2003 FORD F150 lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 156 of 280
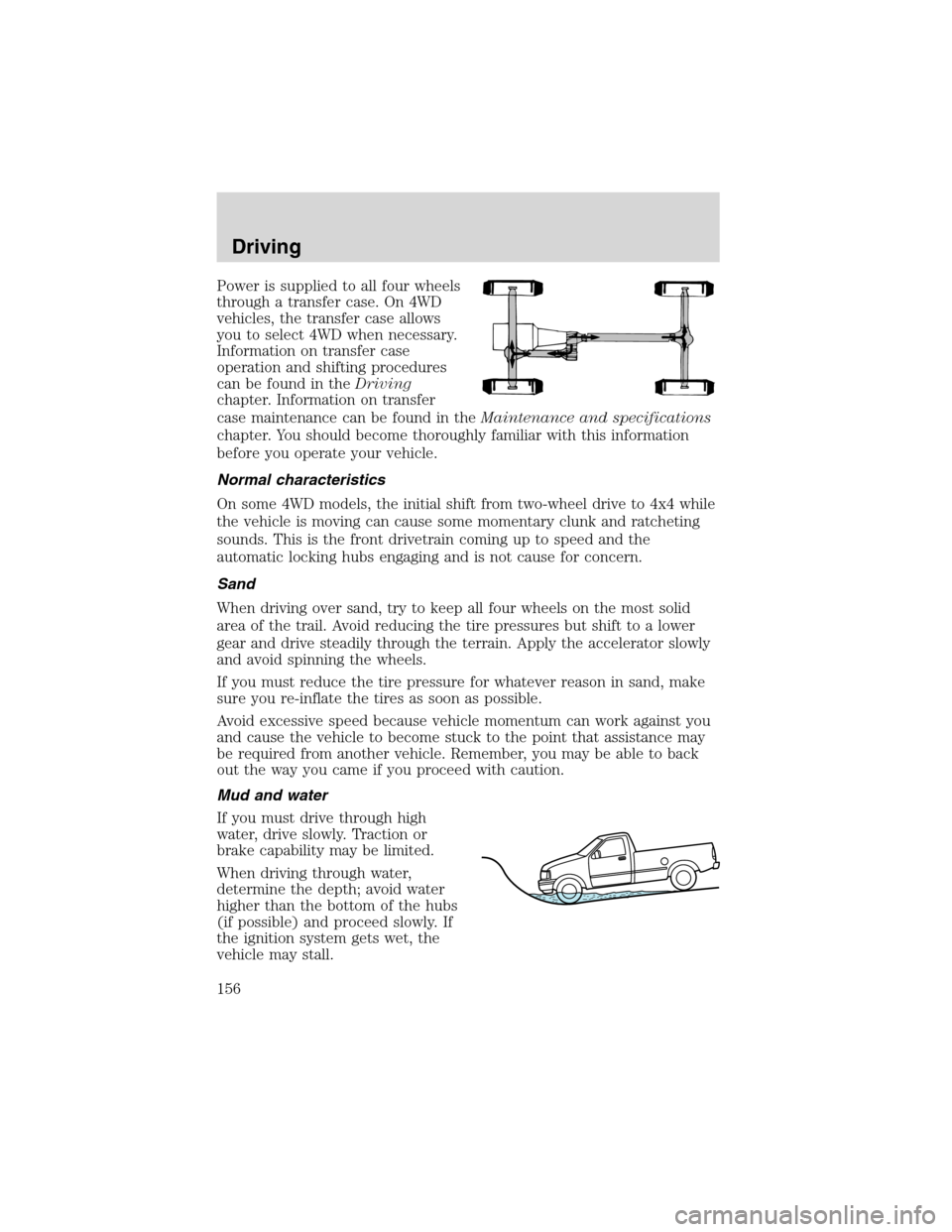
Power is supplied to all four wheels
through a transfer case. On 4WD
vehicles, the transfer case allows
you to select 4WD when necessary.
Information on transfer case
operation and shifting procedures
can be found in theDriving
chapter. Information on transfer
case maintenance can be found in theMaintenance and specifications
chapter. You should become thoroughly familiar with this information
before you operate your vehicle.
Normal characteristics
On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4x4 while
the vehicle is moving can cause some momentary clunk and ratcheting
sounds. This is the front drivetrain coming up to speed and the
automatic locking hubs engaging and is not cause for concern.
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Avoid reducing the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
If you must reduce the tire pressure for whatever reason in sand, make
sure you re-inflate the tires as soon as possible.
Avoid excessive speed because vehicle momentum can work against you
and cause the vehicle to become stuck to the point that assistance may
be required from another vehicle. Remember, you may be able to back
out the way you came if you proceed with caution.
Mud and water
If you must drive through high
water, drive slowly. Traction or
brake capability may be limited.
When driving through water,
determine the depth; avoid water
higher than the bottom of the hubs
(if possible) and proceed slowly. If
the ignition system gets wet, the
vehicle may stall.
Driving
156
Page 158 of 280

When climbing a steep slope or hill,
start in a lower gear rather than
downshifting to a lower gear from a
higher gear once the ascent has
started. This reduces strain on the
engine and the possibility of stalling.
If you do stall out, do not try to
turn around because you might roll
over. It is better to back down to a
safe location.
Apply just enough power to the
wheels to climb the hill. Too much
power will cause the tires to slip,
spin or lose traction, resulting in
loss of vehicle control.
Descend a hill in the same gear you
would use to climb up the hill to
avoid excessive brake application
and brake overheating. Do not
descend in neutral; instead,
disengage overdrive or manually
shift to a lower gear. When
descending a steep hill, avoid
sudden hard braking as you could
lose control. When you brake hard,
the front wheels can’t turn and if
they aren’t turning, you won’tbe
able to steer. The front wheels have to be turning in order to steer the
vehicle. Rapid pumping of the brake pedal will help you slow the vehicle
and still maintain steering control.
If your vehicle has anti-lock brakes, apply the brakes steadily. Do not
“pump”the brakes.
Driving on snow and ice
4WD vehicles have advantages over 2WD vehicles in snow and ice but
can skid like any other vehicle.
Should you start to slide while driving on snowy or icy roads, turn the
steering wheel in the direction of the slide until you regain control.
Avoid sudden applications of power and quick changes of direction on
snow and ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily when starting
from a full stop.
Driving
158
Page 159 of 280

Avoid sudden braking as well. Although a 4WD vehicle may accelerate
better than a two-wheel drive vehicle in snow and ice, it won’t stop any
faster, because as in other vehicles, braking occurs at all four wheels. Do
not become overconfident as to road conditions.
Make sure you allow sufficient distance between you and other vehicles
for stopping. Drive slower than usual and consider using one of the lower
gears. In emergency stopping situations, avoid locking of the wheels. Use
a“squeeze”technique, push on the brake pedal with a steadily increasing
force which allows the wheels to brake yet continue to roll so that you
may steer in the direction you want to travel. If you lock the wheels,
release the brake pedal and repeat the squeeze technique. If your vehicle
is equipped with a Four Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS), apply the
brake steadily. Do not“pump”the brakes. Refer to theBrakessection of
this chapter for additional information on the operation of the anti-lock
brake system.
Never drive with chains on the front tires of 4WD vehicles without also
putting them on the rear tires. This could cause the rear to slide and
swing around during braking.
Tires, Replacement Requirements
Do not use a size and type of tire and wheel other than that
originally provided by Ford Motor Company because it can affect
the safety and performance of your vehicle, which could result in an
increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, and/or serious
personal injury or death.
Make sure all tires and wheels on the vehicle are of the same size, type,
tread design, brand and load-carrying capacity. If you have questions
regarding tire replacement, see an authorized Ford or Lincoln/Mercury
dealer.
If you nevertheless decide to equip your 4WD for off-road use with tires
larger than what Ford Motor Company recommends, you should not use
these tires for highway driving.
If you use any tire/wheel combination not recommended by Ford Motor
Company, it may adversely affect vehicle handling and could cause
steering, suspension, axle or transfer case failure.
Do not use“aftermarket lift kits”or other suspension modifications,
whether or not they are used with larger tires and wheels.
These“aftermarket lift kits”could adversely affect the vehicle’s handling
characteristics, which could lead to loss of vehicle control or rollover and
serious injury.
Driving
159
Page 160 of 280

Tires can be damaged during off-road use. For your safety, tires that are
damaged should not be used for highway driving because they are more
likely to blow out or fail.
You should carefully observe the recommended tire inflation pressure
found on the safety compliance certification label attached to the left
front door lock facing or door latch post pillar. Failure to follow tire
pressure recommendations can adversely affect the way your vehicle
handles. Do not exceed the Ford Motor Company recommended pressure
even if it is less than the maximum pressure allowed for the tire.
Each day before you drive, check
your tires. If one looks lower than
the others, use a tire gauge to check
pressure of all tires, and adjust if
required. Check tire pressure with a
tire gauge every few weeks
(including spare). Safe operation
requires tires that are neither
underinflated nor a vehicle which is
overloaded.
Periodically inspect the tire treads and remove stones, nails, glass or
other objects that may be wedged in the tread grooves. Check for holes
or cuts that may permit air leakage from the tire and make necessary
repairs.
Inspect the tire side walls for cuts, bruises and other damage. If internal
damage to the tire is suspected, have the tire demounted and inspected
in case it needs to be repaired or replaced.
Maintenance and Modifications
The suspension and steering systems on your vehicle have been designed
and tested to provide both reliable and reasonably predictable
performance whether loaded or empty and durable load carrying
capability. For this reason, Ford Motor Company strongly recommends
that you do not make modifications such as adding or removing parts
(such as lift kits or stabilizer bars) or by using replacement parts not
equivalent to the original factory equipment.
Any modifications to a vehicle that raise the center of gravity can make
it more likely the vehicle will roll over as a result of a loss of control.
Ford Motor Company recommends that caution be used with any vehicle
equipped with a high load or device (such as ladder racks or pickup box
cover).
Driving
160
Page 174 of 280

GETTING ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE
To fully assist you should you have a vehicle concern, Ford Motor
Company offers a complimentary roadside assistance program. This
program is separate from the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. The service
is available:
•24–hours, seven days a week
•
for the New Vehicle Limited Warranty period of three years or 60,000 km
(36,000 miles), whichever occurs first on Ford and Mercury vehicles,
and four years or 80,000 km (50,000 miles) on Lincoln vehicles.
Roadside assistance will cover:
•changing a flat tire
•jump-starts
•lock-out assistance
•limited fuel delivery
•towing of your disabled vehicle to the nearest Ford Motor Company
dealership, or your selling dealer if within 56.3 km (35 miles) of the
nearest Ford Motor Company dealership (one tow per disablement).
Even non-warranty related tows, like accidents or getting stuck in the
mud or snow, are covered (some exclusions apply, such as impound
towing or repossession).
Canadian customers refer to your Owner Information Guide for
information on:
•coverage period
•exact fuel amounts
•towing of your disabled vehicle
•emergency travel expense reimbursement
•travel planning benefits
USING ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE
Complete the roadside assistance identification card and place it in your
wallet for quick reference. In the United States, this card is found in the
Owner Guide portfolio in the glove compartment in Ford vehicles and is
mailed to you if you own a Mercury or Lincoln. In Canada, the card is
found in the Owner Information Guide in the glove compartment.
U.S. Ford or Mercury vehicle customers who require roadside assistance,
call 1–800–241–3673; Lincoln vehicle customers call 1–800–521–4140.
Roadside Emergencies
174
Page 178 of 280

The fuses are coded as follows.
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingPassenger Compartment Fuse
Panel Description
1 15A Audio
2 5A Powertrain Control Module
(PCM), Cluster
3 20A Cigar lighter, Data link connector
4 5A Power mirror switch, Mirror turn
signal relays
5 15A Speed control module, Reverse
lamp, Climate mode switch,
Daytime Running Lamps (DRL)
relay, Digital Transmission Range
(DTR) sensor
6 5A Cluster, Brake shift interlock
solenoid, GEM
FUSE1 12 22
21323
617 27
718 28
819 29
930
20
31 21 11 10
RELAY
5 RELAY
4 RELAY
3 RELAY
2 RELAY
1
31424
41525
51626
Roadside Emergencies
178
Page 179 of 280

Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingPassenger Compartment Fuse
Panel Description
7—Not used
8 5A Radio, Remote entry module,
GEM, In-vehicle entertainment
system (SuperCrew only)
9—Not used
10—Not used
11 30A Front washer pump relay, Wiper
run/park relay, Wiper HI/LO relay,
Windshield wiper motor
12—Not used
13 20A Stop lamp switch (Lamps),
Turn/Hazard flasher
14 15A Battery saver relay, Interior lamp
relay
15 5A Stop lamp switch (speed control,
brake shift interlock), GEM, Rear
Anti-lock Brake System (RABS)
module
16 20A Headlamps (hi beams), Cluster
(hi beam indicator)
17—Not used
18 5A Instrument illumination (dimmer
switch power)
19—Not used
20 5A Audio, GEM, PCM, Transmission
range sensor
21 15A DTR sensor, Clutch switch,
Starter relay, I/P fuse 20
22 10A Air bag module, Passenger air bag
deactivation module
Roadside Emergencies
179
Page 180 of 280
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingPassenger Compartment Fuse
Panel Description
23 10A Trailer tow battery Charge relay,
Turn/Hazard flasher, 4x4
solenoids, 4x4 relays, Overhead
console, 4–Wheel Anti-lock Brake
System (4WABS) module, EC
mirror, Heated seats
24 10A Function selector switch assembly
25 10A Heated mirrors
26 10A Right-hand low beam headlamp
27 5A Foglamp relay and foglamp
indicator, Main light switch
(upstream)
28 10A Left-hand low beam headlamp
29 5A Autolamp module, Transmission
overdrive control switch, Central
security module, Beltminder
30 30A Passive Anti-theft transceiver,
Cluster, Ignition coils, PCM relay,
Coil on plugs, Radio noise
capacitor, ECC diode
31—Not used
Relay 1—Interior lamp relay
Relay 2—Battery saver relay
Relay 3—Not used
Relay 4—One-touch down window relay
Relay 5—Accessory delay relay
Power distribution box
The power distribution box is located in the engine compartment. The
power distribution box contains high-current fuses that protect your
vehicle’s main electrical systems from overloads.
Always disconnect the battery before servicing high current
fuses.
Roadside Emergencies
180