2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Check transmission
[x] Cancel search: Check transmissionPage 1653 of 2199

TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
The valve must be removed whenever the cooler
and lines are reverse flushed. The valve can be flow
tested when necessary. The procedure is exactly the
same as for flow testing a cooler.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 254). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The overdrive OFF lamp in the instrument panel
illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The
transmission will not allow fourth gear operation
until fluid temperature decreases to approximately
110ÉC (230ÉF).
Fig. 254 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1654 of 2199

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and transfer plate. The valve
body contains valves and check balls that control
fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch, bands,
and frictional clutches. The valve body contains the
following components (Fig. 255), (Fig. 256), (Fig.
257), and (Fig. 258):
²Regulator valve
²Regulator valve throttle pressure plug
²Line pressure plug and sleeve
²Kickdown valve
²Kickdown limit valve
²1-2 shift valve
²1-2 control valve
²2-3 shift valve²2-3 governor plug
²3-4 shift valve
²3-4 timing valve
²3-4 quick fill valve
²3-4 accumulator
²Throttle valve
²Throttle pressure plug
²Switch valve
²Manual valve
²Converter clutch lock-up valve
²Converter clutch lock-up timing Valve
²Shuttle valve
²Shuttle valve throttle plug
²Boost Valve
²10 check balls
By adjusting the spring pressure acting on the reg-
ulator valve, transmission line pressure can be
adjusted.
Fig. 255 Upper Housing Control Valve Locations
1 - UPPER HOUSING 8 - MANUAL VALVE
2 - REGULATOR VALVE 9 - 1-2 GOVERNOR PLUG
3 - SWITCH VALVE 10 - GOVERNOR PLUG COVER
4 - REGULATOR VALVE SPRING 11 - THROTTLE PLUG
5 - KICKDOWN VALVE 12 - 2-3 GOVERNOR PLUG
6 - KICKDOWN DETENT 13 - SHUTTLE VALVE PRIMARY SPRING
7 - THROTTLE VALVE AND SPRING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 135
Page 1658 of 2199
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
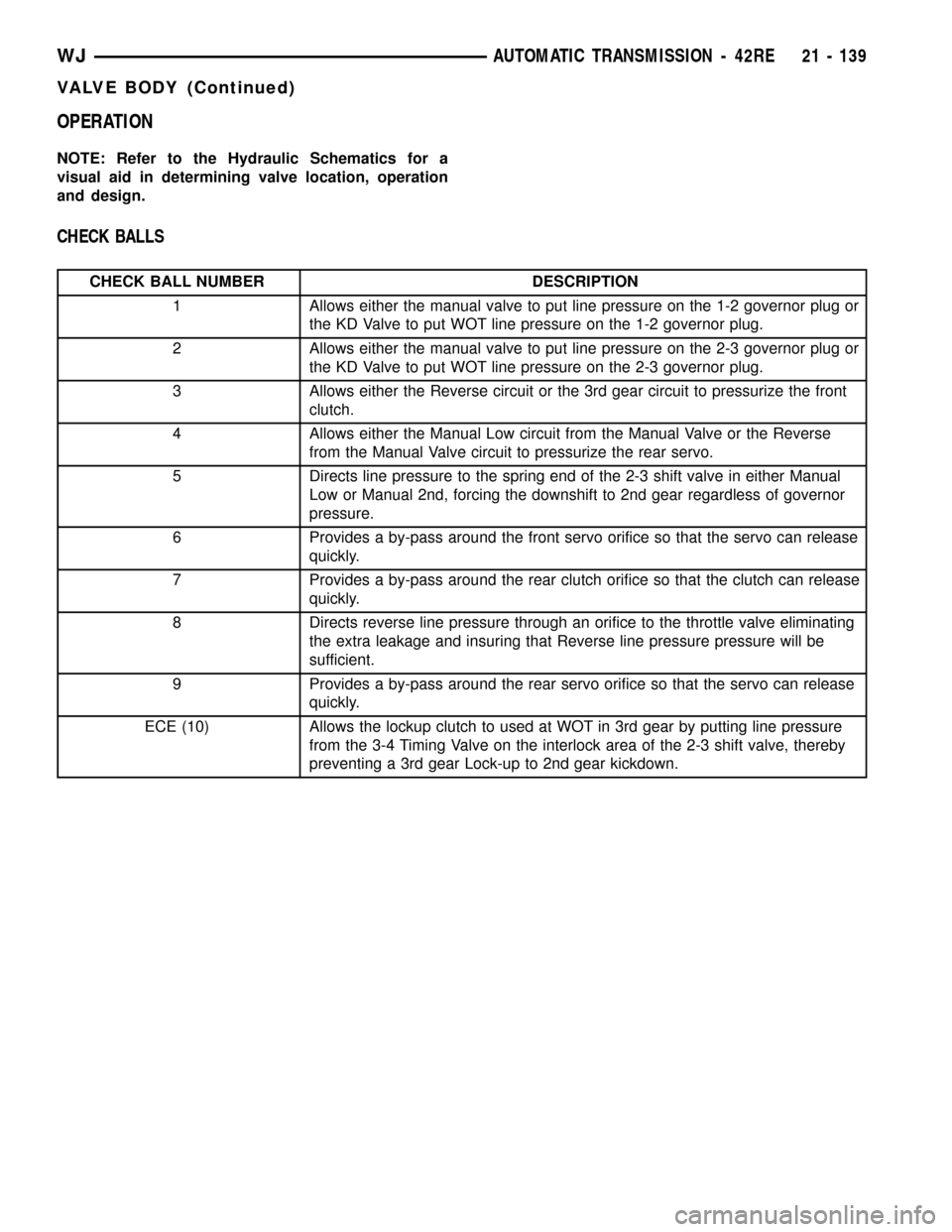
CHECK BALLS
CHECK BALL NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 1-2 governor plug.
2 Allows either the manual valve to put line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug or
the KD Valve to put WOT line pressure on the 2-3 governor plug.
3 Allows either the Reverse circuit or the 3rd gear circuit to pressurize the front
clutch.
4 Allows either the Manual Low circuit from the Manual Valve or the Reverse
from the Manual Valve circuit to pressurize the rear servo.
5 Directs line pressure to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve in either Manual
Low or Manual 2nd, forcing the downshift to 2nd gear regardless of governor
pressure.
6 Provides a by-pass around the front servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
7 Provides a by-pass around the rear clutch orifice so that the clutch can release
quickly.
8 Directs reverse line pressure through an orifice to the throttle valve eliminating
the extra leakage and insuring that Reverse line pressure pressure will be
sufficient.
9 Provides a by-pass around the rear servo orifice so that the servo can release
quickly.
ECE (10) Allows the lockup clutch to used at WOT in 3rd gear by putting line pressure
from the 3-4 Timing Valve on the interlock area of the 2-3 shift valve, thereby
preventing a 3rd gear Lock-up to 2nd gear kickdown.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 139
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1662 of 2199
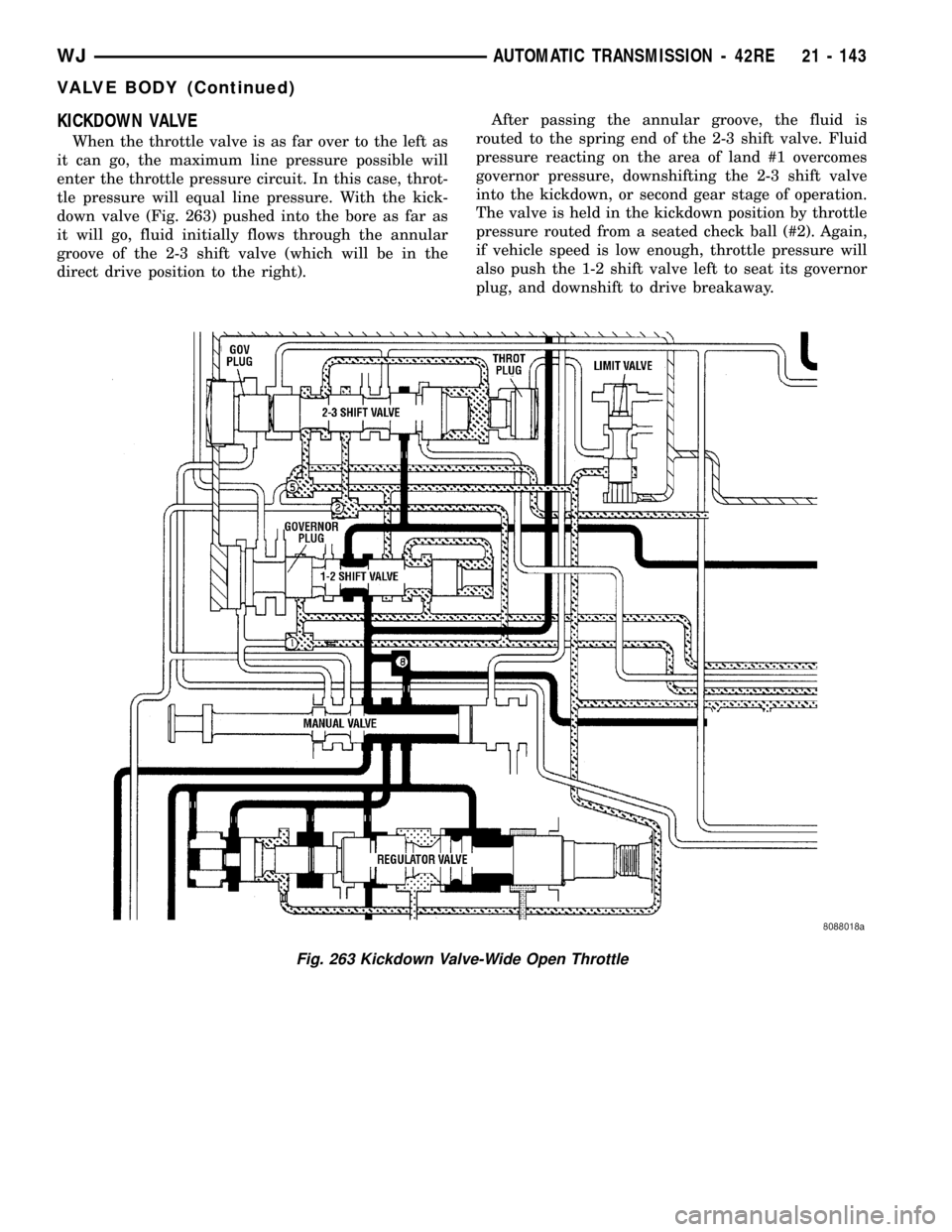
KICKDOWN VALVE
When the throttle valve is as far over to the left as
it can go, the maximum line pressure possible will
enter the throttle pressure circuit. In this case, throt-
tle pressure will equal line pressure. With the kick-
down valve (Fig. 263) pushed into the bore as far as
it will go, fluid initially flows through the annular
groove of the 2-3 shift valve (which will be in the
direct drive position to the right).After passing the annular groove, the fluid is
routed to the spring end of the 2-3 shift valve. Fluid
pressure reacting on the area of land #1 overcomes
governor pressure, downshifting the 2-3 shift valve
into the kickdown, or second gear stage of operation.
The valve is held in the kickdown position by throttle
pressure routed from a seated check ball (#2). Again,
if vehicle speed is low enough, throttle pressure will
also push the 1-2 shift valve left to seat its governor
plug, and downshift to drive breakaway.
Fig. 263 Kickdown Valve-Wide Open Throttle
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 143
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1668 of 2199
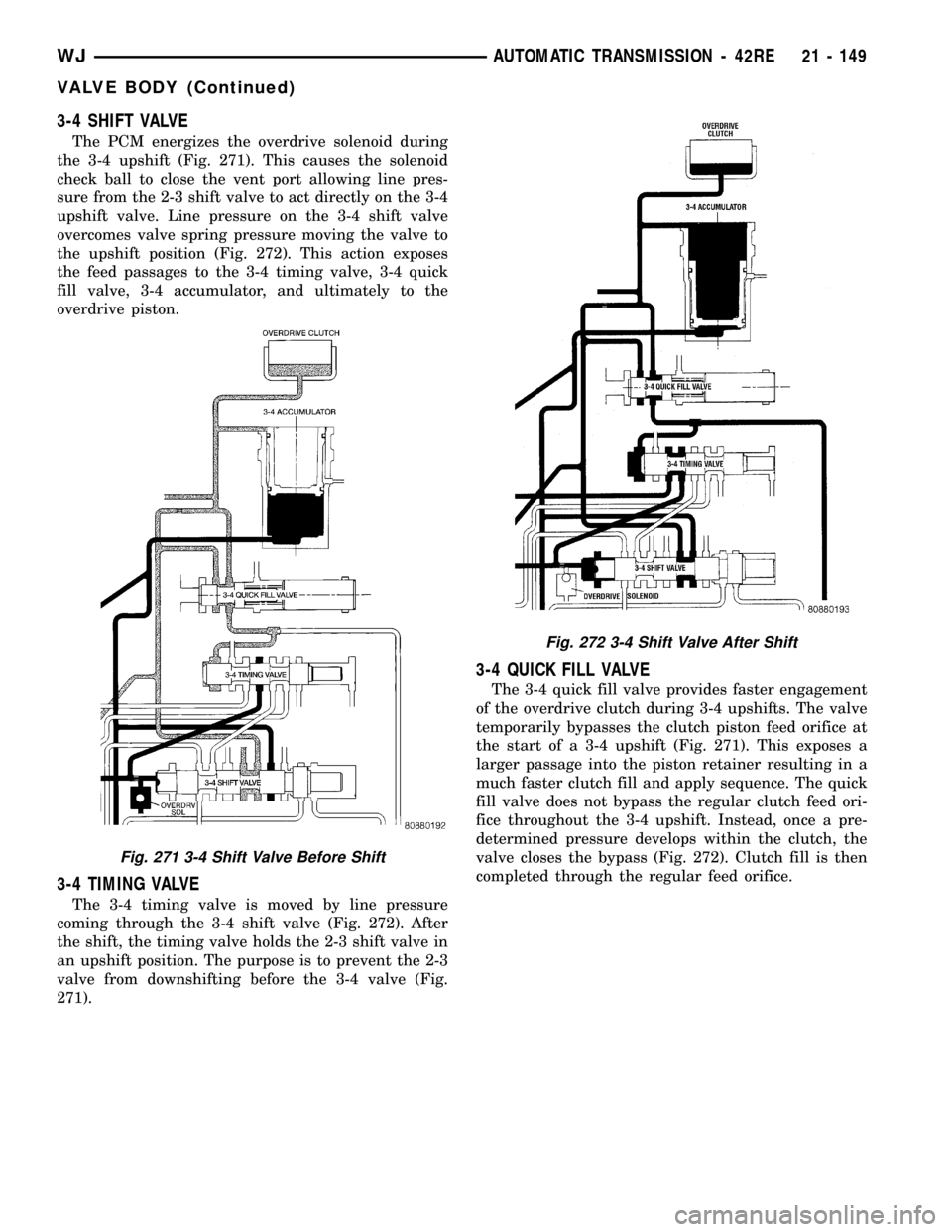
3-4 SHIFT VALVE
The PCM energizes the overdrive solenoid during
the 3-4 upshift (Fig. 271). This causes the solenoid
check ball to close the vent port allowing line pres-
sure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly on the 3-4
upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4 shift valve
overcomes valve spring pressure moving the valve to
the upshift position (Fig. 272). This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston.
3-4 TIMING VALVE
The 3-4 timing valve is moved by line pressure
coming through the 3-4 shift valve (Fig. 272). After
the shift, the timing valve holds the 2-3 shift valve in
an upshift position. The purpose is to prevent the 2-3
valve from downshifting before the 3-4 valve (Fig.
271).
3-4 QUICK FILL VALVE
The 3-4 quick fill valve provides faster engagement
of the overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts. The valve
temporarily bypasses the clutch piston feed orifice at
the start of a 3-4 upshift (Fig. 271). This exposes a
larger passage into the piston retainer resulting in a
much faster clutch fill and apply sequence. The quick
fill valve does not bypass the regular clutch feed ori-
fice throughout the 3-4 upshift. Instead, once a pre-
determined pressure develops within the clutch, the
valve closes the bypass (Fig. 272). Clutch fill is then
completed through the regular feed orifice.
Fig. 271 3-4 Shift Valve Before Shift
Fig. 272 3-4 Shift Valve After Shift
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 149
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1679 of 2199

(25) Remove boost valve connecting tube (Fig.
299). Disengage tube from upper housing port first.
Then rock opposite end of tube back and forth to
work it out of lower housing.
CAUTION: Do not use tools to loosen or pry the
connecting tube out of the valve body housings.
Loosen and remove the tube by hand only.
(26) Turn valve body over so lower housing is fac-
ing upward (Fig. 300). In this position, the two check
balls in upper housing will remain in place and not
fall out when lower housing and separator plate are
removed.
(27) Remove screws attaching valve body lower
housing to upper housing and transfer plate (Fig.300). Note position of boost valve tube brace for
assembly reference.
(28) Remove lower housing and overdrive separa-
tor plate from transfer plate (Fig. 300).
(29) Remove the ECE check ball from the transfer
plate (Fig. 301). The ECE check ball is approximately
4.8 mm (3/16 in.) in diameter.
(30) Remove transfer plate from upper housing
(Fig. 302).
(31) Turn transfer plate over so upper housing sep-
arator plate is facing upward.
(32) Remove upper housing separator plate from
transfer plate (Fig. 303). Note position of filter in
separator plate for assembly reference.
(33) Remove rear clutch and rear servo check balls
from transfer plate. Note check ball location for
assembly reference (Fig. 304).
Fig. 297 Accumulator Housing, Valve Springs And
Plug
1 - 3-4 SHIFT VALVE SPRING
2 - CONVERTER CLUTCH VALVE SPRING AND PLUG
3 - 3-4 ACCUMULATOR HOUSING
Fig. 298 Boost Valve Tube Brace
1 - BOOST VALVE TUBE
2 - TUBE BRACE (DOUBLE TAB)
Fig. 299 Boost Valve Tube
1 - BOOST VALVE TUBE
2 - LOWER HOUSING
3 - DISENGAGE THIS END OF TUBE FIRST
4 - UPPER HOUSING
Fig. 300 Lower Housing
1 - LOWER HOUSING
2 - OVERDRIVE SEPARATOR PLATE
3 - TRANSFER PLATE AND UPPER HOUSING
21 - 160 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1680 of 2199
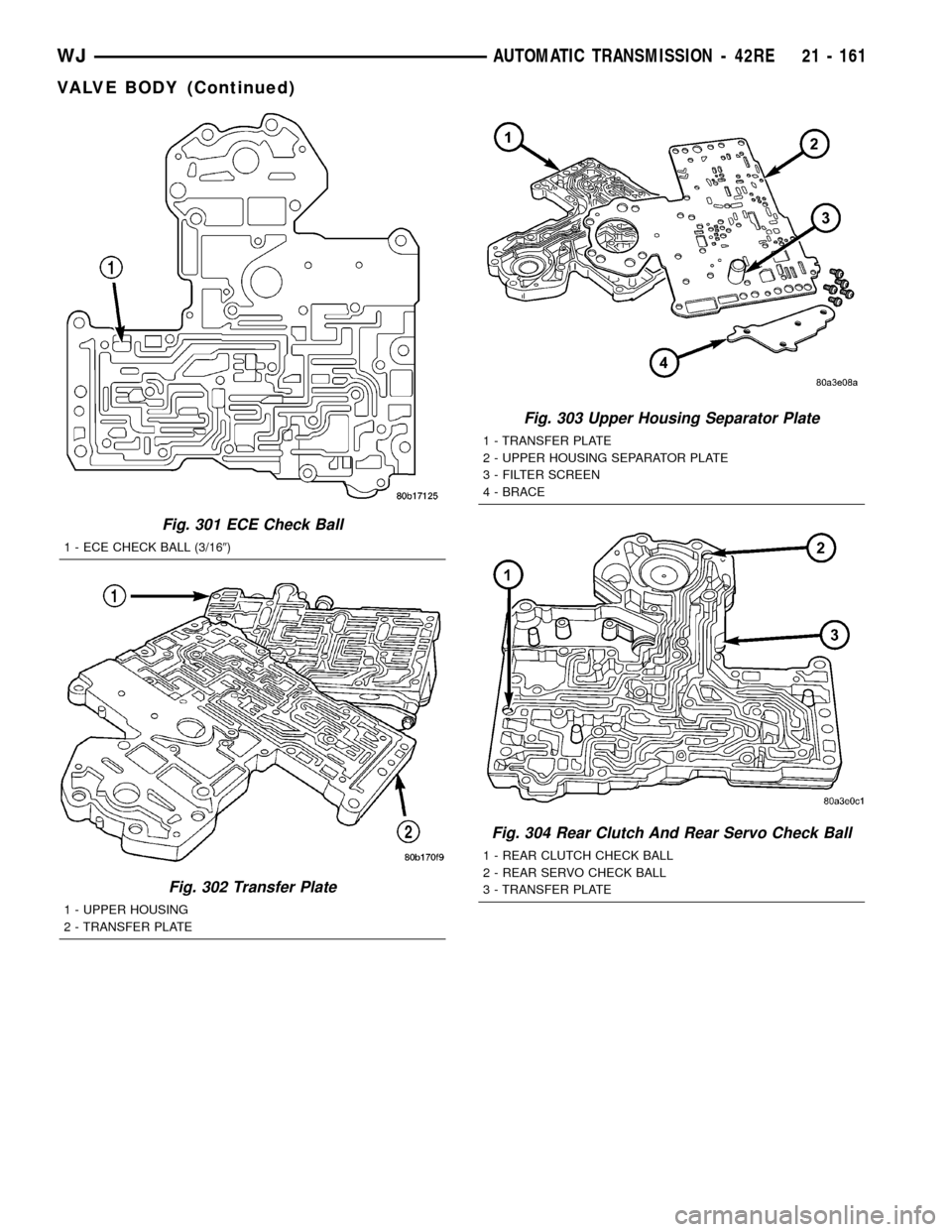

Fig. 301 ECE Check Ball
1 - ECE CHECK BALL (3/169)
Fig. 302 Transfer Plate
1 - UPPER HOUSING
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 303 Upper Housing Separator Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
2 - UPPER HOUSING SEPARATOR PLATE
3 - FILTER SCREEN
4 - BRACE
Fig. 304 Rear Clutch And Rear Servo Check Ball
1 - REAR CLUTCH CHECK BALL
2 - REAR SERVO CHECK BALL
3 - TRANSFER PLATE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 161
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1681 of 2199

VALVE BODY UPPER HOUSING
(1) Note location of check balls in valve body upper
housing (Fig. 305). Then remove the one large diam-
eter and the six smaller diameter check balls.
(2) Remove governor plug and shuttle valve covers
(Fig. 307).
(3) Remove E-clip that secures shuttle valve sec-
ondary spring on valve stem (Fig. 306).
(4) Remove throttle plug, primary spring, shuttle
valve, secondary spring, and spring guides (Fig. 307).
(5) Remove boost valve retainer, spring and valve
if not previously removed.
(6) Remove throttle plug and 1-2 and 2-3 governor
plugs (Fig. 294).
(7) Turn upper housing around and remove limit
valve and shift valve covers (Fig. 308).
(8) Remove limit valve housing. Then remove
retainer, spring, limit valve, and 2-3 throttle plug
from limit valve housing (Fig. 308).(9) Remove 1-2 shift control valve and spring (Fig.
308).
(10) Remove 1-2 shift valve and spring (Fig. 308).
(11) Remove 2-3 shift valve and spring from valve
body (Fig. 308).
(12) Remove pressure plug cover (Fig. 308).
(13) Remove line pressure plug, sleeve, throttle
pressure plug and spring (Fig. 308).
Fig. 305 Check Ball Locations In Upper Housing
1 - SMALL DIAMETER CHECK BALLS (6)
2 - LARGE DIAMETER CHECK BALL (1)
Fig. 306 Shuttle Valve E-Clip And Secondary Spring
Location
1 - E-CLIP
2 - SECONDARY SPRING AND GUIDES
3 - SHUTTLE VALVE
21 - 162 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)