2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE abs cab wiring
[x] Cancel search: abs cab wiringPage 212 of 2199

(7) Raise and support the vehicle.
(8) Remove the wheel and tire assemblies.
(9) Remove the brake calipers, caliper anchors and
rotors.
(10) Remove the ABS sensor wiring harness (Fig.
74)from the rear brake cables.
(11) Remove the cable retainer bolts (Fig. 74) from
the rear spring pads.
(12) Pull the cables out of the upper suspension
arm brackets.
(13) Push the cable in and lift up the end of cable
with a small screw driver to disengage the cable from
the parking brake actuator (Fig. 75).
(14) Remove the cable from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE
(1) Install thecable into the parking brake lever
bracket and equalizer bracket.
(2) Install the front cable to the floor pan and
install retainer nuts.
(3) Engage the front cable ends to the parking
brake lever and equalizer.
(4) Install the front carpet, (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/CARPETS AND FLOOR MATS -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Pull on the lever to release the lock out spring.
(6) Install the center console, (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(7) Fold down the rear carpet cover and rear seat.
INSTALLATION - REAR PARKING BRAKE
CABLES
(1) Install the cables through the caliper anchor
mount. Then push the end of cable strand in to
engage the cable end to the parking brake actuator.
(2) Feed the other end of the cables through the
body and into the equalizer bracket (Fig. 76).
Fig. 74 Left Rear Parking Brake Cable
1 - CABLE BRACKET
2 - UPPER SUSPENSION ARM
3 - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
4 - CABLE RETAINER
5 - ABS SENSOR WIRING
Fig. 75 Parking Brake
1 - CABLE END
2 - SCREW DRIVER
3 - PARKING BRAKE ACTUATOR
4 - BRAKE SHOES
Fig. 76 Equalizer Bracket
1 - EQUALIZER
2 - RIGHT REAR CABLE
3 - LEFT REAR CABLE
4 - FRONT CABLE
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 37
CABLES (Continued)
Page 213 of 2199

(3) Push the cables into the upper suspension arm
brackets.
(4) Install the cable retainer bolts to the rear
spring pads.
(5) Install the ABS sensor wiring harness to the
rear brake cables.
(6) Install the rotors, caliper anchors and brake
calipers.
(7) Install the wheel and tire assemblies.
(8) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(9) Engage the cable ends into the parking brake
equalizer.
(10) Pull on the lever to release the lock out
spring.
(11) Install center console, (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLATION).
(12) Fold down the rear carpet cover and rear seat.
(13) Verify parking brake operation.
LEVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove center console,(Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Lift up rear seat and carpet covering the park-
ing brake cables.
(3) Place a screw driver through the front cable
eyelet (Fig. 77) and pry back on the front cable.(4) Have an assistant pry down the lock out spring
through the hole in the side of the park brake lever
(Fig. 78) with a small screw driver. Then slowly
release the front cable.
NOTE: Their should be slack in the cable if the lock
out spring is engaged.
(5) Disconnect parking brake switch wiring con-
nector.
(6) Disengage front cable end from parking brake
lever.
(7) Compress the cable retainer with a 13 mm
wrench (Fig. 79) and remove the cable from the park-
ing brake lever bracket.
Fig. 77 FRONT CABLE
1 - REAR CABLES
2 - FRONT CABLE EYELET
3 - FRONT CABLE
4 - EQUALIZER
Fig. 78 Lock Out Spring
1 - LOCK OUT SPRING
Fig. 79 Parking Brake Lever Bracket
1 - FRONT CABLE
2 - WRENCH
5 - 38 BRAKES - BASEWJ
CABLES (Continued)
Page 392 of 2199

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HORN SOUNDS
CONTINUOUSLY1. Faulty horn relay. 1. Refer to Horn Relay for the proper horn relay
diagnosis and testing procedures. Replace the
horn relay or repair the shorted horn relay control
circuit, if required.
2. Faulty horn switch. 2. Refer to Horn Switch for the proper horn switch
diagnosis and testing procedures. Replace the
horn switch or repair the shorted horn switch
circuit, if required.
HORN
DESCRIPTION
The dual electromagnetic diaphragm-type horns
are standard equipment on this model. Both horns
are secured to a mounting bracket. The mounting
bracket is secured with a screw to the back side of
the right extension of the radiator closure assembly,
just ahead of the right front wheel house and below
the front wheel house extension. The two horns are
connected in parallel. Each horn is grounded through
its wire harness connector and circuit to an eyelet
secured to the right inner fender shield near the bat-
tery, and receives battery feed through the closed
contacts of the horn relay.
The horns cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, they must be individually
replaced.
OPERATION
Within the two halves of the molded plastic horn
housing are a flexible diaphragm, a plunger, an elec-
tromagnetic coil and a set of contact points. The dia-
phragm is secured in suspension around its
perimeter by the mating surfaces of the horn hous-
ing. The plunger is secured to the center of the dia-
phragm and extends into the center of the
electromagnet. The contact points control the current
flow through the electromagnet.
When the horn is energized, electrical current
flows through the closed contact points to the electro-
magnet. The resulting electromagnetic field draws
the plunger and diaphragm toward it until that
movement mechanically opens the contact points.
When the contact points open, the electromagnetic
field collapses allowing the plunger and diaphragm to
return to their relaxed positions and closing the con-
tact points again. This cycle continues repeating at a
very rapid rate producing the vibration and move-
ment of air that creates the sound that is directed
through the horn outlet.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect the wire harness connector(s) from
the horn connector receptacle(s). Measure the resis-
tance between the ground circuit cavity of the horn(s)
wire harness connector(s) and a good ground. There
should be no measurable resistance. If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the horn relay out-
put circuit cavity of the horn(s) wire harness connec-
tor(s). There should be zero volts. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the shorted horn relay output cir-
cuit or replace the faulty horn relay as required.
(3) Depress the horn switch. There should now be
battery voltage at the horn relay output circuit cavity
of the horn(s) wire harness connector(s). If OK,
replace the faulty horns. If not OK, repair the open
horn relay output circuit to the horn relay as
required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the lower front half of the inner liner
from the right front fender wheel house. (Refer to 23
- BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT FENDER - REMOVAL).
(4) Reach through the front of the right front
fender wheel house opening to access and disconnect
the two right headlamp and dash wire harness con-
nectors from the horn connector receptacles (Fig. 1).
Be certain to disengage the connector lock tabs
before disconnecting them from the horn connector
receptacles.
(5) Remove the screw that secures the horn
mounting bracket to the right extension of the radi-
ator closure assembly.
WJHORN 8H - 3
HORN SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 393 of 2199

(6) Remove both horns and the mounting bracket
from the right extension of the radiator closure
assembly as a unit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position both horns and the mounting bracket
onto the right extension of the radiator closure
assembly as a unit.
(2) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
horn mounting bracket to the right extension of the
radiator closure assembly. Tighten the screw to 11.3
N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the two right headlamp and dash
wire harness connectors to the horn connector recep-
tacles. Be certain to engage the connector lock tabs
after reconnecting them to the horn connector recep-
tacles.
(4) Install the lower front half of the inner liner to
the right front fender wheel house. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT FENDER - INSTALLA-
TION) for the procedure.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HORN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The horn relay is a electromechanical device that
switches battery current to the horn when the horn
switch grounds the relay coil. The horn relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) inthe engine compartment. If a problem is encountered
with a continuously sounding horn, it can usually be
quickly resolved by removing the horn relay from the
PDC until further diagnosis is completed. See the
fuse and relay layout label affixed to the inside sur-
face of the PDC cover for horn relay identification
and location.
The horn relay is a International Standards Orga-
nization (ISO) micro-relay. Relays conforming to the
ISO specifications have common physical dimensions,
current capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal
functions. The ISO micro-relay terminal functions
are the same as a conventional ISO relay. However,
the ISO micro-relay terminal pattern (or footprint) is
different, the current capacity is lower, and the phys-
ical dimensions are smaller than those of the conven-
tional ISO relay.
The horn relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN RELAY
The horn relay (Fig. 2) is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) between the battery and the
right inner fender shield on the passenger side of the
engine compartment. If a problem is encountered
with a continuously sounding horn, it can usually be
quickly resolved by removing the horn relay from the
PDC until further diagnosis is completed. See the
fuse and relay layout label affixed to the inside sur-
face of the PDC cover for horn relay identification
and location. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 1 Horns Remove/Install
1 - RADIATOR CLOSURE ASSEMBLY
2 - HORNS AND MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - RIGHT HEADLAMP AND DASH WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTORS
8H - 4 HORNWJ
HORN (Continued)
Page 601 of 2199

(2) Check for continuity between the two terminals
of the hood ajar switch. There should be continuity
with the switch plunger extended, and no continuity
with the switch plunger depressed. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty hood ajar switch.
(3) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the Body Control Module (BCM).
Check for continuity between the hood ajar switch
sense circuit of the hood ajar switch and a good
ground. There should be no continuity. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, repair the shorted hood ajar switch
sense circuit between the hood ajar switch and the
BCM.
(4) Check for continuity between the hood ajar
switch sense circuit and the instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, proceed to diagnosis of the Vehicle
Theft Security System (VTSS). (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). If not OK, repair the open hood
ajar switch sense circuit between the hood ajar
switch and the BCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - HOOD AJAR SWITCH
(1) Open the hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Squeeze the two switch latch tabs together and
pull the switch upward (Fig. 3)
(4) Disconnect the wiring harness connector.
(5) Remove the hood ajar switch from the mount-
ing bracket.
REMOVAL - HOOD AJAR SWITCH BRACKET
(1) Remove the hood ajar switch from the mount-
ing bracket. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE
THEFT SECURITY/HOOD AJAR SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the two nuts that secure the hood ajar
switch bracket to the left inner fender (Fig. 3)
(3) Remove the hood ajar switch bracket from the
studs on the left inner fender.
REMOVAL - HOOD AJAR SWITCH STRIKER
(1) Open the hood.
(2) Using a trim stick or another suitable wide
flat-blade tool, gently raise the hood ajar switch
striker away from the inner hood panel reinforce-
ment, and remove. (Fig. 4).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - HOOD AJAR SWITCH
(1) Position the hood ajar switch into the hole in
the mounting bracket (Fig. 3)
(2) Reconnect the wiring harness connector.
(3) Press the switch downward into the mounting
bracket until the latch tabs lock it into place.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(5) Close and latch the hood.
INSTALLATION - HOOD AJAR SWITCH
BRACKET
(1) Position the hood ajar switch bracket onto the
studs on the left inner fender (Fig. 3)
(2) Install and tighten the two nuts. Tighten the
nuts to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the hood ajar switch into the mount-
ing bracket. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/VEHICLE
THEFT SECURITY/HOOD AJAR SWITCH -
INSTALLATION).
Fig. 4 Hood Ajar Switch Striker
1 - REINFORCEMENT
2 - STRIKER
3 - HOOD
8Q - 10 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYWJ
HOOD AJAR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1233 of 2199

are only serviced as a unit with the right headlamp
and dash wire harness. If the PDC main housing
unit, fuse wedges or the bus bars are faulty or dam-
aged, the right headlamp and dash wire harness unit
must be replaced.
OPERATION
All of the current from the battery and the generator
output enters the PDC through two cables and a single
two-holed eyelet that is secured with nuts to the two
PDC B(+) terminal studs just inside the front end of the
PDC housing. The PDC cover is unlatched and opened
to access the battery and generator output connection
B(+) terminal studs, the fuses or the relays. Internal
connection of all of the PDC circuits is accomplished by
an intricate combination of hard wiring and bus bars.
Refer toPower Distribution
in Wiring Diagrams for
the location of complete PDC circuit diagrams.
REMOVAL
The Power Distribution Center (PDC) main housing
unit, the PDC fuse wedges and the PDC bus bars can-
not be repaired and are only serviced as a unit with the
right headlamp and dash wire harness. If the PDC
main housing unit, the fuse wedges or the bus bars are
faulty or damaged, the entire PDC and right headlamp
and dash wire harness unit must be replaced.
(1)Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect each of the right headlamp and
dash wire harness connectors. Refer toConnector
Locationsin Wiring Diagrams for the location of
more information on the right headlamp and dash
wire harness connector locations.
(3) Remove all of the fasteners that secure each of
the right headlamp and dash wire harness ground
eyelets to the vehicle body and chassis components.
Refer toConnector Locationsin Wiring Diagrams
for the location of more information on the ground
eyelet locations.
(4) Disengage each of the retainers that secure the
right headlamp and dash wire harness to the vehicle
body and chassis components. Refer toConnector
Locationsin Wiring Diagrams for the location of
more information on the right headlamp and dash
wire harness retainer locations.
(5) Unlatch and open the PDC cover.
(6) Remove the two nuts that secure the two-holed
eyelet of the battery wire harness PDC take outs to
the PDC B(+) terminal studs (Fig. 8).
(7) Remove the battery wire harness PDC take out
eyelet from the B(+) terminal studs.
(8) Disengage the latches on the PDC housing
mounts from the tabs on the PDC mounting stan-
chions of the battery support, and pull the PDC
housing upward to disengage the mounts from the
stanchions (Fig. 9).
Fig. 8 Power Distribution Center Connections
1 - PDC COVER
2 - NUT (2)
3 - EYELET
4 - B(+) TERMINAL STUDS
Fig. 9 Power Distribution Center Remove/Install
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
2 - MOUNTS
3 - STANCHIONS (3)
4 - BATTERY SUPPORT
8W - 97 - 8 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONWJ
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (Continued)
Page 1237 of 2199

PDC LOWER COVER INSTALLATION
(1) Align the PDC housing lower cover on the bot-
tom of the PDC.
(2) Evenly press the lower cover into place until
latches are fully engaged.
(3) Where the right headlamp and dash harness
enters the PDC, tape the harness securely to the
trough formation on the PDC lower cover.
(4) Install the PDC in its mounting location on the
battery support.
(5) Install the battery wire harness over the two
PDC B+ terminal studs. Torque the nuts to 11.3 N´m
(100 in. lbs.).
(6) Install the battery. Refer to Battery System for
the procedure.
(7) Install the PDC cover.
INSTALLATION
The Power Distribution Center (PDC) main hous-
ing unit, the PDC fuse wedges and the PDC bus bars
cannot be repaired and are only serviced as a unit
with the right headlamp and dash wire harness. If
the PDC main housing unit, the fuse wedges or the
bus bars are faulty or damaged, the entire PDC and
right headlamp and dash wire harness unit must be
replaced.
(1) Position the PDC and the right headlamp and
dash wire harness unit in the engine compartment.
(2) Engage the PDC housing mounts with the
stanchions of the battery support and push the unit
downward until the mount latches fully engage the
mounting tabs on the stanchions.
(3) Install the two-holed eyelet of the battery wire
harness PDC take outs onto the two PDC B(+) termi-
nal studs.
(4) Install and tighten the nuts that secure the
eyelet of the battery wire harness PDC take outs to
the B(+) terminal studs. Tighten the nuts to 11.3
N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(5) Engage each of the retainers that secure the
right headlamp and dash wire harness to the vehicle
body and chassis components. Refer toConnector
Locationsin Wiring Diagrams for the location of
more information on the right headlamp and dash
wire harness retainer locations.
(6) Install all of the fasteners that secure each of
the right headlamp and dash wire harness ground
eyelets to the vehicle body and chassis components.
Refer toConnector Locationsin Wiring Diagrams
for the location of more information on the ground
eyelet locations.
(7) Reconnect each of the right headlamp and dash
wire harness connectors. Refer toConnector Loca-
tionsin Wiring Diagrams for the location of more
information on the right headlamp and dash wire
harness connector locations. For connectors securedwith screws, tighten the screws to 4.3 N´m (38 in.
lbs.).
(8) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION - FRONT POWER OUTLET
An accessory power outlet is standard equipment
on this model. The power outlet is installed in the
instrument panel center lower bezel, which is located
near the bottom of the instrument panel center stack
area, below the heater and air conditioner controls.
The power outlet base is secured by a snap fit within
the center lower bezel. A hinged door with an over-
center spring flips closed to conceal and protect the
power outlet base when the power outlet is not being
used, and flips open below the center lower bezel
while the power outlet is in use.
The power outlet receptacle unit and the power
outlet door are each available for service replace-
ment.
OPERATION - FRONT POWER OUTLET
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet receives battery voltage from a fuse
in the junction block at all times.
While the power outlet is very similar to a cigar
lighter base unit, it does not include the two small
spring-clip retainers inside the bottom of the recepta-
cle shell that are used to secure the cigar lighter
heating element to the insulated contact.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toHorn/Ci-
gar Lighter/Power Outletin Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: REFER TO RESTRAINTS BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the junction block.
If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the shorted cir-
cuit or component as required and replace the faulty
fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the junction block. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK,
repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) fuse as required.
(3) Open the power outlet door. Check for continu-
ity between the inside circumference of the power
8W - 97 - 12 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONWJ
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (Continued)
Page 1299 of 2199
(9) Lower the engine until it is properly located on
the engine mounts.
(10) Install the through bolts and tighten the nuts.
(11) Lower the jack stand and remove the piece of
wood.
(12) Install the engine flywheel and transmission
torque converter housing access cover.
(13) Install the engine starter motor. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR -
INSTALLATION).
(14) Connect the exhaust pipe to the hanger and to
the engine exhaust manifold.
(15) Install transmission oil cooling lines (if
equipped) and oxygen sensor wiring supports that
attach to the oil pan studs.
(16) Install the oil pan drain plug (Fig. 81).
Tighten the plug to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(17) Lower the vehicle.
(18) Connect negative cable to battery.
(19) Fill the oil pan with engine oil to the specified
level.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(20) Start the engine and inspect for leaks.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 3±wire, solid-state engine oil pressure sensor
(sending unit) is located in an engine oil pressure
gallery.
OPERATION
The oil pressure sensor uses three circuits. They
are:
²A 5±volt power supply from the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM)
²A sensor ground through the PCM's sensor
return
²A signal to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure
The oil pressure sensor has a 3±wire electrical
function very much like the Manifold Absolute Pres-
sure (MAP) sensor. Meaning different pressures
relate to different output voltages.
A 5±volt supply is sent to the sensor from the PCM
to power up the sensor. The sensor returns a voltage
signal back to the PCM relating to engine oil pres-
sure. This signal is then transferred (bussed) to theinstrument panel on either a CCD or PCI bus circuit
(depending on vehicle line) to operate the oil pressure
gauge and the check gauges lamp. Ground for the
sensor is provided by the PCM through a low-noise
sensor return.
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
A gear-type oil pump is mounted at the underside
of the cylinder block opposite the No.4 main bearing.
(1) Drain the engine oil.
(2) Remove the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
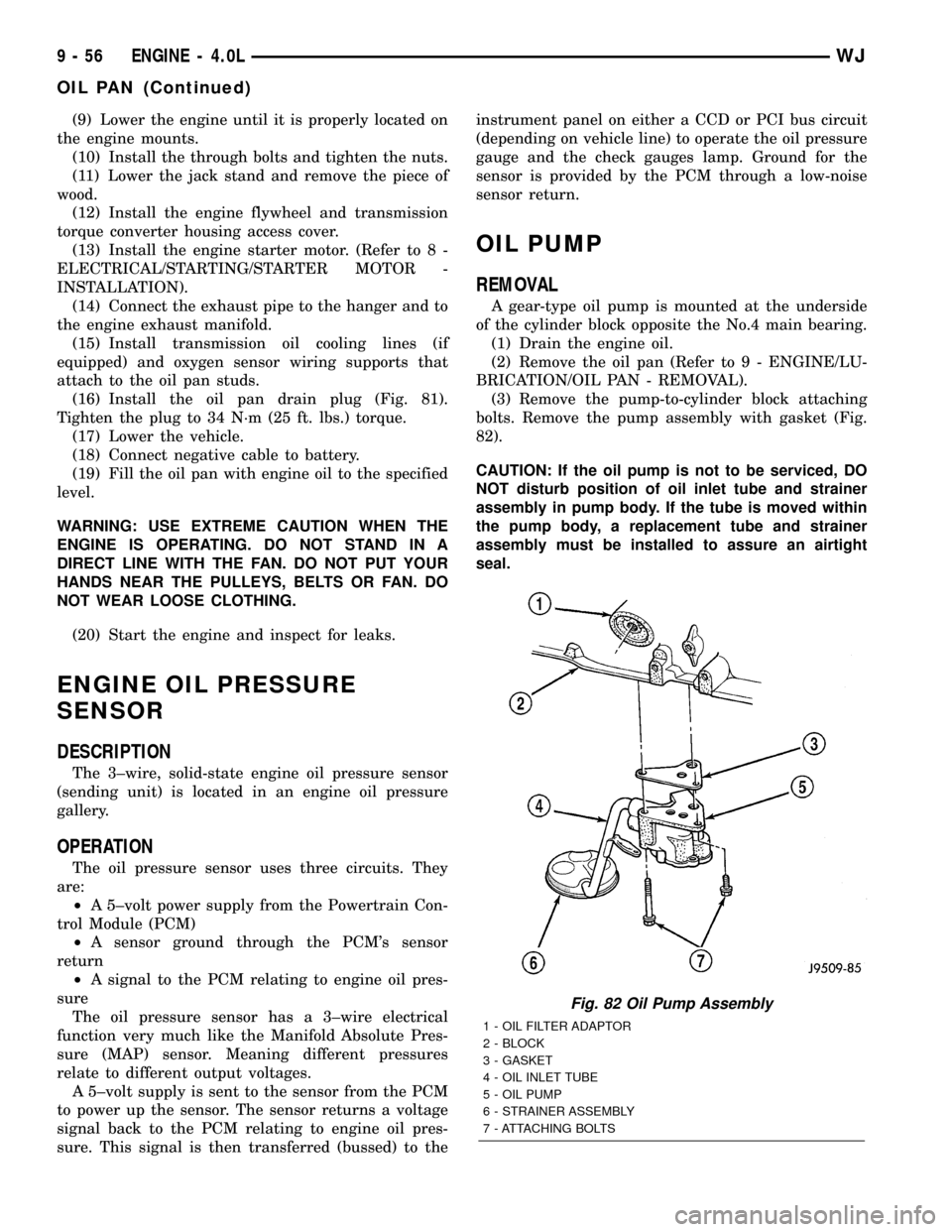
(3) Remove the pump-to-cylinder block attaching
bolts. Remove the pump assembly with gasket (Fig.
82).
CAUTION: If the oil pump is not to be serviced, DO
NOT disturb position of oil inlet tube and strainer
assembly in pump body. If the tube is moved within
the pump body, a replacement tube and strainer
assembly must be installed to assure an airtight
seal.
Fig. 82 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - OIL FILTER ADAPTOR
2 - BLOCK
3 - GASKET
4 - OIL INLET TUBE
5 - OIL PUMP
6 - STRAINER ASSEMBLY
7 - ATTACHING BOLTS
9 - 56 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
OIL PAN (Continued)