Switch Switch ON Battery voltage Lower than battery voltage Approx. 8 (Example)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
2 Lamp Switch ON Battery voltage Approx. 0 (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF Approx. 0 Approx. 0
The voltage value is based on the body ground.
* : If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 1 does not detect battery voltage. Control unit
does not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not supply power to light up the
lamp.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSES FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont’d)
GI-30
Page 34 of 3189

NJGI0006
NOTICE:
Trouble diagnoses indicate work procedures required to diagnose
problems effectively. Observe the following instructions before
diagnosing.
1)Before performing trouble diagnoses, read the “Prelimi-
nary Check”, the “Symptom Chart” or the “Work Flow”.
2)After repairs, re-check that the problem has been com-
pletely eliminated.
3)Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion for the Systems described in each section for
identification/location of components and harness con-
nectors.
4)Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness
connectors in more detail, such as when a sub-harness is
used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section
and Harness Layout in EL section for identification of har-
ness connectors.
5)When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should
be OFF.
6)Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery volt-
age.
7)After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures and Elec-
trical Components Inspection, make sure that all harness
connectors are reconnected as they were.
HOW TO FOLLOW TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GI-32
Page 38 of 3189
NJGI0007
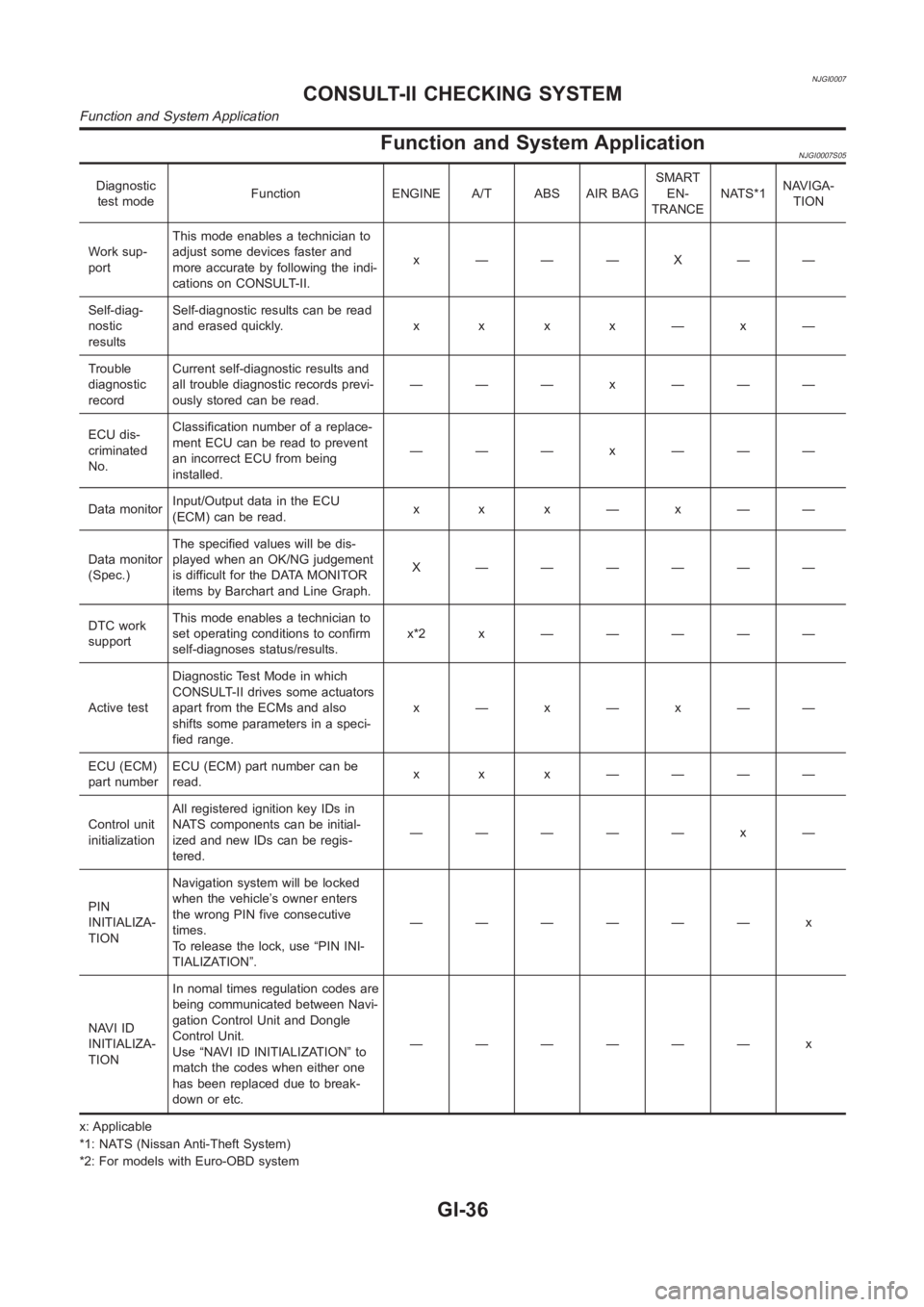
Function and System ApplicationNJGI0007S05
Diagnostic
test modeFunction ENGINE A/T ABS AIR BAGSMART
EN-
TRANCENATS*1NAVIGA-
TION
Work sup-
portThis mode enables a technician to
adjust some devices faster and
more accurate by following the indi-
cations on CONSULT-II.x ———X——
Self-diag-
nostic
resultsSelf-diagnostic results can be read
anderasedquickly. x x x x—x—
Trouble
diagnostic
recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and
all trouble diagnostic records previ-
ously stored can be read.——— x ———
ECU dis-
criminated
No.Classification number of a replace-
ment ECU can be read to prevent
an incorrect ECU from being
installed.——— x ———
Data monitorInput/Output data in the ECU
(ECM) can be read.x x x—x——
Data monitor
(Spec.)The specified values will be dis-
played when an OK/NG judgement
is difficult for the DATA MONITOR
items by Barchart and Line Graph.X ——————
DTC work
supportThis mode enables a technician to
set operating conditions to confirm
self-diagnoses status/results.x*2x —————
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which
CONSULT-II drives some actuators
apart from the ECMs and also
shifts some parameters in a speci-
fied range.x—x—x——
ECU (ECM)
part numberECU (ECM) part number can be
read.x x x ————
Control unit
initializationAll registered ignition key IDs in
NATS components can be initial-
ized and new IDs can be regis-
tered.————— x —
PIN
INITIALIZA-
TIONNavigation system will be locked
when the vehicle’s owner enters
the wrong PIN five consecutive
times.
To release the lock, use “PIN INI-
TIALIZATION”.—————— x
NAVI ID
INITIALIZA-
TIONIn nomal times regulation codes are
being communicated between Navi-
gation Control Unit and Dongle
Control Unit.
Use “NAVI ID INITIALIZATION” to
match the codes when either one
has been replaced due to break-
down or etc.—————— x
x: Applicable
*1: NATS (Nissan Anti-Theft System)
*2: For models with Euro-OBD system
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
Function and System Application
GI-36
Page 39 of 3189

Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Replacement=NJGI0007S06CONSULT-II contains a nickel metal hydride battery. When replacing the battery obey the following:
WARNING:
Replace the nickel metal hydride battery with Genuine CONSULT-II batteryonly. Use of another bat-
tery may present a risk of fire or explosion. The battery may present a fire orchemicalburnhazardif
mistreated. Do not recharge, disassemble of dispose of in fire.
Keep the battery out of reach of children and discard used battery conforming to the local regulations.
Checking EquipmentNJGI0007S07When ordering the below equipment, contact your NISSAN distributor.
Tool name Description
NISSAN CONSULT-II
1CONSULT-II unit (Tester internal soft:
Resident version 3.3.0) and accessories
2Program card AED02D and AEN02B
(For NATS Version 5.6)
To confirm the best combination of these
softwares, refer to CONSULT-II Operation
Manual.
SGI083A
NOTE:
The CONSULT-II must be used in conjunction with a program card.
CONSULT-II does not require loading (Initialization) procedure.
Be sure the CONSULT-II is turned off before installing or removing a program card.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery Replacement
GI-37
Page 40 of 3189

CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit=NJGI0007S08
SGI122A
INSPECTION PROCEDURENJGI0007S0801If the CONSULT-II cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
Symptom Check item
CONSULT-II cannot access any
system.CONSULT-II DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 8) and ground circuit (Terminal 4)
(For detailed circuit, refer to EC-397 (QG) or EC-213 (YD), “MIL & Data LinkConnectors Wiring
Diagram”.)
CONSULT-II DDL cable
CONSULT-II cannot access indi-
vidual system. (Other systems
can be accessed.)CONSULT-II program card (Check the approprite CONSULT-II program card for the system.
Refer to “Checking Equipment” above.)
Power supply and ground circuit for the control unit of the system
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
Open or short circuit between the system and CONSULT-II DLC
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit
GI-38