2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Charge
[x] Cancel search: ChargePage 2151 of 2199

inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser outlet and the con-
denser end of the liquid line. Connect the liquid line
to the condenser outlet. Tighten the retaining nut to
20.16 N´m (180 in. lbs.).
(2) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the evaporator end of the liquid line
and the evaporator inlet. Place the receiver/drier
bracket on the stud and connect the liquid line to the
evaporator inlet.
(3) Remove the tape or plugs from the suction line
and evaporator outlet. Slide the suction line connec-
tion block on the liquid line on the evaporator con-
nection stud. Tighten the retaining nut to 20.16 N´m
( 180 in. lbs.).
(4) Insert a screw for the receiver/drier bracket
and hand turn three turns. Tighten the screw to
10.64 N´m (95 in. lbs.).(5) Install the battery tray and the battery(Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY -
INSTALLATION) and (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLATION).
(6) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM EVACUATE)
(7) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
NOTE: If the receiver/drier is replaced, add 120 mil-
liliters (4 fluid ounces) of refrigerant oil to the
refrigerant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the
type recommended for the compressor in the vehi-
cle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
Fig. 16 2.7L Diesel Compressor-RHD (LHD typical)
1 - SUCTION LINE MOUNTING SCREW
2 - SUCTION LINE TO H-BLOCK
3 - H-BLOCK
4 - RECEIVER DRIER
5 - LIQUID LINE SERVICE PORT6 - LIQUID LINE AND RECEIVER DRIER
7 - A/C COMPRESSOR
8 - A/C COMPRESSOR DRIVE BELT
9 - RADIATOR - CONDENSOR ASSEMBLY
24 - 74 PLUMBINGWJ
RECEIVER / DRIER (Continued)
Page 2152 of 2199

REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant used in this air conditioning sys-
tem is a HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC), type R-134a.
Unlike R-12, which is a ChloroFluoroCarbon (CFC),
R-134a refrigerant does not contain ozone-depleting
chlorine. R-134a refrigerant is a non-toxic, non-flam-
mable, clear, and colorless liquefied gas.
Even though R-134a does not contain chlorine, it
must be reclaimed and recycled just like CFC-type
refrigerants. This is because R-134a is a greenhouse
gas and can contribute to global warming.
OPERATION
R-134a refrigerant is not compatible with R-12
refrigerant in an air conditioning system. Even a
small amount of R-12 added to an R-134a refrigerant
system will cause compressor failure, refrigerant oil
sludge or poor air conditioning system performance.
In addition, the PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG) synthetic
refrigerant oils used in an R-134a refrigerant system
are not compatible with the mineral-based refriger-
ant oils used in an R-12 refrigerant system.
R-134a refrigerant system service ports, service
tool couplers and refrigerant dispensing bottles have
all been designed with unique fittings to ensure that
an R-134a system is not accidentally contaminated
with the wrong refrigerant (R-12). There are also
labels posted in the engine compartment of the vehi-
cle and on the compressor identifying to service tech-
nicians that the air conditioning system is equipped
with R-134a.
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION
The refrigerant oil used in R-134a refrigerant sys-
tems is a synthetic-based, PolyAlkylene Glycol (PAG),
wax-free lubricant. Mineral-based R-12 refrigerant
oils are not compatible with PAG oils, and should
never be introduced to an R-134a refrigerant system.
There are different PAG oils available, and each
contains a different additive package. The 10PA17
compressor used in this vehicle is designed to use an
ND8 PAG refrigerant oil. Use only refrigerant oil of
this same type to service the refrigerant system.
OPERATION
After performing any refrigerant recovery or recy-
cling operation, always replenish the refrigerant sys-
tem with the same amount of the recommended
refrigerant oil as was removed. Too little refrigerant
oil can cause compressor damage, and too much can
reduce air conditioning system performance.PAG refrigerant oil is much more hygroscopic than
mineral oil, and will absorb any moisture it comes
into contact with, even moisture in the air. The PAG
oil container should always be kept tightly capped
until it is ready to be used. After use, recap the oil
container immediately to prevent moisture contami-
nation.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT OIL
LEVEL
When an air conditioning system is assembled at
the factory, all components except the compressor are
refrigerant oil free. After the refrigerant system has
been charged and operated, the refrigerant oil in the
compressor is dispersed throughout the refrigerant
system. The accumulator, evaporator, condenser, and
compressor will each retain a significant amount of
the needed refrigerant oil.
It is important to have the correct amount of oil in
the refrigerant system. This ensures proper lubrica-
tion of the compressor. Too little oil will result in
damage to the compressor. Too much oil will reduce
the cooling capacity of the air conditioning system.
It will not be necessary to check the oil level in the
compressor or to add oil, unless there has been an oil
loss. An oil loss may occur due to a rupture or leak
from a refrigerant line, a connector fitting, a compo-
nent, or a component seal. If a leak occurs, add 30
milliliters (1 fluid ounce) of refrigerant oil to the
refrigerant system after the repair has been made.
Refrigerant oil loss will be evident at the leak point
by the presence of a wet, shiny surface around the
leak.
Refrigerant oil must be added when a accumulator,
evaporator coil, or condenser are replaced. See the
Refrigerant Oil Capacities chart. When a compressor
is replaced, the refrigerant oil must be drained from
the old compressor and measured. Drain all of the
refrigerant oil from the new compressor, then fill the
new compressor with the same amount of refrigerant
oil that was drained out of the old compressor.
Refrigerant Oil Capacities
Component ml fl oz
A/C System 130 4.40
Receiver Drier 70 2.37
Condenser 10 0.34
Evaporator 50 1.69
Compressordrain and measure
the oil from the old
compressor - see
text.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 75
Page 2158 of 2199

(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0057 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0058 (M) 2/2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Problem detected in oxygen sensor heater relay circuit.
P0071 (M) Amb/Bat Temp Sensor Performance
P0106 Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
PO111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Performance
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Coolant Temp Sensor Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0121 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage Low Throttle position sensor input below the acceptable
voltage range.
P0122 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too LowAPPS voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0123 (M) Accelerator Position Sensor (APPS)
Signal Voltage Too HighAPPS voltage input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
P0125 (M) Closed Loop Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0125 (M) Engine is Cold Too Long Engine does not reach operating temperature.
P0130 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
MalfunctionOxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2161 of 2199
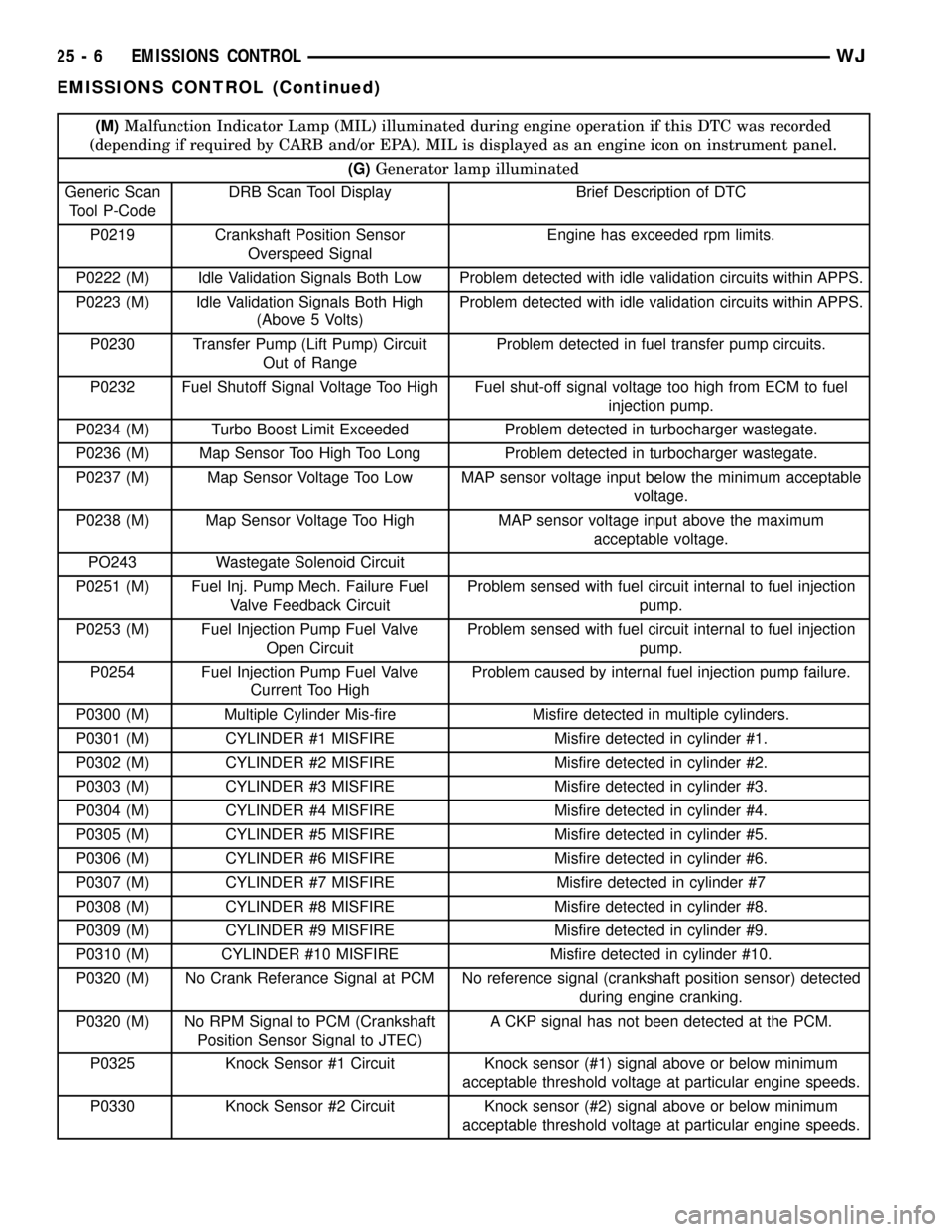
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P0219 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Overspeed SignalEngine has exceeded rpm limits.
P0222 (M) Idle Validation Signals Both Low Problem detected with idle validation circuits within APPS.
P0223 (M) Idle Validation Signals Both High
(Above 5 Volts)Problem detected with idle validation circuits within APPS.
P0230 Transfer Pump (Lift Pump) Circuit
Out of RangeProblem detected in fuel transfer pump circuits.
P0232 Fuel Shutoff Signal Voltage Too High Fuel shut-off signal voltage too high from ECM to fuel
injection pump.
P0234 (M) Turbo Boost Limit Exceeded Problem detected in turbocharger wastegate.
P0236 (M) Map Sensor Too High Too Long Problem detected in turbocharger wastegate.
P0237 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor voltage input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
P0238 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor voltage input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
PO243 Wastegate Solenoid Circuit
P0251 (M) Fuel Inj. Pump Mech. Failure Fuel
Valve Feedback CircuitProblem sensed with fuel circuit internal to fuel injection
pump.
P0253 (M) Fuel Injection Pump Fuel Valve
Open CircuitProblem sensed with fuel circuit internal to fuel injection
pump.
P0254 Fuel Injection Pump Fuel Valve
Current Too HighProblem caused by internal fuel injection pump failure.
P0300 (M) Multiple Cylinder Mis-fire Misfire detected in multiple cylinders.
P0301 (M) CYLINDER #1 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #1.
P0302 (M) CYLINDER #2 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #2.
P0303 (M) CYLINDER #3 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #3.
P0304 (M) CYLINDER #4 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #4.
P0305 (M) CYLINDER #5 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #5.
P0306 (M) CYLINDER #6 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #6.
P0307 (M) CYLINDER #7 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #7
P0308 (M) CYLINDER #8 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #8.
P0309 (M) CYLINDER #9 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #9.
P0310 (M) CYLINDER #10 MISFIRE Misfire detected in cylinder #10.
P0320 (M) No Crank Referance Signal at PCM No reference signal (crankshaft position sensor) detected
during engine cranking.
P0320 (M) No RPM Signal to PCM (Crankshaft
Position Sensor Signal to JTEC)A CKP signal has not been detected at the PCM.
P0325 Knock Sensor #1 Circuit Knock sensor (#1) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
P0330 Knock Sensor #2 Circuit Knock sensor (#2) signal above or below minimum
acceptable threshold voltage at particular engine speeds.
25 - 6 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)