2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Transmission type
[x] Cancel search: Transmission typePage 1775 of 2199
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches. They all have in common the fact
that they are round or circular in shape, located
within a smooth walled cylinder, which is closed at
one end and converts fluid pressure into mechanical
movement. The fluid pressure exerted on the piston
is contained within the system through the use of
piston rings or seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
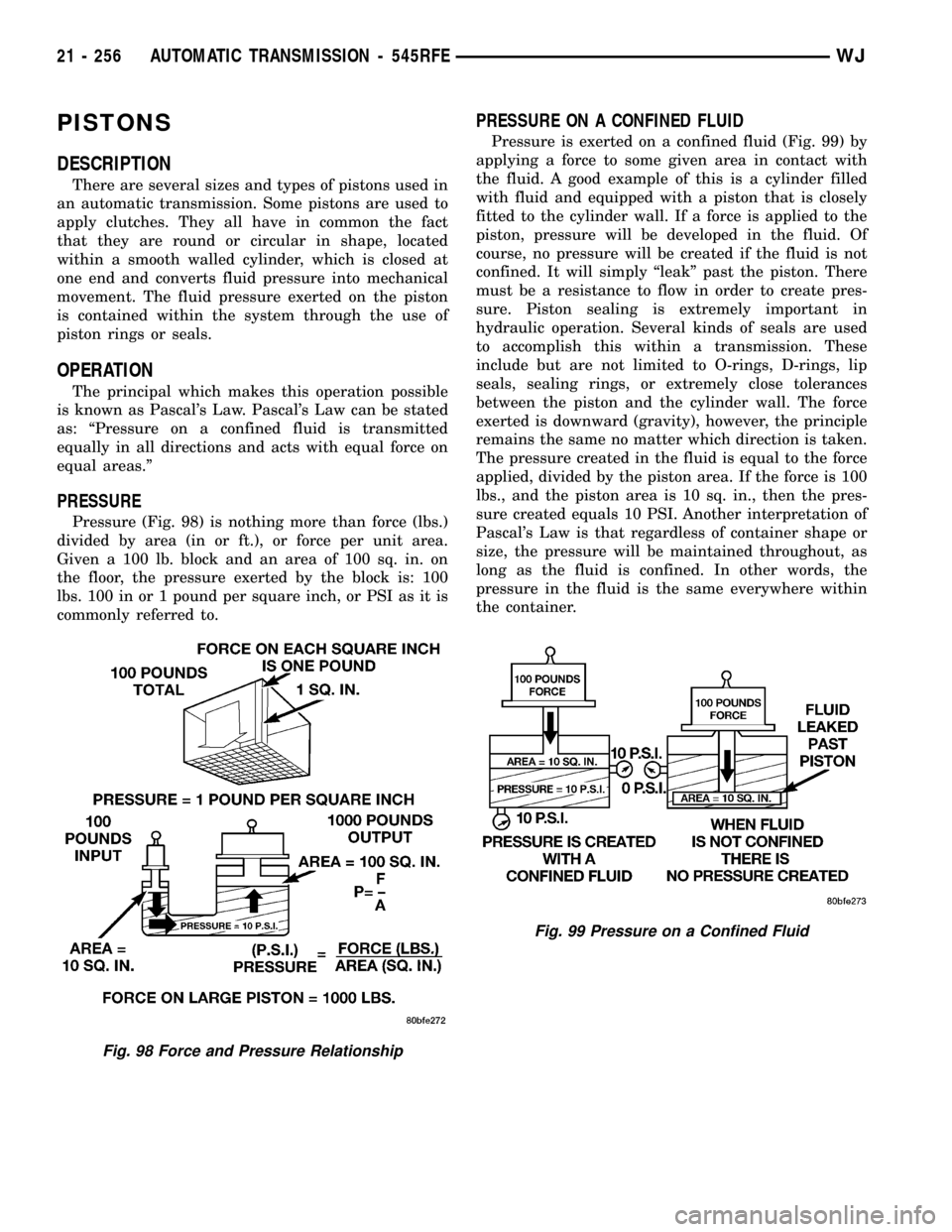
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 98) is nothing more than force (lbs.)
divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit area.
Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in. on
the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100
lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 99) by
applying a force to some given area in contact with
the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder filled
with fluid and equipped with a piston that is closely
fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied to the
piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid. Of
course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is not
confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston. There
must be a resistance to flow in order to create pres-
sure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
Fig. 98 Force and Pressure Relationship
Fig. 99 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
21 - 256 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1796 of 2199

CLEANING
Clean the valve housings, valves, plugs, springs,
and separator plates with a standard parts cleaning
solution only. Do not use gasoline, kerosene, or any
type of caustic solution. (Fig. 131)
Do not immerse any of the electrical components in
cleaning solution. Clean the electrical components by
wiping them off with dry shop towels only.
Dry all except the electrical parts with compressed
air. Make sure all passages are clean and free from
obstructions.Do not use rags or shop towels to
dry or wipe off valve body components. Lint
from these materials can stick to valve body
parts, interfere with valve operation, and clog
filters and fluid passages.
INSPECTION
Inspect all of the valve body mating surfaces for
scratches, nicks, burrs, or distortion. Use a straight-edge to check surface flatness. Minor scratches may
be removed with crocus cloth using only very light
pressure.
Minor distortion of a valve body mating surface
may be corrected by smoothing the surface with a
sheet of crocus cloth. Position the crocus cloth on a
surface plate, sheet of plate glass or equally flat sur-
face. If distortion is severe or any surfaces are
heavily scored, the valve body will have to be
replaced.
Inspect the valves and plugs (Fig. 132) for
scratches, burrs, nicks, or scores. Minor surface
scratches on steel valves and plugs can be removed
with crocus cloth butdo not round off the edges
of the valve or plug lands.Maintaining sharpness
of these edges is vitally important. The edges prevent
foreign matter from lodging between the valves and
plugs and the bore.
Fig. 130 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
Fig. 131 Valve Body Components
1 - SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
2 - MANUAL VALVE
3 - LOW REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
4 - LOW REVERSE ACCUMULATOR
5 - 2ND CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
6 - UNDERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
7 - OVERDRIVE ACCUMULATOR
8 - 4TH CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR
9 - CHECK BALLS (7)
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 277
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1798 of 2199

(8) Position the accumulator cover onto the valve
body.
(9) Install the screws to hold the accumulator
cover onto the valve body. Tighten the screws to 4.5
N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the TRS selector plate onto the valve
body and the manual valve.
(11) Install the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly onto the valve body.
(12) Install the screws to hold the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly onto the valve body.
Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in. lbs.). Tighten
the screws adjacent to the arrows cast into the bot-
tom of the transfer plate first.
(13) Position the detent spring onto the valve body.
(14) Install the screw to hold the detent spring
onto the valve body. Tighten the screw to 4.5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(15) Install new clutch passage seals onto the
valve body, if necessary
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of seals on valve body and the
solenoid and pressure switch assembly. Replace seals
if cut or worn.
(2) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(3) Place the transmission in the PARK position.
(4) Lubricate seal on the solenoid and pressure
switch assembly connector with petroleum jelly.(5) Position valve body in transmission and align
the manual lever on the valve body to the pin on the
transmission manual shift lever.
(6) Seat valve body in case and install one or two
bolts to hold valve body in place.
(7) Tighten valve body bolts alternately and evenly
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(9) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(10) Install screw to hold filter to valve body.
Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly connector.
(12) Install oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, fluid.
(14) Check and adjust gearshift cable, if necessary.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 279
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1800 of 2199
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. It drives the mainshaft through the plan-
etary gear and range hub. The front output shaft is
operated by a drive chain that connects the shaft to a
drive sprocket on the mainshaft. The drive sprocket
is engaged/disengaged by the mode fork, which oper-
ates the mode sleeve and hub. The sleeve and hub
are not equipped with a synchro mechanism for shift-
ing.
OPERATING RANGES
NV242 operating ranges are 2WD (2-wheel drive),
4x4 part-time, 4x4 full time, and 4 Lo.
The 2WD and 4x4 full time ranges can be used at
any time and on any road surface.
The 4x4 part-time and 4 Lo ranges are for off road
use only. The only time these ranges can be used on
hard surface roads, is when the surface is covered
with snow and ice.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case shift linkage
binding.1) Repair or replace linkage as
necessary.
2) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 2) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
3) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Transfer case will not shift through
4X4 part time range (light remains
on)1) Incomplete shift due to drivetrain
torque load.1) Momentarily release the
accelerator pedal to complete the
shift.
2) Incorrect tire pressure. 2) Correct tire pressure as
necessary.
3) Excessive Tire wear. 3) Correct tire condition as
necessary.
4) Excessive vehicle loading. 4) Correct as necessary.
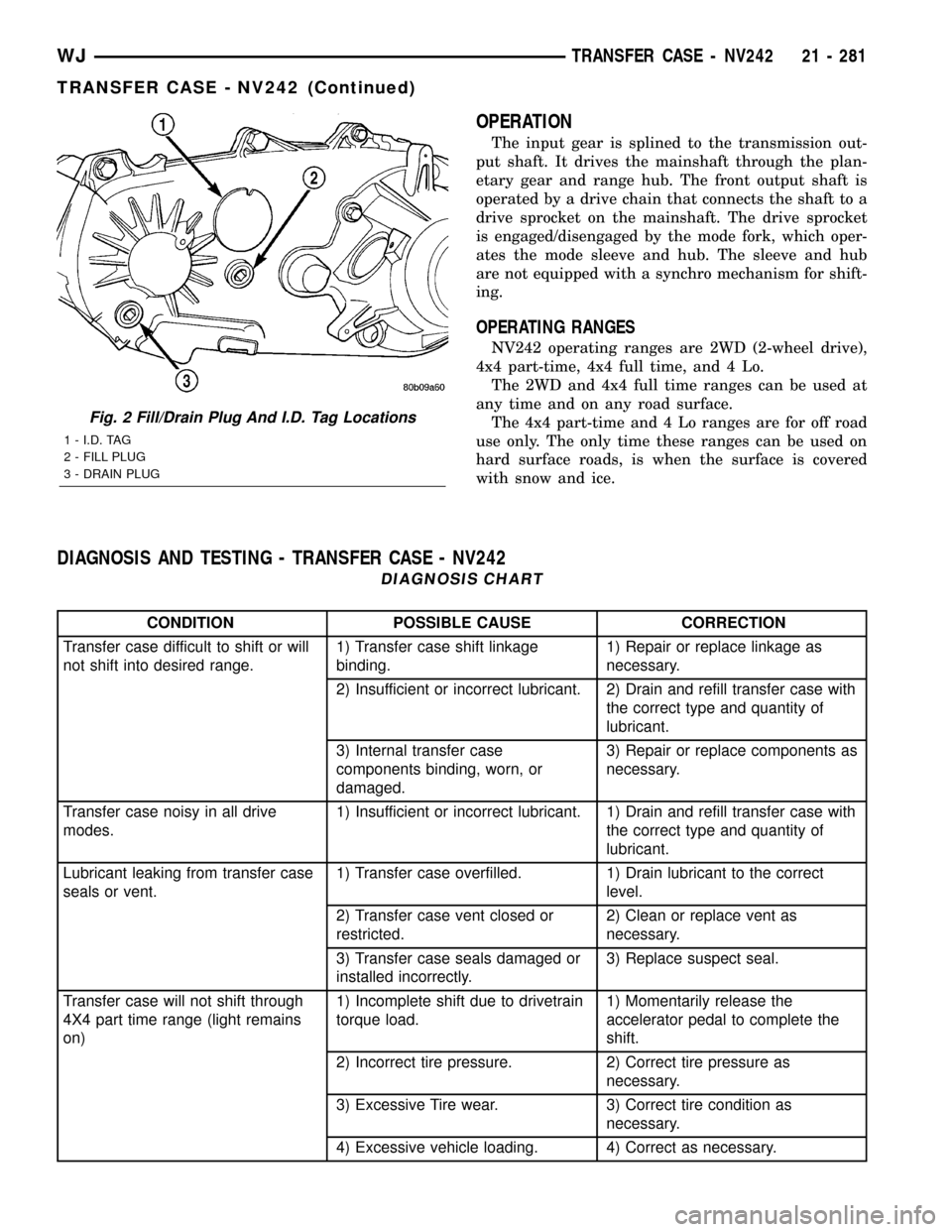
Fig. 2 Fill/Drain Plug And I.D. Tag Locations
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 281
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 2094 of 2199

open circuit to the fuse in the junction block as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is switched
to ground through the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). There should be continuity between this cav-
ity and the A/C compressor clutch relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the PCM wire harness connector C
(gray) at all times. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch relay from the
PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the compressor clutch relay by aligning
the relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The manual temperature control HVAC system
uses a combination of electrical, and vacuum con-trols. The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) HVAC sys-
tem uses only electrical controls. These controls
provide the vehicle operator with a number of setting
options to help control the climate and comfort
within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box for more information on the
suggested operation and use of these controls.
Both a/c heater control panels are located on the
instrument panel inboard of the steering column and
below the radio (Fig. 12). Both control panels contain
rotary-type temperature control knob(s), a rotary-
type mode control switch knob, a rotary-type blower
motor speed switch knob and an air conditioning
compressor push button switch. The rear window
defogger push button switch is also located on a/c
heater control panel. The AZC control panel also fea-
tures a recirculation push button switch and a vac-
uum fluorescent display area.
OPERATION
The AZC control module uses infrared sensing
technology to control occupant comfort levels, not the
actual passenger compartment air temperature. Dual
infrared sensors mounted in the face of the control
unit independently measure the surface temperature
to maintain customer-perceived comfort temperature
under changing conditions. Dual Zone temperature
control provides wide side-to-side variation in comfort
temperature to exceed the needs of either front seat
occupant. This sensing system replaces interior air
temperature and solar sensors used to approximate
direct sensing control through complex control pro-
grams.
Fig. 11 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
2 - NEGATIVE CABLE
3 - POSITIVE CABLE
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
Fig. 12 A/C HEATER CONTROL PANELS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 17
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2107 of 2199

BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The blend door for all models is actuated by an
electric actuator, while the AZC system uses 2 sepa-
rate actuators to allow the driver and passenger to
select individual comfort levels. In the following pro-
cedures, service for both types of actuators is cov-
ered.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
The blend door actuator is used on all models,
whether equipped with manual or Automatic Zone
Control (AZC). This actuator is located on the front of
the HVAC housing to the right of the floor panel
transmission tunnel, and can be removed from the
passenger compartment without instrument panel or
HVAC housing removal.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the glove box door. Refer to Instrument
Panel System for the procedures.
(3) Remove the lower I/P glove box door surround
panel. Refer to Instrument Panel System for the pro-
cedures.
(4) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
blend door actuator (Fig. 17).
(5) Remove the 2 screws that secure the blend
door actuator to the HVAC housing.
(6) Remove the blend door actuator from the
HVAC housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the blend door actuator on the HVAC
housing and tighten the two mounting screws to 2.2
N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(2) Plug in the wire harness connector to the blend
door actuator.
(3) Install the glove box door. Refer to Instrument
Panel System for the procedures.
(4) Install the lower I/P glove box door surround
panel. Refer to Instrument Panel System for the pro-
cedures.
(5) Connect and the battery negative cable.
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The mode door actuators for vehicles equipped with
the standard equipment manual temperature control
system are vacuum controlled. The optional Auto-
matic Zone Control (AZC) system uses electric motors
to actuate all mode doors. The service procedures for
both types of actuators are covered by the following
procedures.
Fig. 17 BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
1 - BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
24 - 30 CONTROLSWJ
Page 2140 of 2199

(11) Remove the bolts that secure the upper con-
denser and transmission cooler.
(12) Carefully lift the condenser out of the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
CAUTION: Before removing the condenser, note the
location of each of the radiator and condenser air
seals. These seals are used to direct air through the
condenser and radiator. The air seals must be rein-
stalled in their proper locations in order for the air
conditioning and engine cooling systems to per-
form as designed.
(1) Carefully position the condenser in the vehicle.
(2) Install the bolts that secure the upper con-
denser and transmission cooler.
(3) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser inlet and the discharge
line. Connect the discharge line to the condenser
inlet. Tighten the retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.).
(4) Remove the tape or plugs from the refrigerant
line fittings on the condenser outlet and the liquid
line. Connect the liquid line to the condenser outlet.
Tighten the retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the headlamp mounting module and
front fascia. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(6) Install the engine air filter inlet duct.
(7) Install the bolts that secure the radiator to the
upper crossmember.(8) Install the nuts that secure the hood latch and
brace to the upper crossmember.
(9) Install the headlamps in their mounts.
(10) Install the screws attaching the grille and
headlamp mounting module to the upper crossmem-
ber of the vehicle. Refer to Body for this and further
steps in the procedure.
(11) Evacuate and Recharge the refrigerant sys-
tem. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE) (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYS-
TEM CHARGE)
(12) Connect the battery negative cable.
NOTE: If the condenser is replaced, add 30 millili-
ters (1 fluid ounce) of refrigerant oil to the refriger-
ant system. Use only refrigerant oil of the type
recommended for the compressor in the vehicle.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
A/C DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.7L TURBO DIESEL
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN THE FRONT OF THIS SECTION BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - CAUTION)
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Recover the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY)
(3) Remove both headlamps from the vehicle. Refer
to Lamps/Lighting for the procedure.
(4) Remove the a/c high pressure transducer(Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CON-
TROLS/A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER - REMOV-
AL).
(5) Remove the front fascia from the vehicle. Refer
to Front Fascia for the procedure (Fig. 7).
(6) Remove the refrigerant line retaining fastener
from the condenser inlet fitting. Remove the line and
cap the condenser inlet tube to prevent contamina-
tion of the system.
WJPLUMBING 24 - 63
A/C CONDENSER (Continued)