2002 NISSAN TERRANO engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 669 of 1767
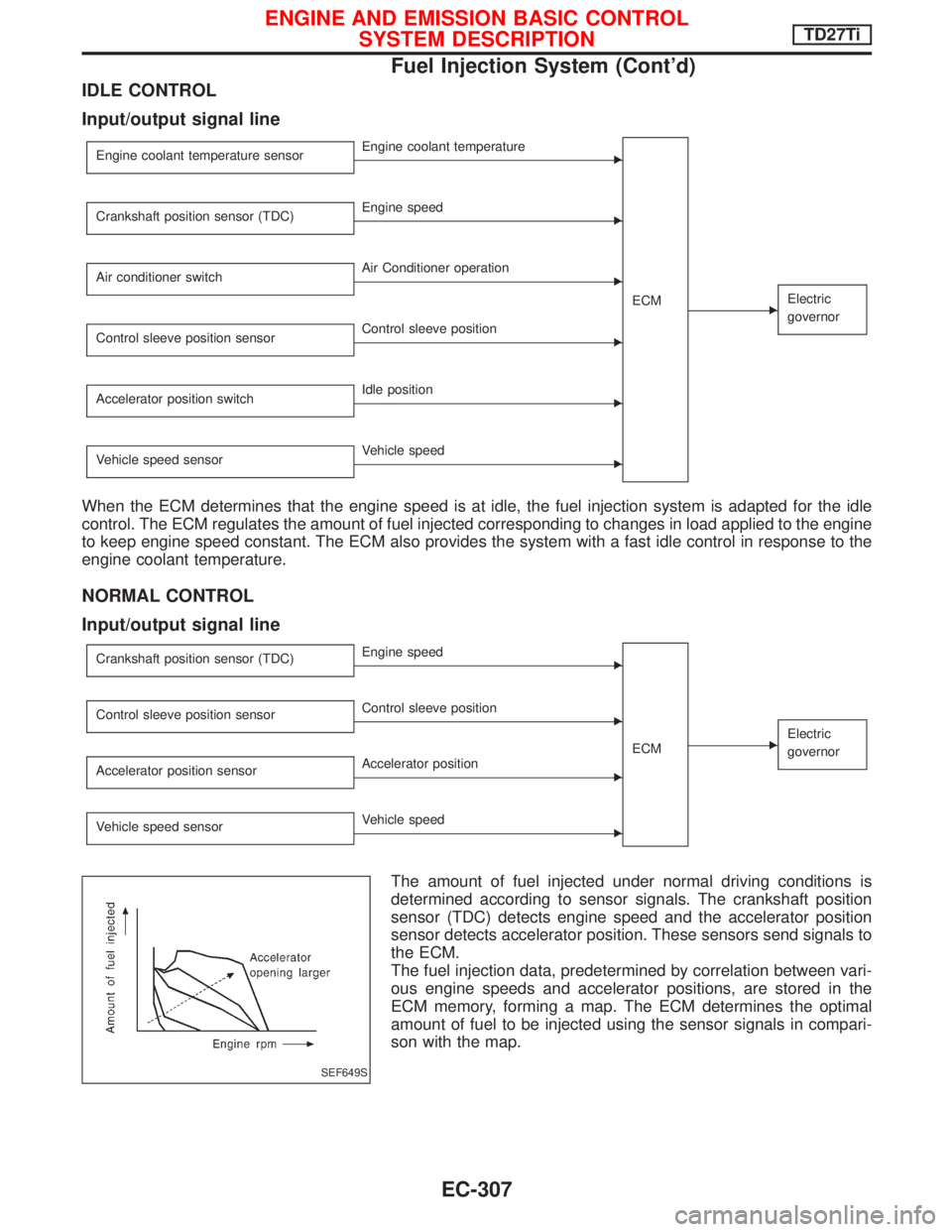
IDLE CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Engine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
ECM
EElectric
governor
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
Air conditioner switch
EAir Conditioner operation
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
Accelerator position switch
EIdle position
Vehicle speed sensor
EVehicle speed
When the ECM determines that the engine speed is at idle, the fuel injection system is adapted for the idle
control. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected corresponding to changes in load applied to the engine
to keep engine speed constant. The ECM also provides the system with a fast idle control in response to the
engine coolant temperature.
NORMAL CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
EElectric
governor
Control sleeve position sensorEControl sleeve position
Accelerator position sensor
EAccelerator position
Vehicle speed sensor
EVehicle speed
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is
determined according to sensor signals. The crankshaft position
sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position
sensor detects accelerator position. These sensors send signals to
the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between vari-
ous engine speeds and accelerator positions, are stored in the
ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the optimal
amount of fuel to be injected using the sensor signals in compari-
son with the map.
SEF649S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Fuel Injection System (Cont'd)
EC-307
Page 670 of 1767

FUEL TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION
Input/output signal line
Fuel temperature sensorEFuel temperature
ECM
EElectric
governorCrankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
The amount of fuel leaking at or around high-pressure parts inside the fuel injection pump varies with the fuel
temperature and engine speed. This will result in a difference between the target amount of fuel injected and
the actual amount. The ECM compensates for the actual amount depending on the signal obtained from the
fuel temperature sensor.
DECELERATION CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Accelerator position sensorEAccelerator position
ECM
EElectric
governor
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
The ECM cuts power supply delivery to the electric governor during deceleration for better fuel efficiency. The
ECM determines the time of deceleration according to signals from the accelerator position sensor and crank-
shaft position sensor (TDC).
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Fuel Injection System (Cont'd)
EC-308
Page 671 of 1767
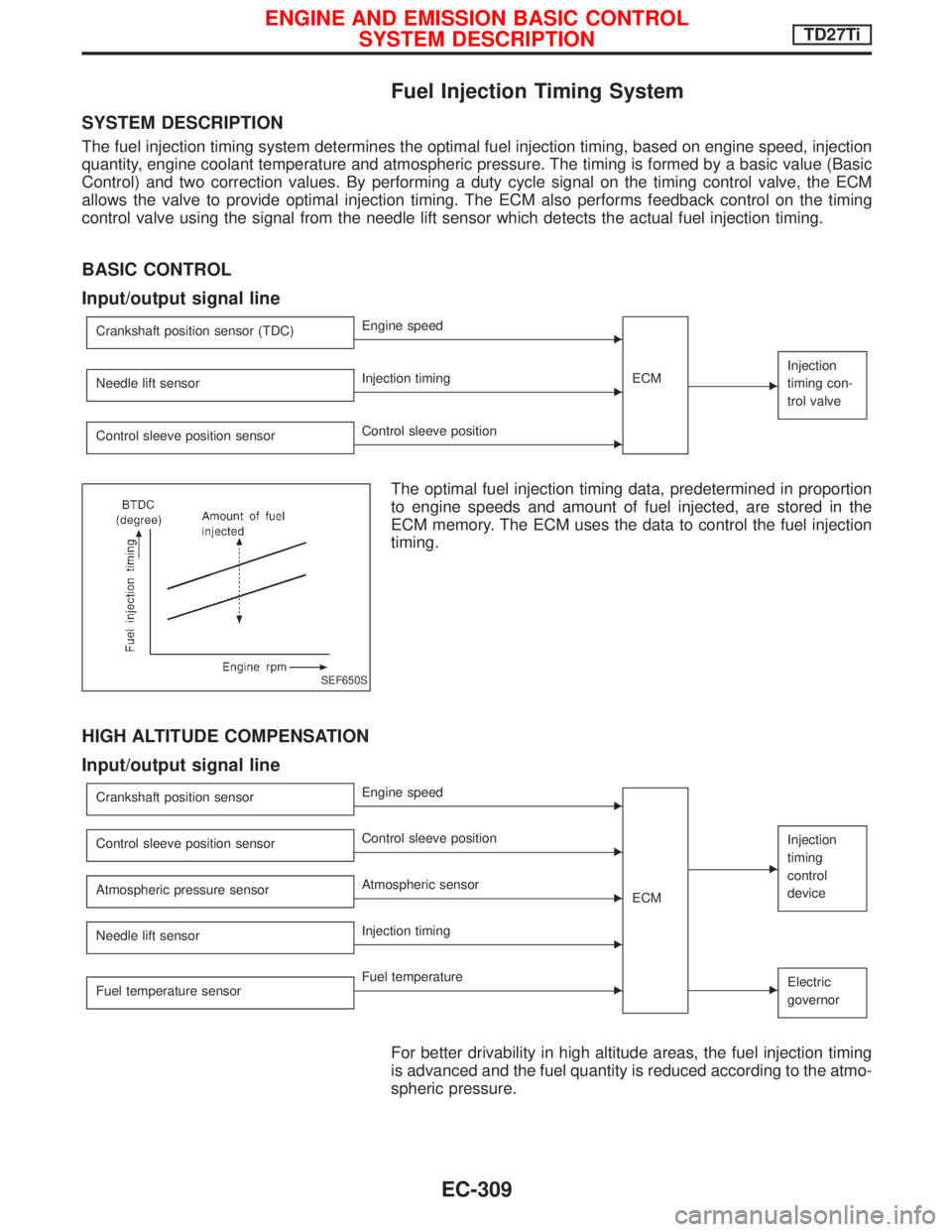
Fuel Injection Timing System
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The fuel injection timing system determines the optimal fuel injection timing, based on engine speed, injection
quantity, engine coolant temperature and atmospheric pressure. The timing is formed by a basic value (Basic
Control) and two correction values. By performing a duty cycle signal on the timing control valve, the ECM
allows the valve to provide optimal injection timing. The ECM also performs feedback control on the timing
control valve using the signal from the needle lift sensor which detects the actual fuel injection timing.
BASIC CONTROL
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
E
Injection
timing con-
trol valve
Needle lift sensorEInjection timing
Control sleeve position sensor
EControl sleeve position
The optimal fuel injection timing data, predetermined in proportion
to engine speeds and amount of fuel injected, are stored in the
ECM memory. The ECM uses the data to control the fuel injection
timing.
HIGH ALTITUDE COMPENSATION
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensorEEngine speed
ECM
E
Injection
timing
control
deviceControl sleeve position sensorEControl sleeve position
Atmospheric pressure sensor
EAtmospheric sensor
Needle lift sensor
EInjection timing
Fuel temperature sensor
EFuel temperatureEElectric
governor
For better drivability in high altitude areas, the fuel injection timing
is advanced and the fuel quantity is reduced according to the atmo-
spheric pressure.
SEF650S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
EC-309
Page 672 of 1767
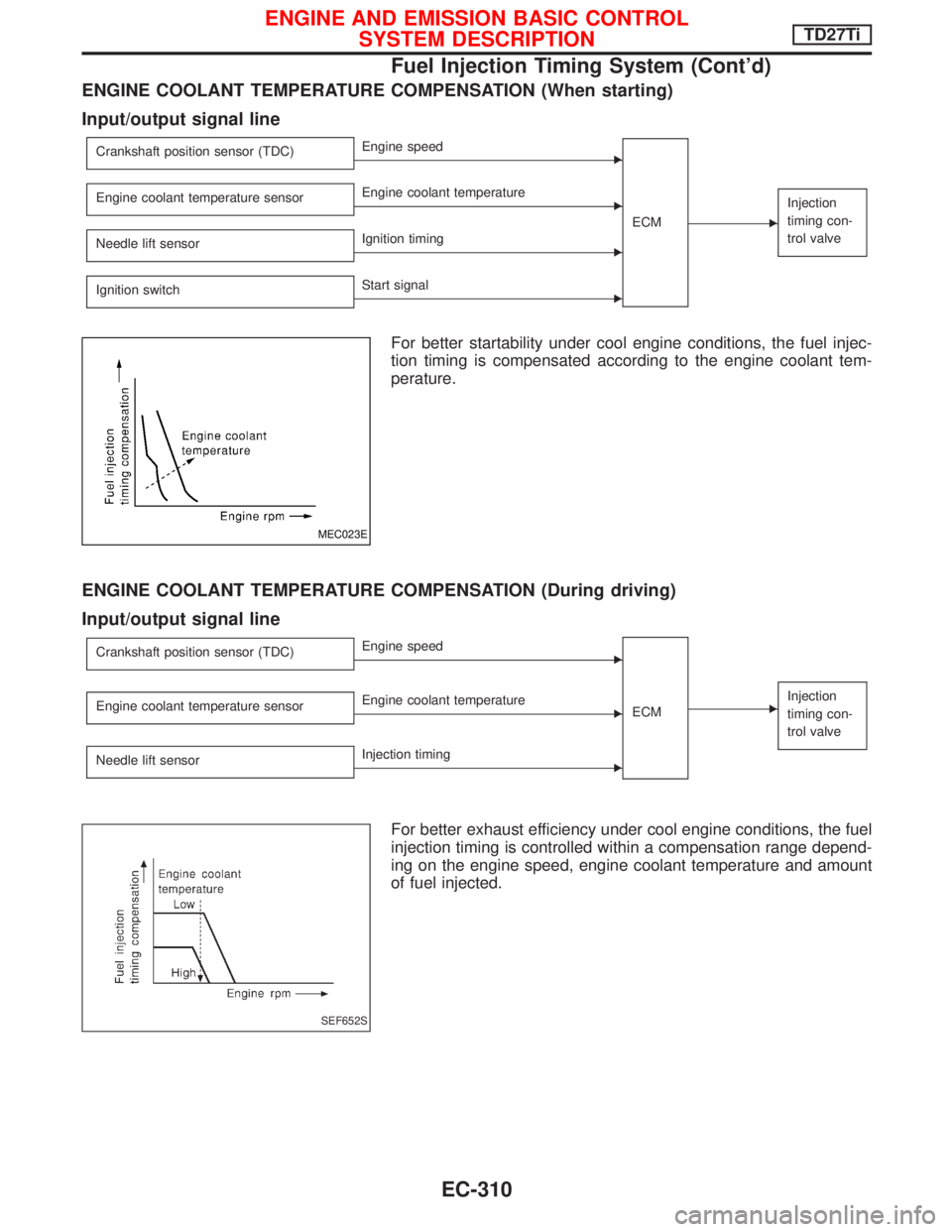
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION (When starting)
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
E
Injection
timing con-
trol valveEngine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
Needle lift sensor
EIgnition timing
Ignition switch
EStart signal
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the fuel injec-
tion timing is compensated according to the engine coolant tem-
perature.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION (During driving)
Input/output signal line
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECM
EInjection
timing con-
trol valveEngine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
Needle lift sensor
EInjection timing
For better exhaust efficiency under cool engine conditions, the fuel
injection timing is controlled within a compensation range depend-
ing on the engine speed, engine coolant temperature and amount
of fuel injected.
MEC023E
SEF652S
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Fuel Injection Timing System (Cont'd)
EC-310
Page 673 of 1767
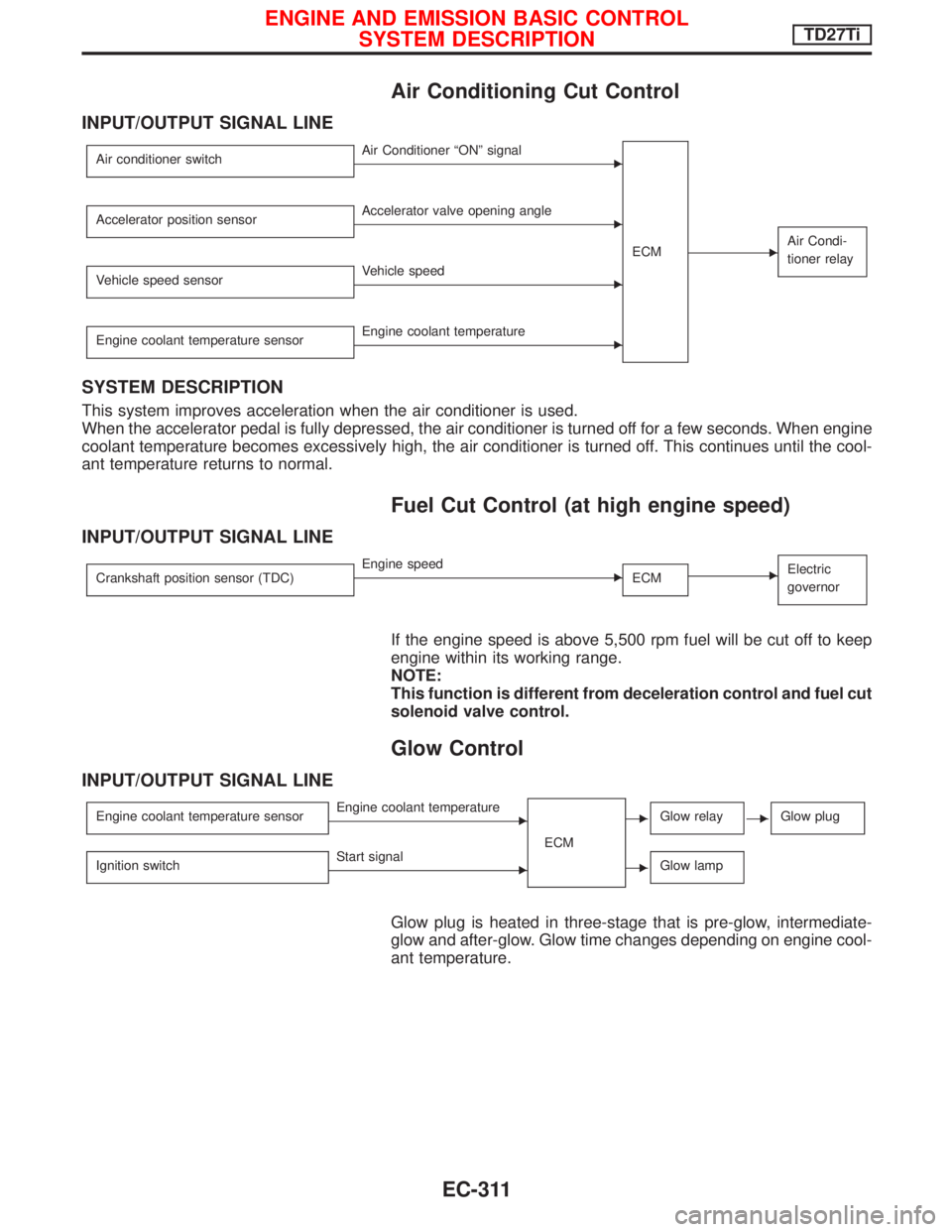
Air Conditioning Cut Control
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
Air conditioner switchEAir Conditioner ªONº signal
ECM
EAir Condi-
tioner relay
Accelerator position sensorEAccelerator valve opening angle
Vehicle speed sensor
EVehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor
EEngine coolant temperature
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
This system improves acceleration when the air conditioner is used.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the air conditioner is turned off for a few seconds. When engine
coolant temperature becomes excessively high, the air conditioner is turned off. This continues until the cool-
ant temperature returns to normal.
Fuel Cut Control (at high engine speed)
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)EEngine speed
ECMEElectric
governor
If the engine speed is above 5,500 rpm fuel will be cut off to keep
engine within its working range.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control and fuel cut
solenoid valve control.
Glow Control
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL LINE
Engine coolant temperature sensorEEngine coolant temperature
ECMEGlow relayEGlow plug
Ignition switchEStart signalEGlow lamp
Glow plug is heated in three-stage that is pre-glow, intermediate-
glow and after-glow. Glow time changes depending on engine cool-
ant temperature.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL
SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
EC-311
Page 675 of 1767

CAUTION:
IDo not disassemble No. 1 nozzle (with needle lift sensor).
Entrust disassembly or adjustment to BOSCH service
shop.
Plug flare nut with a cap or rag so that no dust enters the
nozzle. Cover nozzle tip for protection of needle.
Removal and Installation
1. Remove fuel injection tube and spill tube.
2. Remove injection nozzle assembly.
Also remove washers from nozzle end.
3. Install injection nozzle in the reverse order of removal.
Injection nozzle to engine:
:54-64N×m (5.5 - 6.5 kg-m, 40 - 47 ft-lb)
Injection nozzle to tube:
:20-25N×m (2.0 - 2.5 kg-m, 14 - 18 ft-lb)
a. Always clean the nozzle holes.
b. Always use new injection nozzle gasket.
c. Note that small washer should be installed in specified
direction.
d. Bleed air from fuel system.
Disassembly (No.2-4nozzle)
1. Loosen nozzle nut while preventing nozzle top from turning.
2. Arrange all disassembled parts in the order shown at left.
SEM621B
NEM244
NEF459
SEF785
MEC996D
INJECTION NOZZLETD27Ti
EC-313
Page 683 of 1767

DTC and MI Detection Logic
When a malfunction is detected for the first time, the malfunction (DTC) is stored in the ECM memory.
The MI will light up each time the ECM detects a malfunction. However, if the same malfunction is experienced
in two consecutive driving patterns and the engine is still running, the MI will stay lit up. For a description of
diagnostic items causing the MI to light up, refer to ªTROUBLE DIAGNOSIS Ð INDEXº, EC-293.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
HOW TO READ DTC
The DTC can be read by the following methods.
Without CONSULT-II
ECM displays the DTC by a set of four digit numbers with MI illumination in the diagnostic test mode II (Self-
diagnostic results). Example: 0102, 0103, 0104, etc.
With CONSULT-II
CONSULT-II displays the DTC in ªSELF-DIAG RESULTSº mode. Examples: P0100, P0115, P0500, etc.
These DTCs are prescribed by ISO15031-6.
(CONSULT-II also displays the malfunctioning component or system.)
IOutput of the trouble code means that the indicated circuit has a malfunction. However, in the Mode
II it does not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring or occurred in the past and returned
to normal.
CONSULT-II can identify them. Therefore, using CONSULT-II (if available) is recommended.
HOW TO ERASE DTC
How to Erase DTC (
With CONSULT-II)
1. If the ignition switch stays ªONº after repair work, be sure to turn ignition switch ªOFFº once. Wait at least
5 seconds and then turn it ªONº (engine stopped) again.
2. Touch ªENGINEº.
3. Touch ªSELF-DIAG RESULTSº.
4. Touch ªERASEº. (The DTC in the ECM will be erased.)
The emission related diagnostic information in the ECM can be erased by selecting ªERASEº in the ªSELF-
DIAG RESULTSº mode with CONSULT-II.
SEF246Z
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
EC-321
Page 684 of 1767

How to Erase DTC (Without CONSULT-II)
1. If the ignition switch stays ªONº after repair work, be sure to turn ignition switch ªOFFº once. Wait at least
5 seconds and then turn it ªONº (engine stopped) again.
2. Change the diagnostic test mode from Mode II to Mode I by using the data link connector. (See EC-323.)
The emission related diagnostic information in the ECM can be erased by changing the diagnostic test mode.
IIf the battery is disconnected, the emission-related diagnostic information will be lost after approx.
24 hours.
IErasing the emission-related diagnostic information using CONSULT-II is easier and quicker than
switching the diagnostic test mode using the data link connector.
Malfunction Indicator (MI)
1. The malfunction indicator will light up when the ignition switch
is turned ON without the engine running. This is a bulb check.
IIf the malfunction indicator does not light up, refer to EL sec-
tion (ªWARNING LAMPS/WIRING DIAGRAMº) or see MI &
DATA LINK CONNECTORS.
2. When the engine is started, the malfunction indicator should go
off.
If the lamp remains on, the on board diagnostic system has
detected an engine system malfunction.
If MI illuminates or flashes irregularly after starting engine,
water may have accumulated in fuel filter. Drain water from
fuel filter.
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FUNCTION
The on board diagnostic system has the following three functions.
Diagnostic
Test ModeKEY and ENG.
StatusFunction Explanation of Function
Mode IIgnition switch in
ON position
Engine stoppedBULB CHECKThis function checks the MI bulb for damage (blown, open
circuit, etc.).
If the MI does not come on, check MI circuit. (See EC-452.)
Engine running
MALFUNCTION
WARNINGThis is a usual driving condition. When ECM detects a
malfunction, the MI will light up to inform the driver that a mal-
function has been detected.
Mode IIIgnition switch in
ON position
Engine stopped
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC
RESULTSThis function allows DTCs to be read.
SAT652J
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONTD27Ti
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) (Cont'd)
EC-322