2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE fluid
[x] Cancel search: fluidPage 1751 of 2199

(3) Install nuts to hold seal plate to floor pan.
Tighten nuts to 7 N´m (65 in.lbs.).
(4) Install the shift cable to the shifter assembly
bracket. Push cable into the bracket until secure.
(5) Place the floor shifter lever in PARK position.
(6) Loosen the adjustment screw on the shift cable.
(7) Snap the shift cable onto the shift lever pin.
(8) Raise the vehicle.
(9) Install the shift cable to the shift cable support
bracket.
(10) Shift the transmission into PARK. PARK is
the rearmost detent position on the transmission
manual shift lever.
(11) Snap the shift cable onto the transmission
manual shift lever.
(12) Lower vehicle.
(13) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(14) Tighten the adjustment screw to 7 N´m (65
in.lbs.).
(15) Verify correct shifter operation.
(16) Install any console parts removed for access to
shift lever assembly and shift cable. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
ADJUSTMENTS - GEARSHIFT CABLE
Check adjustment by starting the engine in PARK
and NEUTRAL. Adjustment is CORRECT if the
engine starts only in these positions. Adjustment is
INCORRECT if the engine starts in one but not both
positions. If the engine starts in any position other
than PARK or NEUTRAL, or if the engine will not
start at all, the park/neutral position switch or TRS
may be faulty.
(1) Shift transmission into PARK.
(2) Remove floor console as necessary for access to
the shift cable adjustment. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - REMOVAL)
(3) Loosen the shift cable adjustment screw (Fig.
64).
(4) Raise vehicle.
(5) Unsnap cable eyelet from transmission shift
lever (Fig. 65).
(6) Verify transmission shift lever is in PARK
detent by moving lever fully rearward. Last rearward
detent is PARK position.
(7) Verify positive engagement of transmission
park lock by attempting to rotate propeller shaft.
Shaft will not rotate when park lock is engaged.
(8) Snap cable eyelet onto transmission shift lever.
(9) Lower vehicle
(10) Tighten the shift cable adjustment screw to 7
N´m (65 in.lbs.).
(11) Verify correct operation.(12) Install any floor console components removed
for access. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR
CONSOLE - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 64 Shift Cable at the Shifter
1 - SHIFT LEVER PIN
2 - ADJUSTMENT SCREW
3 - SHIFT CABLE
4 - SHIFTER ASSEMBLY BRACKET
Fig. 65 Shift Cable at Transmission
1 - TRANSMISSION SHIFTER CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
3 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE
4 - TRANSFER CASE SHIFTER CABLE BRACKET RETAINING
BOLT(S)
5 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE BRACKET RETAINING BOLT
6 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
7 - TRANSMISSION FLUID LINES
21 - 232 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
GEARSHIFT CABLE (Continued)
Page 1753 of 2199
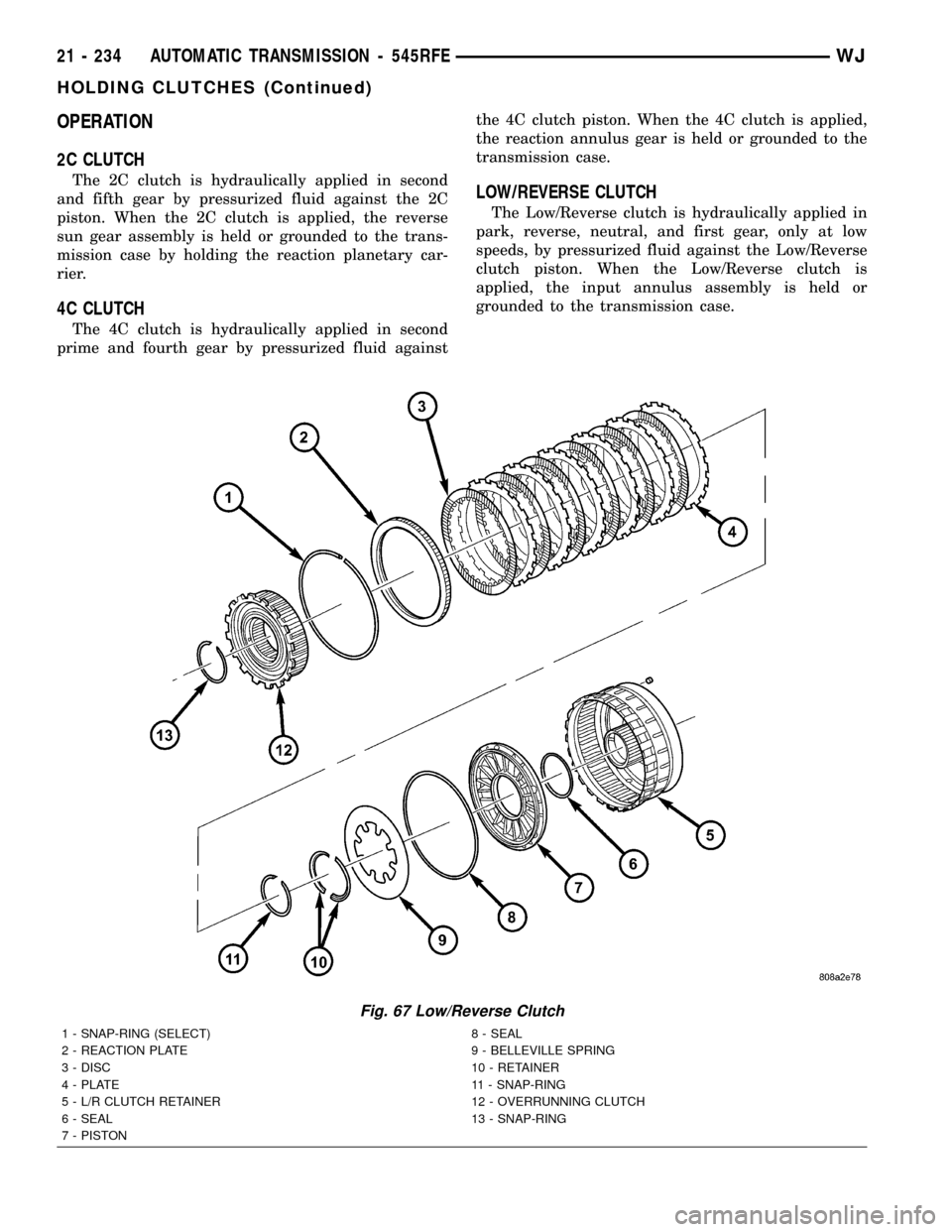
OPERATION
2C CLUTCH
The 2C clutch is hydraulically applied in second
and fifth gear by pressurized fluid against the 2C
piston. When the 2C clutch is applied, the reverse
sun gear assembly is held or grounded to the trans-
mission case by holding the reaction planetary car-
rier.
4C CLUTCH
The 4C clutch is hydraulically applied in second
prime and fourth gear by pressurized fluid againstthe 4C clutch piston. When the 4C clutch is applied,
the reaction annulus gear is held or grounded to the
transmission case.
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
The Low/Reverse clutch is hydraulically applied in
park, reverse, neutral, and first gear, only at low
speeds, by pressurized fluid against the Low/Reverse
clutch piston. When the Low/Reverse clutch is
applied, the input annulus assembly is held or
grounded to the transmission case.
Fig. 67 Low/Reverse Clutch
1 - SNAP-RING (SELECT) 8 - SEAL
2 - REACTION PLATE 9 - BELLEVILLE SPRING
3 - DISC 10 - RETAINER
4 - PLATE 11 - SNAP-RING
5 - L/R CLUTCH RETAINER 12 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
6 - SEAL 13 - SNAP-RING
7 - PISTON
21 - 234 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
HOLDING CLUTCHES (Continued)
Page 1754 of 2199
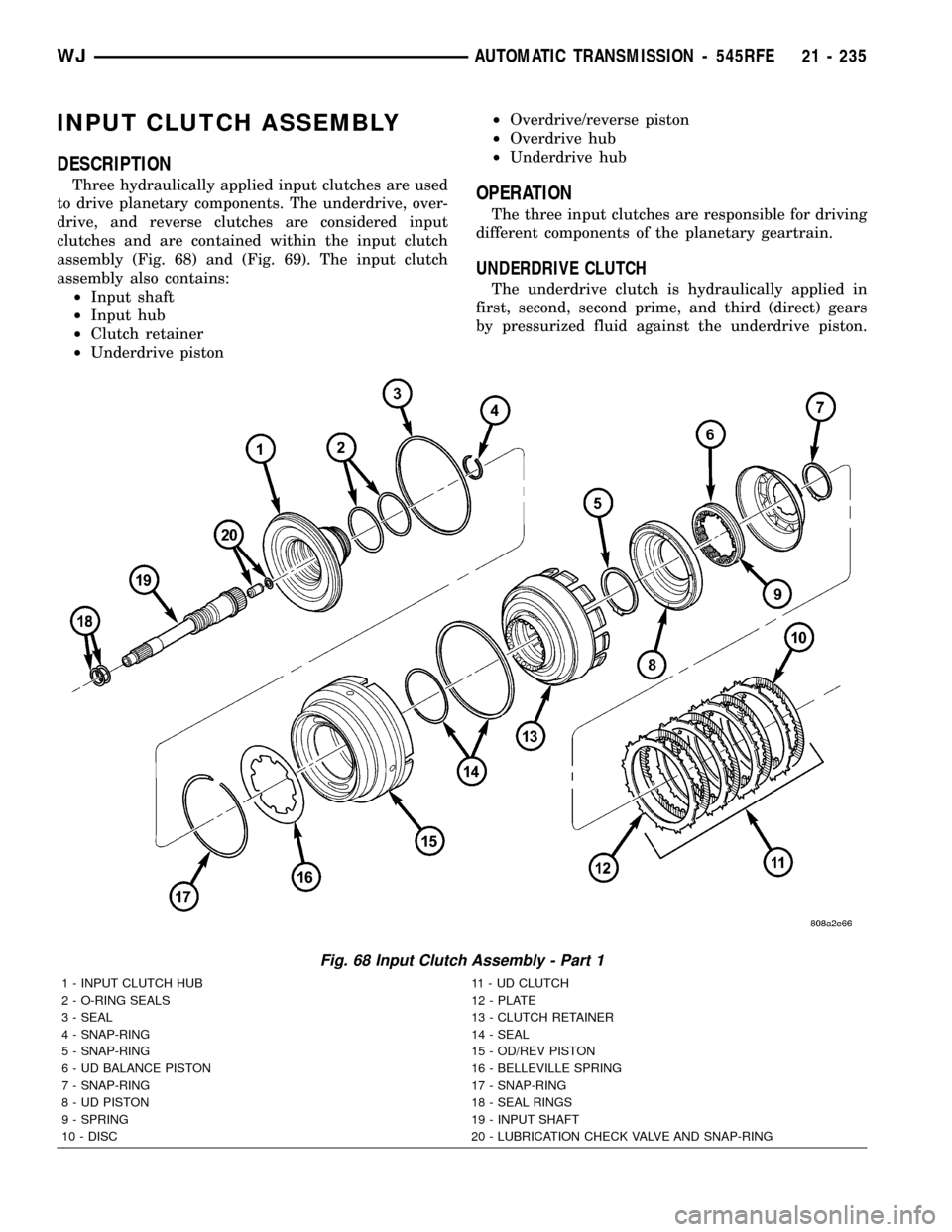
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
Three hydraulically applied input clutches are used
to drive planetary components. The underdrive, over-
drive, and reverse clutches are considered input
clutches and are contained within the input clutch
assembly (Fig. 68) and (Fig. 69). The input clutch
assembly also contains:
²Input shaft
²Input hub
²Clutch retainer
²Underdrive piston²Overdrive/reverse piston
²Overdrive hub
²Underdrive hubOPERATION
The three input clutches are responsible for driving
different components of the planetary geartrain.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
The underdrive clutch is hydraulically applied in
first, second, second prime, and third (direct) gears
by pressurized fluid against the underdrive piston.
Fig. 68 Input Clutch Assembly - Part 1
1 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB 11 - UD CLUTCH
2 - O-RING SEALS 12 - PLATE
3 - SEAL 13 - CLUTCH RETAINER
4 - SNAP-RING 14 - SEAL
5 - SNAP-RING 15 - OD/REV PISTON
6 - UD BALANCE PISTON 16 - BELLEVILLE SPRING
7 - SNAP-RING 17 - SNAP-RING
8 - UD PISTON 18 - SEAL RINGS
9 - SPRING 19 - INPUT SHAFT
10 - DISC 20 - LUBRICATION CHECK VALVE AND SNAP-RING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 235
Page 1755 of 2199
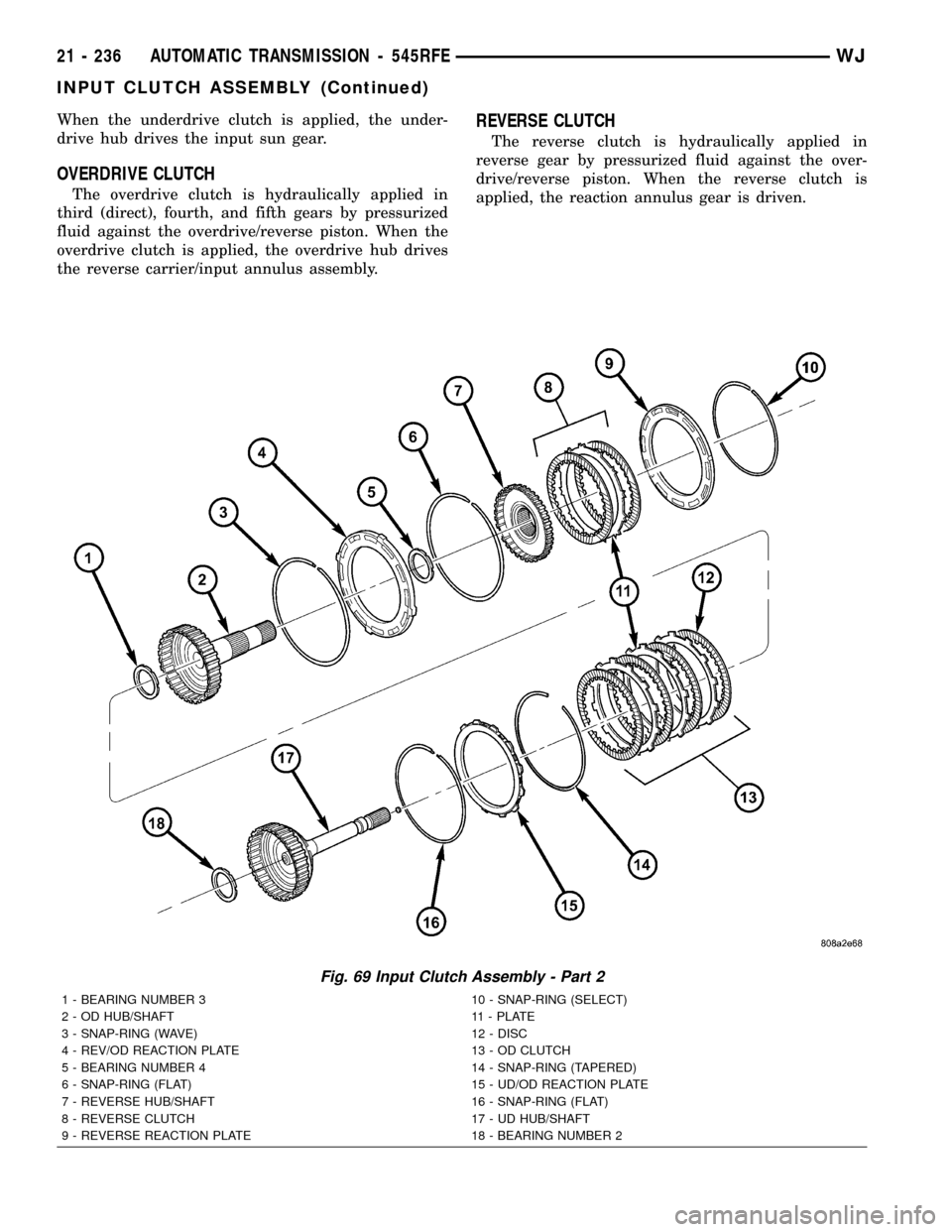
When the underdrive clutch is applied, the under-
drive hub drives the input sun gear.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
The overdrive clutch is hydraulically applied in
third (direct), fourth, and fifth gears by pressurized
fluid against the overdrive/reverse piston. When the
overdrive clutch is applied, the overdrive hub drives
the reverse carrier/input annulus assembly.
REVERSE CLUTCH
The reverse clutch is hydraulically applied in
reverse gear by pressurized fluid against the over-
drive/reverse piston. When the reverse clutch is
applied, the reaction annulus gear is driven.
Fig. 69 Input Clutch Assembly - Part 2
1 - BEARING NUMBER 3 10 - SNAP-RING (SELECT)
2 - OD HUB/SHAFT 11 - PLATE
3 - SNAP-RING (WAVE) 12 - DISC
4 - REV/OD REACTION PLATE 13 - OD CLUTCH
5 - BEARING NUMBER 4 14 - SNAP-RING (TAPERED)
6 - SNAP-RING (FLAT) 15 - UD/OD REACTION PLATE
7 - REVERSE HUB/SHAFT 16 - SNAP-RING (FLAT)
8 - REVERSE CLUTCH 17 - UD HUB/SHAFT
9 - REVERSE REACTION PLATE 18 - BEARING NUMBER 2
21 - 236 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1763 of 2199

(23) Install the reverse clutch pack into the input
clutch retainer (Fig. 77).
(24) Install the reverse reaction plate into the
input clutch retainer.
(25) Install the reverse reaction plate selective
snap-ring into the input clutch retainer.
(26) Mount a dial indicator to the assembly, push
down on the clutch discs, pull up on the reaction
plate to ensure the plate is properly seated and zero
the indicator against the reverse clutch discs (Fig.
81). Apply 20 psi of air pressure to the reverse clutch
and record the dial indicator reading. Measure and
record Reverse clutch pack measurement in four (4)
places, 90É apart. Take average of four measurements
and compare with Reverse clutch pack clearance
specification. The correct clutch clearance is 0.58-1.47
mm (0.023-0.058 in.). Adjust as necessary. Install the
chosen snap-ring and re-measure to verify selection.
(27) Remove the reverse clutch pack from the
input clutch retainer.
(28) Install the number 2 bearing onto the under-
drive hub with outer race against the hub with petro-
leum jelly.
(29) Install the underdrive hub into the input
clutch retainer.
(30) Install the number 3 bearing into the over-
drive hub with the outer race against the hub with
petroleum jelly.
(31) Install the overdrive hub into the input clutch
retainer.
(32) Install the number 4 bearing into the reverse
hub with outer race against the hub with petroleum
jelly.(33) Install the reverse hub into the input clutch
retainer.
(34) Install the complete reverse clutch pack.
(35) Install the reverse reaction plate and snap-
ring.
(36) Push up on reaction plate to allow reverse
clutch to move freely.
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the input
speed sensor (Fig. 82).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the input speed sensor
to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the input speed sensor from the trans-
mission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the input speed sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the input speed sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
Fig. 81 Measuring Reverse Clutch Clearance
1 - TOOL C-3339
2 - REVERSE CLUTCH PACK
21 - 244 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1764 of 2199

(3) Install the wiring connector onto the input
speed sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The TCM utilizes a closed-loop system to control
transmission line pressure. The system contains a
variable force style solenoid, the Pressure Control
Solenoid, mounted on the side of the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly. The solenoid is duty cycle
controlled by the TCM to vent the unnecessary line
pressure supplied by the oil pump back to the sump.
The system also contains a variable pressure style
sensor, the Line Pressure Sensor, which is a direct
input to the TCM. The line pressure solenoid moni-
tors the transmission line pressure and completes the
feedback loop to the TCM. The TCM uses this infor-
mation to adjust its control of the pressure control
solenoid to achieve the desired line pressure.
OPERATION
The TCM calculates the desired line pressure
based upon inputs from the transmission and engine.
The TCM calculates the torque input to the trans-
mission and uses that information as the primary
input to the calculation. The line pressure is set to a
predetermined value during shifts and when the
transmission is in the PARK and NEUTRAL posi-tions. This is done to ensure consistent shift quality.
During all other operation, the actual line pressure is
compared to the desired line pressure and adjust-
ments are made to the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the line
pressure sensor (Fig. 83).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the line pressure sen-
sor to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the line pressure sensor from the
transmission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the line pressure sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the line pressure sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
(3) Install the wiring connector onto the line pres-
sure sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 82 Input Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 83 Line Pressure Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 245
INPUT SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1767 of 2199

OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump (Fig. 87) is located at the front of the
transmission inside the bell housing and behind the
transmission front cover. The oil pump consists of
two independent pumps (Fig. 88), a number of valves
(Fig. 89), a front seal (Fig. 90), and a bolt on reaction
shaft. The converter clutch switch and regulator
valves, pressure regulator valve, and converter pres-
sure limit valve are all located in the oil pump valve
body.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the oil pump drive gear. As the drive gear
rotates both driven gears, a vacuum is created when
the gear teeth come out of mesh. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
gear teeth come back into mesh, pressurized fluid is
forced into the pump outlet and to the oil pump
valves.
At low speeds, both sides of the pump supply fluid
to the transmission. As the speed of the torque con-
verter increases, the flow from both sides increases
until the flow from the primary side alone is suffi-
cient to meet system demands. At this point, the
check valve located between the two pumps closes.
The secondary side is shut down and the primary
side supplies all the fluid to the transmission.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The converter clutch switch valve is used to control
the hydraulic pressure supplied to the front (OFF)
side of the torque converter clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH REGULATOR VALVE
The converter clutch regulator valve is used to con-
trol the hydraulic pressure supplied to the back (ON)
side of the torque converter clutch.
TORQUE CONVERTER LIMIT VALVE
The torque converter limit valve serves to limit the
available line pressure to the torque converter clutch
to approximately 120 psi.
Fig. 87 Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP TO CASE BOLT (6)
2 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 88 Oil Pump Gears
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - DRIVE GEAR
3 - DRIVEN GEARS
Fig. 89 Oil Pump Valves
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR VALVE
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
4 - PUMP VALVE BODY
5 - PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE
6 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH LIMIT VALVE
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1768 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring the oil pump output volume will deter-
mine if sufficient oil flow to the transmission oil
cooler exists, and whether or not an internal trans-
mission failure is present.
Verify that the transmission fluid is at the proper
level. Refer to the Fluid Level Check procedure in
this section. If necessary, fill the transmission to the
proper level with MopartATF +4, type 9602, Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid.
(1) Disconnect theTo coolerline at the cooler
inlet and place a collecting container under the dis-
connected line.CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat 1800 rpm, with the shift
selector in neutral. Verify that the transmission fluid
temperature is below 104.5É C (220É F) for this test.
(3) If one quart of transmission fluid is collected in
the container in 30 seconds or less, oil pump flow vol-
ume is within acceptable limits. If fluid flow is inter-
mittent, or it takes more than 30 seconds to collect
one quart of fluid, refer to the Hydraulic Pressure
tests in this section for further diagnosis.
(4) Re-connect theTo coolerline to the transmis-
sion cooler inlet.
Fig. 90 Oil Pump Reaction Shaft
1 - PUMP HOUSING 4 - SEAL RING (5)
2 - SEAL 5 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - OIL FILTER SEAL 6 - PUMP VALVE BODY
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 249
OIL PUMP (Continued)