2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Steering
[x] Cancel search: SteeringPage 216 of 2199

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES............................42
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM......................42
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................43
G-SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................45
OPERATION...........................45
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front brakes are controlled individually and the
rear brakes in tandem.
The ABS electrical system is separate from other
vehicle electrical circuits. A separate controller oper-
ates the system.
OPERATION
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching 20 to 30 percent of
actual vehicle speed during braking. Periods of high
wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high pedal
pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB ignition ter-
minal when the ignition switch is turned to Run posi-
tion. The CAB performs a system initialization
procedure at this point. Initialization consists of a
static and dynamic self check of system electrical
components.
The static check occurs after the ignition switch is
turned to Run position. The dynamic check occurs
when vehicle road speed reaches approximately 30kph (18 mph). During the dynamic check, the CAB
briefly cycles the pump and solenoids to verify oper-
ation.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ANTILOCK BRAKING
The antilock system prevents lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a high slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel. The valves are all located within the
HCU valve body and work in pairs to either increase,
hold, or decrease apply pressure as needed in the
individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 41
Page 218 of 2199

ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
The electronic brake distribution (EBD) functions
like a rear proportioning valve. The EBD system uses
the ABS system to control the slip of the rear wheels
in partial braking range. The braking force of the
rear wheels is controlled electronically by using the
inlet and outlet valves located in the HCU.
OPERATION
Upon entry into EBD the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure the outlet valve for
the rear brake circuit is pulsed. This allows fluid to
enter the low pressure accumulator (LPA) in the
HCU resulting in a drop in fluid pressure to the rear
brakes. In order to increase the rear brake pressure
the outlet valve is switched off and the inlet valve is
pulsed. This increases the pressure to the rear
brakes. This will continue until the required slip dif-
ference is obtained. At the end of EBD braking (no
brake application) the fluid in the LPA drains back to
the master cylinder by switching on the outlet valve
and draining through the inlet valve check valve. At
the same time the inlet valve is switched on to pre-
vent a hydraulic short circiut in case of another
brake application.
The EBD will remain functional during many ABS
fault modes. If the red and amber warning lamps are
illuminated the EBD may have a fault.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
A wheel speed sensor is used at each wheel. The
front sensors are mounted to the steering knuckles.
The rear sensors are mounted at the outboard end of
the axle. Tone wheels are mounted to the outboard
ends of the front and rear axle shafts. The gear type
tone wheel serves as the trigger mechanism for each
sensor.
OPERATION
The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digi-
tal signal. The CAB sends 12 volts to the sensors.
The sensor has an internal magneto resistance
bridge that alters the voltage and amperage of the
signal circuit. This voltage and amperage is changed
by magnetic induction when the toothed tone wheel
passes the wheel speed sensor. This digital signal issent to the CAB. The CAB measures the voltage and
amperage of the digital signal for each wheel.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel sensor mounting bolt
(Fig. 1).
(3) Remove the sensor from the steering knuckle.
(4) Disengage the sensor wire from the brackets
(Fig. 1)on the steering knuckle.
(5) Disconnect the sensor from the sensor harness
(Fig. 2)and (Fig. 3).
(6) Remove the sensor and wire.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the sensor on the steering knuckle.
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctitet242 to
the sensor mounting bolt. Use new sensor bolt if orig-
inal bolt is worn or damaged.
(3) Install the sensor mounting bolt and tighten
bolt to 12-14 N´m (106-124 in. lbs.).
(4) Engage the grommets on the sensor wire to the
steering knuckle brackets.
(5) Connect the sensor wire to the harness connec-
tor.
(6) Check the sensor wire routing. Be sure the
wire is clear of all chassis components and is not
twisted or kinked at any spot.
(7) Remove the support and lower vehicle.
Fig. 1 Sensor Location
1 - BRACKET
2 - BRACKET
3 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
4 - MOUNTING BOLT
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 43
Page 220 of 2199

(3) Connect the harness to the switch. Be sure the
harness connector is firmly seated.
(4) Place the carpet in position and fold the rear
seat back down.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
A wheel speed sensor is used at each wheel. The
front sensors are mounted to the steering knuckles.The rear sensors are mounted at the outboard end of
the axle. Tone wheels are mounted to the outboard
ends of the front and rear axle shafts. The gear type
tone wheel serves as the trigger mechanism for each
sensor.
OPERATION
The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digi-
tal signal. The CAB sends 12 volts to the sensors.
The sensor has an internal magneto resistance
bridge that alters the voltage and amperage of the
signal circuit. This voltage and amperage is changed
by magnetic induction when the toothed tone wheel
passes the wheel speed sensor. This digital signal is
sent to the CAB. The CAB measures the voltage and
amperage of the digital signal for each wheel.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and fold the rear seat forward. Then
move the carpeting aside for access to the rear sensor
connectors.
(2) Disconnect the rear sensor wire at the harness
connectors (Fig. 7).
(3) Push the sensor wires and grommets through
the floorpan holes.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
(5) Disengage the sensor wire from the axle and
the chassis brackets and from the brake line retain-
ers.
(6) Remove the sensor mounting bolt from the rear
brake backing plate. (Fig. 8).
(7) Remove the sensor from the backing plate.
Fig. 5 G-Switch Mounting
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS
2 - CONNECTOR
3 - G-SWITCH
Fig. 6 G-Switch
1 - SWITCH PART NUMBER
2 - ARROW INDICATES FRONT OF SWITCH FOR PROPER
MOUNTING
Fig. 7 Rear Sensor Connector
1 - RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - G-SWITCH SENSOR
4 - PARKING BRAKE CABLES
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 45
G-SWITCH (Continued)
Page 224 of 2199

COOLING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L
ENGINE..............................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
ROUTING 4.7L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM 4.0L
ENGINE..............................1
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM
ROUTING 4.0L ENGINE..................1
DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS...........1
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM.........2
OPERATIONÐHOSE CLAMPS............2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)...................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐPRELIMINARY
CHECKS.............................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART.............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM LEAKS......................10DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING
SYSTEM DEAERATION.................12
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐDRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L ENGINE.........12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L ENGINE.........12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE........13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFILLING
COOLING SYSTEM - 4.0L ENGINE........13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ADDING
ADDITIONAL COOLANT.................13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING
SYSTEM - REVERSE FLUSHING..........14
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................14
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING...........................15
ACCESSORY DRIVE......................16
ENGINE...............................24
TRANSMISSION.........................55
COOLING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM 4.7L
ENGINE
The cooling system consists of the following items:
²Hydraulic cooling fan and fan drive assembly
²Radiator
²Power steering oil cooler
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an
automatic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM ROUTING
4.7L ENGINE
For cooling system routing refer to (Fig. 1).
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM 4.0L
ENGINE
The cooling system consists of:
²A radiator
²Mechanical Cooling Fan
²Thermal viscous fan drive-Low disengaged
²Fan shroud (Fig. 2)
²Radiator pressure cap
²Thermostat
²Coolant reserve/overflow system
²Transmission oil cooler (if equipped with an
automatic transmission)
²Coolant
²Water pump
²Hoses and hose clamps
²Accessory drive belt
DESCRIPTIONÐCOOLING SYSTEM ROUTING
4.0L ENGINE
For cooling system routing refer to (Fig. 3).
DESCRIPTIONÐHOSE CLAMPS
The cooling system utilizes both worm drive and
spring type hose clamps. If a spring type clamp
WJCOOLING 7 - 1
Page 230 of 2199

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
17. Viscous fan drive not operating
properly.17. Check fan drive operation and replace as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
18. Cylinder head gasket leaking. 18. Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING). For repair, (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
19. Heater core leaking. 19. Check heater core for leaks. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/HEATER CORE - REMOVAL).
Repair as necessary.
20. Hydraulic fan speed too low or
inopertive.20. Check for
DTC code.
Check fan operation speeds.
Refer to fan speed operation table.
Low power steering pump output. Refer to
power steering pump diagnosis - 4.7L engine.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
READING IS
INCONSISTENT
(FLUCTUATES, CYCLES
OR IS ERRATIC)1. During cold weather operation,
with the heater blower in the high
position, the gauge reading may
drop slightly.1. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary.
2. Temperature gauge or engine
mounted gauge sensor defective or
shorted. Also, corroded or loose
wiring in this circuit.2. Check operation of gauge and repair if
necessary. Refer to Group 8J, Instrument
cluster.
3. Gauge reading rises when vehicle
is brought to a stop after heavy use
(engine still running)3. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. Gauge should return to normal
range after vehicle is driven.
4. Gauge reading high after
re-starting a warmed up (hot)
engine.4. A normal condition. No correction is
necessary. The gauge should return to
normal range after a few minutes of engine
operation.
5. Coolant level low in radiator (air
will build up in the cooling system
causing the thermostat to open late).5. Check and correct coolant leaks. (Refer to
7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Cylinder head gasket leaking
allowing exhaust gas to enter
cooling system causing a thermostat
to open late.6. (a) Check for cylinder head gasket leaks.
(Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(b) Check for coolant in the engine oil.
Inspect for white steam emitting from the
exhaust system. Repair as necessary.
WJCOOLING 7 - 7
COOLING (Continued)
Page 238 of 2199

DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
4.0L 4 Ð 32
4.7L 2 Ð 17
Fan Blade Assy. to Viscous
DriveÐ
Bolts 4.0L 23 Ð 200
Generator MountingÐBolts
4.0L57 42 Ð
Radiator Upper Isolator to
CrossmemberÐNuts 3 Ð 20
Radiator Upper Isolator to
RadiatorÐ
Nuts 4 Ð 36
Radiator BraceÐBolts 10 Ð 90
Thermostat HousingÐBolts
4.0L 22 16 Ð
4.7L 13 Ð 115
Upper Radiator Crossmember
to
BodyÐBolts 10 Ð 90
Water PumpÐBolts
4.0L 23 17 Ð
4.7L 54 40 Ð
Water Pump Pulley to Water
PumpÐ
Bolts 4.0L 28 Ð 250
High Pressure Inlet Hose to
Hydraulic Fan DriveÐ1/2 inch
Fitting49 36 Ð
High Pressure Outlet Hose to
Steering GearÐ3/8 inch
Fitting29 21.5 Ð
Fan Shroud to Radiator
Mounting Bolts6Ð50SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING
Pliers 6094
Pressure Tester 7700±A
WJCOOLING 7 - 15
COOLING (Continued)
Page 242 of 2199
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BELT BROKEN (NOTE: IDENTIFY
AND CORRECT PROBLEM
BEFORE NEW BELT IS
INSTALLED)1. Excessive tension. 1. Replace belt and automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Incorrect belt. 2. Replace belt.
3. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation.3. Replace belt.
4. Severe misalignment. 4. Check and replace.
5. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure. 5. Replace defective component
and belt.
NOISE (OBJECTIONABLE
SQUEAL, SQUEAK, OR RUMBLE
IS HEARD OR FELT WHILE
DRIVE BELT IS IN OPERATION)1. Belt slippage. 1. Replace belt or automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Bearing noise. 2. Locate and repair.
3. Belt misalignment. 3. Replace belt.
4. Belt-to-pulley mismatch. 4. Install correct belt.
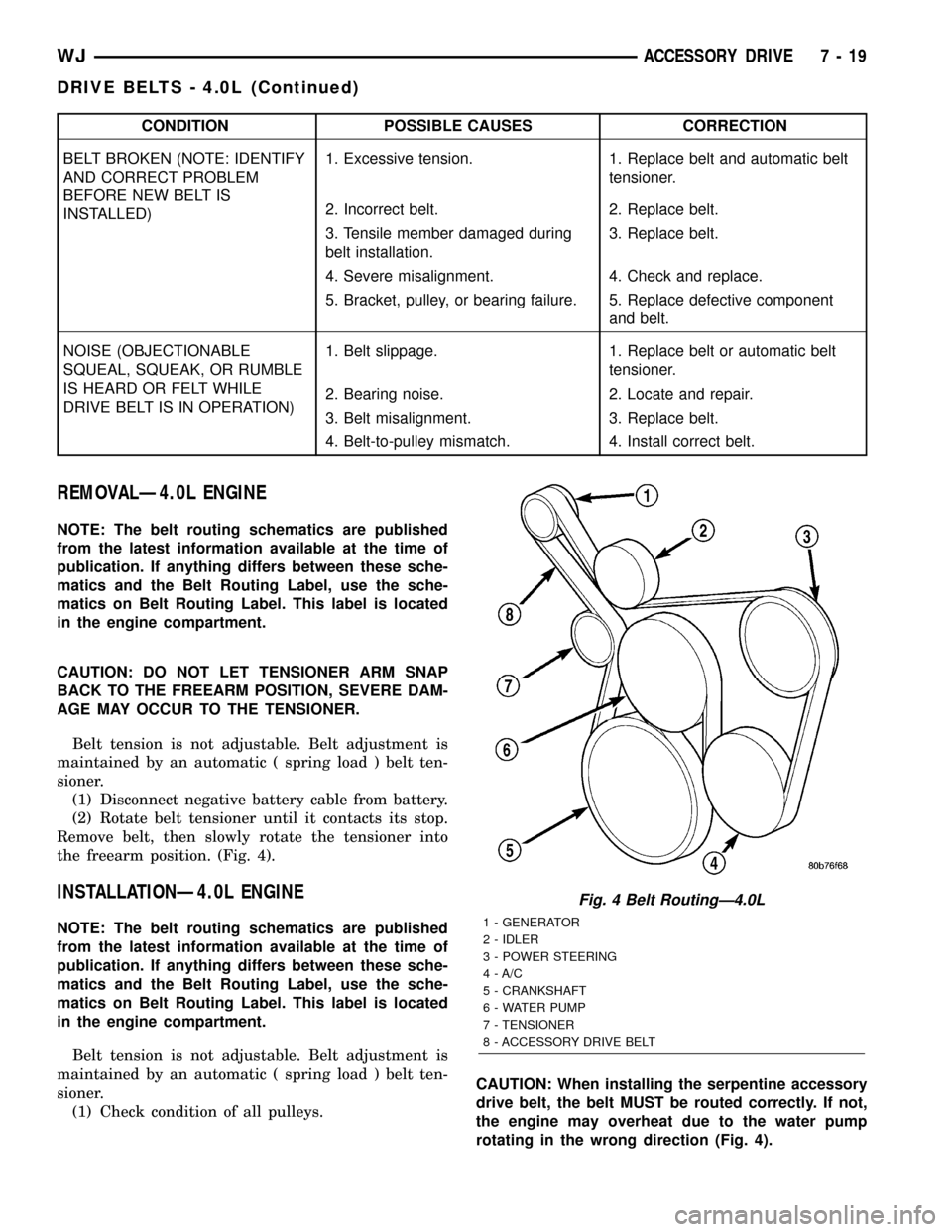
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
CAUTION: DO NOT LET TENSIONER ARM SNAP
BACK TO THE FREEARM POSITION, SEVERE DAM-
AGE MAY OCCUR TO THE TENSIONER.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Rotate belt tensioner until it contacts its stop.
Remove belt, then slowly rotate the tensioner into
the freearm position. (Fig. 4).
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Check condition of all pulleys.CAUTION: When installing the serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. If not,
the engine may overheat due to the water pump
rotating in the wrong direction (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4 Belt RoutingÐ4.0L
1 - GENERATOR
2 - IDLER
3 - POWER STEERING
4 - A/C
5 - CRANKSHAFT
6 - WATER PUMP
7 - TENSIONER
8 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
WJACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 19
DRIVE BELTS - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 245 of 2199
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BELT BROKEN (NOTE: IDENTIFY
AND CORRECT PROBLEM
BEFORE NEW BELT IS
INSTALLED)1. Excessive tension. 1. Replace belt and automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Incorrect belt. 2. Replace belt.
3. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation.3. Replace belt.
4. Severe misalignment. 4. Check and replace.
5. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure. 5. Replace defective component
and belt.
NOISE (OBJECTIONABLE
SQUEAL, SQUEAK, OR RUMBLE
IS HEARD OR FELT WHILE
DRIVE BELT IS IN OPERATION)1. Belt slippage. 1. Replace belt or automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Bearing noise. 2. Locate and repair.
3. Belt misalignment. 3. Replace belt.
4. Belt-to-pulley mismatch. 4. Install correct belt.
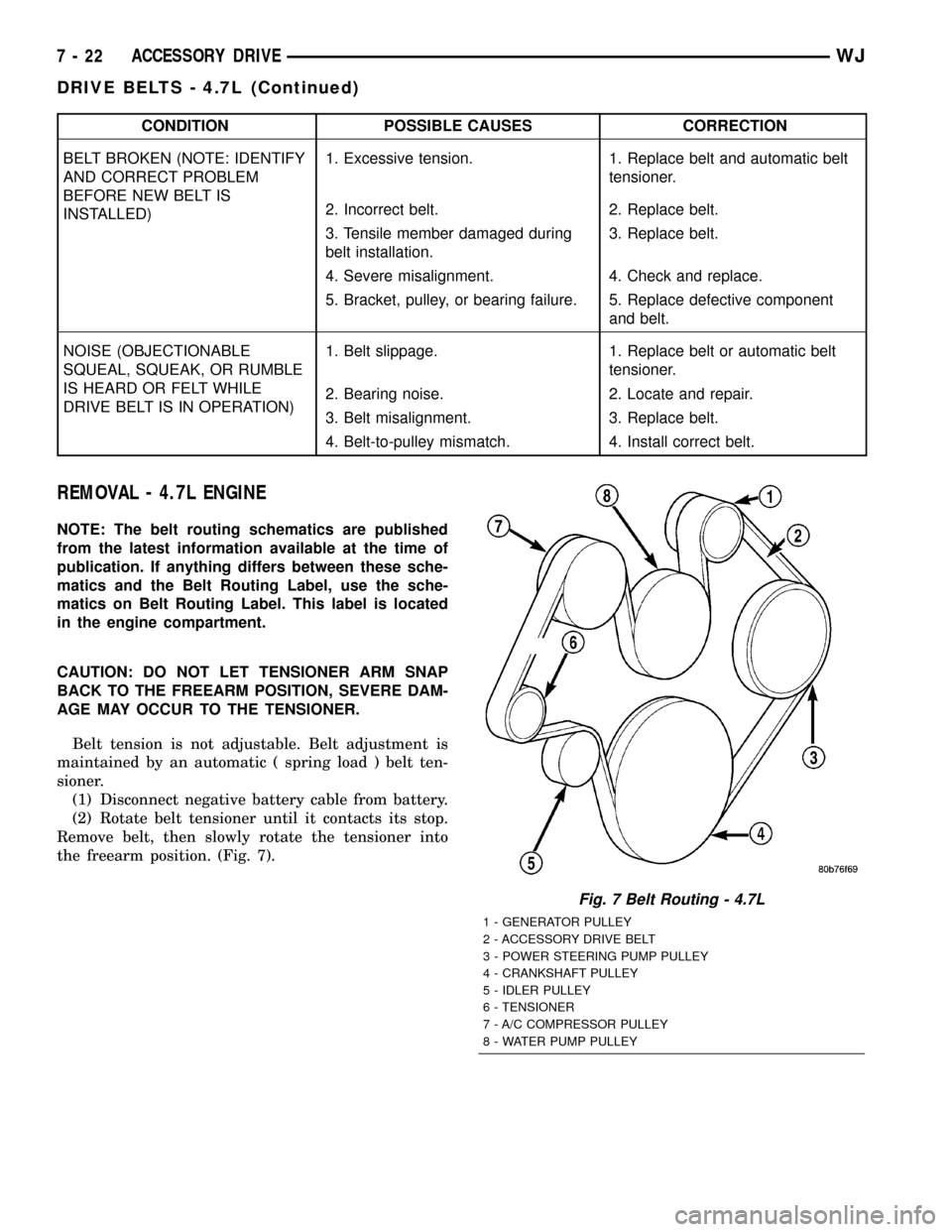
REMOVAL - 4.7L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
CAUTION: DO NOT LET TENSIONER ARM SNAP
BACK TO THE FREEARM POSITION, SEVERE DAM-
AGE MAY OCCUR TO THE TENSIONER.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Rotate belt tensioner until it contacts its stop.
Remove belt, then slowly rotate the tensioner into
the freearm position. (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7 Belt Routing - 4.7L
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
4 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - IDLER PULLEY
6 - TENSIONER
7 - A/C COMPRESSOR PULLEY
8 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
7 - 22 ACCESSORY DRIVEWJ
DRIVE BELTS - 4.7L (Continued)