2002 JEEP LIBERTY head gasket
[x] Cancel search: head gasketPage 1307 of 1803

(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Install a new oil filter.
(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN IIis used to seal
components exposed to engine oil. This material is a
specially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Alwaysinspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTVis a specifically designed
black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and
sealing properties to seal components exposed to
automatic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKERis an anaerobic type
gasket material. The material cures in the absence of
air when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It
will not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The
anaerobic material is for use between two machined
surfaces. Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtBED PLATE SEALANTis a unique
(green-in-color) anaerobic type gasket material that
is specially made to seal the area between the bed-
plate and cylinder block without disturbing the bear-
ing clearance or alignment of these components. The
material cures slowly in the absence of air when
torqued between two metallic surfaces, and will rap-
idly cure when heat is applied.
MOPARtGASKET SEALANTis a slow drying,
permanently soft sealer. This material is recom-
mended for sealing threaded fittings and gaskets
against leakage of oil and coolant. Can be used on
threaded and machined parts under all tempera-
tures. This material is used on engines with multi-
layer steel (MLS) cylinder head gaskets. This
material also will prevent corrosion. MopartGasket
Sealant is available in a 13 oz. aerosol can or 4oz./16
oz. can w/applicator.
SEALER APPLICATION
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
9s - 10 ENGINEKJ
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1308 of 1803

MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE GASKET
SURFACE PREPARATION
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
Neveruse the following to clean gasket surfaces:
²Metal scraper
²Abrasive pad or paper to clean cylinder block
and head
²High speed power tool with an abrasive pad or a
wire brush (Fig. 3)
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Only use the following for cleaning gasket surfaces:
²Solvent or a commercially available gasket
remover
²Plastic or wood scraper (Fig. 3)
²Drill motor with 3M RolocŸ Bristle Disc (white
or yellow) (Fig. 3)
CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 4). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metricscale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare clearance measurements to specs found in
engine specifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).Plastigage generally is accompa-
nied by two scales. One scale is in inches, the
other is a metric scale.
Fig. 3 Proper Tool Usage For Surface Preparation
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCŸ BRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
Fig. 4 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIGAGE
KJENGINE9s-11
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1312 of 1803
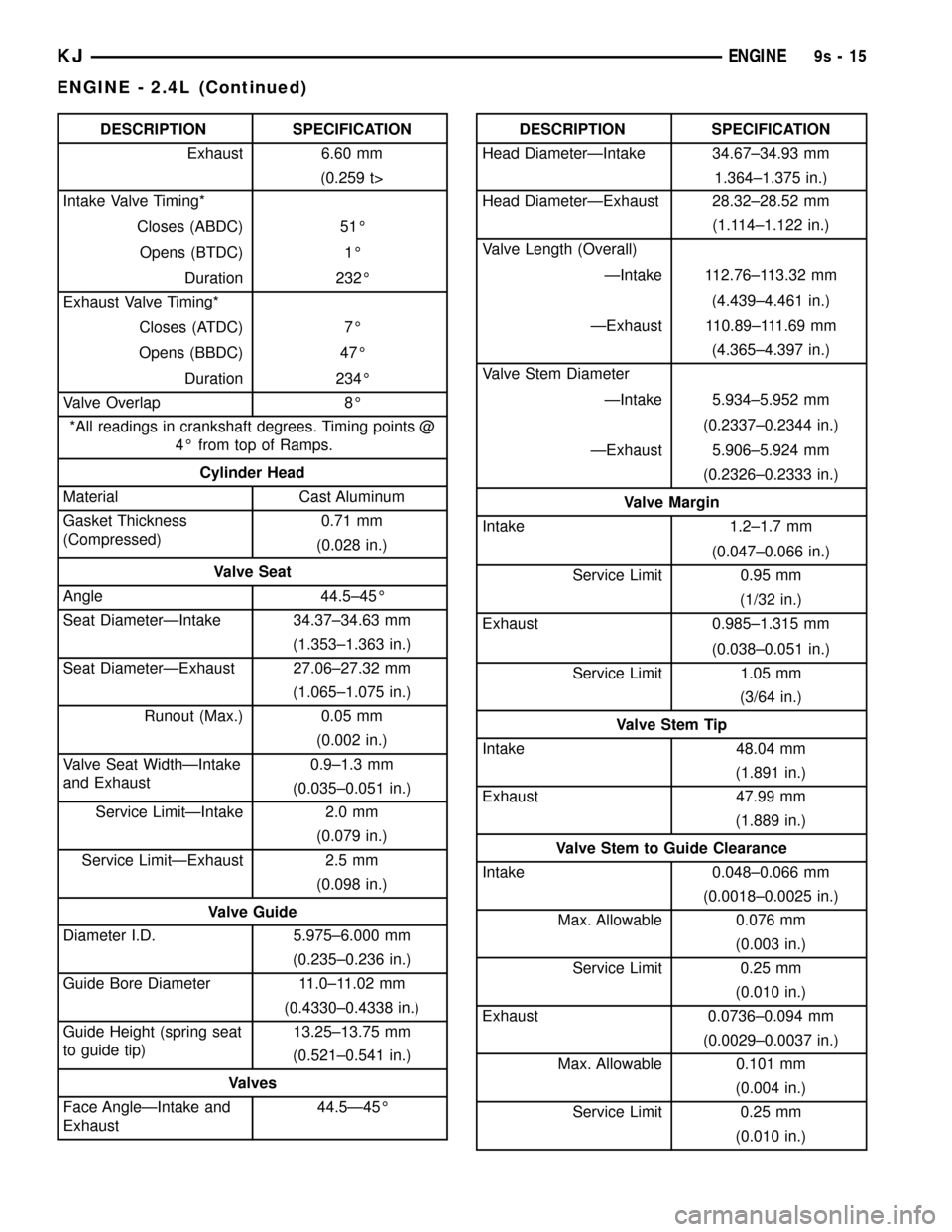
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Exhaust 6.60 mm
(0.259 t>
Intake Valve Timing*
Closes (ABDC) 51É
Opens (BTDC) 1É
Duration 232É
Exhaust Valve Timing*
Closes (ATDC) 7É
Opens (BBDC) 47É
Duration 234É
Valve Overlap 8É
*All readings in crankshaft degrees. Timing points @
4É from top of Ramps.
Cylinder Head
Material Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness
(Compressed)0.71 mm
(0.028 in.)
Valve Seat
Angle 44.5±45É
Seat DiameterÐIntake 34.37±34.63 mm
(1.353±1.363 in.)
Seat DiameterÐExhaust 27.06±27.32 mm
(1.065±1.075 in.)
Runout (Max.) 0.05 mm
(0.002 in.)
Valve Seat WidthÐIntake
and Exhaust0.9±1.3 mm
(0.035±0.051 in.)
Service LimitÐIntake 2.0 mm
(0.079 in.)
Service LimitÐExhaust 2.5 mm
(0.098 in.)
Valve Guide
Diameter I.D. 5.975±6.000 mm
(0.235±0.236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter 11.0±11.02 mm
(0.4330±0.4338 in.)
Guide Height (spring seat
to guide tip)13.25±13.75 mm
(0.521±0.541 in.)
Valves
Face AngleÐIntake and
Exhaust44.5Ð45ÉDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Head DiameterÐIntake 34.67±34.93 mm
1.364±1.375 in.)
Head DiameterÐExhaust 28.32±28.52 mm
(1.114±1.122 in.)
Valve Length (Overall)
ÐIntake 112.76±113.32 mm
(4.439±4.461 in.)
ÐExhaust 110.89±111.69 mm
(4.365±4.397 in.)
Valve Stem Diameter
ÐIntake 5.934±5.952 mm
(0.2337±0.2344 in.)
ÐExhaust 5.906±5.924 mm
(0.2326±0.2333 in.)
Valve Margin
Intake 1.2±1.7 mm
(0.047±0.066 in.)
Service Limit 0.95 mm
(1/32 in.)
Exhaust 0.985±1.315 mm
(0.038±0.051 in.)
Service Limit 1.05 mm
(3/64 in.)
Valve Stem Tip
Intake 48.04 mm
(1.891 in.)
Exhaust 47.99 mm
(1.889 in.)
Valve Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.048±0.066 mm
(0.0018±0.0025 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Exhaust 0.0736±0.094 mm
(0.0029±0.0037 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.101 mm
(0.004 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
KJENGINE9s-15
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1316 of 1803

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 2.4L
Housing removal is not necessary for element (fil-
ter) replacement.
(1) Disconnect air intake duct at side of element
cover.
(2) Pry up 2 spring clips from front of housing
cover (spring clips retain cover to housing).
(3) Release housing cover from locating tabs
located on rear of housing, and remove cover.
(4) Remove air cleaner element (filter) from hous-
ing.
(5) Clean inside of housing before replacing ele-
ment.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install element into housing.
(2) Position housing cover into housing locating
tabs.
(3) Pry up spring clips and lock cover to housing.
(4) Connect air intake duct.
If any air filter, air resonator, air intake tubes or
air filter housing clamps had been loosened or
removed, tighten them to 5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 5). The valves are arrange in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the left
side of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the right
side. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metalvalve guides and seats. The cylinder head is sealed to
the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and
retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries providing lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
OPERATION
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber,
allowing the pistons to compress the fuel/air mixture
for ignition. The valves are actuated by the lobe pro-
files on the camshaft to open and close at specified
duration to either allow clean air in the combustion
chamber or the exhaust gases out; depending on the
stroke of the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Combustion Leak Tester C-3685-A
Cylinder Compression Pressure Adaptor 8116
Fig. 5 Cylinder Head and Camshafts
CAM PLUG - NOT SHOWN
1 - CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS
2 - PLUG
3 - CAMSHAFT
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
KJENGINE9s-19
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1317 of 1803

Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs.(Refer to 14 -FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - SPECIFICA-
TIONS)
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(3) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Remove air filter housing and inlet tube.
(5) Remove intake manifold.
(6) Remove heater tube support bracket from cyl-
inder head.
(7) Disconnect radiator upper and heater supply
hoses from water outlet connections.
(8) Remove accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL)
(9) Raise vehicle and remove exhaust pipe from
manifold.
(10) Remove power steering pump and set aside.
Do not disconnect lines.
(11) Remove accessory drive bracket
(12) Remove ignition coil and wires from engine.
(13) Disconnect cam sensor and fuel injector wir-
ing connectors.
(14) Remove timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(15) Remove timing belt idler pulley and rear tim-
ing belt cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIM-
ING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) -
REMOVAL)
(16) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(17) Remove camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Identify rocker arm position to ensure cor-
rect re-installation in original position, if reused.
(18) Remove rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove cylinder head bolts in REVERSE
sequence of tightening.
(20) Remove cylinder head from engine block.
(21) Inspect and clean cylinder head. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSPECTION) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - CLEANING)
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
9s - 20 ENGINEKJ
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1318 of 1803

Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE). Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
Clean all engine oil passages.
INSPECTION
(1) Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 in.) (Fig. 6).
(2) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for scoring.
(3) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(4) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 7). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS) Replace guides if they are not within
specification.
(5) Check valve guide height (Fig. 8).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD
NOTE: The Cylinder head bolts should be examined
BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked down, the
bolts must be replaced (Fig. 9).
Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale, the bolt should be replaced.
(1) Before installing the bolts, the threads should
be coated with engine oil.
(2) Position cylinder head gasket on engine block
(Fig. 10).
(3) Install cylinder head on engine block.
(4) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the sequence
shown in (Fig. 11). Using the 4 step torque turn
method, tighten according to the following values:
²First All to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
²Second All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 6 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 7 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
1-TOP
2 - MIDDLE
3 - BOTTOM
4 - CUT AWAY VIEW OF VALVE GUIDE MEASUREMENT
LOCATIONS
Fig. 8 Valve Guide Height
1 - VALVE GUIDE
2 - 13.25 - 13.75 MM (.521 - .541 IN.)
3 - SPRING SEAT
Fig. 9 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
KJENGINE9s-21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1319 of 1803

²Third All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
CAUTION: Do not use a torque wrench for the fol-
lowing step.
²Fourth Turn an additional 1/4 Turn,
(5) Install rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLA-
TION)
(6) Install camshafts. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(8) Install timing belt rear cover and timing belt
idler pulley. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION)
(9) Install timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION)
(10) Connect cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.(11) Install ignition coil and wires. Connect igni-
tion coil wiring connector.
(12) Install accessary drive bracket.
(13) Install power steering pump to cylinder head.
(14) Raise vehicle and install the exhaust pipe to
the manifold.
(15) Install accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION)
(16) Install heater tube support bracket to cylinder
head.
(17) Install intake manifold.
(18) Connect all vacuum lines, electrical wiring,
ground straps and fuel line.
(19) Fill cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(20) Connect battery negative cable.
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove timing belt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(2) Hold each camshaft sprocket with Special Tool
6847 while removing center bolt (Fig. 12).
(3) Remove camshaft sprockets.
(4) Remove exhaust camshaft target ring.
(5) Remove exhaust camshaft sensor.
CAUTION: Inspect sensor and target ring for exces-
sive wear. Clean sensor face and install new spacer
pad.
(6) Remove rear timing belt cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(7) Remove camshaft seal using Special Tool
C-4679-A (Fig. 13).
CAUTION: Do not nick shaft seal surface or seal
bore.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Clean and inspect sensor and target ring for
excessive wear. Clean sensor face and always
install a new spacer pad.
(1) Shaft seal surface must be free of varnish, dirt
or nicks. Polish with 400 grit paper if necessary.
(2) Install camshaft seals into cylinder head using
Special Tool MD-998306 until flush with head (Fig.
14).
Fig. 10 Cylinder Head Gasket Positioning
1 - PART NUMBER FACES UP
2 - NO. 1 CYLINDER
Fig. 11 Cylinder Head Tightening Sequence
9s - 22 ENGINEKJ
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1322 of 1803

INSPECTION
(1) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for damage
and binding (Fig. 19). If journals are binding, check
the cylinder head for damage. Also check cylinder
head oil holes for clogging.
(2) Check the cam lobe and bearing surfaces for
abnormal wear and damage. Replace camshaft if
defective.
NOTE: If camshaft is replaced due to lobe wear or
damage, always replace the rocker arms.
(3) Measure the lobe actual wear (unworn area -
wear zone = actual wear) (Fig. 19) and replace cam-
shaft if out of limit. Standard value is 0.0254 mm
(0.001 in.), wearlimitis 0.254 mm (0.010 in.).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Ensure that NONE of the pistons are at
top dead center when installing the camshafts.
(1) Lubricate all camshaft bearing journals, rocker
arms and camshaft lobes.
(2) Install all rocker arms in original positions, if
reused.
(3) Position camshafts on cylinder head bearing
journals. Install right and left camshaft bearing caps
No.2±5andright No. 6. Tighten M6 fasteners to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) in sequence shown in (Fig. 20).
(4) Apply MopartGasket Maker to No. 1 and No.
6 bearing caps (Fig. 21). Install bearing caps and
tighten M8 fasteners to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).NOTE: Bearing end caps must be installed before
seals can be installed.
(5) Install camshaft oil seals. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT OIL
SEAL(S) - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install camshaft target magnet and camshaft
position sensor.
(7) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(8) Install timing belt rear cover and camshaft
sprocket. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION)
(9) Install timing belt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 19 Checking Camshaft(s) for Wear
1 - UNWORN AREA
2 - ACTUAL WEAR
3 - BEARING JOURNAL
4 - LOBE
5 - WEAR ZONE
Fig. 20 Camshaft Bearing Cap Tightening Sequence
Fig. 21 Camshaft Bearing Cap Sealing
1 - 1.5 mm (.060 in.) DIAMETER BEAD OF MOPAR GASKET
MAKER
KJENGINE9s-25
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)