2003 CHEVROLET S10 change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 215 of 432

·Check your mirrors, glance over your shoulder, and
start your left lane change signal before moving out
of the right lane to pass. When you are far
enough ahead of the passed vehicle to see its front
in your inside mirror, activate your right lane
change signal and move back into the right lane.
(Remember that your right outside mirror is convex.
The vehicle you just passed may seem to be
farther away from you than it really is.)
·Try not to pass more than one vehicle at a time on
two-lane roads. Reconsider before passing the
next vehicle.
·Don't overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly.
Even though the brake lamps are not ¯ashing, it
may be slowing down or starting to turn.
·If you're being passed, make it easy for the
following driver to get ahead of you. Perhaps you
can ease a little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let's review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes,
steering and acceleration) don't have enough friction
where the tires meet the road to do what the driver has
asked.
In any emergency, don't give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not
ªoverdrivingº those conditions. But skids are always
possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle's
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren't rolling. In the steering or cornering skid, too much
speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and lose
cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too much
throttle causes the driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.
4-13
Page 219 of 432

Getting Familiar with Off-Road Driving
It's a good idea to practice in an area that's safe
and close to home before you go into the wilderness.
Off-road driving does require some new and different
skills. Here's what we mean.
Tune your senses to different kinds of signals. Your
eyes, for example, need to constantly sweep the terrain
for unexpected obstacles. Your ears need to listen
for unusual tire or engine sounds. With your arms,
hands, feet and body, you'll need to respond to
vibrations and vehicle bounce.Controlling your vehicle is the key to successful off-road
driving. One of the best ways to control your vehicle
is to control your speed. Here are some things to keep
in mind. At higher speeds:
·you approach things faster and you have less time
to scan the terrain for obstacles.
·you have less time to react.
·you have more vehicle bounce when you drive over
obstacles.
·you'll need more distance for braking, especially
since you're on an unpaved surface.
{CAUTION:
When you are driving off-road, bouncing and
quick changes in direction can easily throw
you out of position. This could cause you to
lose control and crash. So, whether you're
driving on or off the road, you and your
passengers should wear safety belts.
4-17
Page 220 of 432

Scanning the Terrain
Off-road driving can take you over many different kinds
of terrain. You need to be familiar with the terrain
and its many different features. Here are some things to
consider.
Surface Conditions:Off-roading can take you over
hard-packed dirt, gravel, rocks, grass, sand, mud, snow
or ice. Each of these surfaces affects the steering,
acceleration and braking of your vehicle in different
ways. Depending upon the kind of surface you are on,
you may experience slipping, sliding, wheel spinning,
delayed acceleration, poor traction and longer braking
distances.
Surface Obstacles:Unseen or hidden obstacles can
be hazardous. A rock, log, hole, rut or bump can startle
you if you're not prepared for them. Often these
obstacles are hidden by grass, bushes, snow or even
the rise and fall of the terrain itself. Here are some
things to consider:
·Is the path ahead clear?
·Will the surface texture change abruptly up ahead?
·Does the travel take you uphill or downhill?
(There's more discussion of these subjects later.)
·Will you have to stop suddenly or change direction
quickly?When you drive over obstacles or rough terrain, keep a
®rm grip on the steering wheel. Ruts, troughs or
other surface features can jerk the wheel out of your
hands if you're not prepared.
When you drive over bumps, rocks, or other obstacles,
your wheels can leave the ground. If this happens,
even with one or two wheels, you can't control
the vehicle as well or at all.
Because you will be on an unpaved surface, it's
especially important to avoid sudden acceleration,
sudden turns or sudden braking.
In a way, off-road driving requires a different kind of
alertness from driving on paved roads and highways.
There are no road signs, posted speed limits or
signal lights. You have to use your own good judgment
about what is safe and what isn't.
Drinking and driving can be very dangerous on any
road. And this is certainly true for off-road driving. At the
very time you need special alertness and driving
skills, your re¯exes, perceptions and judgment can be
affected by even a small amount of alcohol. You
could have a serious Ð or even fatal Ð accident if you
drink and drive or ride with a driver who has been
drinking. See
Drunken Driving on page 4-3.
4-18
Page 256 of 432

Towing a Trailer
{CAUTION:
If you don't use the correct equipment and
drive properly, you can lose control when you
pull a trailer. For example, if the trailer is too
heavy, the brakes may not work well -- or even
at all. You and your passengers could be
seriously injured. Pull a trailer only if you have
followed all the steps in this section. Ask your
dealer for advice and information about towing
a trailer with your vehicle.
Notice:Pulling a trailer improperly can damage
your vehicle and result in costly repairs not covered
by your warranty. To pull a trailer correctly, follow
the advice in this part, and see your dealer for
important information about towing a trailer with
your vehicle. Additional rear axle maintenance
is required for a vehicle used to tow a trailer. See
ªScheduled Maintenance Servicesº in the Index.Your vehicle may be able to tow a trailer. To identify
what the vehicle trailering capacity is for your vehicle,
you should read the information in
ªWeight of the Trailerºthat appears later in this section.
If yours was built with trailering options, as many are,
it's ready for heavier trailers. But trailering is different
than just driving your vehicle by itself. Trailering means
changes in handling, durability and fuel economy.
Successful, safe trailering takes correct equipment, and
it has to be used properly.
That's the reason for this part. In it are many time-tested,
important trailering tips and safety rules. Many of
these are important for your safety and that of your
passengers. So please read this section carefully before
you pull a trailer.
4-54
Page 288 of 432

Automatic Transmission Fluid
When to Check and Change
A good time to check your automatic transmission ¯uid
level is when the engine oil is changed.
Change both the ¯uid and ®lter every 15,000 miles
(25 000 km) if the vehicle is mainly driven under one or
more of these conditions:
·In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature
regularly reaches 90ÉF (32ÉC) or higher.
·In hilly or mountainous terrain.
·When doing frequent trailer towing.
·Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery
service.
If you do not use your vehicle under any of these
conditions, change the ¯uid and ®lter every
50,000 miles (83 000 km).
See
Part A: Scheduled Maintenance Services on
page 6-4.
How to Check
Because this operation can be a little difficult, you may
choose to have this done at the dealership service
department.
If you do it yourself, be sure to follow all the instructions
here, or you could get a false reading on the dipstick.
Notice:Too much or too little ¯uid can damage
your transmission. Too much can mean that some
of the ¯uid could come out and fall on hot engine
part or exhaust system parts, starting a ®re.
Too little ¯uid could cause the transmission to
overheat. Be sure to get an accurate reading if you
check your transmission ¯uid.
Wait at least 30 minutes before checking the
transmission ¯uid level if you have been driving:
·When outside temperatures are above 90ÉF (32ÉC).
·At high speed for quite a while.
·In heavy traffic±especially in hot weather.
·While pulling a trailer.
5-22
Page 291 of 432

Manual Transmission Fluid
When to Check
A good time to have it checked is when the engine oil is
changed. However, the ¯uid in your manual transmission
doesn't require changing.
How to Check
Because this operation can be a little difficult, you may
choose to have this done at your GM dealership
service department.
If you do it yourself, be sure to follow all the instructions
here, or you could get a false reading.
Notice:Too much or too little ¯uid can damage
your transmission. Too much can mean that some
of the ¯uid could come out and fall on hot engine
part or exhaust system parts, starting a ®re.
Too little ¯uid could cause the transmission to
overheat. Be sure to get an accurate reading if you
check your transmission ¯uid.
Check the ¯uid level only when your engine is off, the
vehicle is parked on a level place and the transmission
is cool enough for you to rest your ®ngers on the
transmission case.Then, follow these steps:
1. Remove the ®ller plug.
2. Check that the lubricant level is up to the bottom of
the ®ller plug hole.
3. If the ¯uid level is good, install the plug and be sure
it is fully seated. If the ¯uid level is low, add more
¯uid as described in the next steps.
5-25
Page 311 of 432

Brake Adjustment
Every time you make a brake stop, your disc brakes
adjust for wear.
If you don't have four-wheel drive and your brake pedal
goes down farther than normal, your rear drum
brakes may need adjustment. Adjust them by backing
up and ®rmly applying the brakes a few times.
Replacing Brake System Parts
The braking system on a vehicle is complex. Its many
parts have to be of top quality and work well together if
the vehicle is to have really good braking. Your vehicle
was designed and tested with top-quality GM brake parts.
When you replace parts of your braking system Ð for
example, when your brake linings wear down and you
need new ones put in Ð be sure you get new approved
GM replacement parts. If you don't, your brakes may no
longer work properly. For example, if someone puts in
brake linings that are wrong for your vehicle, the balance
between your front and rear brakes can change Ð for the
worse. The braking performance you've come to expect
can change in many other ways if someone puts in the
wrong replacement brake parts.
Battery
Your new vehicle comes with a maintenance free
ACDelcožbattery. When it's time for a new battery, get
one that has the replacement number shown on the
original battery's label. We recommend an ACDelco
ž
battery. SeeEngine Compartment Overview on
page 5-12for battery location.
Warning:Battery posts, terminals and related
accessories contain lead and lead compounds,
chemicals known to the State of California to cause
cancer and reproductive harm. Wash hands after
handling.
5-45
Page 331 of 432
{CAUTION:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to
which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later, if you need to, to
get all the rust or dirt off. See ªChanging a Flat
Tireº in the Index.
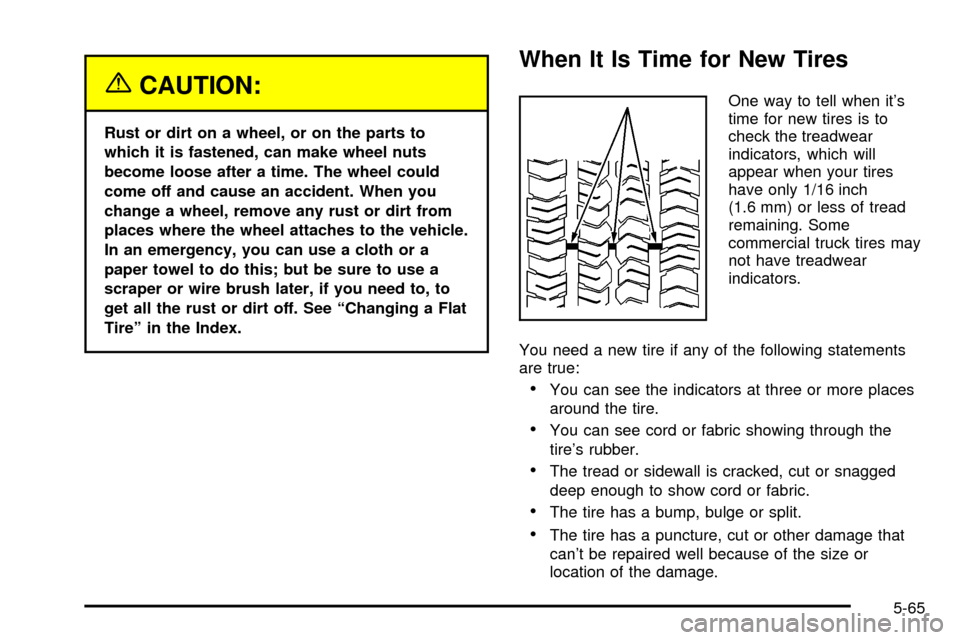
When It Is Time for New Tires
One way to tell when it's
time for new tires is to
check the treadwear
indicators, which will
appear when your tires
have only 1/16 inch
(1.6 mm) or less of tread
remaining. Some
commercial truck tires may
not have treadwear
indicators.
You need a new tire if any of the following statements
are true:
·You can see the indicators at three or more places
around the tire.
·You can see cord or fabric showing through the
tire's rubber.
·The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged
deep enough to show cord or fabric.
·The tire has a bump, bulge or split.
·The tire has a puncture, cut or other damage that
can't be repaired well because of the size or
location of the damage.
5-65