2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE seat
[x] Cancel search: seatPage 2155 of 2199

(14) Remove the snap ring from the hub and
remove the clutch field coil (Fig. 22). Slide the clutch
field coil off of the hub.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
(1) Install Viscous Heater to engine mounting
bracket.
(2) Install the Viscous Heater mounting bolts and
tighten to 33 N´m ( 25 ft. lbs.).
(3) Plug the wiring harness electrical connector to
the Viscous Heater clutch.
(4) Install heater hoses to the Viscous Heater con-
nections.
(5) Install heater hose clamps to Viscous Heater
connections.
(6) Install the engine accessory drive belt(Refer to
7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Refill the engine cooling system(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(9) Operate vehicle and check for any coolant
leaks, repair as required.
INSTALLATION - VISCOUS HEATER CLUTCH
(1) Install the clutch field coil and snap ring.
(2) Install the screw and retainer on the clutch coil
lead wire harness on the viscous heater housing.
Tighten the screw to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.)
(3) Align the rotor assembly squarely on the front
housing hub.
(4) Install the rotor bearing asembly with the
installer (Special Tool C-6871 or equalivent). Threadthe installer on the shaft, then turn the nut until the
rotor asembly is seated.
(5) Install the external front housing snap ring
with snap ring pliers. The bevel side of the snap ring
must be facing outward. Press the snap ring to make
sure it is properly seated in the groove.
CAUTION: If the snap ring is not fully seated in the
groove it will vibrate out, resulting in a clutch fail-
ure and severe damage to the front housing of the
compressor.
(6) Install the original clutch shims on the shaft.
(7) Install the clutch plate. Install the shaft hex
nut and tighten to 15±20 N´m (11±15 ft. lbs.).
(8) Check the clutch air gap with a feeler gauge
(Fig. 23). If the gap does not meet specification, add
or substract shims as required. The air gap specifica-
tion if 0.41 to 0.79 millimeters (0.016 to 0.031 inch-
es).
NOTE: The air gap is determined by the spacer
shims. When installing an original, or a new clutch
assembly, try the original shims first. When install-
ing a new clutch (and not having the old shims
available) use a 1.0, 0.50 and 0.13 millimeter (0.040,
0.020 and 0.005 inch) shim from the new clutch
hardware package that is provided with the new
clutch.
(9) Reinstall the viscous heater to the mounting
bracket. Tighten the mounting screws to 33 N´m (25
ft. lbs.).
(10) Reinstall the battery negative cable.
Fig. 22 CLUTCH FIELD COIL SNAP RING REMOVE-
typical
1 - COIL
2 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 23 CHECK CLUTCH AIR GAP-typical
1 - FEELER GAUGE
24 - 78 PLUMBINGWJ
VISCOUS HEATER (Continued)
Page 2167 of 2199
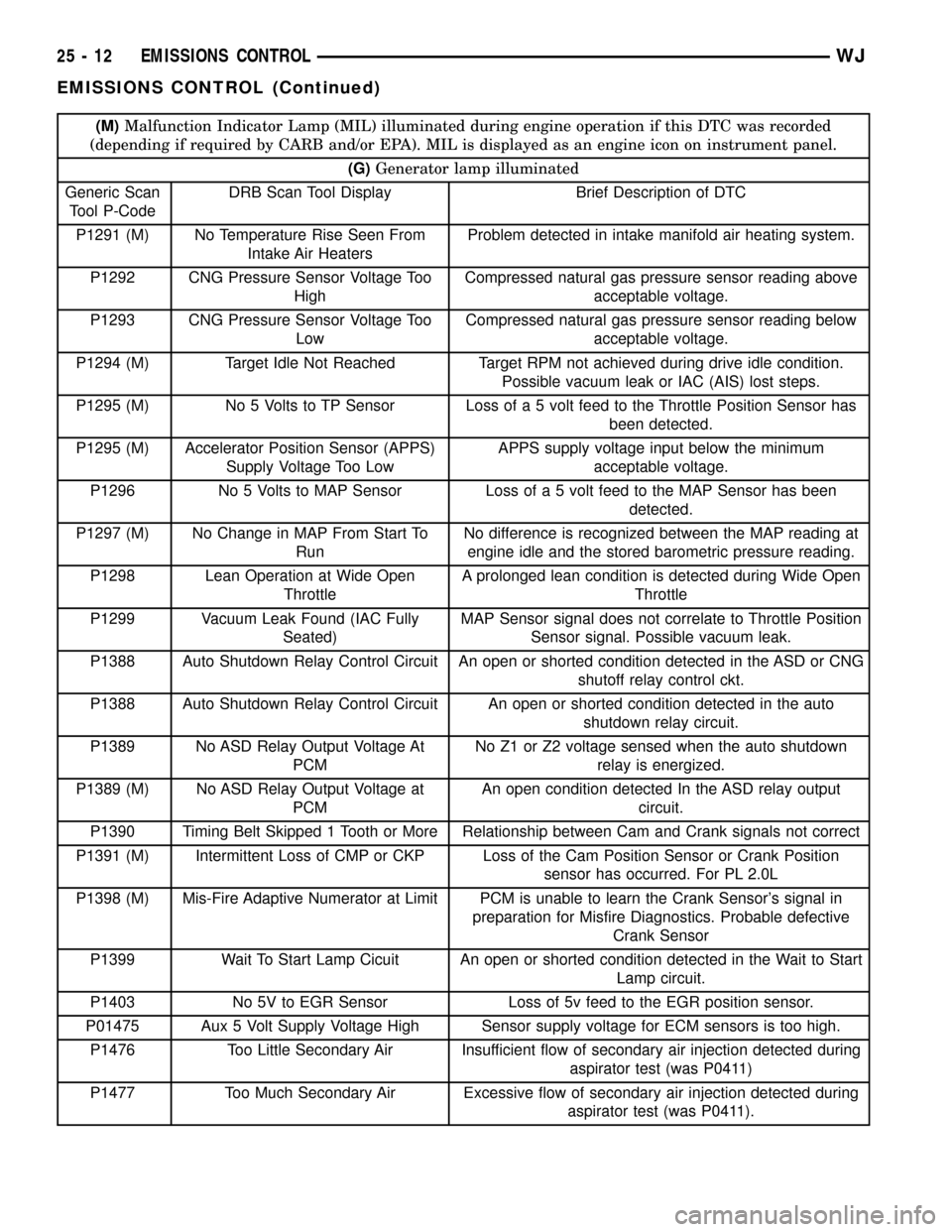
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1291 (M) No Temperature Rise Seen From
Intake Air HeatersProblem detected in intake manifold air heating system.
P1292 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
HighCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading above
acceptable voltage.
P1293 CNG Pressure Sensor Voltage Too
LowCompressed natural gas pressure sensor reading below
acceptable voltage.
P1294 (M) Target Idle Not Reached Target RPM not achieved during drive idle condition.
Possible vacuum leak or IAC (AIS) lost steps.
P1295 (M) No 5 Volts to TP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the Throttle Position Sensor has
been detected.
P1295 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Supply Voltage Too LowAPPS supply voltage input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
P1296 No 5 Volts to MAP Sensor Loss of a 5 volt feed to the MAP Sensor has been
detected.
P1297 (M) No Change in MAP From Start To
RunNo difference is recognized between the MAP reading at
engine idle and the stored barometric pressure reading.
P1298 Lean Operation at Wide Open
ThrottleA prolonged lean condition is detected during Wide Open
Throttle
P1299 Vacuum Leak Found (IAC Fully
Seated)MAP Sensor signal does not correlate to Throttle Position
Sensor signal. Possible vacuum leak.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or CNG
shutoff relay control ckt.
P1388 Auto Shutdown Relay Control Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
P1389 No ASD Relay Output Voltage At
PCMNo Z1 or Z2 voltage sensed when the auto shutdown
relay is energized.
P1389 (M) No ASD Relay Output Voltage at
PCMAn open condition detected In the ASD relay output
circuit.
P1390 Timing Belt Skipped 1 Tooth or More Relationship between Cam and Crank signals not correct
P1391 (M) Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Loss of the Cam Position Sensor or Crank Position
sensor has occurred. For PL 2.0L
P1398 (M) Mis-Fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit PCM is unable to learn the Crank Sensor's signal in
preparation for Misfire Diagnostics. Probable defective
Crank Sensor
P1399 Wait To Start Lamp Cicuit An open or shorted condition detected in the Wait to Start
Lamp circuit.
P1403 No 5V to EGR Sensor Loss of 5v feed to the EGR position sensor.
P01475 Aux 5 Volt Supply Voltage High Sensor supply voltage for ECM sensors is too high.
P1476 Too Little Secondary Air Insufficient flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411)
P1477 Too Much Secondary Air Excessive flow of secondary air injection detected during
aspirator test (was P0411).
25 - 12 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2181 of 2199

²a PCV valve mounted to the oil filler housing
(Fig. 3). The PCV valve is sealed to the oil filler
housing with an o-ring.
²the air cleaner housing
²two interconnected breathers threaded into the
rear of each cylinder head (Fig. 4).
²tubes and hose to connect the system compo-
nents.
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM
The CCV system performs the same function as a
conventional PCV system, but does not use a vacuum
controlled PCV valve.
The fixed orifice fitting meters the amount of
crankcase vapors drawn out of the engine.
When the engine is operating, fresh air enters the
engine and mixes with crankcase vapors. Engine vac-uum draws the vapor/air mixture through the fixed
orifice and into the intake manifold. The vapors are
then consumed during engine combustion.
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM
The PCV system operates by engine intake mani-
fold vacuum. Filtered air is routed into the crankcase
through the air cleaner hose and crankcase breath-
ers. The metered air, along with crankcase vapors,
are drawn through the PCV valve and into a passage
in the intake manifold. The PCV system manages
crankcase pressure and meters blow-by gases to the
intake system, reducing engine sludge formation.
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
This plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum.
TYPICALPCV valves are shown in (Fig. 5), (Fig.
6) and (Fig. 7).
When the engine is not operating, or during an
engine pop-back, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat (Fig. 5). This will prevent vapors
from flowing through the valve.
Fig. 3 PCV Valve/Oil Filler Tube (Housing)Ð4.7L
Engine
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 4 PCV System Hoses/TubesÐ4.7L Engine
1 - FRESH AIR FITTING
2 - CONNECTING TUBES/HOSES
3 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2)
4 - RUBBER HOSE
5 - AIR CLEANER RESONATOR
25 - 26 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS (Continued)
Page 2186 of 2199

OPERATION
The main purpose of the LDP is to pressurize the
fuel system for leak checking. It closes the EVAP sys-
tem vent to atmospheric pressure so the system can
be pressurized for leak testing. The diaphragm is
powered by engine vacuum. It pumps air into the
EVAP system to develop a pressure of about 7.59
H2O (1/4) psi. A reed switch in the LDP allows the
PCM to monitor the position of the LDP diaphragm.
The PCM uses the reed switch input to monitor how
fast the LDP is pumping air into the EVAP system.
This allows detection of leaks and blockage. The LDP
assembly consists of several parts (Fig. 12). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM, and it connects the
upper pump cavity to either engine vacuum or atmo-
spheric pressure. A vent valve closes the EVAP sys-
tem to atmosphere, sealing the system during leak
testing. The pump section of the LDP consists of a
diaphragm that moves up and down to bring air in
through the air filter and inlet check valve, and
pump it out through an outlet check valve into the
EVAP system. The diaphragm is pulled up by engine
vacuum, and pushed down by spring pressure, as the
LDP solenoid turns on and off. The LDP also has a
magnetic reed switch to signal diaphragm position to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is down, the switch is
closed, which sends a 12 V (system voltage) signal to
the PCM. When the diaphragm is up, the switch is
open, and there is no voltage sent to the PCM. This
allows the PCM to monitor LDP pumping action as it
turns the LDP solenoid on and off.
LDP AT REST (NOT POWERED)
When the LDP is at rest (no electrical/vacuum) the
diaphragm is allowed to drop down if the internal
(EVAP system) pressure is not greater than the
return spring. The LDP solenoid blocks the engine
vacuum port and opens the atmospheric pressure
port connected through the EVAP system air filter.
The vent valve is held open by the diaphragm. This
allows the canister to see atmospheric pressure (Fig.
13).
DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
When the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid, the
solenoid blocks the atmospheric port leading through
the EVAP air filter and at the same time opens the
engine vacuum port to the pump cavity above the
diaphragm. The diaphragm moves upward when vac-
uum above the diaphragm exceeds spring force. This
upward movement closes the vent valve. It also
causes low pressure below the diaphragm, unseating
the inlet check valve and allowing air in from the
EVAP air filter. When the diaphragm completes its
upward movement, the LDP reed switch turns from
closed to open (Fig. 14).
DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
Based on reed switch input, the PCM de-energizes
the LDP solenoid, causing it to block the vacuum
port, and open the atmospheric port. This connects
the upper pump cavity to atmosphere through the
EVAP air filter. The spring is now able to push the
diaphragm down. The downward movement of the
diaphragm closes the inlet check valve and opens the
outlet check valve pumping air into the evaporative
system. The LDP reed switch turns from open to
closed, allowing the PCM to monitor LDP pumping
(diaphragm up/down) activity (Fig. 15). During the
pumping mode, the diaphragm will not move down
far enough to open the vent valve. The pumping cycle
is repeated as the solenoid is turned on and off.
When the evaporative system begins to pressurize,
the pressure on the bottom of the diaphragm will
begin to oppose the spring pressure, slowing the
pumping action. The PCM watches the time from
when the solenoid is de-energized, until the dia-
phragm drops down far enough for the reed switch to
Fig. 12 EVAP LEAK DETECTION SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
1 - Reed Switch
2 - Solenoid
3 - Spring
4 - Pump Cavity
5 - Diaphragm
6 - Inlet Check Valve
7 - Vent Valve
8 - From Air Filter
9 - To Canister
10 - Outlet Check Valve
11 - Engine Vacuum
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 31
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2190 of 2199

set a temporary fault without turning on the MIL
and continue the leak portion of the test. However,
the PCM will assume that the system is already
pressurized and skip the rapid pump cycles.
Always diagnose leaks, if possible, before discon-
necting connections. Disconnecting connections may
mask a leak condition.
Keep in mind that if the purge solenoid seat is
leaking, it could go undetected since the leak would
end up in the intake manifold. Disconnect the purge
solenoid at the manifold when leak checking. In addi-
tion, a pinched hose fault (P1486) could set if the
purge solenoid does not purge the fuel system prop-
erly (blocked seat). The purge solenoid must vent the
fuel system prior to the LDP system test. If the
purge solenoid cannot properly vent the system the
LDP cannot properly complete the test for P1486 and
this fault can set due to pressure being in the EVAP
system during the test sequence.
Multiple actuation's of the DRB IIItLeak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) Monitor Test can hide a 0.020 leak
because of excess vapor generation. Additionally, any
source for additional vapor generation can hide a
small leak in the EVAP system. Excess vapor gener-
ation can delay the fall of the LDP diaphragm thus
hiding the small leak. An example of this condition
could be bringing a cold vehicle into a warm shop for
testing or high ambient temperatures.
Fully plugged and partially plugged underhood
vacuum lines have been known to set MIL condi-
tions. P1494 and P0456 can be set for this reason.
Always, thoroughly, check plumbing for pinches or
blockage before condemning components.
TEST EQUIPMENT The Evaporative Emission
Leak Detector (EELD) Miller Special Tool 8404 is
capable of visually detecting leaks in the evaporative
system and will take the place of the ultrasonic leak
detector 6917A. The EELD utilizes shop air and a
smoke generator to visually detect leaks down to
0.020 or smaller. The food grade oil used to make the
smoke includes an UV trace dye that will leave tell-
tale signs of the leak under a black light. This is
helpful when components have to be removed to
determine the exact leak location. For detailed test
instructions, follow the operators manual packaged
with the EELD.
NOTE: Be sure that the PCM has the latest software
update. Reprogram as indicated by any applicable
Technical Service Bulletin. After LDP repairs are
completed, verify the repair by running the DRB IIIT
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Monitor Test as
described in Technical Service Bulletin 18-12-99.REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the left quarter panel behind the left/rear wheel (Fig.
16). It is attached to a two-piece support bracket
(Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are replaced (ser-
viced) as one unit.
(1) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(2) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17).
(4) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 19).
(5) To separate and lower front section of two-piece
support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on bottom
of support bracket (Fig. 17). While lowering support
bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(6) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP (Fig.
20).
(7) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP
(Fig. 20).
(8) Remove LDP.
INSTALLATION
The LDP is located in the left quarter panel behind
the left/rear wheel. It is attached to a two-piece sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Position LDP and carefully install vapor/vac-
uum lines to LDP and LDP filter.The vapor/vac-
uum lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 16 LOCATION, LDP / EVAP CANISTER
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
2 - EVAP CANISTER
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 35
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)