2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE engine pressure
[x] Cancel search: engine pressurePage 2134 of 2199
(10) Allow three to five minutes for the refrigerant
system to stabilize, then take a second set of thermo-
couple measurements. Record the temperature differ-
ence to determine if an additional charge is required.(11) Record the compressor discharge pressure. If
the reading is higher than the pressure shown in the
Compressor Discharge Pressure Chart, the system
could be overcharged. If the reading is equal to, or
lower, than the pressure shown in the chart, continue
with this procedure.
Compressor Discharge Pressure Chart
Ambient
Temperature16ÉC
(60ÉF)21ÉC
(70ÉF)27ÉC
(80ÉF)32ÉC
(90ÉF)38ÉC
(100ÉF)43ÉC
(110ÉF)
Compressor
Discharge
Pressure1378 kPa
(200 psi)1516 kPa
(220 psi)1723 kPa
(250psi)1930 kPa
(280 psi)2206 kPa
(320 psi)2413 kPa
(350 psi)
(12)EXAMPLE:The ambient temperature is 21É
C (70É F). The evaporator inlet tube temperature is
12É C (54É F) and the evaporator outlet tube temper-
ature is 10É C (50É F). Subtract the inlet tube tem-
perature from the outlet tube temperature. The
difference is -2É C (-4É F). With a -2É C (-4É F) tem-
perature differential at 21É C (70É F) ambient tem-
perature, the system is fully charged.
(13) Add enough refrigerant to bring the refriger-
ant system up to a full charge.
(14) Remove the jumper wire from the low pres-
sure cycling clutch switch wire harness connector
and plug the connector back into the switch.
SPECIFICATIONS
CHARGE CAPACITY
The R-134a refrigerant system charge capacity for
this vehicle is 0.765 kilograms (1.687 pounds/27
ounces).
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The air conditioning system uses a Nippondenso
10PA17 ten cylinder, double-acting swash plate-type
compressor on all models. This compressor has a
fixed displacement of 170 cubic centimeters (10.374
cubic inches), and has both the suction and discharge
ports located on the cylinder head. A label identifying
the use of R-134a refrigerant is located on the com-
pressor.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the com-
pressor manifold, which is on the side of the com-
pressor. This mechanical valve is designed to vent
refrigerant from the system to protect against dam-
age to the compressor and other system components,
caused by condenser air flow restriction or an over-
charge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The compressor is driven by the engine through an
electric clutch, drive pulley and belt arrangement.
The compressor is lubricated by refrigerant oil that is
circulated throughout the refrigerant system with the
refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor, which is then
pumped to the condenser through the compressor dis-
charge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley, and coil, are
available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes
when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 57
PLUMBING (Continued)
Page 2135 of 2199

The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean that the valve is faulty.
The high pressure relief valve is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The valve cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and must not be removed or otherwise dis-
turbed. The valve is only serviced as a part of the
compressor assembly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
NOISE
When investigating an air conditioning related
noise, you must first know the conditions under
which the noise occurs. These conditions include:
weather, vehicle speed, transmission in gear or neu-
tral, engine speed, engine temperature, and any
other special conditions. Noises that develop during
air conditioning operation can often be misleading.
For example: What sounds like a failed front bearing
or connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts,
mounting brackets, or a loose compressor clutch
assembly.
Drive belts are speed sensitive. At different engine
speeds and depending upon belt tension, belts can
develop noises that are mistaken for a compressor
noise. Improper belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor clutch is engaged, which
may not occur when the compressor clutch is disen-
gaged. Check the serpentine drive belt condition and
tension as described in Cooling before beginning this
procedure.
(1) Select a quiet area for testing. Duplicate the
complaint conditions as much as possible. Switch the
compressor on and off several times to clearly iden-
tify the compressor noise. Listen to the compressor
while the clutch is engaged and disengaged. Probe
the compressor with an engine stethoscope or a long
screwdriver with the handle held to your ear to bet-
ter localize the source of the noise.
(2) Loosen all of the compressor mounting hard-
ware and retighten. Tighten the compressor clutch
mounting nut. Be certain that the clutch coil is
mounted securely to the compressor, and that the
clutch plate and pulley are properly aligned and have
the correct air gap. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH - INSTALLATION)
(3) To duplicate a high-ambient temperature condi-
tion (high head pressure), restrict the air flow
through the condenser. Install a manifold gauge set
to be certain that the discharge pressure does not
exceed 2760 kPa (400 psi).
(4) Check the refrigerant system plumbing for
incorrect routing, rubbing or interference, which cancause unusual noises. Also check the refrigerant lines
for kinks or sharp bends that will restrict refrigerant
flow, which can cause noises. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAU-
TION - REFRIGERANT HOSES/LINES/TUBES
PRECAUTIONS)
(5) If the noise is from opening and closing of the
high pressure relief valve, reclaim, evacuate, and
recharge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIG-
ERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)If the high pressure relief valve still
does not seat properly, replace the a/c compressor.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL)
(6) If the noise is from liquid slugging on the suc-
tion line, check the refrigerant oil level and the
refrigerant system charge. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGER-
ANT OIL - STANDARD PROCEDURE) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
SPECIFICATIONS - CHARGE CAPACITY).
(7) If the noise continues, replace the compressor
and repeat Step 1.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
The compressor may be removed and repositioned
without disconnecting the refrigerant lines or dis-
charging the refrigerant system. Discharging is not
necessary if servicing the compressor clutch or clutch
coil, the engine, the cylinder head, or the generator.
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Recover the refrigerant from the system. (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY)
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the serpentine drive belt. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch coil wire harness
connector.
24 - 58 PLUMBINGWJ
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2136 of 2199

(5) Remove the (2) refrigerant line retaining bolts
that secure the suction line and discharge line to the
compressor. Install plugs in, or tape over all of the
opened refrigerant fittings.
(6) Remove the bolts that secure the compressor
(Fig. 2) or (Fig. 3) and (Fig. 4).
(7) Remove the compressor.
Fig. 2 COMPRESSOR REMOVE/INSTALL - 4.0L
ENGINE
1 - POWER STEERING PUMP MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - BOLT
3 - BRACE
4 - BOLT
5 - BOLT
6 - A/C COMPRESSOR
7 - BOLT
Fig. 3 COMPRESSOR AND A/C LINES - V8
1 - DISCHARGE LINE
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - SUCTION LINE
4 - A/C/ CONDENSOR
5 - DISCHARGE LINE TO CONDENSOR
6 - A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER SWITCH
7 - A/C/ SERVICE PORT
8 - RECEIVER DRIER
Fig. 4 COMPRESSOR REMOVE/INSTALL - V8
ENGINE - RIGHT VIEW
1 - BOLT
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - BOLT
WJPLUMBING 24 - 59
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2139 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(8) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(9) Connect the negative battery cable.
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION
The condenser is located in the air flow in front of
the engine cooling radiator. The condenser is a heat
exchanger that allows the high-pressure refrigerant
gas being discharged by the compressor to give up its
heat to the air passing over the condenser fins.
OPERATION
When the refrigerant gas gives up its heat, it con-
denses. When the refrigerant leaves the condenser, it
has become a high-pressure liquid refrigerant. The
volume of air flowing over the condenser fins is crit-
ical to the proper cooling performance of the air con-
ditioning system. Therefore, it is important that
there are no objects placed in front of the radiator
grille openings in the front of the vehicle or foreign
material on the condenser fins that might obstruct
proper air flow. Also, any factory-installed air seals or
shrouds must be properly reinstalled following radia-
tor or condenser service.
The condenser cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS GROUP BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
CAUTION: Before removing the condenser, note the
location of each of the radiator and condenser air
seals. These seals are used to direct air through the
condenser and radiator. The air seals must be rein-
stalled in their proper locations in order for the air
conditioning and engine cooling systems to per-
form as designed.(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Recover the refrigerant from the refrigerant
system. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY)
(3) Remove the screws attaching the grille and
headlamp mounting module to the upper crossmem-
ber of the vehicle. Refer to Body for this and further
steps in the procedure.
(4) Remove the headlamps from their mounts.
(5) Remove the nuts that secure the hood latch
and brace to the upper crossmember.
(6) The radiator upper crossmember can be
adjusted left or right through the use of its slotted
mounting holes. Before removal, mark the original
position of the crossmember.
(7) Remove the bolts that secure the radiator to
the upper crossmember and set it aside (Fig. 6).
(8) Remove the engine air filter inlet duct secured
at the headlamp mounting module.
(9) Remove the headlamp mounting module and
front fascia for access to the condenser and fittings.
(10) Disconnect the discharge line and liquid line
refrigerant line fittings from the condenser. Install
plugs in, or tape over all of the opened refrigerant
line fittings.Fig. 6 CONDENSER MOUNTING - TYPICAL
1 - CONDENSER-TO-RADIATOR MOUNTING BRACKETS (2)
2 - UPPER CROSSMEMBER
3 - FAN SHROUD
4 - ALIGNMENT TABS
5 - RADIATOR
6 - ALIGNMENT DOWELS (2)
7 - RUBBER ISOLATORS (2)
8 - RUBBER GROMMETS (2)
9 - LOWER CROSSMEMBER
10 - CONDENSER
24 - 62 PLUMBINGWJ
A/C COMPRESSOR (Continued)
Page 2140 of 2199

(11) Remove the bolts that secure the upper con-
denser and transmission cooler.
(12) Carefully lift the condenser out of the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
CAUTION: Before removing the condenser, note the
location of each of the radiator and condenser air
seals. These seals are used to direct air through the
condenser and radiator. The air seals must be rein-
stalled in their proper locations in order for the air
conditioning and engine cooling systems to per-
form as designed.
(1) Carefully position the condenser in the vehicle.
(2) Install the bolts that secure the upper con-
denser and transmission cooler.
(3) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser inlet and the discharge
line. Connect the discharge line to the condenser
inlet. Tighten the retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.).
(4) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser outlet and the liquid
line. Connect the liquid line to the condenser outlet.
Tighten the retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the headlamp mounting module and
front fascia. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(6) Install the engine air filter inlet duct.
(7) Install the bolts that secure the radiator to the
upper crossmember.(8) Install the nuts that secure the hood latch and
brace to the upper crossmember.
(9) Install the headlamps in their mounts.
(10) Install the screws attaching the grille and
headlamp mounting module to the upper crossmem-
ber of the vehicle. Refer to Body for this and further
steps in the procedure.
(11) Evacuate and Recharge the refrigerant sys-
tem. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(12) Connect the battery negative cable.
NOTE: If the condenser is replaced, add 30 millili-
ters (1 fluid ounce) of refrigerant oil to the refriger-
ant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
A/C DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.7L TURBO DIESEL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Recover the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY)
(3) Remove both headlamps from the vehicle. Refer
to Lamps/Lighting for the procedure.
(4) Remove the a/c high pressure transducer(Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CON-
TROLS/A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - REMOV-
AL).
(5) Remove the front fascia from the vehicle. Refer
to Front Fascia for the procedure (Fig. 7).
(6) Remove the refrigerant line retaining fastener
from the condenser inlet fitting. Remove the line and
cap the condenser inlet tube to prevent contamina-
tion of the system.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 63
A/C CONDENSER (Continued)
Page 2142 of 2199

ING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C
PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - INSTALLATION).
(9) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(10) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(11) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Remove the tape or plugs from the discharge
line block fitting and the manifold on the compressor.
Install the discharge line block fitting to the manifold
on the compressor. Tighten the mounting bolt to 25.4
N´m (225 in. lbs.).
(2) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser inlet and the discharge
line. Connect the discharge line to the condenser
inlet. Tighten the retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.).
(3) Install the a/c high pressure transducer(Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CON-
TROLS/A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - INSTAL-
LATION).
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)(6) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
A/C EXPANSION VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The ªHº valve type thermal expansion valve (TXV)
is located at the front of the heater-A/C housing
between the liquid and suction lines and the evapo-
rator coil.
The expansion valve is a factory calibrated unit
and cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty or dam-
aged, the expansion valve must be replaced.
OPERATION
High-pressure, high temperature liquid refrigerant
from the liquid line passes through the expansion
valve orifice, converting it inot a low-pressure, low-
temperature mixture of liquid and gas before it
enters the evaporator coil. A temperature sensor in
the expansion valve control head monitors the tem-
perature of the refrigerant leaving the evaporator coil
throught the suction line, and adjusts the orifice size
at the liquid line to let the proper amoount of refrig-
erant into the evaporator coil to meet the vehicle
cooling requirements. Controlling the refrigerant flow
through the evaporator ensures that none of the
refrigerant leaving the evaporator is still in a liquid
state, which could damage the compressor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C EXPANSION
VALVE
The expansion valve is located on the engine side
of the dash panel near the shock tower.
The expansion valve can fail in three different
positions (open, closed or restricted).
In an Open Position: this will result in a noisy
compressor or no cooling. The cause can be broken
spring, broken ball or excessive moisture in the A/C
system. If the spring or ball are found to be defective,
replace the expansion valve. If excessive moisture is
found in the A/C system, recycle the refrigerant.
In a Closed Position: There will be low suction
pressure and no cooling. This may be caused by a
failed power dome or excessive moisture in the A/C
system. If the power dome on the expansion valve is
found to be defective replace the expansion valve. If
excessive moisture is found recycle the refrigerant.
A Restricted Orifice: There will be low suction
pressure and no cooling. This may be caused by
debris in the refrigerant system. If debris is believed
to be the cause, recycle the refrigerant and replace
the expansion valve and the receiver/drier.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 65
A/C DISCHARGE LINE (Continued)
Page 2148 of 2199

HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the HVAC housing,
under the instrument panel. It is a heat exchanger
made of rows of tubes and fins.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flows
through the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The temperature
control door allows control of the heater output air
temperature by controlling how much of the air flow-
ing through the HVAC housing is directed through
the heater core. The blower motor speed controls the
volume of air flowing through the HVAC housing.
The heater core cannot be repaired and, if faulty or
damaged, it must be replaced. Refer to Cooling for
more information on the engine cooling system, the
engine coolant and the heater hoses.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Remove the HVAC housing from the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the foam gasket surrounding the core
tubes.
NOTE: Notice the orientation of the irregularly
shaped gasket on the tubes. The gasket must be
placed correctly to ensure proper sealing against
the body during reinstallation.(3)
Remove the screws and retainers that secure the
heater core and tubes to the HVAC housing (Fig. 12).
(4) Remove the mode door actuator if necessary,
for clearance to remove the core.
(5) Lift the heater core straight up and out of the
HVAC housing (Fig. 13).
(6) When replacing individual tubes, loosen and
remove the round tube-to-core clamp, and pull tube
from core.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
Fig. 12 HEATER CORE, TUBES, AND RETAINERS
1 - TUBE-TO-CORE CLAMPS
2 - GROUND STRAP
3 - HVAC HOUSING
4 - TUBE RETAINERS AND SCREWS
5 - HEATER CORE
WJPLUMBING 24 - 71
Page 2149 of 2199

pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) When installing individual tubes, insert tube
into core ensuring that tube O-ring is seated in core
and not pinched. Hold tube in seated position while
installing the round tube-to-core clamp (Fig. 14).
NOTE: The round tube-to-heater-core clamp should
be left loose enough to turn the tube in the core.
Position the core in the housing, and then tighten
the tube-to-heater-core clamp after orienting the
tubes to the molded HVAC housing.
(2) Lower the heater core into the HVAC housing.
(3) Install the mode door actuator, if removed from
housing for core removal.
(4) Position the retainers over the heater core
tubes. Install and tighten the screws that secure the
heater core and retainers to the HVAC housing.
Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).NOTE: The grounding strap is to be attached to the
lower heater core tube retainer.
(5) Reinstall the HVAC housing to the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
DISTRIBUTION/HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLA-
TION)
RECEIVER / DRIER
DESCRIPTION
The receiver/drier is mounted in the engine com-
partment between the condenser and is part of the
liquid line assembly. The filter/drier cannot be
repaired, if the filter/drier is faulty, damaged, left
open to the atmosphere or contaminated the line
assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
The filter-drier performs a filtering action to pre-
vent foreign material in the refrigerant from contam-
inating the expansion valve. A desiccant bag is
mounted inside the filter-drier canister to absorb any
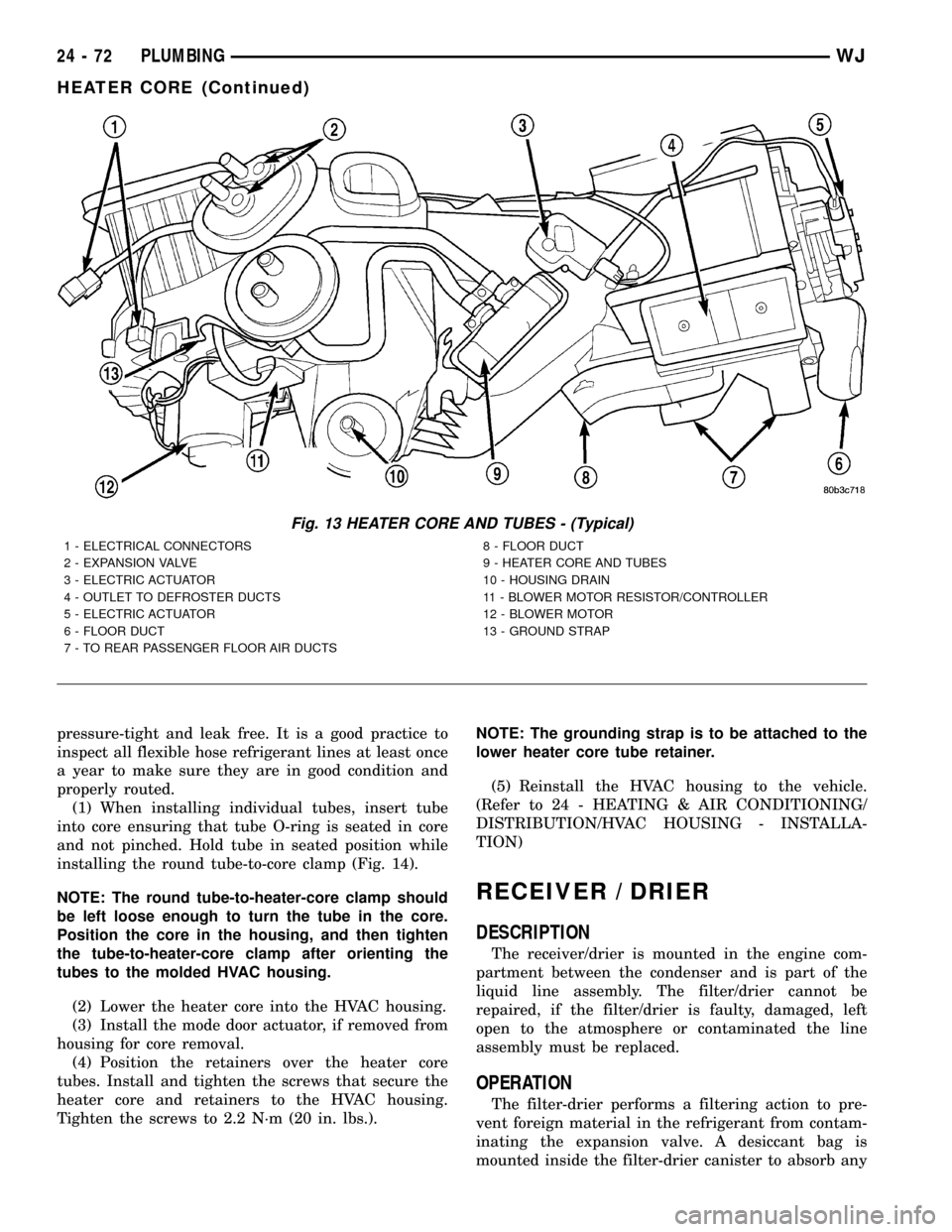
Fig. 13 HEATER CORE AND TUBES - (Typical)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
2 - EXPANSION VALVE
3 - ELECTRIC ACTUATOR
4 - OUTLET TO DEFROSTER DUCTS
5 - ELECTRIC ACTUATOR
6 - FLOOR DUCT
7 - TO REAR PASSENGER FLOOR AIR DUCTS8 - FLOOR DUCT
9 - HEATER CORE AND TUBES
10 - HOUSING DRAIN
11 - BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR/CONTROLLER
12 - BLOWER MOTOR
13 - GROUND STRAP
24 - 72 PLUMBINGWJ
HEATER CORE (Continued)