2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Rear light
[x] Cancel search: Rear lightPage 1580 of 2199

BANDS
DESCRIPTION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown, or ªfrontº, band (Fig. 67) holds the
common sun gear of the planetary gear sets. The
front (kickdown) band is made of steel, and faced on
its inner circumference with a friction-type lining.
One end of the band is anchored to the transmissioncase, and the other is acted on with a pushing force
by a servo piston. The front band is a single-wrap
design (the band does not completely encompass/
wrap the drum that it holds).
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) BAND
The low/reverse band, or ªrearº, band (Fig. 68) is
similar in appearance and operation to the front
band. The rear band is slightly different in that it
does not use a link bar, but is acted directly on by
the apply lever. This is referred to as a double-wrap
band design (the drum is completely encompassed/
wrapped by the band). The double-wrap band pro-
vides a greater holding power in comparison to the
single-wrap design.
OPERATION
KICKDOWN (FRONT) BAND
The kickdown band holds the common sun gear of
the planetary gear sets by applying and holding the
front clutch retainer, which is splined to the sun gear
driving shell, and in turn splined directly to the sun
gear. The application of the band by the servo is typ-
ically done by an apply lever and link bar.
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) BAND
The rear band holds the rear planet carrier sta-
tionary by being mounted around and applied to the
low/reverse drum.
Fig. 65 Accumulator in SECOND Gear Position
1 - BOTTOM OF BORE
2 - LINE PRESSURE
3 - SHUTTLE VALVE
Fig. 66 Accumulator Components
1 - INNER SPRING
2 - ACCUMULATOR PISTON
3 - OUTER SPRING
4 - SEAL RINGS
Fig. 67 Front Band
1 - FRONT BAND
2 - TRANSMISSION HOUSING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 61
BANDS (Continued)
Page 1605 of 2199
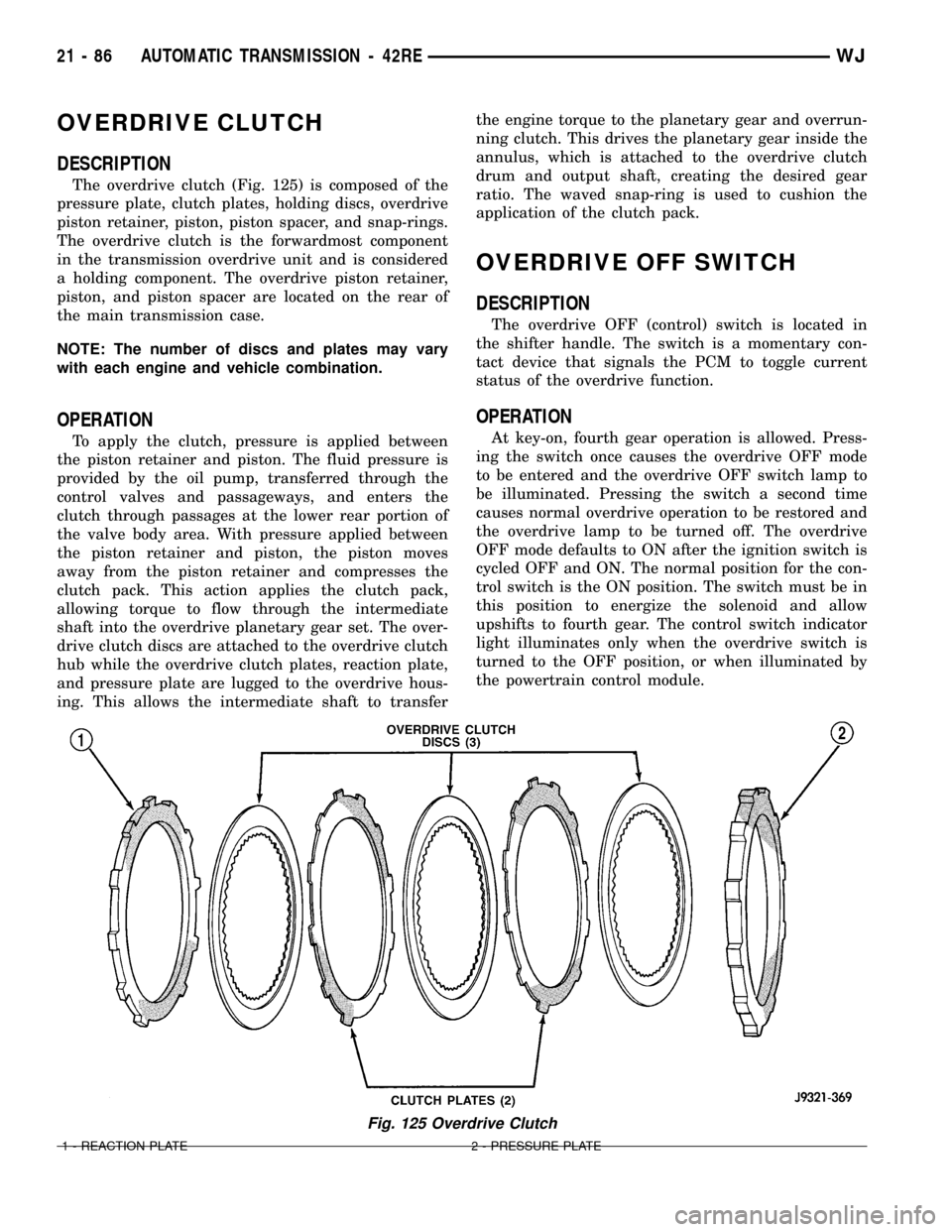
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive clutch (Fig. 125) is composed of the
pressure plate, clutch plates, holding discs, overdrive
piston retainer, piston, piston spacer, and snap-rings.
The overdrive clutch is the forwardmost component
in the transmission overdrive unit and is considered
a holding component. The overdrive piston retainer,
piston, and piston spacer are located on the rear of
the main transmission case.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the piston retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through passages at the lower rear portion of
the valve body area. With pressure applied between
the piston retainer and piston, the piston moves
away from the piston retainer and compresses the
clutch pack. This action applies the clutch pack,
allowing torque to flow through the intermediate
shaft into the overdrive planetary gear set. The over-
drive clutch discs are attached to the overdrive clutch
hub while the overdrive clutch plates, reaction plate,
and pressure plate are lugged to the overdrive hous-
ing. This allows the intermediate shaft to transferthe engine torque to the planetary gear and overrun-
ning clutch. This drives the planetary gear inside the
annulus, which is attached to the overdrive clutch
drum and output shaft, creating the desired gear
ratio. The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the
application of the clutch pack.
OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive OFF (control) switch is located in
the shifter handle. The switch is a momentary con-
tact device that signals the PCM to toggle current
status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, fourth gear operation is allowed. Press-
ing the switch once causes the overdrive OFF mode
to be entered and the overdrive OFF switch lamp to
be illuminated. Pressing the switch a second time
causes normal overdrive operation to be restored and
the overdrive lamp to be turned off. The overdrive
OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition switch is
cycled OFF and ON. The normal position for the con-
trol switch is the ON position. The switch must be in
this position to energize the solenoid and allow
upshifts to fourth gear. The control switch indicator
light illuminates only when the overdrive switch is
turned to the OFF position, or when illuminated by
the powertrain control module.
Fig. 125 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
21 - 86 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1617 of 2199

(15) Mount assembled output shaft, annulus gear,
and clutch drum in shop press. Direct clutch spring,
hub and clutch pack are easier to install with assem-
bly mounted in press.
(16) Align splines in hubs of planetary gear and
overrunning clutch with Alignment tool 6227-2 (Fig.
165). Insert tool through sun gear and into splines of
both hubs. Be sure alignment tool is fully seated
before proceeding.
(17) Install direct clutch spring (Fig. 166). Be sure
spring is properly seated on spring plate.
NOTE: The 42RE transmission has 6 direct clutch
discs and 5 clutch plates.
(18) Assemble and install direct clutch pack on
hub as follows:
(a) Assemble clutch pack components (Fig. 167).
(b) Install direct clutch reaction plate on clutch
hub first. Note that one side of reaction plate is
counterbored. Be sure this side faces rearward.
Splines at rear of hub are raised slightly. Counter-
bore in plate fits over raised splines. Plate should
be flush with this end of hub (Fig. 168).
(c) Install first clutch disc followed by a steel
plate until all discs and plates have been installed.
(d) Install pressure plate. This is last clutch
pack item to be installed. Be sure plate is installed
with shoulder side facing upward (Fig. 169).
(19) Install clutch hub and clutch pack on direct
clutch spring (Fig. 170). Be sure hub is started on
sun gear splines before proceeding.
Fig. 164 Sun Gear Installation
1 - SUN GEAR AND SPRING PLATE ASSEMBLY
Fig. 165 Alignment Tool Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6227-2
2 - PRESS PLATES
3 - ASSEMBLED DRUM AND ANNULUS GEAR
4 - SUN GEAR
Fig. 166 Direct Clutch Spring Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6227-2
2 - DIRECT CLUTCH SPRING
3 - CLUTCH HUB
4 - PRESS PLATES
21 - 98 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1625 of 2199

between the rollers and cam. This increased clear-
ance between the rollers and cam results in a free-
wheeling condition. When the inner race attempts to
rotate counterclockwise, the action causes the rollers
to roll in the same direction as the race, aided by the
pushing of the springs. As the rollers try to move in
the same direction as the inner race, they are
wedged between the inner and outer races due to the
design of the cam. In this condition, the clutch is
locked and acts as one unit.
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: To service the overrunning clutch cam and
the overdrive piston retainer, the transmission
geartrain and the overdrive unit must be removed
from the transmission.
(1) Remove the overdrive piston (Fig. 190).
(2) Remove the overdrive piston retainer bolts.
(3) Remove overdrive piston retainer.
(4) Remove case gasket.
(5) Mark the position of the overrunning clutch
cam in the case (Fig. 191).
(6) Remove the overrunning clutch cam bolts.
(7) Remove the overrunning clutch cam.
CLEANING
Clean the overrunning clutch assembly, clutch cam,
low-reverse drum, and overdrive piston retainer in
solvent. Dry them with compressed air after clean-
ing.
INSPECTION
Inspect condition of each clutch part after cleaning.
Replace the overrunning clutch roller and spring
assembly if any rollers or springs are worn or dam-
aged, or if the roller cage is distorted, or damaged.
Replace the cam if worn, cracked or damaged.
Replace the low-reverse drum if the clutch race,
roller surface or inside diameter is scored, worn or
damaged.Do not remove the clutch race from
the low-reverse drum under any circumstances.
Replace the drum and race as an assembly if
either component is damaged.
Examine the overdrive piston retainer carefully for
wear, cracks, scoring or other damage. Be sure the
retainer hub is a snug fit in the case and drum.
Replace the retainer if worn or damaged.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Examine bolt holes in overrunning clutch cam.
Note that one hole isnot threaded(Fig. 192). This
hole must align with blank area in clutch cam bolt
circle (Fig. 193). Mark hole location on clutch cam
and blank area in case with grease pencil, paint
stripe, or scribe mark for assembly reference.
(2) Mark location of non-threaded hole in clutch
cam and blank area in bolt circle with grease pencil.
(3) Align and install overrunning clutch and cam
in case (Fig. 194). Be sure cam is correctly installed.
Bolt holes in cam are slightly countersunk on one
side. Be sure this side of cam faces rearward (toward
piston retainer).
(4) Verify that non-threaded hole in clutch cam is
properly aligned. Check alignment by threading a
bolt into each bolt hole. Adjust clutch cam position if
necessary.
Fig. 190 Overdrive Piston Removal
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH PISTON
2 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
3 - SELECTIVE SPACER
4 - PISTON RETAINER
Fig. 191 Overrunning Clutch Cam Removal
1 - ALIGN MARKS IDENTIFYING NON-THREADED HOLE IN
CAM AND CASE
2 - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
21 - 106 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1638 of 2199
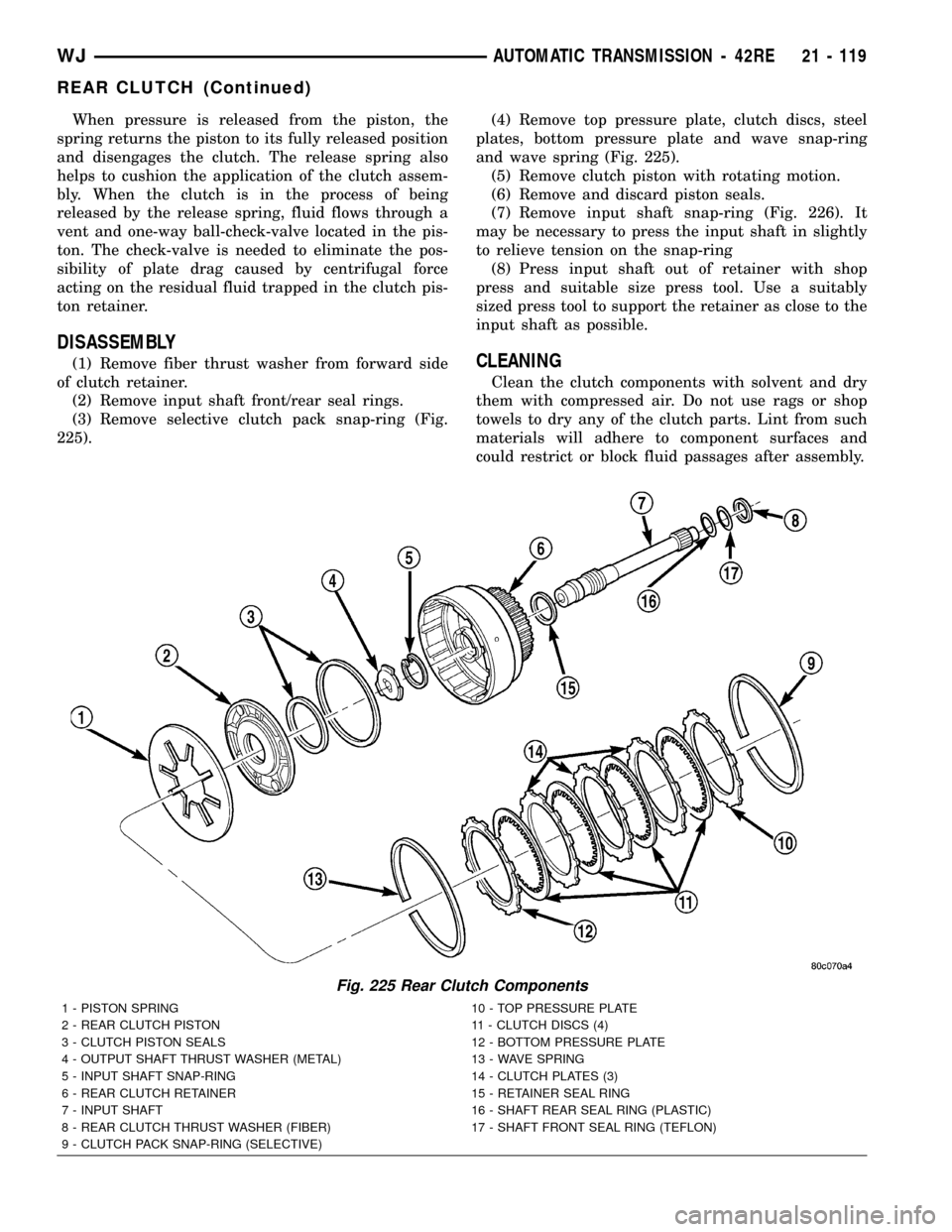
When pressure is released from the piston, the
spring returns the piston to its fully released position
and disengages the clutch. The release spring also
helps to cushion the application of the clutch assem-
bly. When the clutch is in the process of being
released by the release spring, fluid flows through a
vent and one-way ball-check-valve located in the pis-
ton. The check-valve is needed to eliminate the pos-
sibility of plate drag caused by centrifugal force
acting on the residual fluid trapped in the clutch pis-
ton retainer.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove fiber thrust washer from forward side
of clutch retainer.
(2) Remove input shaft front/rear seal rings.
(3) Remove selective clutch pack snap-ring (Fig.
225).(4) Remove top pressure plate, clutch discs, steel
plates, bottom pressure plate and wave snap-ring
and wave spring (Fig. 225).
(5) Remove clutch piston with rotating motion.
(6) Remove and discard piston seals.
(7) Remove input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226). It
may be necessary to press the input shaft in slightly
to relieve tension on the snap-ring
(8) Press input shaft out of retainer with shop
press and suitable size press tool. Use a suitably
sized press tool to support the retainer as close to the
input shaft as possible.CLEANING
Clean the clutch components with solvent and dry
them with compressed air. Do not use rags or shop
towels to dry any of the clutch parts. Lint from such
materials will adhere to component surfaces and
could restrict or block fluid passages after assembly.
Fig. 225 Rear Clutch Components
1 - PISTON SPRING 10 - TOP PRESSURE PLATE
2 - REAR CLUTCH PISTON 11 - CLUTCH DISCS (4)
3 - CLUTCH PISTON SEALS 12 - BOTTOM PRESSURE PLATE
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT THRUST WASHER (METAL) 13 - WAVE SPRING
5 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING 14 - CLUTCH PLATES (3)
6 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER 15 - RETAINER SEAL RING
7 - INPUT SHAFT 16 - SHAFT REAR SEAL RING (PLASTIC)
8 - REAR CLUTCH THRUST WASHER (FIBER) 17 - SHAFT FRONT SEAL RING (TEFLON)
9 - CLUTCH PACK SNAP-RING (SELECTIVE)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 119
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1639 of 2199

INSPECTION
Replace the clutch discs if warped, worn, scored,
burned/charred, the lugs are damaged, or if the fac-
ing is flaking off. Replace the top and bottom pres-
sure plates if scored, warped, or cracked. Be sure the
driving lugs on the pressure and clutch plates are
also in good condition. The lugs must not be bent,
cracked or damaged in any way.
Replace the piston spring and wave spring if either
part is distorted, warped or broken.
Check the lug grooves in the clutch retainer. The
clutch and pressure plates should slide freely in the
slots. Replace the retainer if the grooves are worn or
damaged. Also check action of the check balls in the
retainer and piston. Each check ball must move
freely and not stick.
Replace the retainer bushing if worn, scored, or
doubt exists about bushing condition.
Inspect the piston and retainer seal surfaces for
nicks or scratches. Minor scratches can be removed
with crocus cloth. However, replace the piston and/or
retainer if the seal surfaces are seriously scored.
Check condition of the fiber thrust washer and
metal output shaft thrust washer. Replace either
washer if worn or damaged.
Check condition of the seal rings on the input shaft
and clutch retainer hub. Replace the seal rings only
if worn, distorted, or damaged. The input shaft front
seal ring is teflon with chamfered ends. The rear ring
is metal with interlocking ends.
Check the input shaft for wear, or damage. Replace
the shaft if worn, scored or damaged in any way.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Soak clutch discs in transmission fluid while
assembling other clutch parts.
(2) Install new seal rings on clutch retainer hub
and input shaft, if necessary, (Fig. 227) and (Fig.
228).
(a) Be sure clutch hub seal ring is fully seated in
groove and is not twisted.
(3) Lubricate splined end of input shaft and clutch
retainer with transmission fluid. Then press input
shaft into retainer (Fig. 229). Use a suitably sized
press tool to support retainer as close to input shaft
as possible.
(4) Install input shaft snap-ring (Fig. 226).
(5) Invert retainer and press input shaft in oppo-
site direction until snap-ring is seated.
(6) Install new seals on clutch piston. Be sure lip
of each seal faces interior of clutch retainer.
(7) Lubricate lip of piston seals with generous
quantity of MopartDoor Ease. Then lubricate
retainer hub and bore with light coat of transmission
fluid.
(8) Install clutch piston in retainer. Use twisting
motion to seat piston in bottom of retainer. A thin
strip of plastic (about 0.0209thick), can be used to
guide seals into place if necessary.
CAUTION: Never push the clutch piston straight in.
This will fold the seals over causing leakage and
clutch slip. In addition, never use any type of metal
tool to help ease the piston seals into place. Metal
tools will cut, shave, or score the seals.
(9) Install piston spring in retainer and on top of
piston (Fig. 230). Concave side of spring faces down-
ward (toward piston).
(10) Install wave spring in retainer (Fig. 230). Be
sure spring is completely seated in retainer groove.
(11) Install bottom pressure plate (Fig. 225).
Ridged side of plate faces downward (toward piston)
and flat side toward clutch pack.
(12) Install first clutch disc in retainer on top of
bottom pressure plate. Then install a clutch plate fol-
lowed by a clutch disc until entire clutch pack is
installed (4 discs and 3 plates are required) (Fig.
225).
(13) Install top pressure plate.
(14) Install selective snap-ring. Be sure snap-ring
is fully seated in retainer groove.
(15) Using a suitable gauge bar and dial indicator,
measure clutch pack clearance (Fig. 231).
(a) Position gauge bar across the clutch drum
with the dial indicator pointer on the pressure
plate (Fig. 231).
(b) Using two small screw drivers, lift the pres-
sure plate and release it.
Fig. 226 Removing Input Shaft Snap-Ring
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - INPUT SHAFT SNAP-RING
3 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
21 - 120 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1640 of 2199

(c) Zero the dial indicator.
(d) Lift the pressure plate until it contacts the
snap-ring and record the dial indicator reading.Clearance should be 0.559 - 0.914 mm (0.022 -
0.036 in.). If clearance is incorrect, steel plates, discs,
selective snap ring and pressure plates may have to
be changed.
Fig. 227 Rear Clutch Retainer And Input Shaft Seal
Ring Installation
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER HUB SEAL RING
2 - INPUT SHAFT SEAL RINGS
Fig. 228 Input Shaft Seal Ring Identification
1 - PLASTIC REAR SEAL RING
2 - TEFLON FRONT SEAL RING (SQUEEZE RING TOGETHER
SLIGHTLY BEFORE INSTALLATION FOR BETTER FIT)
Fig. 229 Pressing Input Shaft Into Rear Clutch
Retainer
1 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
3 - PRESS RAM
Fig. 230 Piston Spring/Wave Spring Position
1 - REAR CLUTCH RETAINER
2 - PISTON SPRING
3 - WAVE SPRING
4 - CLUTCH PISTON
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 121
REAR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1651 of 2199

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 251) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 252).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the overrun-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
Fig. 251 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 132 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)