2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 164 of 2199

(12) Install cover and tighten bolts in a criss-cross
pattern to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.).
(13) Refill the differential with Mopar Hypoid
Gear Lubricant or equivalent to bottom of the fill
plug hole.
(14) Install fill hole plug.
(15) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
The most common problem is a chatter noise when
turning corners. Before removing the unit for repair,
drain, flush and refill the axle with the specified
lubricant. A container of Mopar Trac-loktLubricant
(friction modifier) should be added after repair ser-
vice or during a lubricant change.
After changing the lubricant, drive the vehicle and
make 10 to 12 slow, figure-eight turns. This maneu-
ver will pump lubricant through the clutches. This
will correct the condition in most instances. If the
chatter persists, clutch damage could have occurred.
DIFFERENTIAL TEST
The differential can be tested without removing the
differential case by measuring rotating torque. Make
sure brakes are not dragging during this measure-
ment.
(1) Place blocks in front and rear of both front
wheels.
(2) Raise one rear wheel until it is completely off
the ground.
(3) Engine off, transmission in neutral, and park-
ing brake off.
(4) Remove wheel and bolt Special Tool 6790 or
equivalent tool to studs.
(5) Use torque wrench on special tool to rotate
wheel and read rotating torque (Fig. 56).
(6) If rotating torque is less than 41 N´m (56 ft.
lbs.) or more than 271 N´m (200 ft. lbs.) on either
wheel the unit should be serviced.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Clamp side gear Holding Fixture 6965 in a vise
and position the differential case on the Holding Fix-
ture (Fig. 57).
(2) Remove ring gear if the ring gear is to be
replaced. The Trac-loktdifferential can be serviced
with the ring gear installed.
Fig. 56 ROTATING TORQUE TEST
1 - SPECIAL TOOL WITH BOLT IN CENTER HOLE
2 - TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 57 DIFFERENTIAL CASE FIXTURE
1 - HOLDING FIXTURE
2 - VISE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 119
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 166 of 2199

(8) Install Forcing Screw C-6960-4 and tighten
screw to 122 N´m (90 ft. lbs.) maximum to compress
Belleville springs in clutch packs (Fig. 62).
(9) With a feeler gauge remove thrust washers
from behind the pinion gears (Fig. 63).(10) Insert Turning Bar C-6960-2 into the pinion
mate shaft hole in the case (Fig. 64).
(11) Loosen the Forcing Screw in small increments
until the clutch pack tension is relieved and the dif-
ferential case can be turned using Turning Bar.
(12) Rotate differential case until the pinion gears
can be removed.
(13) Remove pinion gears from differential case.
(14) Remove Forcing Screw, Step Plate and
Threaded Adapter.
(15) Remove top side gear, clutch pack retainer
and clutch pack. Keep plates in correct order during
removal (Fig. 65).
(16) Remove differential case from the Holding
Fixture. Remove side gear, clutch pack retainer and
clutch pack. Keep plates in correct order during
removal.
CLEANING
Clean all components in cleaning solvent and dry
components with compressed air.
INSPECTION
Inspect clutch pack plates for wear, scoring or dam-
age. Replace both clutch packs if any one component
in either pack is damaged. Inspect side and pinion
gears for cracks chips or damage and replace as nec-
essary. Inspect differential case and pinion shaft and
replace if worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
Clean all components in cleaning solvent and dry
components with compressed air. Inspect clutch pack
plates for wear, scoring or damage. Replace both
clutch packs if any one component in either pack is
Fig. 62 COMPRESS BELLEVILLE SPRING
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - TOOL ASSEMBLED
3 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
Fig. 63 PINION GEAR THRUST WASHER
1 - THRUST WASHER
2 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 64 PINION GEARS
1 - PINION GEARS
2 - TURNING BAR
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 121
DIFFERENTIAL - TRAC-LOK (Continued)
Page 173 of 2199

(8) Install anewcollapsible preload spacer on pin-
ion shaft and install pinion gear in the housing (Fig.
84).
(9) Install yoke with Installer C-3718 and Spanner
Wrench 6958 (Fig. 85).(10) Install the yoke washer and a new nut on the
pinion gear and tighten the pinion nut until there is
zero bearing end-play.
(11) Tighten the nut to 298 N´m (220 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Never loosen pinion gear nut to decrease
pinion rotating torque and never exceed specified
preload torque. If preload torque or rotating torque
is exceeded a new collapsible spacer must be
installed.
(12) Using Spanner Wrench 6958 and a torque
wrench set at 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.), (Fig. 86) slowly
tighten the nut in 6.8 N´m (5 ft. lbs.) increments
until the rotating torque is achieved. Measure the
rotating torque frequently to avoid over crushing the
collapsible spacer (Fig. 87).
NOTE: If more than 380 N´m (280 ft. lbs.) torque is
required to crush the collapsible spacer, the spacer
is defective and must be replaced.
Fig. 84 COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
1 - COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
2 - SHOULDER
3 - PINION GEAR
4 - DEPTH SHIM
5 - REAR BEARING
Fig. 85 PINION YOKE INSTALLER
1 - INSTALLER
2 - PINION YOKE
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
4 - SPANNER WRENCH
Fig. 86 PINION NUT
1 - SPANNER WRENCH
2 - PIPE
3 - TORQUE WRENCH
3 - 128 REAR AXLE - 226RBAWJ
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR (Continued)
Page 174 of 2199

(13) Check bearing rotating torque with a inch
pound torque wrench (Fig. 87). The pinion gear rotat-
ing torque should be:
²
Original Bearings: 1 to 2.25 N´m (10 to 20 in. lbs.).
²New Bearings: 2.8 to 4 N´m (25 to 35 in. lbs.).
(14) Invert the differential case and start two ring
gear bolts. This will provide case-to-ring gear bolt
hole alignment.
(15) Invert the differential case in the vise.
(16) Installnewring gear bolts and alternately
tighten to 129-142 N´m (95-105 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 88).
CAUTION: Never reuse the ring gear bolts. The
bolts can fracture causing extensive damage.
NOTE: If equipped with Veri-LokTdifferential install
oil feed plenum and side bearing.
(17) Install differential in housing.
CAUTION: When installing a Vari-lokTdifferential
(Fig. 89), the oil feed tube must point to the bottom
of the housing. If differential is installed with the oil
feed tube pointed toward the top, the anti-rotation
tabs will be damaged.
(18)
Verify differential bearing preload, gear mesh
and contact pattern. Refer to Ajustments for procedure.
(19) Install differential cover and fill with gear
lubricant.(20) Install the propeller shaft with the reference
marks aligned.
(21) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
Fig. 87 PINION ROTATING TORQUE
1 - PINION YOKE/COMPANION FLANGE
2 - INCH POUND TORQUE WRENCH
Fig. 88 RING GEAR
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
2 - RING GEAR BOLT
3 - RING GEAR
4 - CASE
Fig. 89 VARI-LOK
1 - ANTI-ROTATION TAB
2 - OIL FEED TUBE
WJREAR AXLE - 226RBA 3 - 129
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR (Continued)
Page 176 of 2199

BRAKES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE........................... 1BRAKES - ABS........................... 41
BRAKES - BASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION..........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM.............................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANUAL
BLEEDING............................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PRESSURE
BLEEDING............................5
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE COMPONENTS..................6
TORQUE CHART......................6
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASE BRAKES........................7
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
RED BRAKE WARN INDICATOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RED BRAKE
WARNING LAMP.......................7
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION..........................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE HOSES
AND LINES...........................8
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DOUBLE
INVERTED FLARING....................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ISO FLARING . . . 9
BRAKE PADS / SHOES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - FRONT DISC BRAKE
SHOES.............................10DESCRIPTION - REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES . 10
OPERATION
OPERATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES . 10
OPERATION - REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES . . 10
REMOVAL
REMOVAL- FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES . . . 11
REMOVAL - REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES....12
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE
SHOES.............................13
INSTALLATION - REAR DISC BRAKE
SHOES.............................14
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER . 14
REMOVAL - REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER . . 15
DISASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY - FRONT DISC BRAKE
CALIPER............................17
DISASSEMBLY - REAR DISC BRAKE
CALIPER............................18
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE CALIPER.........19
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE CALIPER.......19
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY - FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER . 20
ASSEMBLY - REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER . 21
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE
CALIPER............................22
INSTALLATION - REAR DISC BRAKE
CALIPER............................22
FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION.....................22
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID........................23
FLUID RESERVOIR
REMOVAL.............................23
WJBRAKES 5 - 1
Page 181 of 2199
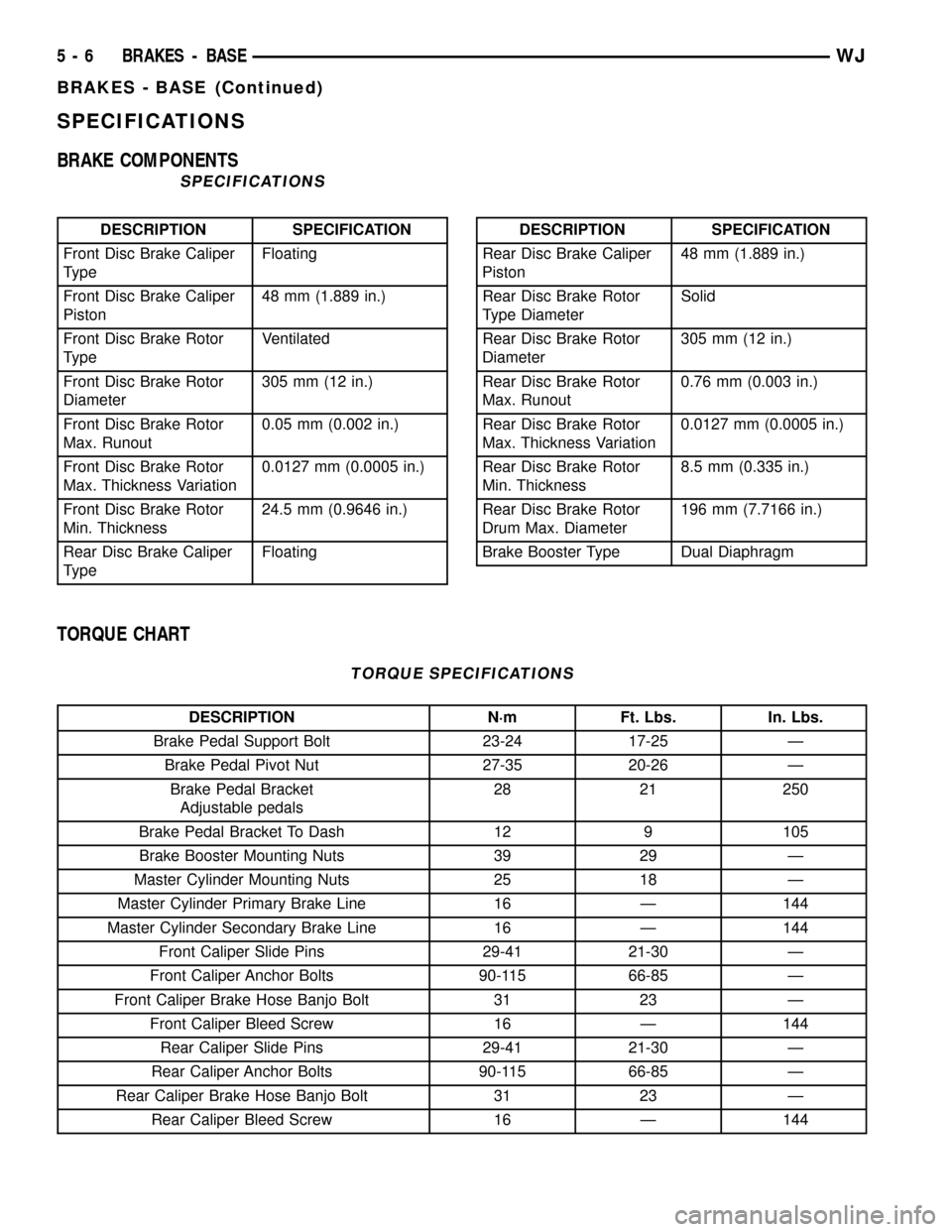
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE COMPONENTS
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Front Disc Brake Caliper
TypeFloating
Front Disc Brake Caliper
Piston48 mm (1.889 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
TypeVentilated
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Diameter305 mm (12 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Runout0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Thickness Variation0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Min. Thickness24.5 mm (0.9646 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
TypeFloatingDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
Piston48 mm (1.889 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Type DiameterSolid
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Diameter305 mm (12 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Runout0.76 mm (0.003 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Thickness Variation0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Min. Thickness8.5 mm (0.335 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Drum Max. Diameter196 mm (7.7166 in.)
Brake Booster Type Dual Diaphragm
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Brake Pedal Support Bolt 23-24 17-25 Ð
Brake Pedal Pivot Nut 27-35 20-26 Ð
Brake Pedal Bracket
Adjustable pedals28 21 250
Brake Pedal Bracket To Dash 12 9 105
Brake Booster Mounting Nuts 39 29 Ð
Master Cylinder Mounting Nuts 25 18 Ð
Master Cylinder Primary Brake Line 16 Ð 144
Master Cylinder Secondary Brake Line 16 Ð 144
Front Caliper Slide Pins 29-41 21-30 Ð
Front Caliper Anchor Bolts 90-115 66-85 Ð
Front Caliper Brake Hose Banjo Bolt 31 23 Ð
Front Caliper Bleed Screw 16 Ð 144
Rear Caliper Slide Pins 29-41 21-30 Ð
Rear Caliper Anchor Bolts 90-115 66-85 Ð
Rear Caliper Brake Hose Banjo Bolt 31 23 Ð
Rear Caliper Bleed Screw 16 Ð 144
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASEWJ
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 183 of 2199

ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the steering column opening cover
(Fig. 2)(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER - REMOV-
AL).
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Remove the switch from the steering column
opening cover by squeezing the retaining clips
together and pushing the switch outwards (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the switch to the steering column open-
ing cover by pushing the switch inwards seating the
retaining clips to the steering column opening cover
(Fig. 3).
(2) Reconnect the electrical connector to the
adjustable pedal switch.
(3) Install the steering column opening cover (Fig.
2)(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTAL-
LATION).
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes,
rear brakes and at the rear axle junction block. Dou-
ble walled steel tubing is used. Double inverted style
and ISO style flares are used on the brake lines.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE HOSES
AND LINES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front and rear
brakes and at the rear axle junction block. Inspect
the hoses whenever the brake system is serviced, at
every engine oil change, or whenever the vehicle is in
for service.
Inspect the hoses for surface cracking, scuffing, or
worn spots. Replace any brake hose immediately if
the fabric casing of the hose is exposed due to cracks
or abrasions.
Also check brake hose installation. Faulty installa-
tion can result in kinked, twisted hoses, or contact
with the wheels and tires or other chassis compo-
nents. All of these conditions can lead to scuffing,
cracking and eventual failure.
The steel brake lines should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of corrosion, twists, kinks, leaks, or
other damage. Heavily corroded lines will eventually
rust through causing leaks. In any case, corroded or
damaged brake lines should be replaced.
Factory replacement brake lines and hoses are rec-
ommended to ensure quality, correct length and supe-
rior fatigue life. Care should be taken to make sure
that brake line and hose mating surfaces are clean
and free from nicks and burrs. Also remember that
right and left brake hoses are not interchangeable.
Use new copper gaskets at all caliper connections.
Be sure brake line connections are properly made
(not cross threaded) and tightened to recommended
torque.
Fig. 2 STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
REMOVAL/INSTALL
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP PAD
2 - STEERING COLUMN OPENING COVER
3 - SCREW (3)
Fig. 3 ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
1 - RETAINING CLIPS
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
5 - 8 BRAKES - BASEWJ
Page 216 of 2199

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES............................42
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM......................42
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................43
G-SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................45
OPERATION...........................45
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front brakes are controlled individually and the
rear brakes in tandem.
The ABS electrical system is separate from other
vehicle electrical circuits. A separate controller oper-
ates the system.
OPERATION
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching 20 to 30 percent of
actual vehicle speed during braking. Periods of high
wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high pedal
pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB ignition ter-
minal when the ignition switch is turned to Run posi-
tion. The CAB performs a system initialization
procedure at this point. Initialization consists of a
static and dynamic self check of system electrical
components.
The static check occurs after the ignition switch is
turned to Run position. The dynamic check occurs
when vehicle road speed reaches approximately 30kph (18 mph). During the dynamic check, the CAB
briefly cycles the pump and solenoids to verify oper-
ation.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ANTILOCK BRAKING
The antilock system prevents lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a high slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel. The valves are all located within the
HCU valve body and work in pairs to either increase,
hold, or decrease apply pressure as needed in the
individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 41