2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Brake components
[x] Cancel search: Brake componentsPage 180 of 2199

NOTE: The front outer brake shoes are equipped
with a wear indicator. The indicator will produce an
audible noise when it contacts the rotor surface.
BRAKE CHATTER
Brake chatter is usually caused by loose or worn
components, or glazed/burnt lining. Rotors with hard
spots can also contribute to chatter. Additional causes
of chatter are out-of-tolerance rotors, brake lining not
securely attached to the shoes, loose wheel bearings
and contaminated brake lining.
THUMP/CLUNK NOISE
Thumping or clunk noises during braking are fre-
quentlynotcaused by brake components. In many
cases, such noises are caused by loose or damaged
steering, suspension, or engine components.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANUAL BLEEDING
Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent quality
fluid meeting SAE J1703-F and DOT 3 standards
only. Use fresh, clean fluid from a sealed container at
all times.
Do not pump the brake pedal at any time while
bleeding. Air in the system will be compressed into
small bubbles that are distributed throughout the
hydraulic system. This will make additional bleeding
operations necessary.
Do not allow the master cylinder to run out of fluid
during bleed operations. An empty cylinder will allow
additional air to be drawn into the system. Check the
cylinder fluid level frequently and add fluid as
needed.
Bleed only one brake component at a time in the
following sequence:
(1) Fill the master cylinder reservoir with brake
fluid.
(2) If calipers are overhauled, open all caliper
bleed screws. Then close each bleed screw as fluid
starts to drip from it. Top off master cylinder reser-
voir once more before proceeding.
(3) Attach one end of bleed hose to bleed screw
and insert opposite end in glass container partially
filled with brake fluid (Fig. 1). Be sure end of bleed
hose is immersed in fluid.
(4) Open up bleeder, then have a helper press
down the brake pedal. Once the pedal is down close
the bleeder. Repeat bleeding until fluid stream is
clear and free of bubbles. Then move to the next
wheel.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PRESSURE
BLEEDING
Use Mopar brake fluid, or an equivalent quality
fluid meeting SAE J1703-F and DOT 3 standards
only. Use fresh, clean fluid from a sealed container at
all times.
Do not pump the brake pedal at any time while
bleeding. Air in the system will be compressed into
small bubbles that are distributed throughout the
hydraulic system. This will make additional bleeding
operations necessary.
Do not allow the master cylinder to run out of fluid
during bleed operations. An empty cylinder will allow
additional air to be drawn into the system. Check the
cylinder fluid level frequently and add fluid as
needed.
Bleed only one brake component at a time in the
following sequence:
Follow the manufacturers instructions carefully
when using pressure equipment. Do not exceed the
tank manufacturers pressure recommendations. Gen-
erally, a tank pressure of 51-67 kPa (15-20 psi) is suf-
ficient for bleeding.
Fill the bleeder tank with recommended fluid and
purge air from the tank lines before bleeding.
Do not pressure bleed without a proper master cyl-
inder adapter. The wrong adapter can lead to leak-
age, or drawing air back into the system. Use
adapter provided with the equipment or Adapter
6921.
Fig. 1 Bleed Hose Setup
1 - BLEED HOSE
2 - FLUID CONTAINER PARTIALLY FILLED WITH FLUID
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 5
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 181 of 2199
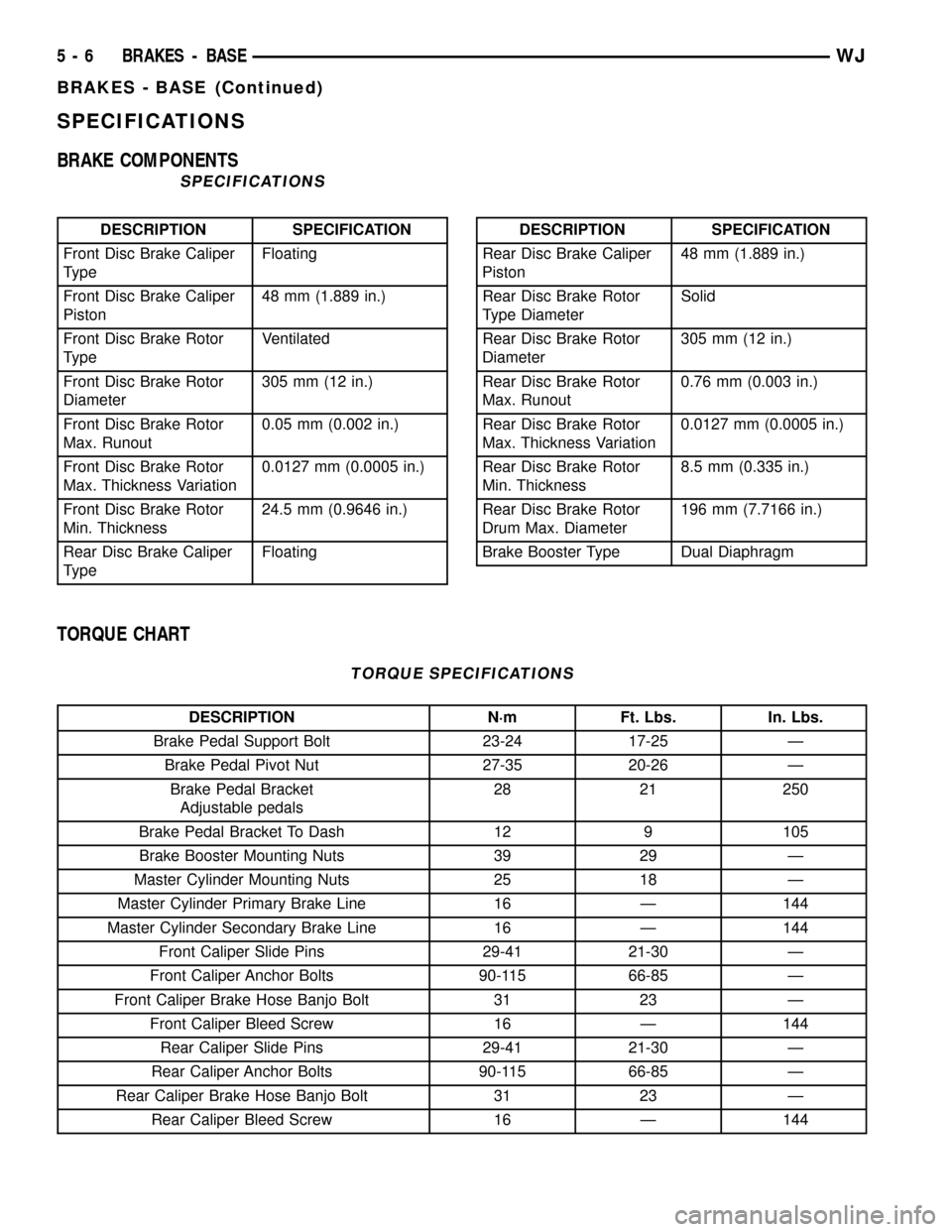
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE COMPONENTS
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Front Disc Brake Caliper
TypeFloating
Front Disc Brake Caliper
Piston48 mm (1.889 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
TypeVentilated
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Diameter305 mm (12 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Runout0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Thickness Variation0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Min. Thickness24.5 mm (0.9646 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
TypeFloatingDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
Piston48 mm (1.889 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Type DiameterSolid
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Diameter305 mm (12 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Runout0.76 mm (0.003 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Thickness Variation0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Min. Thickness8.5 mm (0.335 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Drum Max. Diameter196 mm (7.7166 in.)
Brake Booster Type Dual Diaphragm
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Brake Pedal Support Bolt 23-24 17-25 Ð
Brake Pedal Pivot Nut 27-35 20-26 Ð
Brake Pedal Bracket
Adjustable pedals28 21 250
Brake Pedal Bracket To Dash 12 9 105
Brake Booster Mounting Nuts 39 29 Ð
Master Cylinder Mounting Nuts 25 18 Ð
Master Cylinder Primary Brake Line 16 Ð 144
Master Cylinder Secondary Brake Line 16 Ð 144
Front Caliper Slide Pins 29-41 21-30 Ð
Front Caliper Anchor Bolts 90-115 66-85 Ð
Front Caliper Brake Hose Banjo Bolt 31 23 Ð
Front Caliper Bleed Screw 16 Ð 144
Rear Caliper Slide Pins 29-41 21-30 Ð
Rear Caliper Anchor Bolts 90-115 66-85 Ð
Rear Caliper Brake Hose Banjo Bolt 31 23 Ð
Rear Caliper Bleed Screw 16 Ð 144
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASEWJ
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 194 of 2199

(4) Remove caliper piston dust boot with a suitable
pry tool (Fig. 34) and discard.
(5) Remove piston seal from the caliper (Fig.
35)and discard.
CAUTION: Do not scratch the piston bore while
removing the seal.
(6) Remove caliper slide pin bushings (Fig. 36).
(7) Remove caliper bleed screw.
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
Clean the caliper components with clean brake
fluid or brake clean only. Wipe the caliper and piston
dry with lint free towels or use low pressure com-
pressed air.
CAUTION: Do not use gasoline, kerosene, paint
thinner, or similar solvents. These products may
leave a residue that could damage the piston and
seal.
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
The piston is made from a phenolic resin (plastic
material) and should be smooth and clean.
The piston must be replaced if cracked or scored.
Do not attempt to restore a scored piston surface by
sanding or polishing.
CAUTION: If the caliper piston is replaced, install
the same type of piston in the caliper. Never inter-
change phenolic resin and steel caliper pistons.
The pistons, seals, seal grooves, caliper bore and
piston tolerances are different.
The bore can belightlypolished with a brake
hone to remove very minor surface imperfections
(Fig. 37). The caliper should be replaced if the bore is
severely corroded, rusted, scored, or if polishing
would increase bore diameter more than 0.025 mm
(0.001 inch).
Fig. 34 Caliper Piston Dust
1 - PISTON DUST BOOT
2 - CALIPER
Fig. 35 Piston Seal Removal
1 - CALIPER
2 - PISTON BORE
3 - PISTON SEAL
Fig. 36 Slide Pin And Bushing
1 - BUSHING
2 - CALIPER SLIDE PIN
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 19
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS (Continued)
Page 201 of 2199

tions also allows the driver to set steering wheel tilt
and seat position to the most comfortable position.
The position of the brake and accelerator pedals can
be adjusted without compromising safety or comfort
in actuating the pedals. Repositioning the pedals
does not change the effort required for actuation.
Change of pedal position is accomplished by means
of a motor driven screw. Operating the adjustable
pedal switch activates the pedal drive motor. The
pedal drive motor turns a screw that changes the
position of the brake and accelerator pedals. The
pedal can be moved rearward (closer to the driver) or
forward (away from driver). The brake pedal is
moved on its drive screw to a position where the
driver feels most comfortable (Fig. 52).
The accelerator pedal is moved at the same time
and the same distance as the brake pedal. The accel-
erator pedal adjustment screw is turned by a flexible
shaft slaved off the brake adjustment screw.
Neither the pedal drive motor nor drive mecha-
nism are subject to the mechanical stress of brake or
accelerator application.
²SYSTEM FEATURES:
²Range of Adjustment: The pedals may be
adjusted up to 3 in. (75 mm)
²Pedal Adjustment Speed: 0.5 in./sec (12.5
mm/sec)
²Pedal Adjustment Inhibitors: Pedal adjust-
ment is inhibited when the vehicle is in reverse or
when cruise control is activated.
²Memory: An optional memory feature is avail-
able. This allows storing of one or two preferred
pedal positions in the Adjustable Pedal Module
(APM). A preferred position can be stored and
recalled using the door-mounted switches. A stored
pedal position can be recalled (but not stored)
using the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE).
²
Adjustable Pedal Feedback Message: The Elec-
tronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) will display
a message when the APS is disabled. ie:9Adjustable
Pedal Disabled - Cruise Control Engaged9or9Adjust-
able Pedal Disabled - Vehicle in Reverse9.
²Damage Prevention: Foot pressure or debris
can stall pedal adjustment. In order to avoid dam-
age to system components during pedal adjust-
ment, the APM will monitor pedal position sensor
voltage. If the APM does not detect expected volt-
age change within 1.5 seconds, it will cut power to
the adjustable pedal motor.
OPERATION
The brake pedal is attached to the booster push
rod. When the pedal is depressed, the primary
booster push rod is depressed which moves the
booster secondary rod. The booster secondary rod
depresses the master cylinder piston.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - NON-ADJUSTABLE PEDAL
(1) Remove retainer clip that holds booster to
pedal pin (Fig. 53).
Fig. 52 ADJUSTABLE PEDALS ASSEMBLY
1 - HARNESS
2 - ADJUSTABLE PEDAL BRACKET
3 - CABLE
4 - ACCELERATOR PEDAL
5 - BRAKE PEDAL
6 - ADJUSTABLE PEDAL MOTOR
7 - BRAKE LIGHT SWITCH
8 - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS MODULE
Fig. 53 Push Rod Retainer Clip
1 - RETAINER CLIP
2 - PUSH ROD
3 - PEDAL PIN
5 - 26 BRAKES - BASEWJ
PEDAL (Continued)
Page 216 of 2199

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................41
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTILOCK
BRAKES............................42
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BLEEDING ABS
BRAKE SYSTEM......................42
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................42
ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
REMOVAL.............................43INSTALLATION.........................43
G-SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................45
OPERATION...........................45
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................47
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The hydraulic system is a three channel design.
The front brakes are controlled individually and the
rear brakes in tandem.
The ABS electrical system is separate from other
vehicle electrical circuits. A separate controller oper-
ates the system.
OPERATION
The antilock CAB activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching 20 to 30 percent of
actual vehicle speed during braking. Periods of high
wheel slip occur when brake stops involve high pedal
pressure and rate of vehicle deceleration.
Battery voltage is supplied to the CAB ignition ter-
minal when the ignition switch is turned to Run posi-
tion. The CAB performs a system initialization
procedure at this point. Initialization consists of a
static and dynamic self check of system electrical
components.
The static check occurs after the ignition switch is
turned to Run position. The dynamic check occurs
when vehicle road speed reaches approximately 30kph (18 mph). During the dynamic check, the CAB
briefly cycles the pump and solenoids to verify oper-
ation.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the CAB illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ANTILOCK BRAKING
The antilock system prevents lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the CAB for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The ABS system has three fluid pressure control
channels. The front brakes are controlled separately
and the rear brakes in tandem. A speed sensor input
signal indicating a high slip condition activates the
CAB antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel. The valves are all located within the
HCU valve body and work in pairs to either increase,
hold, or decrease apply pressure as needed in the
individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 41
Page 218 of 2199

ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
The electronic brake distribution (EBD) functions
like a rear proportioning valve. The EBD system uses
the ABS system to control the slip of the rear wheels
in partial braking range. The braking force of the
rear wheels is controlled electronically by using the
inlet and outlet valves located in the HCU.
OPERATION
Upon entry into EBD the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure the outlet valve for
the rear brake circuit is pulsed. This allows fluid to
enter the low pressure accumulator (LPA) in the
HCU resulting in a drop in fluid pressure to the rear
brakes. In order to increase the rear brake pressure
the outlet valve is switched off and the inlet valve is
pulsed. This increases the pressure to the rear
brakes. This will continue until the required slip dif-
ference is obtained. At the end of EBD braking (no
brake application) the fluid in the LPA drains back to
the master cylinder by switching on the outlet valve
and draining through the inlet valve check valve. At
the same time the inlet valve is switched on to pre-
vent a hydraulic short circiut in case of another
brake application.
The EBD will remain functional during many ABS
fault modes. If the red and amber warning lamps are
illuminated the EBD may have a fault.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
A wheel speed sensor is used at each wheel. The
front sensors are mounted to the steering knuckles.
The rear sensors are mounted at the outboard end of
the axle. Tone wheels are mounted to the outboard
ends of the front and rear axle shafts. The gear type
tone wheel serves as the trigger mechanism for each
sensor.
OPERATION
The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digi-
tal signal. The CAB sends 12 volts to the sensors.
The sensor has an internal magneto resistance
bridge that alters the voltage and amperage of the
signal circuit. This voltage and amperage is changed
by magnetic induction when the toothed tone wheel
passes the wheel speed sensor. This digital signal issent to the CAB. The CAB measures the voltage and
amperage of the digital signal for each wheel.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel sensor mounting bolt
(Fig. 1).
(3) Remove the sensor from the steering knuckle.
(4) Disengage the sensor wire from the brackets
(Fig. 1)on the steering knuckle.
(5) Disconnect the sensor from the sensor harness
(Fig. 2)and (Fig. 3).
(6) Remove the sensor and wire.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the sensor on the steering knuckle.
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctitet242 to
the sensor mounting bolt. Use new sensor bolt if orig-
inal bolt is worn or damaged.
(3) Install the sensor mounting bolt and tighten
bolt to 12-14 N´m (106-124 in. lbs.).
(4) Engage the grommets on the sensor wire to the
steering knuckle brackets.
(5) Connect the sensor wire to the harness connec-
tor.
(6) Check the sensor wire routing. Be sure the
wire is clear of all chassis components and is not
twisted or kinked at any spot.
(7) Remove the support and lower vehicle.
Fig. 1 Sensor Location
1 - BRACKET
2 - BRACKET
3 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
4 - MOUNTING BOLT
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 43
Page 324 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - POWER GROUNDS
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has 2 main
grounds. Both of these grounds are referred to as
power grounds. All of the high-current, noisy, electri-
cal devices are connected to these grounds as well as
all of the sensor returns. The sensor return comes
into the sensor return circuit, passes through noise
suppression, and is then connected to the power
ground.
The power ground is used to control ground cir-
cuits for the following PCM loads:
²Generator field winding
²Fuel injectors
²Ignition coil(s)
²Certain relays/solenoids
²Certain sensors
DESCRIPTION - SENSOR RETURN
The Sensor Return circuits are internal to the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM).
Sensor Return provides a low±noise ground refer-
ence for all engine control system sensors. Refer to
Power Grounds for more information.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PCM
(1) Also refer to Modes of Operation.
The PCM operates the fuel system. The PCM is a
pre-programmed, triple microprocessor digital com-
puter. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain
transmission features, speed control, air conditioning
compressor clutch engagement and idle speed. The
PCM can adapt its programming to meet changing
operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operations
through different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to as Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Outputs. The sensors and switches that pro-
vide inputs to the PCM are considered Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) Inputs.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based upon
inputs it receives from sensors that react to: engine
rpm, manifold absolute pressure, engine coolant tem-
perature, throttle position, transmission gear selec-
tion (automatic transmission), vehicle speed and the
brake switch.
The PCM adjusts idle speed based on inputs it
receives from sensors that react to: throttle position,
vehicle speed, transmission gear selection, engine
coolant temperature and from inputs it receives from
the air conditioning clutch switch and brake switch.Based on inputs that it receives, the PCM adjusts
ignition coil dwell. The PCM also adjusts the gener-
ator charge rate through control of the generator
field and provides speed control operation.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²A/C request
²Auto shutdown (ASD) sense
²Battery temperature
²Battery voltage
²Brake switch
²J1850 bus circuits
²Camshaft position sensor signal
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Data link connections for DRB scan tool
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Five volts (primary)
²Five volts (secondary)
²Fuel level
²Generator (battery voltage) output
²Ignition circuit sense (ignition switch in on/off/
crank/run position)
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Leak detection pump (switch) sense (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Oil pressure
²Overdrive/override switch
²Oxygen sensors
²Park/neutral switch (auto. trans. only)
²Power ground
²Sensor return
²Signal ground
²Speed control multiplexed single wire input
²Throttle position sensor
²Transmission governor pressure sensor
²Transmission temperature sensor
²Vehicle speed (from ABS module)
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²A/C clutch relay
²Auto shutdown (ASD) relay
²J1850 (+/-) circuits for: speedometer, voltmeter,
fuel gauge, oil pressure gauge/lamp, engine temp.
gauge and speed control warn. lamp
²Data link connection for DRBIIItscan tool
²EGR valve control solenoid (if equipped)
²EVAP canister purge solenoid
²Fuel injectors
²Fuel pump relay
²Generator field driver (-)
²Generator field driver (+)
²Generator lamp (if equipped)
²Idle air control (IAC) motor
²Ignition coil
²Leak detection pump
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 349 of 2199

The battery cables (Fig. 17) or (Fig. 18) are large
gauge, stranded copper wires sheathed within a
heavy plastic or synthetic rubber insulating jacket.
The wire used in the battery cables combines excel-
lent flexibility and reliability with high electrical cur-
rent carrying capacity. Refer toWiring Diagrams
for battery cable wire gauge information.
A clamping type female battery terminal made of
soft lead is die cast onto one end of the battery cable
wire. A square headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are
installed at the open end of the female battery termi-
nal clamp. Large eyelet type terminals are crimped
onto the opposite end of the battery cable wire and
then solder-dipped. The battery positive cable wires
have a red insulating jacket to provide visual identi-
fication and feature a larger female battery terminal
clamp to allow connection to the larger battery posi-
tive terminal post. The battery negative cable wires
have a black insulating jacket and a smaller female
battery terminal clamp.
The battery cables cannot be repaired and, if dam-
aged or faulty they must be replaced. Both the bat-
tery positive and negative cables are available for
service replacement only as a unit with the battery
wire harness, which may include portions of the wir-
ing circuits for the generator and other components
on some models. Refer toWiring Diagramsfor more
information on the various wiring circuits included in
the battery wire harness for the vehicle being ser-
viced.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a path back to the battery for electrical
current generated by the charging system for restor-
ing the voltage potential of the battery. The female
battery terminal clamps on the ends of the battery
cable wires provide a strong and reliable connection
of the battery cable to the battery terminal posts.
The terminal pinch bolts allow the female terminal
clamps to be tightened around the male terminal
posts on the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals
secured to the opposite ends of the battery cable
wires from the female battery terminal clamps pro-
vide secure and reliable connection of the battery
cables to the vehicle electrical system.
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is die
cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distribution
Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eyelet ter-
minal that connects the battery positive cable to the
B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor sole-
noid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp is
also die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wirehas an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the right side of the engine cylinder block. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the right front fender inner shield,
near the battery.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cable. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached.EXAM-
PLE:When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive
terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet
terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud,
you are reading the combined voltage drop in the
battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal
post connection and the battery positive cable.
VOLTAGE DROP TEST
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:
²The battery is fully-charged and load tested.
Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
charging and load test procedures.
²Fully engage the parking brake.
²If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent the engine from starting, remove the
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC), in
the engine compartment. See the fuse and relay lay-
out label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover
for ASD relay identification and location.
8F - 18 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)