2003 CHRYSLER VOYAGER air suspension
[x] Cancel search: air suspensionPage 196 of 2177

Here is how the height sensing proportioning valve
differs from a standard proportioning valve. As the
height of the rear suspension changes, the height
sensing portion of the proportioning valve changes
the split point of the proportioning valve. When the
height of the rear suspension is low, the proportion-
ing valve interprets this as extra load and the split
point of the proportioning valve is raised to a higher
pressure to allow for more rear braking. When the
height of the rear suspension is high, the proportion-
ing valve interprets this as a light load and the split
point of the proportioning valve is lowered to a lower
pressure and rear braking is reduced.
The height sensing proportioning valve regulates
the pressure by sensing the load condition of the
vehicle through the movement of the proportioning
valve actuator lever (Fig. 72). As the position of the
rear axle changes, depending on the load the vehicle
is carrying, the movement is transferred to the pro-
portioning valve. The proportioning valve adjusts the
hydraulic pressure accordingly.
The height sensing proportioning valve allows the
brake system to maintain the optimal front to rear
brake balance regardless of the vehicle load condi-
tion. Under a light load condition, hydraulic pressure
to the rear brakes is minimized. As the rear load con-
dition increases, so does the hydraulic pressure to
the rear brakes.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PROPORTIONING
VALVE (HEIGHT SENSING)
CAUTION: The use of aftermarket load leveling or
load capacity increasing devices on this vehicle is
prohibited. Using air shock absorbers or helpersprings on this vehicle will cause the height sens-
ing proportioning valve to inappropriately reduce
the hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes. This inap-
propriate reduction in hydraulic pressure potentially
could result in increased stopping distance of the
vehicle.
When a premature rear wheel skid is obtained on a
brake application, it may be an indication that the
hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes is above the
specified output from the proportioning valve. This
condition indicates a possible malfunction of the
height sensing proportioning valve, which will
require testing to verify that it is properly controlling
the hydraulic pressure allowed to the rear brakes.
Premature rear wheel skid may also be caused by
contaminated front or rear brake linings.
Prior to testing a proportioning valve for function,
check that all tire pressures are correct. Also, ensure
the front and rear brake linings are in satisfactory
condition.It is also necessary to verify that the
brakes shoe assemblies on a vehicle being
tested are either original equipment manufac-
turers (OEM) or original replacement brake
shoe assemblies meeting the OEM lining mate-
rial specification. This vehicles brake system is
not balanced for aftermarket brake shoe assem-
bly lining material.
If both front and rear brakes check OK, proceed
with the following test procedure for the height sens-
ing proportioning valve.
(1) Road test the vehicle to determine which rear
wheel brake is exhibiting premature wheel skid.
(2) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(3) Remove the chassis brake tube going to the
rear brake in question at the proportioning valve.
Remove the chassis brake tube coming from the junc-
tion block at the proportioning valve (Fig. 73).
(4) Install the appropriate fittings from Pressure
Test Fittings, Special Tool 6833, into the open ports
of the proportioning valve.
(5) Install the previously removed brake lines into
the Pressure Test Fittings. Tighten all tube nuts to
17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).
(6) Install a pressure gauge from Gauge Set, Spe-
cial Tool C-4007-A into the open port on each pres-
sure test fitting. Bleed air out of hose from pressure
test fittings to pressure gauges at the pressure
gauges. Then bleed air out of the brake line being
tested at that rear wheel brake bleeder.
NOTE: Actuator rod is a linear spring and is meant
to flex by design. When rod is raised, it will have
some curvature to it.
Fig. 72 HEIGHT SENSING PROPORTIONING VALVE
1 - PROPORTIONING VALVE
2 - ACTUATOR LEVER
3 - AXLE BRACKET
4 - REAR AXLE
RSBRAKES - BASE5-49
PROPORTIONING VALVE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 203 of 2177

SUPPORT PLATE - DRUM
BRAKE
REMOVAL
(1) Using a brake pedal depressor, move and
secure brake pedal to a position past its first 1 inch
of travel. This will prevent brake fluid from draining
out of master cylinder when brake tube is remove
from wheel cylinder.
(2) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(3) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(4) Disconnect brake tube from rear of wheel cylin-
der. Cap open ends
(5) Remove brake drum.
(6) Remove brake shoes from brake support plate.
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the 2 bolts attaching the wheel cylin-
der to the brake support plate.
(8) Remove the wheel cylinder from the brake sup-
port plate.
(9) Disconnect the park brake cable from the park
brake actuation lever.
(10) Using a suitable tool such as a 14 mm box
wrench (Fig. 84) or an aircraft type hose clamp, com-
press the flared legs on park brake cable retainer.
Then pull the park brake cable out of brake support
plate.
(11) Remove the rear hub and bearing. (Refer to 2
- SUSPENSION/REAR/HUB / BEARING -
REMOVAL)(12) Remove the rear brake support plate from the
rear axle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the 4 hub and bearing to axle mounting
bolts into the mounting holes in the flange of the
rear axle.
(2) Install the rear brake support plate on the 4
mounting bolts installed in the flange of the rear axle
(Fig. 85).
(3) Install the rear hub and bearing (and connect
wheel speed sensor where applicable) stopping short
of installing the brake drum. (Refer to 2 - SUSPEN-
SION/REAR/HUB / BEARING - INSTALLATION)
(4) Install the rear park brake cable into its
mounting hole in the rear brake support plate.
(5) Install the park brake cable on the park brake
actuation lever.
(6) Apply sealant such as Mopar Gasket-In-A-Tube
or equivalent around the wheel cylinder opening in
the brake support plate.
(7) Install wheel cylinder onto brake support.
Install and tighten the wheel cylinder to brake sup-
port plate attaching bolts to 8 N´m (75 in. lbs.)
torque.
(8) Install brake tube into wheel cylinder. Tighten
tube nut to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Install the rear brake shoes on the brake sup-
port plate. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/ME-
CHANICAL/BRAKE PADS/SHOES -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install brake drum.
(11) Install wheel and tire.
(12) Tighten wheel stud nuts to 135 N´m (100 ft.
lbs.).
Fig. 84 Removing Park Brake Cable From Brake
Support Plate
1 - PARK BRAKE CABLE
2 - CABLE RETAINER
3 - 14 mm BOX WRENCH
4 - BRAKE SUPPORT PLATE
Fig. 85 Brake Support Plate Mounted On Bearing
Attaching Bolts
1 - REAR BRAKE SUPPORT PLATE
2 - HUB/BEARING MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - 56 BRAKES - BASERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 222 of 2177

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ANTILOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM............................75
DESCRIPTION - ANTILOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM (EXPORT)....................75
DESCRIPTION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING...............75
DESCRIPTION - TRACTION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................76
OPERATION
OPERATION - ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM . . 76
OPERATION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING...............77
OPERATION - TRACTION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................77
CAUTION
CAUTIONS..........................78
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ANTILOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM BLEEDING...................78
SPECIFICATIONS
ABS FASTENER TORQUE...............79
TONE WHEEL RUNOUT................79
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR AIR GAP........79
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL.............................79
INSTALLATION.........................80
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - AWD
REMOVAL.............................80INSTALLATION.........................80
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - FWD
REMOVAL.............................81
INSTALLATION.........................81
TONE WHEEL
INSPECTION - TONE WHEEL..............82
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRACTION
CONTROL SWITCH....................82
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
OPERATION - HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND
VALVES .............................83
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................89
OPERATION...........................89
ICU (INTEGRATED CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION.........................89
OPERATION...........................90
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD......................90
REMOVAL - RHD......................91
DISASSEMBLY - ICU....................93
ASSEMBLY - ICU.......................94
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LHD..................94
INSTALLATION - RHD..................95
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
This section covers the physical and operational
descriptions and the on-car service procedures for the
Mark 20e Antilock Brake System and the Mark 20e
Antilock Brake System with traction control.
The purpose of the antilock brake system (ABS) is
to prevent wheel lockup under braking conditions on
virtually any type of road surface. Antilock braking is
desirable because a vehicle that is stopped without
locking the wheels retains directional stability and
some steering capability. This allows the driver to
retain greater control of the vehicle during braking.
DESCRIPTION - ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
(EXPORT)
Four-wheel disc antilock brakes are standard on all
models. The Mark 20e antilock brake system is used
on all models. Depending on whether the vehicle is a
left-hand drive (LHD) or right-hand drive (RHD)
model, the integrated control unit (ICU) is located in
one of two locations. On LHD models, the ICU is
mounted above the front suspension cradle/cross-
member below the master cylinder. On RHD models,
the ICU is located behind the front suspension cra-
dle/crossmember on the left side of the vehicle.
DESCRIPTION - ELECTRONIC VARIABLE
BRAKE PROPORTIONING
Vehicles equipped with ABS use electronic variable
brake proportioning (EVBP) to balance front-to-rear
braking. The EVBP is used in place of a rear propor-
RSBRAKES - ABS5-75
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1356 of 2177

FRONT CRADLE
CROSSMEMBER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - FRONT CRADLE
CROSSMEMBER
This vehicle uses a one piece cast aluminum cradle
for the front cradle crossmember. The cradle cross-
member is used as the attaching points for the lower
control arms, stabilizer bar and steering gear. The
cradle also has the power steering hoses and the
chassis brake tubes attached to it.
WARNING: If a threaded hole in the suspension cra-
dle needs to be repaired, only use the type of
thread insert and installation procedure specified
for this application.
The threaded holes in the front cradle crossmem-
ber that are used for attachment of the lower control
arm rear bushing retainer, power steering hose and
chassis brake tubes can be repaired. The repair is
done by the installation of a Heli-Coiltthread insert
which has been specifically developed for this appli-
cation. Refer to the Mopar Parts Catalog for the spec-
ified Heli-Coiltthread insert to be used for this
application. The procedure for installing the Heli-
Coiltthread insert is detailed in the Service Proce-
dures section in this group of the service manual.
DESCRIPTION - FRONT CRADLE
CROSSMEMBER THREAD REPAIR
WARNING: When performing this procedure use
only the thread inserts which are specified in the
Mopar Parts Catalog for this repair procedure.
These thread inserts have been specifically devel-
oped for this application and use of other types of
thread inserts can result in an inferior long term
repair.
The threaded holes in the front cradle crossmem-
ber, if damaged, can repaired by installing a Heli-
Coiltthread insert.
The threaded holes that are repairable using the
thread insert, are the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer mounting bolt holes, routing bracket attach-
ing locations for the power steering hoses, and brake
hose attachment holes.
This repair procedure now allows the threaded
holes in the cradle crossmember to be repaired, elim-
inating the need to replace the cradle crossmember if
damage occurs to one of the threaded holes.The thread inserts for this application are specified
by part number in the Mopar Parts Catalog.Do not
use a substitute thread insert.
The specific tools and equipment required to install
the thread insert are listed below. Refer to the
instructions included with the thread insert for the
detailed procedure used for the installation of the
thread insert.
NOTE: The thread inserts for this application are for
the repair of M8x1.25 and M10x1.5 threads. Be sure
the correct tools are used for the required thread
insert size.
TOOL REQUIREMENT FOR M8x1.25 Thread
²8.3mm (5/16 in.) Drill Bit
²120É Countersink
²Heli-CoiltTap #4863-8
²Heli-CoiltGage #4624-8
²Heli-CoiltHand Inserting Tool 7751-8
²Needle Nose Pliers ± For Removal Of Thread
Insert Driving Tang
TOOL REQUIREMENT FOR M10x1.5 Thread
²10.5mm (25/64 in.) Drill Bit
²120É Countersink
²Heli-CoiltTap #4863-10
²Heli-CoiltGage #4624-10
²Heli-CoiltHand Inserting Tool 7751-10
²Needle Nose Pliers ± For Removal Of Thread
Insert Driving Tang
REMOVAL
The front cradle crossmember must be installed in
the design location to achieve proper front end sus-
pension alignment. If the cradle crossmember is
removed without applying reference marks on the
frame rails, align the cradle crossmember according
to the dimensions provided in this group.
NOTE: If the caged nuts in the frame rails become
damaged and cannot be reused, a replacement nut
can be obtained through MoparT.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove steering column lower cover from
instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPENING
COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove steering column cover backing plate
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN COVER BACKING PLATE - REMOV-
AL).
RSFRAME & BUMPERS13-9
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1357 of 2177

(4) Position steering so front wheels are straight
ahead.
CAUTION: Do not rotate steering wheel after disen-
gaging lower coupling from steering gear, damage
to air bag clock spring can result.
(5) Remove clinch bolt attaching steering column
coupling to steering gear shaft (Fig. 10).
(6) Remove steering column coupling from tele-
scoping steering gear shaft.
(7) Hoist vehicle and support on safety stands.
(8) Position a drain pan under power steering
pump and oil return hose coupling.
(9) Using a hose pinch-off pliers (C-4390), pinch
power steering oil return hose off between the cross-
member coupling and the pump.
(10) Loosen hose clamp at the cradle crossmember
coupling.
(11) Disconnect return hose from metal tube.
(12) While holding pressure relief valve nut on
back of power steering pump, Remove flare nut
attaching high pressure hose to back of pump.
(13) Remove high pressure hose from pump.
(14) Allow power steering fluid to drain into pan.
(15) Remove bolts attaching anti-lock brake sensor
leads to cradle crossmember.
(16) Position anti-lock brake leads out of the way.
(17) Disconnect stabilizer bar links from ends of
stabilizer bar.
(18) Disconnect lower ball joints from lower steer-
ing knuckles (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/
LOWER BALL JOINT - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove the rear engine mount heat shield
(Fig. 11).
(20) Remove through bolt attaching rear engine
mount to cradle crossmember (Fig. 12).
(21) Using paint or grease pencil, mark outline of
cradle crossmember on frame rails to aid installation.
(22) Support cradle crossmember on suitable lift-
ing device (Fig. 14).
(23) Remove bolts attaching crossmember to front
frame rails (Fig. 13).
(24) Remove cradle crossmember from vehicle (Fig.
14).
Fig. 10 STEERING COUPLING
1 - STEERING SHAFT BOOT
2 - STEERING SHAFT
3 - CROSSMEMBER
4 - STEERING GEAR
5 - MOUNT
6 - TRANSAXLE
Fig. 11 REAR MOUNT HEAT SHIELD
1 - BOLT
2 - HEAT SHIELD
3 - CLIP
4 - REAR ENGINE MOUNT
13 - 10 FRAME & BUMPERSRS
FRONT CRADLE CROSSMEMBER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1398 of 2177

(6) Start engine and let idle just long enough to
circulate power steering fluid through the analyzer
and hoses. Shut off engine.
(7) Check power steering fluid level and add fluid
as necessary. Start engine again and let idle until the
air is out of the fluid.
(8) Gauge should read below 300 psi (2068 kPa). If
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the range
of 100-275 psi (689-1896 kPa) depending on fluid
temperature. The flow meter should read above 1.5
GPM.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than four seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
NOTE:
Power steering pump maximum pressure for
2.4L engines is 1,200 ± 1,350 psi (8,274 ± 9,308 kPa).
Power steering pump maximum pressure for all other
engines is 1,400 ± 1,500 psi (9,653 ± 10,342 kPa).
(9) Close analyzer valve fully three times and
record highest pressure indicated each time. All three
readings must be within specifications. If any of the
three power steering pump pressures are above orbelow specifications, replace pump. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - REMOVAL)
CAUTION: Do not force the steering to operate
against the stops for more than 4 seconds at a time
because pump damage can result.
(10) Once the pump has been verified as working
correctly, completely open the valve on the Power
Steering Analyzer. Turn the steering wheel to the
extreme left until the stop in the steering gear is
met. Hold it there for 2±4 seconds, then release it.
Now turn the steering wheel to the right until the
right stop is met. Hold it there for 2±4 seconds, then
release it. Record the stabilized pressure at each
position. Compare the recorded readings to the spec-
ifications. If the output pressures are not within 100
psi (689 kPa) of one another against either stop or
are below specifications, the steering gear is leaking
internally and must be replaced. (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/GEAR - REMOVAL)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
NOTE: There are three diagnosis charts following
that cover POWER STEERING NOISE, STEERING
WHEEL FEEL, and POWER STEERING FLUID.
POWER STEERING NOISE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONABLE HISS
OR WHISTLE*1. Damaged or mispositioned
steering column shaft/coupling dash
panel seal.1. Reposition or replace steering column
shaft/coupling dash panel seal.
2. Noisy valve in power steering
gear.2. Replace power steering gear.
3. Mis-routed power steering hose. 3. Check routing of power steering
hoses. Ensure hoses do not come in
unwanted contact with other components
and objects.
RATTLE OR EXCESSIVE
CLUNK**1. Power steering gear loose on front
suspension crossmember.1. Inspect power steering gear mounting
bolts. Replace as necessary. Tighten to
the specified torque.
2. Front suspension crossmember
mounting fasteners loose at frame.2. Tighten the front suspension
crossmember mounting fasteners to the
specified torque.
3. Loose tie rod (outer or inner). 3. Check tie rod pivot points for wear.
Replace worn/loose parts as required.
4. Loose lower control arm mounting
bolts at front suspension
crossmember.4. Tighten control arm mounting bolts to
the specified torques.
RSSTEERING19-3
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1399 of 2177
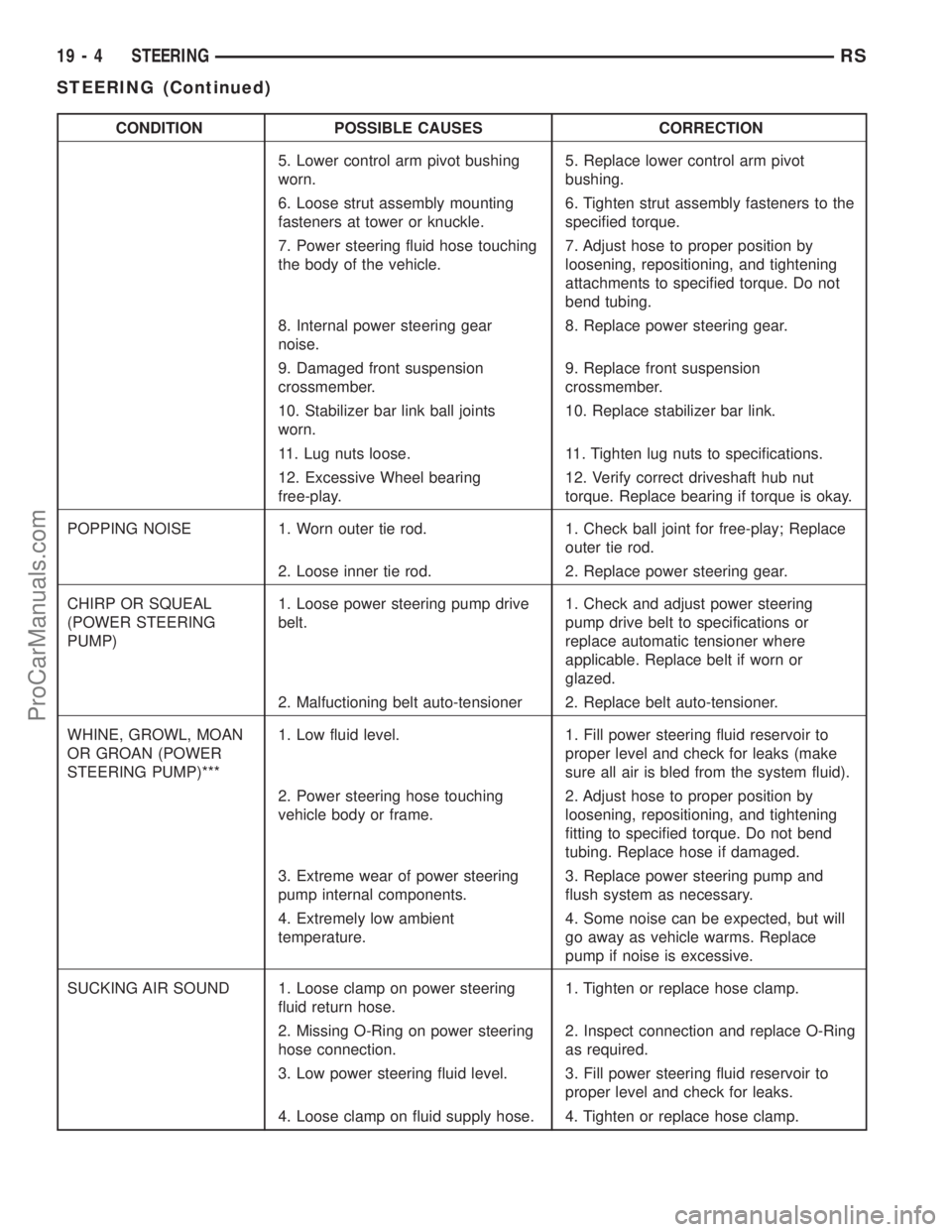
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
5. Lower control arm pivot bushing
worn.5. Replace lower control arm pivot
bushing.
6. Loose strut assembly mounting
fasteners at tower or knuckle.6. Tighten strut assembly fasteners to the
specified torque.
7. Power steering fluid hose touching
the body of the vehicle.7. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
attachments to specified torque. Do not
bend tubing.
8. Internal power steering gear
noise.8. Replace power steering gear.
9. Damaged front suspension
crossmember.9. Replace front suspension
crossmember.
10. Stabilizer bar link ball joints
worn.10. Replace stabilizer bar link.
11. Lug nuts loose. 11. Tighten lug nuts to specifications.
12. Excessive Wheel bearing
free-play.12. Verify correct driveshaft hub nut
torque. Replace bearing if torque is okay.
POPPING NOISE 1. Worn outer tie rod. 1. Check ball joint for free-play; Replace
outer tie rod.
2. Loose inner tie rod. 2. Replace power steering gear.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL
(POWER STEERING
PUMP)1. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.1. Check and adjust power steering
pump drive belt to specifications or
replace automatic tensioner where
applicable. Replace belt if worn or
glazed.
2. Malfuctioning belt auto-tensioner 2. Replace belt auto-tensioner.
WHINE, GROWL, MOAN
OR GROAN (POWER
STEERING PUMP)***1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks (make
sure all air is bled from the system fluid).
2. Power steering hose touching
vehicle body or frame.2. Adjust hose to proper position by
loosening, repositioning, and tightening
fitting to specified torque. Do not bend
tubing. Replace hose if damaged.
3. Extreme wear of power steering
pump internal components.3. Replace power steering pump and
flush system as necessary.
4. Extremely low ambient
temperature.4. Some noise can be expected, but will
go away as vehicle warms. Replace
pump if noise is excessive.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose clamp on power steering
fluid return hose.1. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
2. Missing O-Ring on power steering
hose connection.2. Inspect connection and replace O-Ring
as required.
3. Low power steering fluid level. 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
proper level and check for leaks.
4. Loose clamp on fluid supply hose. 4. Tighten or replace hose clamp.
19 - 4 STEERINGRS
STEERING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1407 of 2177

WARNING: THE AIR BAG SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE,
COMPLEX ELECTRO-MECHANICAL UNIT. BEFORE
ATTEMPTING TO DIAGNOSE, REMOVE OR INSTALL
THE AIR BAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS YOU MUST
FIRST DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY
NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE. THEN WAIT TWO
MINUTES FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DIS-
CHARGE. FAILURE TO DO SO COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF THE AIR BAG AND
POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY. THE FASTENERS,
SCREWS, AND BOLTS, ORIGINALLY USED FOR
THE AIR BAG COMPONENTS, HAVE SPECIAL
COATINGS AND ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED
FOR THE AIR BAG SYSTEM. THEY MUST NEVER
BE REPLACED WITH ANY SUBSTITUTES. ANYTIME
A NEW FASTENER IS NEEDED, REPLACE WITH
THE CORRECT FASTENERS PROVIDED IN THE
SERVICE PACKAGE OR FASTENERS LISTED IN
THE PARTS BOOKS.
WARNING: SAFETY GOGGLES SHOULD BE WORN
AT ALL TIMES WHEN WORKING ON STEERING
COLUMNS.
CAUTION: Disconnect negative (ground) cable from
the battery before servicing any column compo-
nent.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to remove the pivot pins
to disassemble the tilting mechanism. Damage will
occur.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
COLUMN
For diagnosis of conditions relating to the steering
column (Refer to 19 - STEERING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING) and (Refer to 19 - STEERING - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
REMOVAL
NOTE: Before proceeding, (Refer to 19 - STEERING/
COLUMN - WARNING).
(1) Make sure the front wheels of the vehicle are
in the STRAIGHT AHEAD position before beginning
the column removal procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative (ground) cable from the
battery and isolate cable from battery terminal.
(3) Remove the lower shroud (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD - REMOV-
AL).
(4) Remove the traction off switch.
(5) Remove the upper shroud.
(6) Remove the cluster trim bezel (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove the knee blocker (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN
OPENING COVER - REMOVAL).
(8) Remove the parking brake handle link.
(9) Remove the knee blocker reinforcement (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/KNEE
BLOCKER - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the airbag (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/RESTRAINTS/DRIVER AIRBAG - REMOVAL).
(11) Remove the steering wheel retaining nut.
(12) Remove the vibration damper weight.
(13) Remove the steering wheel (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/STEERING WHEEL -
REMOVAL). (Fig. 3)
(14) Disconnect the wiring harness connectors
from the clockspring, multi-function switch, halo
lamp, SKIM module, ignition switch and BTSI sole-
noid.
(15) Disconnect the shift cable at the lever. (Fig. 4)
(16) Remove the pinch side clip, then remove the
cable from the bracket on the column.
(17) Remove the pinch bolt coupling. (Fig. 5)
(18) Loosen the two lower mounting nuts.
(19) Remove the two upper mounting nuts
(20) Remove the steering column.
1 - CLOCKSPRING WIRING
2 - STEERING WHEEL
3 - UPPER SHROUD
4 - FIXED SHROUD
5 - SCREW
6 - STEERING COLUMN MOUNTING PLATE
7 - NUT
8 - DASH PANEL STEERING COLUMN MOUNTING BRACKET
9 - STUDS (4)
10 - STEERING COLUMN LOCKING PIN
11 - NUT/WASHER ASSEMBLY
12 - STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY
13 - LOWER SHROUD
14 - SCREWS
15 - STEERING WHEEL RETAINING NUT16 - STEERING WHEEL DAMPER
17 - CLOCKSPRING
18 - SCREW
19 - MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH
20 - PINCH BOLT
21 - STEERING COLUMN COUPLER
22 - PINCH BOLT RETAINING PIN
23 - DASH PANEL
24 - SILENCER SHELL
25 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT SHIELD AND SEAL
26 - INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
27 - ROLL PIN
28 - POWER STEERING GEAR
29 - FRONT SUSPENSION CRADLE/CROSSMEMBER
19 - 12 COLUMNRS
COLUMN (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com