2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Transmission part location
[x] Cancel search: Transmission part locationPage 1772 of 2199

ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Make sure
that all passages are thoroughly cleaned and are free
from dirt or debris. Make sure that all valves move
freely in their proper bore. Make sure that all gear
pockets and bushings are free from excessive wear
and scoring. Replace the oil pump if any excessive
wear or scoring is found.
(2) Coat the gears with MopartATF +4, type 9602,
and install into their original locations.
(3) Lubricate the oil pump valves with Mopart
ATF +4, type 9602, and install the valve, spring and
retainer into the appropriate oil pump valve body
bore (Fig. 93) (Fig. 94).
(4) Place the separator plate onto the oil pump
body (Fig. 92).
(5) Install the screws to hold the separator plate
onto the oil pump body (Fig. 92). Tighten the screws
to 4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(6) Position the oil pump cover onto the locating
dowels (Fig. 91).
(7) Seat the two oil pump halves together and
install all bolts finger tight.
(8) Torque all bolts down slowly starting in the
center and working outward. The correct torque is
4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(9) Verify that the oil pump gears rotate freely and
smoothly.
(10) Position the reaction shaft support into the oil
pump (Fig. 91).
(11) Install and torque the bolts to hold the reac-
tion shaft support to the oil pump (Fig. 91). The cor-
rect torque is 12 N´m (105 in.lbs.).
OIL PUMP FRONT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission from the vehicle.
(2) Remove the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
(3) Using a screw mounted in a slide hammer,
remove the oil pump front seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean seal bore of the oil pump of any residue
or particles from the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the oil pump housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 95).
Fig. 95 Install Oil Pump Front Seal
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 253
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1780 of 2199

Replace the driving shell if worn, cracked or dam-
aged.
Replace planetary gear sets if gears, pinion pins, or
carrier are damaged in any way. Replace the annulus
gears and supports if either component is worn or
damaged.
Replace the output shaft if the machined surfaces
are scored, pitted, or damaged in any way. Also
replace the shaft if the splines are damaged, or
exhibits cracks at any location.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.
(2) Install the number 11 bearing into the input
planetary carrier so that the inner race will be
toward the front of the transmission (Fig. 104).
(3) Install the input sun gear into the input carrier
(Fig. 104).
(4) Install the number 10 bearing onto the rear of
the reverse planetary carrier with the inner race
toward the carrier (Fig. 104).
(5) Install the number 9 bearing onto the front of
the reverse planetary carrier with the outer race
toward the carrier and the inner race facing upward
(Fig. 104).
(6) Install the reverse planetary gear carrier into
the input carrier (Fig. 104).
(7) Install the input annulus gear into the input
carrier (Fig. 104).
(8) Install the snap-ring to hold the input annulus
gear into the input carrier (Fig. 104).
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²Park (P)
²Reverse (R)
²Neutral (N)
²Drive (D)
²Manual second (2)
²Manual low (1)
OPERATION
MANUAL LOW (1) range provides FIRST gear
only. Overrun braking is also provided in this range.
MANUAL SECOND (2) range provides FIRST and
SECOND gear only.
DRIVE range provides FIRST, SECOND, THIRD
and OVERDRIVE FOURTH and FIFTH gear ranges.
The shift into OVERDRIVE FOURTH and FIFTH
gear range occurs only after the transmission hascompleted the shift into D THIRD gear range. No
further movement of the shift mechanism is required
to complete the 3-4 or 4-5 shifts.
The FOURTH and FIFTH gear upshifts occurs
automatically when the overdrive selector switch is
in the ON position. An upshift to FOURTH and
FIFTH gears may not occur or may be delayed in
some of the possible shift schedules. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove any necessary console parts for access
to shift lever assembly and shifter cables. (Refer to
23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
REMOVAL)
(2) Shift transmission into PARK.
(3) Disconnect the transmission shift cable at shift
lever and shifter assembly bracket (Fig. 105).
(4) Disconnect the park lock cable from the shifter
BTSI lever and the shifter assembly bracket. (Fig.
106)
(5) Disconnect the transfer case shift cable from
the transfer case shift lever pin (Fig. 107), if
equipped.
(6) Remove the clip holding the transfer case shift
cable to the shifter assembly bracket, if equipped.
(7) Remove the transfer case shift cable from the
shifter assembly bracket, if equipped.
(8) Disengage all wiring connectors from the
shifter assembly.
(9) Remove all nuts holding the shifter assembly to
the floor pan (Fig. 108).
Fig. 105 Transmission Shift Cable
1 - SHIFT LEVER PIN
2 - ADJUSTMENT SCREW
3 - SHIFT CABLE
4 - SHIFTER ASSEMBLY BRACKET
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 261
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN (Continued)
Page 1786 of 2199

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 112) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 113).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 114) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmission
and buffer the powertrain against torsional vibrations,
the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Solenoid to achieve
a smooth application of the torque converter clutch.
This function, referred to as Electronically Modulated
Converter Clutch (EMCC) can occur at various times
depending on the following variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle
²Engine speed
Fig. 112 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 113 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 114 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 267
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1800 of 2199
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. It drives the mainshaft through the plan-
etary gear and range hub. The front output shaft is
operated by a drive chain that connects the shaft to a
drive sprocket on the mainshaft. The drive sprocket
is engaged/disengaged by the mode fork, which oper-
ates the mode sleeve and hub. The sleeve and hub
are not equipped with a synchro mechanism for shift-
ing.
OPERATING RANGES
NV242 operating ranges are 2WD (2-wheel drive),
4x4 part-time, 4x4 full time, and 4 Lo.
The 2WD and 4x4 full time ranges can be used at
any time and on any road surface.
The 4x4 part-time and 4 Lo ranges are for off road
use only. The only time these ranges can be used on
hard surface roads, is when the surface is covered
with snow and ice.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case shift linkage
binding.1) Repair or replace linkage as
necessary.
2) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 2) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
3) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Transfer case will not shift through
4X4 part time range (light remains
on)1) Incomplete shift due to drivetrain
torque load.1) Momentarily release the
accelerator pedal to complete the
shift.
2) Incorrect tire pressure. 2) Correct tire pressure as
necessary.
3) Excessive Tire wear. 3) Correct tire condition as
necessary.
4) Excessive vehicle loading. 4) Correct as necessary.
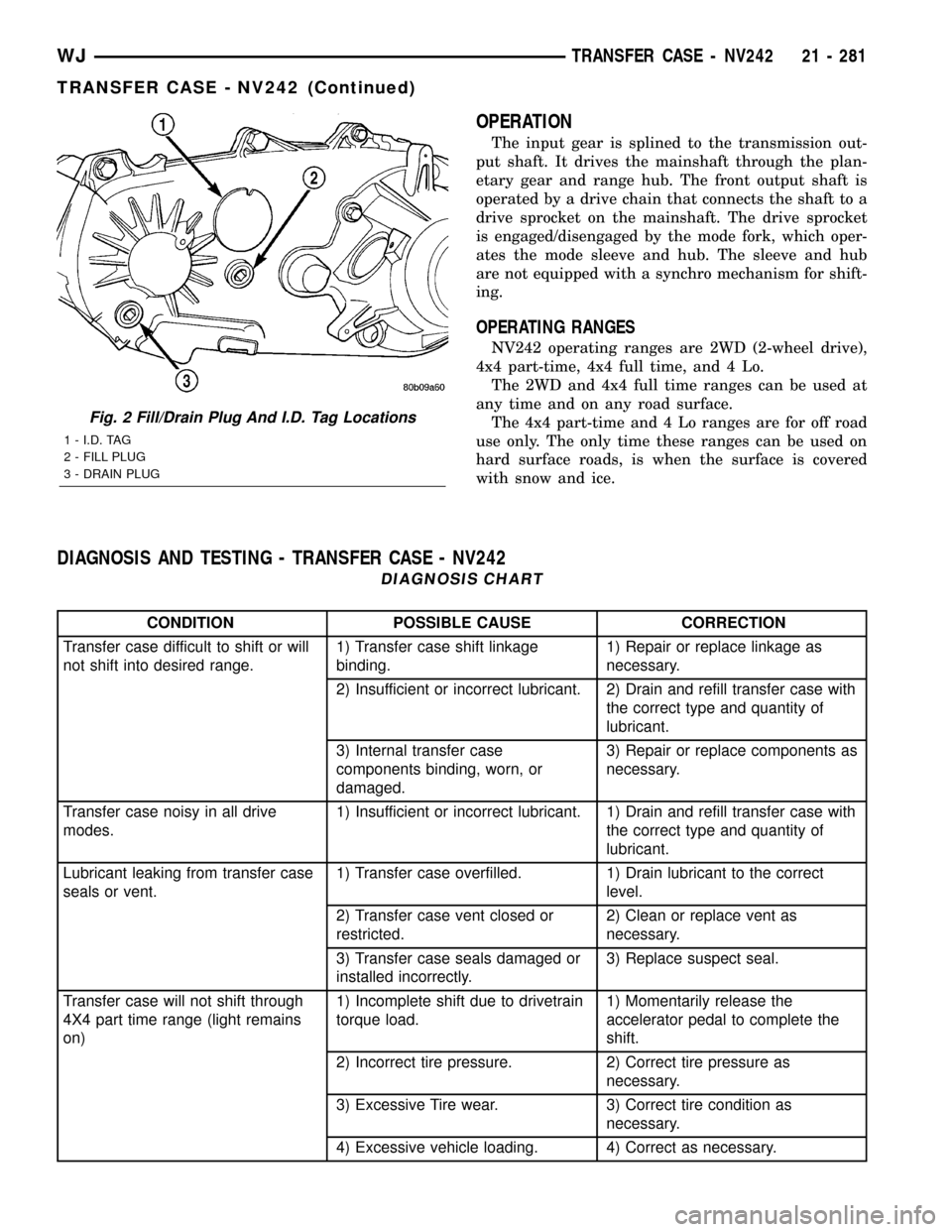
Fig. 2 Fill/Drain Plug And I.D. Tag Locations
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 281
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 2094 of 2199

open circuit to the fuse in the junction block as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is switched
to ground through the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). There should be continuity between this cav-
ity and the A/C compressor clutch relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the PCM wire harness connector C
(gray) at all times. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch relay from the
PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the compressor clutch relay by aligning
the relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The manual temperature control HVAC system
uses a combination of electrical, and vacuum con-trols. The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) HVAC sys-
tem uses only electrical controls. These controls
provide the vehicle operator with a number of setting
options to help control the climate and comfort
within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box for more information on the
suggested operation and use of these controls.
Both a/c heater control panels are located on the
instrument panel inboard of the steering column and
below the radio (Fig. 12). Both control panels contain
rotary-type temperature control knob(s), a rotary-
type mode control switch knob, a rotary-type blower
motor speed switch knob and an air conditioning
compressor push button switch. The rear window
defogger push button switch is also located on a/c
heater control panel. The AZC control panel also fea-
tures a recirculation push button switch and a vac-
uum fluorescent display area.
OPERATION
The AZC control module uses infrared sensing
technology to control occupant comfort levels, not the
actual passenger compartment air temperature. Dual
infrared sensors mounted in the face of the control
unit independently measure the surface temperature
to maintain customer-perceived comfort temperature
under changing conditions. Dual Zone temperature
control provides wide side-to-side variation in comfort
temperature to exceed the needs of either front seat
occupant. This sensing system replaces interior air
temperature and solar sensors used to approximate
direct sensing control through complex control pro-
grams.
Fig. 11 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
2 - NEGATIVE CABLE
3 - POSITIVE CABLE
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
Fig. 12 A/C HEATER CONTROL PANELS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 17
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)