2003 CHRYSLER CARAVAN wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 1729 of 2177

white letters. To remove the protective coating, apply
warm water and let it soak for a few minutes. After-
wards, scrub the coating away with a soft bristle
brush. Steam cleaning may also be used to remove
the coating.
CAUTION: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-
based solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL
Original equipment wheels are designed for proper
operation at all loads up to the specified maximum
vehicle capacity.
All models use either steel or aluminum drop-cen-
ter wheels. Every wheel has raised sections between
the rim flanges and rim drop well called safety
humps (Fig. 28). Initial inflation of the tires forces
the bead over these raised sections. In case of air
loss, the safety humps hold the tire in position on the
wheel until the vehicle can be brought to a safe stop.
Cast aluminum wheels require special balance
weights to fit on the flange of the rim (Fig. 29).
When wheel alignment is necessary on a vehicle
with cast aluminum wheels, special wheel clamps are
required to avoid damage to the wheel's finish.
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
wheel applications and must be replaced with equiv-
alent parts.
All aluminum wheels have wheel mounting (lug)
nuts with an enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is
necessary to ensure proper retention of the wheels.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive runout
²Dents, cracks or irregular bends
²Damaged wheel stud (lug) holes
²Air Leaks
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged, an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they must be equivalent in load
carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset, pilot
hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the same
as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE.
WARNING: REPLACEMENT WITH USED WHEELS IS
NOT RECOMMENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF
THE WHEEL MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREAT-
MENT OR VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD
FAIL WITHOUT WARNING.
CLEANING - ALUMINUM WHEEL CARE
Chrome plated and painted aluminum wheels
should be cleaned regularly using mild soap and
water to maintain their luster and to prevent corro-
sion.
Fig. 28 Safety Rim
1 - TIRE
2 - WELL
3 - SAFETY HUMPS
4 - FLANGE
Fig. 29 Styled Aluminum Wheel Weight
1 - TIRE
2 - WHEEL
3 - STYLED WHEEL WEIGHT
22 - 18 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1730 of 2177

Care must be taken in the selection of tire and
wheel cleaning chemicals and equipment to prevent
damage to the wheels. Any of the ªDO NOT USEº
items listed below WILL damage chrome plated and
painted aluminum wheels.
DO NOT USE:
²any abrasive metal cleaner
²any abrasive cleaning pad or brush
²any cleaner that contains an acid (this will
immediately react with and discolor the chromium
surface)
²chrome polish (unless it is buffed off immedi-
ately after application)
²oven cleaner
²a car wash that uses carbide-tipped wheel clean-
ing brushes
SPECIFICATIONS
WHEEL
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Wheel Mounting (Lug)
Nut Hex Size19 mm
Wheel Mounting Stud
SizeM12 x 1.5 mm
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
TPM Sensor Mounting Nut 4 Ð 35
Wheel Mounting (Lug ) Nut 135 100 Ð
WHEEL COVER
DESCRIPTION
This vehicle uses a bolt-on type wheel cover (Fig.
30).
This bolt-on wheel cover cannot be removed from
the wheel until three of the five wheel mounting nuts
shown are removed (Fig. 30). The bolt-on wheel cover
can then be removed with the remaining two wheel
nuts tightened in place.
REMOVAL
(1) Noting the location of the valve stem in rela-
tionship to the wheel mounting nuts, remove the
three wheel mounting nuts securing the wheel cover
to the wheel and hub (Fig. 30).
CAUTION: When removing the wheel cover, do not
pry the wheel cover from the wheel. This can resultin damage to the wheel cover. The wheel cover is
removed by pulling it off the wheel by hand.
(2) Grasp the wheel cover at the edges in line with
the remaining installed wheel nuts and pull straight
outward from the wheel. This will pop the wheel
cover retaining tabs over the two remaining wheel
nuts, removing the wheel cover from the wheel.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Wheel mounting nuts must be installed on
the studs as shown to allow installation of the
wheel cover (Fig. 31).
Fig. 30 Nuts Securing Wheel Cover
1 - VALVE STEM
2 - BOLT-ON WHEEL COVER
3 - NUTS SECURING WHEEL COVER
Fig. 31 Two Wheel Mounting Nuts Installed
1 - WHEEL
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - HUB PILOT
4 - NUTS
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-19
WHEELS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1731 of 2177

(1) Place the wheel cover on the wheel in the fol-
lowing fashion:
(a) Align the valve notch in the wheel cover with
the valve stem on the wheel.
(b) At the same time, align the two holes in the
wheel cover having the retaining tabs with the two
installed wheel nuts (Fig. 32).
(c) Press in on center of wheel cover until wheel
cover retaining tabs push past and engage rear of
previously installed wheel mounting nuts (Fig. 32).
This will hold the wheel cover in place.
(2) Install andlightly tightenthe three remain-
ing wheel mounting nuts, securing the wheel cover in
place (Fig. 30).
(3) Tighten all five wheel mounting nuts in the
proper sequence (Fig. 33). Tighten wheel nuts to a
torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS -
FRONT
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If a wheel mounting stud needs to be
replaced in the hub and bearing assembly, the
studs MUST NOT be hammered out of the hub
flange. If a stud is removed by hammering it out of
the bearing flange, damage to the hub and bearing
assembly will occur leading to premature bearing
failure.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove the front wheel and tire assembly from
the vehicle.
(3) Remove the two adapter mounting bolts secur-
ing both the disc brake caliper adapter to the steer-
ing knuckle (Fig. 34).
(4) Remove the disc brake caliper and adapter as
an assembly from the steering knuckle (Fig. 34).
Hang the assembly out of the way using wire or a
bungee cord. Use care not to overextend the brake
hose when doing this.
(5) Remove brake rotor from hub by pulling it
straight off wheel mounting studs (Fig. 34).
(6) On the wheel mounting stud to be removed,
install a wheel mounting (lug) nut far enough so the
threads on the stud are even with end of nut. Install
Fig. 32 Wheel Cover Installation Over Two Nuts
1 - RETAINING TABS
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - BOLT-ON WHEEL COVER
Fig. 33 Nut Tightening Sequence
Fig. 34 Front Brake Mounting
1 - BRAKE ROTOR
2 - HUB AND BEARING
3 - STEERING KNUCKLE
4 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - BRAKE CALIPER
6 - ADAPTER
7 - CLIP
22 - 20 TIRES/WHEELSRS
WHEEL COVER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1732 of 2177

Remover, Special Tool C-4150A on hub and bearing
assembly flange and wheel stud (Fig. 35).
(7) Tighten down on special tool, pushing wheel
stud out of the hub flange. When shoulder of wheel
stud is past flange, remove special tool from hub and
bearing. Remove nut from stud and remove stud
from hub flange.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install replacement wheel stud into flange of
hub and bearing assembly. Install washers on wheel
stud, then install a wheel mounting (lug) nut on stud
with flat side of lug nut against washers as shown
(Fig. 36).
(2) Tighten the nut, pulling the wheel stud into
the flange of the hub and bearing. When the head of
the stud is fully seated against the rear of the hub
flange, remove nut and washers from stud.
(3) Install the brake rotor back on the hub and
bearing (Fig. 34).
(4) Install brake caliper and adapter back over
brake rotor aligning adapter with mounting holes on
steering knuckle (Fig. 34).
(5) Install the two adapter mounting bolts securing
the adapter to the steering knuckle. Tighten the
mounting bolts to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install wheel and tire assembly on vehicle.
Tighten the wheel mounting lug nuts in proper
sequence until all nuts are torqued to half specifica-
tion, then repeat the tightening sequence to the full
specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle to the ground.
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS -
REAR
REMOVAL
CAUTION: If a wheel attaching stud needs to be
replaced in the hub and bearing assembly the studs
MUST NOT be hammered out of the hub flange. If a
stud is removed by hammering it out of the bearing
flange, damage to the hub and bearing assembly
will occur leading to premature hub and bearing
failure.
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
(2) Remove the rear wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the brake drum or disc brake caliper
and rotor. Refer to Brakes.
(4) Install a lug nut on the wheel stud to be
removed from the hub and bearing assembly (Fig. 37)
so the threads on stud are even with end of lug nut.
Install Remover, Special Tool C-4150A on hub and
bearing assembly flange and wheel stud (Fig. 37).
(5) Tightening down on special tool will push
wheel stud out of the hub and bearing assembly
flange.
(6) Remove lug nut from stud and remove wheel
stud from flange.
Fig. 35 Wheel Stud Removal (Typical)
1 - WHEEL MOUNTING (LUG) NUT
2 - HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
3 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4150A
4 - STEERING KNUCKLE
5 - WHEEL STUD
Fig. 36 Installing Wheel Stud (Typical)
1 - WASHERS
2 - HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
3 - WHEEL MOUNTING (LUG) NUT
4 - STEERING KNUCKLE
RSTIRES/WHEELS22-21
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - FRONT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1733 of 2177

INSTALLATION
(1) Install replacement wheel stud into flange of
hub and bearing assembly. Install washers on wheel
stud, then install a wheel lug nut on stud with flat
side of lug nut against washers (Fig. 38).
(2) Tighten the wheel lug nut, pulling the wheel
stud into the flange of the hub and bearing assembly.
When the head of the stud is fully seated against the
bearing flange, remove lug nut and washers from
wheel stud.(3) Install the brake drum or disc brake rotor and
caliper on the hub and bearing assembly.
(4) Install wheel and tire assembly on vehicle.
Tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in proper
sequence until all nuts are torqued to half specifica-
tion. Then repeat the tightening sequence to the full
specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(5) Lower vehicle to the ground.
Fig. 37 Wheel Stud Removal From Hub And Bearing
1 - HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
2 - WHEEL MOUNTING (LUG) NUT
3 - WHEEL STUD
4 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4150A
Fig. 38 Wheel Stud Installation
1 - WHEEL MOUNTING (LUG) NUT
2 - HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
3 - WASHERS
4 - WHEEL STUD
22 - 22 TIRES/WHEELSRS
WHEEL MOUNTING STUDS - REAR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1737 of 2177
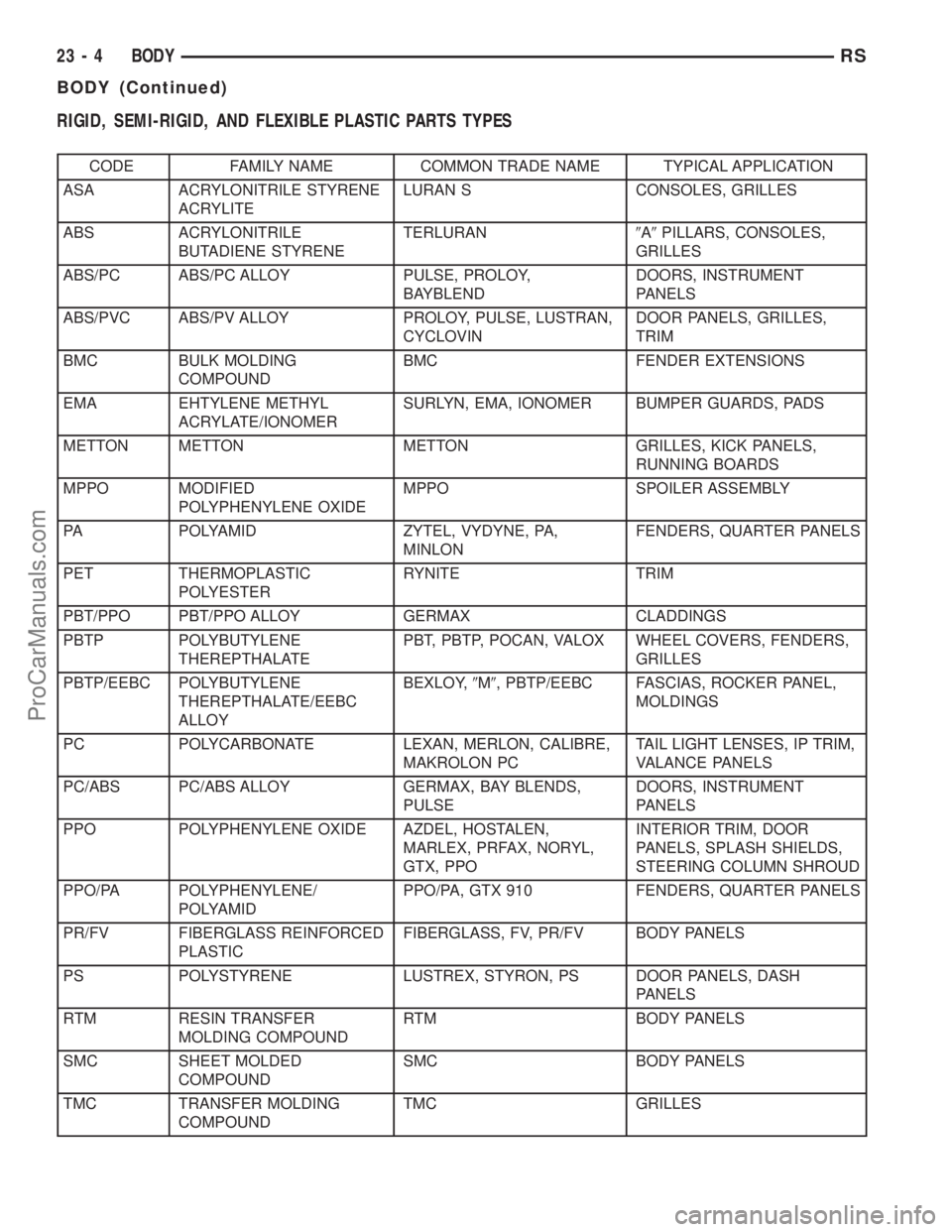
RIGID, SEMI-RIGID, AND FLEXIBLE PLASTIC PARTS TYPES
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
ASA ACRYLONITRILE STYRENE
ACRYLITELURAN S CONSOLES, GRILLES
ABS ACRYLONITRILE
BUTADIENE STYRENETERLURAN9A9PILLARS, CONSOLES,
GRILLES
ABS/PC ABS/PC ALLOY PULSE, PROLOY,
BAYBLENDDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
ABS/PVC ABS/PV ALLOY PROLOY, PULSE, LUSTRAN,
CYCLOVINDOOR PANELS, GRILLES,
TRIM
BMC BULK MOLDING
COMPOUNDBMC FENDER EXTENSIONS
EMA EHTYLENE METHYL
ACRYLATE/IONOMERSURLYN, EMA, IONOMER BUMPER GUARDS, PADS
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER PANELS
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,9M9, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VALANCE PANELS
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER PANELS
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PANELS
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
23 - 4 BODYRS
BODY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1738 of 2177

CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
MPU FOAM POLYURETHANE MPU SPOILERS
PE POLYETHYLENE ALATHON, DYLAN,
LUPOLEN, MARLEX-
PP POLYPROPYLENE
(BLENDS)NORYL, AZDEL, MARLOX,
DYLON, PRAVEXINNER FENDER, SPOILERS,
KICK PANELS
PP/EPDM PP/EPDM ALLOY PP/EPDM SPOILERS, GRILLES
PUR POLYURETHANE COLONELS, PUR, PU FASCIAS, BUMPERS
PUR/PC PUR/PC ALLOY TEXIN BUMPERS
PVC POLYVINYL CHLORIDE APEX, GEON, VINYLITE BODY MOLDINGS, WIRE
INSULATION, STEERING
WHEELS
RIM REACTION INJECTED
MOLDED POLYURETHANERIM, BAYFLEX FRONT FASCIAS, MODULAR
WINDOWS
RRIM REINFORCED REACTION
INJECTED MOLDEDPUR, RRIM FASCIAS, BODY PANELS,
BODY TRIMS
TPE THERMO POLYETHYLENE TPE, HYTREL, BEXLOY-V FASCIAS, BUMPERS,
CLADDINGS
TPO THERMOPOLYOLEFIN POLYTROPE, RENFLEX,
SANTOPRENE, VISAFLEX,
ETA, APEX, TPO, SHIELDS,
CLADDINGSBUMPERS, END CAPS,
TELCAR, RUBBER, STRIPS,
SIGHT, INTERIOR B POST
TPP THERMO-
POLYPROPYLENETPP BUMPERS
TPU THERMOPOLYURETHANE,
POLYESTERTPU, HYTREL, TEXIN,
ESTANEBUMPERS, BODY SIDE,
MOLDINGS, FENDERS,
FASCIAS
RSBODY23-5
BODY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1740 of 2177

²Panel repair for both flexible and rigid panels
are basically the same. The primary difference
between flexible panel repair and rigid panel repair
is in the adhesive materials used (Fig. 5).
²The technician should first decide what needs to
be done when working on any type of body panel.
One should determine if it is possible to return the
damage part to its original strength and appearance
without exceeding the value of the replacement part.
²When plastic repairs are required, it is recom-
mended that the part be left on the vehicle when
every possible. That will save time, and the panel
will remain stationary during the repair. Misalign-
ment can cause stress in the repair areas and can
result in future failure.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Composite materials can mask the severity of an
accident. Adhesive bond lines, interior structure of
the doors, and steel structures need to be inspected
carefully to get a true damage assessment. Close
inspection may require partial removal of interior
trim or inner panels.
Identify the type of repair: Puncture or Crack -
Damage that has penetrated completely through the
panel. Damage is confined to one general area; a
panel section is not required. However, a backer
panel, open fiberglass tape, or matted material must
be bonded from behind (Fig. 7) (Fig. 6).
PANEL SURFACE PREPARATION
If a body panel has been punctured, cracked, or
crushed, the damaged area must be removed from
the panel to achieve a successful repair. All spider
web cracks leading away from a damaged area must
be stopped or removed. To stop a running crack in a
panel, drilla6mm(0.250 in.) hole at the end of the
crack farthest away from the damage. If spider web
cracks can not be stopped, the panel would require
replacement. The surfaces around the damaged area
should be stripped of paint and freed from wax and
oil. Scuff surfaces around repair area with 360 grit
wet/dry sandpaper, or equivalent, to assure adhesion
of repair materials.
PATCHING PANELS
An panel that has extensive puncture type damage
can be repaired by cutting out the damaged material
(Fig. 7). Use a suitable reciprocating saw or cut off
wheel to remove the section of the panel that is dam-
aged. The piece cut out can be used as a template to
shape the new patch. It is not necessary to have
access to the back of the panel to install a patch.
Bevel edges of cutout at 20 degrees to expose a larger
bonding area on the outer side. This will allow for an
increased reinforcement areas.
PANEL PATCH FABRICATIONS
A patch can be fabricated from any rigid fiberglass
panel that has comparable contour with the repair
area. Lift gates and fenders can be used to supply
patch material. If existing material is not available
or compatible, a patch can be constructed with adhe-
sive and reinforcement mesh (dry wall tape). Perform
the following operation if required:
Fig. 4 BEVELING ANGLE - 20 DEGREE
Fig. 5 FIBERGLASS TAPE
Fig. 6 DAMAGE COMPONENT
1 - PUNCTURE
RSBODY23-7
BODY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com