2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE speed control
[x] Cancel search: speed controlPage 1866 of 2199

²Unsatisfactory ride
²Vehicle drift
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the
Tire Inflation Pressure Chart provided with the vehi-
cles Owners Manual. A Certification Label on the
drivers side door pillar provides the minimum tire
and rim size for the vehicle. The label also list the
cold inflation pressure for these tires at full load
operation
Tire pressures have been chosen to provide safe
operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth ride. Tire
pressure should be checked cold once a month. Tire
pressure decreases as the ambient temperature
drops. Check tire pressure frequently when ambient
temperature varies widely.
Tire inflation pressures are cold inflation pressure.
The vehicle must sit for at least 3 hours to obtain the
correct cold inflation pressure reading. Or be drivenless than one mile after sitting for 3 hours. Tire
inflation pressures may increase from 2 to 6 pounds
per square inch (psi) during operation. Do not reduce
this normal pressure build-up.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES CAN
AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING AND TREAD WEAR.
THIS MAY CAUSE THE TIRE TO FAIL SUDDENLY,
RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE CONTROL.
DESCRIPTION - TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH
SPEED
Where speed limits allow the vehicle to be driven
at high speeds, correct tire inflation pressure is very
important. For speeds up to and including 120 km/h
(75 mph), tires must be inflated to the pressures
shown on the tire placard. For continuous speeds in
excess of 120 km/h (75 mph), tires must be inflated
to the maximum pressure specified on the tire side-
wall.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES
The original equipment tires provide a proper bal-
ance of many characteristics such as:
²Ride
²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capability
It is recommended that tires equivalent to the orig-
inal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehi-
cle.
The use of oversize tires may cause interference
with vehicle components. Under extremes of suspen-
sion and steering travel, interference with vehicle
components may cause tire damage.
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
Fig. 13 Under Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE THREAD AREAS
Fig. 14 Over Inflation Wear
1 - THIN TIRE THREAD AREA
WJTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 7
TIRES (Continued)
Page 1969 of 2199

SUNROOF
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
SUNROOF
DESCRIPTION.........................96
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUNROOF......96
DRAIN TUBE
REMOVAL............................100
INSTALLATION........................100
CONTROL MODULE
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................101
DRIVE MOTOR
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................101
WIND DEFLECTOR
REMOVAL............................102INSTALLATION........................102
GLASS PANEL
REMOVAL............................102
INSTALLATION........................103
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENTS - FIT.................103
ADJUSTMENT - TIMING...............103
SUNSHADE
REMOVAL............................103
INSTALLATION........................103
HOUSING ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL............................104
INSTALLATION........................104
SUNROOF
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Keep fingers and other body parts out
of sunroof opening at all times.
The sunroof features a power sliding glass panel
and a sunshade which can be manually positioned
anywhere along its travel, rearward of glass panel
front edge.
The sunroof is electrically operated from a switch
located on the mini overhead console. To operate the
sunroof the ignition switch must be in the On/Run
position. The sunroof has both manual and Express
Open modes of operation when opening. To open the
sunroof in the Express Open mode, the switch is
pressed rearward for less than1 second.This causes
the sunroof glass to automatically retract and stop at
a position slightly forward of full open that reduces
low speed wind buffeting. The sunroof can also be
opened manually by pressing and holding the switch
rearward. Once the switch is held reward for more
than1 second,the glass will retract in the manual
mode. Releasing the switch at any time during travel
will cause the sunroof to stop at the current position.
To close the sunroof from an open position, the
switch must be pushed forward and held until the
sunroof glass comes to a complete stop. Releasing the
switch at any time in this mode will cause the sun-
roof to stop at the current position.
To vent the sunroof from the closed position, the
switch is pushed forward and held. Releasing theswitch at any time during travel will cause the sun-
roof to stop at the current vent position. To reach the
fully vented position, continue to hold the switch for-
ward until vent motion stops. To close the sunroof
from the vent position, push and hold the switch
rearward until the glass comes to a complete stop.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUNROOF
CAUTION: The sunroof motor is only to be powered
through the vehicle battery and vehicle wire har-
ness. Applying power to the sunroof motor leads
will cause failure of the sunroof control unit.
Before beginning sunroof diagnostics verify that all
other power accessories are in proper operating con-
dition. Refer to Sunroof Diagnostic Chart for possible
causes. If not, a common electrical problem may
exist. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams, of this
publication for circuit, splice and component descrip-
tions. Check the condition of the circuit protection
(20 amp high current fuse (battery feed) located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Check the
cover of the PDC for location of the fuse. Check for
correct operation of the sunroof delay relay. Inspect
all wiring connector pins for proper engagement and
continuity. Check for battery voltage at battery and
ignition pins of the power sunroof express module
wiring connector. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams, for circuit information. The controller will not
operate at less than 10 volts. Check the ground at
the sunroof express module.
Before beginning diagnosis for wind noise or water
leaks, verify that the problem was not caused by
23 - 96 SUNROOFWJ
Page 2079 of 2199

OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
Outside fresh air enters the vehicle through the
cowl top opening at the base of the windshield, and
passes through a plenum chamber to the HVAC sys-
tem blower housing. Air flow velocity can then be
adjusted with the blower motor speed selector switch
on the a/c heater control panel. The air intake open-
ings must be kept free of snow, ice, leaves, and other
obstructions for the HVAC system to receive a suffi-
cient volume of outside air.
It is also important to keep the air intake openings
clear of debris because leaf particles and other debris
that is small enough to pass through the cowl ple-
num screen can accumulate within the HVAC hous-
ing. The closed, warm, damp and dark environment
created within the HVAC housing is ideal for the
growth of certain molds, mildews and other fungi.
Any accumulation of decaying plant matter provides
an additional food source for fungal spores, which
enter the housing with the fresh air. Excess debris,
as well as objectionable odors created by decaying
plant matter and growing fungi can be discharged
into the passenger compartment during HVAC sys-
tem operation.
Both the manual and AZC heater and air condi-
tioner are blend-air type systems. In a blend-air sys-
tem, a blend door controls the amount of
unconditioned air (or cooled air from the evaporator)
that is allowed to flow through, or around, the heater
core. A temperature control knob on the a/c heater
control panel determines the discharge air tempera-
ture by energizing the blend door actuator, which
operates the blend door. This allows an almost imme-
diate control of the output air temperature of the sys-
tem. The AZC system will have separate blend doors
and temperature controls for each front seat occu-
pant.
The mode control knob on the a/c heater control
panel is used to direct the conditioned air to the
selected system outlets. On manual temperature con-
trol systems, the mode control knob switches engine
vacuum to control the mode doors, which are oper-
ated by vacuum actuators. On AZC systems, the
mode control knob switches electrical current to con-
trol the mode doors, which are operated by electronic
actuators.
The outside air intake can be shut off on manual
temperature control systems by selecting the Recircu-
lation Mode with the mode control knob. The outside
air intake can be shut off on Automatic Zone Control
(AZC) type system by pushing the Recirculation
Mode button. This will operate the recirculation door
that closes off the outside fresh air intake and recir-
culates the air that is already inside the vehicle.The air conditioner for all models is designed for
the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant. The air con-
ditioning system has an evaporator to cool and dehu-
midify the incoming air prior to blending it with the
heated air. This air conditioning system uses a ther-
mal expansion valve to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
system utilizes an evaporator thermister probe with
the appropriate operating logic located in the body
control module (BCM).
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the liq-
uid line near the receiver/drier. The low pressure ser-
vice port is located on the suction line near the
evaporator at the rear of the engine compartment.
Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low specific humidity air. The evaporator, located
in the HVAC housing on the dash panel below the
instrument panel, is cooled to temperatures near the
freezing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the tempera-
ture of the air delivered to the interior of the vehicle. It
is important to understand the effect that humidity has
on the performance of the air conditioning system.
When humidity is high, the evaporator has to perform a
double duty. It must lower the air temperature, and it
must lower the temperature of the moisture in the air
that condenses on the evaporator fins. Condensing the
moisture in the air transfers heat energy into the evap-
orator fins and tubing. This reduces the amount of heat
the evaporator can absorb from the air. High humidity
greatly reduces the ability of the evaporator to lower
the temperature of the air.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGWJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2080 of 2199
However, evaporator capacity used to reduce the
amount of moisture in the air is not wasted. Wring-
ing some of the moisture out of the air entering the
vehicle adds to the comfort of the passengers.
Although, an owner may expect too much from their
air conditioning system on humid days. A perfor-
mance test is the best way to determine whether the
system is performing up to standard. This test also
provides valuable clues as to the possible cause of
trouble with the air conditioning system.
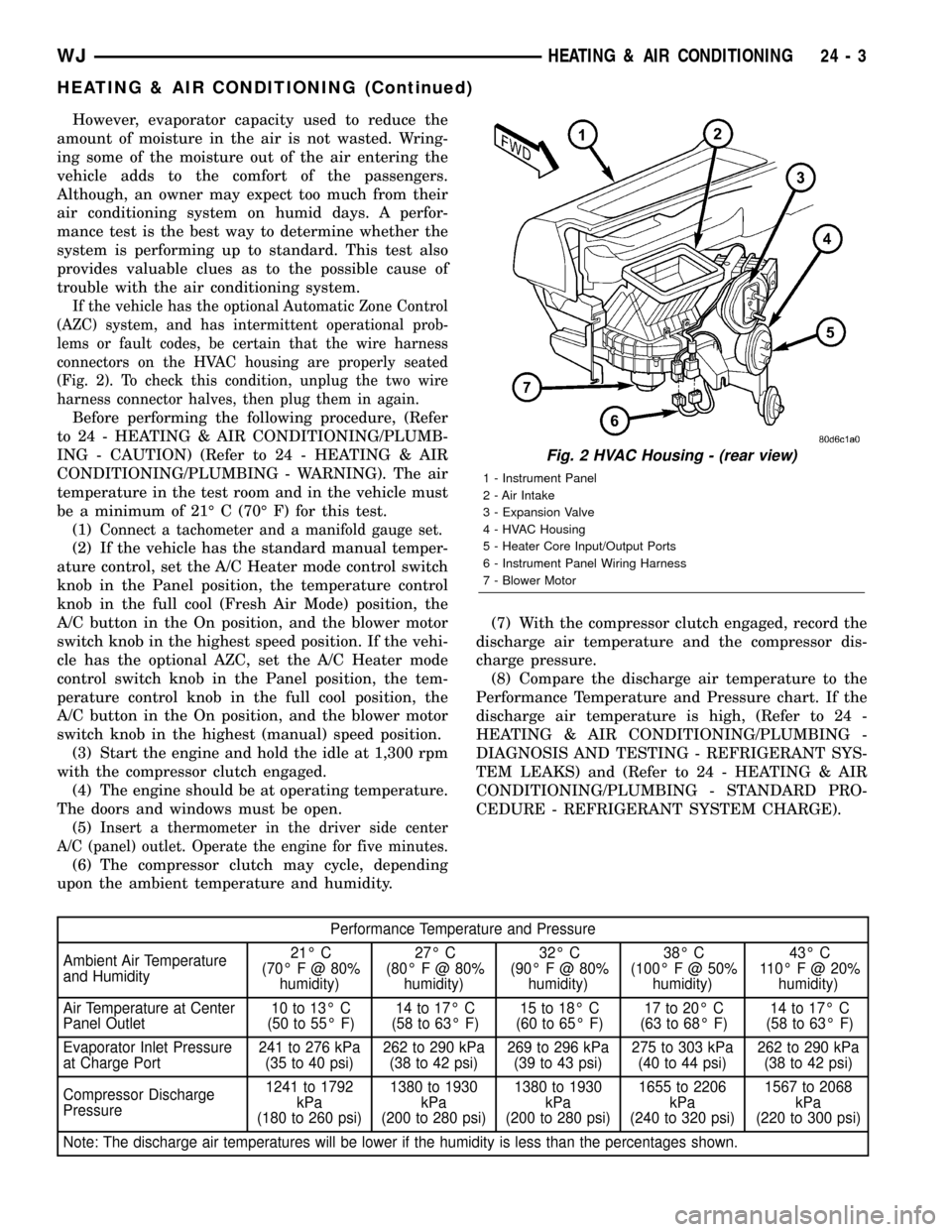
If the vehicle has the optional Automatic Zone Control
(AZC) system, and has intermittent operational prob-
lems or fault codes, be certain that the wire harness
connectors on the HVAC housing are properly seated
(Fig. 2). To check this condition, unplug the two wire
harness connector halves, then plug them in again.
Before performing the following procedure, (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - CAUTION) (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING). The air
temperature in the test room and in the vehicle must
be a minimum of 21É C (70É F) for this test.
(1)
Connect a tachometer and a manifold gauge set.
(2) If the vehicle has the standard manual temper-
ature control, set the A/C Heater mode control switch
knob in the Panel position, the temperature control
knob in the full cool (Fresh Air Mode) position, the
A/C button in the On position, and the blower motor
switch knob in the highest speed position. If the vehi-
cle has the optional AZC, set the A/C Heater mode
control switch knob in the Panel position, the tem-
perature control knob in the full cool position, the
A/C button in the On position, and the blower motor
switch knob in the highest (manual) speed position.
(3) Start the engine and hold the idle at 1,300 rpm
with the compressor clutch engaged.
(4) The engine should be at operating temperature.
The doors and windows must be open.
(5)
Insert a thermometer in the driver side center
A/C (panel) outlet. Operate the engine for five minutes.
(6) The compressor clutch may cycle, depending
upon the ambient temperature and humidity.(7) With the compressor clutch engaged, record the
discharge air temperature and the compressor dis-
charge pressure.
(8) Compare the discharge air temperature to the
Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. If the
discharge air temperature is high, (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM LEAKS) and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE).
Performance Temperature and Pressure
Ambient Air Temperature
and Humidity21É C
(70É F @ 80%
humidity)27É C
(80É F @ 80%
humidity)32É C
(90É F @ 80%
humidity)38É C
(100ÉF@50%
humidity)43É C
110É F @ 20%
humidity)
Air Temperature at Center
Panel Outlet10 to 13É C
(50 to 55É F)14 to 17É C
(58 to 63É F)15 to 18É C
(60 to 65É F)17 to 20É C
(63 to 68É F)14 to 17É C
(58 to 63É F)
Evaporator Inlet Pressure
at Charge Port241 to 276 kPa
(35 to 40 psi)262 to 290 kPa
(38 to 42 psi)269 to 296 kPa
(39 to 43 psi)275 to 303 kPa
(40 to 44 psi)262 to 290 kPa
(38 to 42 psi)
Compressor Discharge
Pressure1241 to 1792
kPa
(180 to 260 psi)1380 to 1930
kPa
(200 to 280 psi)1380 to 1930
kPa
(200 to 280 psi)1655 to 2206
kPa
(240 to 320 psi)1567 to 2068
kPa
(220 to 300 psi)
Note: The discharge air temperatures will be lower if the humidity is less than the percentages shown.
Fig. 2 HVAC Housing - (rear view)
1 - Instrument Panel
2 - Air Intake
3 - Expansion Valve
4 - HVAC Housing
5 - Heater Core Input/Output Ports
6 - Instrument Panel Wiring Harness
7 - Blower Motor
WJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2083 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the radiator coolant
level, serpentine drive belt tension, radiator air flow
and the radiator fan operation. Also be certain that
the accessory vacuum supply line is connected at the
engine intake manifold for the manual temperature
control system.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling at
normal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor heat position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62.2É C
(144É F)63.8É C
(147É F)65.5É C
(150É F)67.2É C
(153É F)
If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW
Possible locations or causes of obstructed coolant
flow:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS
Possible locations or causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A blend door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob(s) on the
A/C Heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²The A/C heater control.
²The blend door actuator(s).
²The wire harness circuits for the A/C heater con-
trol or the blend door actuator(s).²The blend door(s).
²Improper engine coolant temperature.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Locate the diode in the harness, and remove
the protective covering.
(3) Remove the diode from the harness, pay atten-
tion to the current flow direction (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove the insulation from the wires in the
harness. Only remove enough insulation to solder in
the new diode.
Fig. 3 DIODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - CURRENT FLOW
2 - BAND AROUND DIODE INDICATES CURRENT FLOW
3 - DIODE AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAMS
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGWJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2087 of 2199

VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
CONTROLS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SYSTEM
Vacuum control is used to operate the mode doors
in the standard equipment manual temperature con-
trol system HVAC housing. Testing of the A/C Heater
mode control switch operation will determine if the
vacuum and electrical controls are functioning. How-
ever, it is possible that a vacuum control system that
operates perfectly at engine idle (high engine vac-
uum) may not function properly at high engine
speeds or loads (low engine vacuum). This can be
caused by leaks in the vacuum system, or a faulty
vacuum check valve.
A vacuum system test will help to identify the
source of poor vacuum system performance or vac-
uum system leaks. Before starting this test, stop the
engine and make certain that the problem isn't a dis-
connected vacuum supply tube at the engine intake
manifold vacuum tap or the vacuum reservoir.
Use an adjustable vacuum test set (Special Tool
C-3707-B) and a suitable vacuum pump to test the
HVAC vacuum control system. With a finger placed
over the end of the vacuum test hose probe (Fig. 1),
adjust the bleed valve on the test set gauge to obtain
a vacuum of exactly 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.). Release and
block the end of the probe several times to verify that
the vacuum reading returns to the exact 27 kPa (8
in. Hg.) setting. Otherwise, a false reading will be
obtained during testing.
VACUUM CHECK VALVES
(1) Remove the vacuum check valve to be tested.
The valves are located in the (black) vacuum supply
tubes at either the engine intake manifold vacuum
tap, or on the bottom of the HVAC unit behind the
passenger front floor duct.
(2) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
A/C Heater control side of the valve. When connected
to this side of the check valve, no vacuum should
pass and the test set gauge should return to the 27
kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
(3) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
engine vacuum side of the valve. When connected to
this side of the check valve, vacuum should flow
through the valve without restriction. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
(1) Connect the test set vacuum probe to the
HVAC vacuum supply (black) tube in the engine com-
partment. Position the test set gauge so that it can
be viewed from the passenger compartment.
(2) Place the A/C Heater mode control switch knob
in each mode position, one position at a time, and
pause after each selection. The test set gauge should
return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after
each selection is made. If not OK, a component or
vacuum line in the vacuum circuit of the selected
mode has a leak. See the procedure in Locating Vac-
uum Leaks.
CAUTION: Do not use lubricant on the switch ports
or in the holes in the plug, as lubricant will ruin the
vacuum valve in the switch. A drop of clean water
in the connector plug holes will help the connector
slide onto the switch ports.
Fig. 1 ADJUST VACUUM TEST BLEED VALVE -
TYPICAL
1 - VACUUM PUMP TOOL C-4289
2 - VACUUM TEST SET C-3707
3 - BLEED VALVE
4 - PROBE
24 - 10 CONTROLSWJ
Page 2090 of 2199

A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch assembly consists of a sta-
tionary electromagnetic coil, a hub bearing and pul-
ley assembly, and a clutch plate (Fig. 4). The
electromagnetic coil unit and the hub bearing and
pulley assembly are each retained on the nose of the
compressor front housing with snap rings. The clutch
plate is keyed to the compressor shaft and secured
with a bolt.
OPERATION
The compressor clutch components provide the
means to engage and disengage the compressor from
the engine serpentine accessory drive belt. When the
clutch coil is energized, it magnetically draws the
clutch into contact with the pulley and drives the
compressor shaft. When the coil is not energized, the
pulley freewheels on the clutch hub bearing, which is
part of the pulley. The compressor clutch and coil are
the only serviced parts on the compressor.
The compressor clutch engagement is controlled by
several components: the a/c switch on the a/c heater
control panel, the Automatic Zone Control (AZC) con-
trol module (if the vehicle is so equipped), the evap-
orator probe, the a/c high pressure transducer, the
a/c compressor clutch relay, the body control module
(BCM) and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The PCM may delay compressor clutch engagement
for up to thirty seconds. Refer to Electronic Control
Modules for more information on the PCM controls.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring diagrams. The battery must be
fully-charged before performing the following tests.
Refer to Battery for more information.
(1) Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0 to 20 volt scale) with clip-type leads for measuring
the voltage across the battery and the compressor
clutch coil.
(2) With the a/c heater mode control switch in any
a/c mode, the a/c heater control a/c switch in the ON
position, and the blower motor switch in the lowest
speed position, start the engine and run it at normal
idle.
(3) The compressor clutch coil voltage should read
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage. If there is
voltage at the clutch coil, but the reading is not
within 0.2 volts of the battery voltage, test the clutch
coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair
as required. If there is no voltage reading at the
clutch coil, use a DRBIIItscan tool and the appro-
priate diagnostic information for testing of the com-
pressor clutch circuit. The following components
must be checked and repaired as required before you
can complete testing of the clutch coil:
²Fuses in the junction block and the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC)
²A/C heater mode control switch
²A/C compressor clutch relay
²A/C high pressure transducer
²A/C evaporator probe
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Body Control Module (BCM)
(4) The compressor clutch coil is acceptable if the
current draw measured at the clutch coil is 2.0 to 3.9
amperes with the electrical system voltage at 11.5 to
12.5 volts. This should only be checked with the work
area temperature at 21É C (70É F). If system voltage
is more than 12.5 volts, add electrical loads by turn-
ing on electrical accessories until the system voltage
drops below 12.5 volts.
(a) If the clutch coil current reading is four
amperes or more, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced.
(b) If the clutch coil current reading is zero, the
coil is open and should be replaced.
Fig. 4 COMPRESSOR CLUTCH - TYPICAL
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SHAFT KEY
3 - PULLEY
4 - COIL
5 - CLUTCH SHIMS
6 - SNAP RING
7 - SNAP RING
WJCONTROLS 24 - 13
Page 2091 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new compressor clutch has been installed,
cycle the compressor clutch approximately twenty
times (five seconds on, then five seconds off). During
this procedure, set the A/C Heater control in the
Recirculation Mode, the A/C button in the on posi-
tion, the blower motor switch in the highest speed
position, and the engine speed at 1500 to 2000 rpm.
This procedure (burnishing) will seat the opposing
friction surfaces and provide a higher compressor
clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, pulley, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(3) Remove the bolt that secures the compressor
clutch to the compressor shaft (Fig. 5). A band-type
oil filter wrench may be used to secure the clutch
during bolt removal.
(4) Tap the clutch plate with a plastic mallet to
release it from the splines on the compressor shaft.
Remove the clutch plate and shim(s) from the com-
pressor shaft (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Do not pry between the clutch plate
assembly and the pulley to remove it from the com-
pressor shaft. Prying may damage the clutch plate
assembly.(5) Remove the external snap ring that secures the
compressor clutch pulley to the nose of the compres-
sor front housing with snap ring pliers (Special Tool
C-4574) and slide the pulley assembly off of the com-
pressor (Fig. 7).
(6) Remove the screw and retainer from the clutch
coil lead wire harness on the compressor front hous-
ing.
Fig. 5 COMPRESSOR SHAFT BOLT
1 - COMPRESSOR CLUTCH PLATE
2 - COMPRESSOR SHAFT BOLT
Fig. 6 CLUTCH PLATE AND SHIM(S)
1 - COMPRESSOR SHAFT
2 - CLUTCH PLATE
3 - CLUTCH PLATE SHIM
Fig. 7 PULLEY SNAP RING
1 - SNAP RING
24 - 14 CONTROLSWJ
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)