2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE fill tube
[x] Cancel search: fill tubePage 1591 of 2199

(7) While holding pan level, lower pan and gasket
away from transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9) Remove screws holding filter to valve body
(Fig. 90).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and pour fluid
in filter into drain pan.
(11) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter properly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position a new transmission oil filter onto the
valve body.
(2) Install the screws to hold the filter to the valve
body. Tighten the screws to 4 N´m (35 in.lbs.).
(3) Clean the gasket surfaces of the transmission
oil pan and transmission pan rail.NOTE: The transmission pan oil gasket is reusable.
Inspect the sealing surfaces of the gasket. If the
sealing ribs on both surfaces appear to be in good
condition, clean the gasket of any foreign material
and reinstall.
(4) Position the oil pan gasket onto the oil pan.
(5) Position the oil pan and gasket onto the trans-
mission and install several bolts to hold the pan and
gasket to the transmission.
(6) Install the remainder of the oil pan bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 13.6 N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(7) Lower vehicle and fill transmission. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC/
FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4, type 9602, to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add3
pints (1-1/2 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add12 pints (6 quarts)of ATF
+4 to transmission.
(3) Apply parking brakes.
(4)
Start and run engine at normal curb idle speed.
(5) Apply service brakes, shift transmission
through all gear ranges then back to NEUTRAL, set
parking brake, and leave engine running at curb idle
speed.
(6) Remove funnel, insert dipstick and check fluid
level. If level is low,add fluid to bring level to
MIN mark on dipstick.Check to see if the oil level
is equal on both sides of the dipstick. If one side is
noticably higher than the other, the dipstick has
picked up some oil from the dipstick tube. Allow the
oil to drain down the dipstick tube and re-check.
(7) Drive vehicle until transmission fluid is at nor-
mal operating temperature.
(8) With the engine running at curb idle speed, the
gear selector in NEUTRAL, and the parking brake
applied, check the transmission fluid level.
CAUTION: Do not overfill transmission, fluid foam-
ing and shifting problems can result.
(9) Add fluid to bring level up to MAX arrow
mark.
When fluid level is correct, shut engine off, release
park brake, remove funnel, and install dipstick in fill
tube.
Fig. 89 Transmission Pan
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - GASKET
3-PAN
Fig. 90 Transmission Filter
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - FILTER
21 - 72 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1717 of 2199

(5) Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then
rotate converter back and forth until fully seated in
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with steel scale and
straightedge (Fig. 52). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
(8) Position transmission on jack and secure it
with chains.
(9) Check condition of converter driveplate.
Replace the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.
Also be sure transmission dowel pins are seated
in engine block and protrude far enough to
hold transmission in alignment.
(10) Apply a light coating of MopartHigh Temp
Grease to the torque converter hub pocket in the rear
pocket of the engine's crankshaft.
(11) Raise transmission and align the torque con-
verter with the drive plate and the transmission con-
verter housing with the engine block.
(12) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower,
or tilt transmission to align the converter housing
with the engine block dowels.
(13) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft. Verify that no wires, or the transmission
vent hose, have become trapped between the engine
block and the transmission.
(14) Install two bolts to attach the transmission to
the engine.(15) Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
(16) Install rear transmission crossmember.
Tighten crossmember to frame bolts to 68 N´m (50
ft.lbs.).
(17) Install rear support to transmission. Tighten
bolts to 47 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(18) Lower transmission onto crossmember and
install bolts attaching transmission mount to cross-
member. Tighten clevis bracket to crossmember bolts
to 47 N´m (35 ft.lbs.). Tighten the clevis bracket to
rear support bolt to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
(19) Remove engine support fixture.
(20) Install new plastic retainer grommet on any
shift cable that was disconnected. Grommets should
not be reused. Use pry tool to remove rod from grom-
met and cut away old grommet. Use pliers to snap
new grommet into cable and to snap grommet onto
lever.
(21) Connect gearshift cable to transmission.
(22) Connect wires to solenoid and pressure switch
assembly connector, input and output speed sensors,
and line pressure sensor. Be sure transmission har-
nesses are properly routed.
CAUTION: It is essential that correct length bolts be
used to attach the converter to the driveplate. Bolts
that are too long will damage the clutch surface
inside the converter.
(23) Install all torque converter-to-driveplate bolts
by hand.
(24) Verify that the torque converter is pulled
flush to the driveplate. Tighten bolts to 31 N´m (270
in. lbs.).
(25) Install starter motor and cooler line bracket.
(26) Connect cooler lines to transmission.
(27) Install transmission fill tube.
(28) Install exhaust components.
(29) Install transfer case. Tighten transfer case
nuts to 35 N´m (26 ft.lbs.).
(30) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
cable support bracket and the transfer case shift
lever.
(31) Install the transmission collar onto the trans-
mission and the engine. Tighten the bolts to 54 N´m
(40 ft.lbs.).
(32) Align and connect propeller shaft(s).
(33) Adjust gearshift cable if necessary.
(34) Lower vehicle.
(35) Fill transmission with MopartATF +4, type
9602, Automatic Transmission fluid.
Fig. 52 Checking Torque Converter Seating - Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
21 - 198 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2199

(8) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL gate positions only.
Engine starts must not be possible in any other gate
positions other than PARK or NEUTRAL.
(9) With shifter lever handle push-button not
depressed and lever detent in:
²PARK position- apply forward force on center of
handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²PARK position- apply rearward force on center
of handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²NEUTRAL position- engine start must be possi-
ble.
²NEUTRAL position, engine running and brakes
applied- Apply forward force on center of shift han-
dle. Transmission should not be able to shift into
REVERSE detent.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary cool-
ers as well. The torque converter should also be
replaced whenever a failure generates sludge and
debris. This is necessary because normal converter
flushing procedures will not remove all contami-
nants.
21 - 228 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1748 of 2199
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator opera-
tion. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the
transmission vent where it may be mistaken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P (PARK)
and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever
in P (PARK) to be sure that the fluid level check is
accurate.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
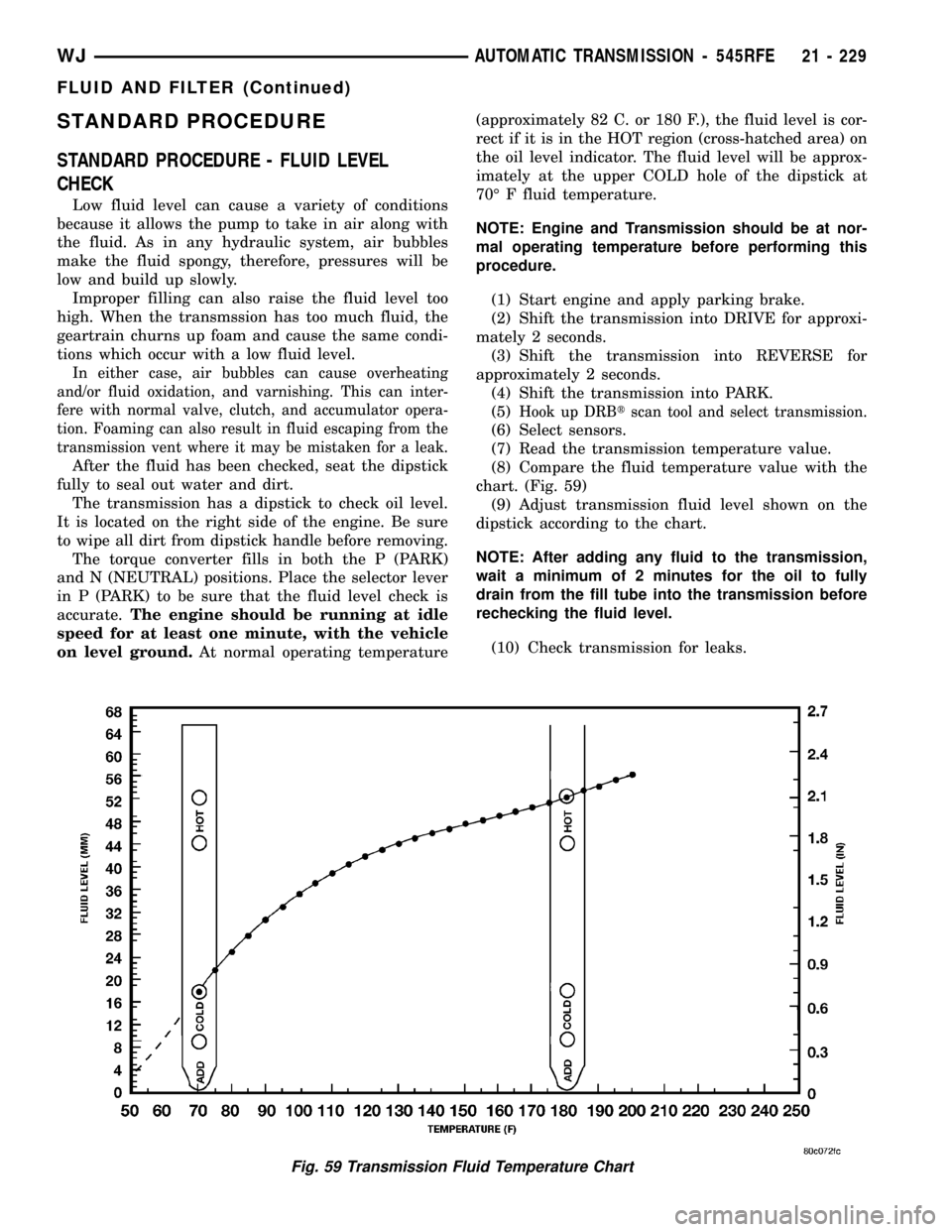
on level ground.At normal operating temperature(approximately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is cor-
rect if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on
the oil level indicator. The fluid level will be approx-
imately at the upper COLD hole of the dipstick at
70É F fluid temperature.
NOTE: Engine and Transmission should be at nor-
mal operating temperature before performing this
procedure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approxi-
mately 2 seconds.
(3) Shift the transmission into REVERSE for
approximately 2 seconds.
(4) Shift the transmission into PARK.
(5)
Hook up DRBtscan tool and select transmission.
(6) Select sensors.
(7) Read the transmission temperature value.
(8) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
chart. (Fig. 59)
(9) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
dipstick according to the chart.
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission,
wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully
drain from the fill tube into the transmission before
rechecking the fluid level.
(10) Check transmission for leaks.
Fig. 59 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 229
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1749 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission.
(4)
Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmission.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan away from trans-
mission allowing the fluid to drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolts hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan away from
transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9)
Remove screw holding filter to valve body (Fig. 60).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and oil pump
and pour fluid in filter into drain pan.
(11) Remove and discard the oil filter seal from the
bottom of the oil pump.
(12) If replacing the cooler return filter, use Oil
Filter Wrench 8321 to remove the filter from the
transmission.
(13) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter(s) prop-
erly.
INSPECTION
Inspect bottom of pan and magnet for excessive
amounts of metal. A light coating of clutch material
on the bottom of the pan does not indicate a problemunless accompanied by a slipping condition or shift
lag. If fluid and pan are contaminated with excessive
amounts of debris, refer to the diagnosis section of
this group.
CLEANING
(1) Using a suitable solvent, clean pan and mag-
net.
(2) Using a suitable gasket scraper, clean original
sealing material from surface of transmission case
and the transmission pan.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(2) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(3) Install screw to hold filter to valve body (Fig.
60). Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install new cooler return filter onto the trans-
mission, if necessary. Torque the filter to 14.12 N´m
(125 in.lbs.).
(5) Place bead of MopartRTV sealant onto the
transmission case sealing surface.
(6) Place pan in position on transmission.
(7) Install bolts to hold pan to transmission.
Tighten bolts to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602 fluid.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4 to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add10
pints (5 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add24 pints (12 quarts)of
ATF +4 to transmission.
(3) Check the transmission fluid (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
45RFE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE) and
adjust as required.
Fig. 60 Transmission Filters - 4X4 Shown
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
21 - 230 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1814 of 2199

REAR OUTPUT SHAFT/YOKE/DRIVE CHAIN
Check condition of the seal contact surfaces of the
yoke slinger (Fig. 49). This surface must be clean and
smooth to ensure proper seal life. Replace the yoke
nut and seal washer as neither part should be
reused.
Inspect the shaft threads, sprocket teeth, and bear-
ing surfaces. Minor nicks on the teeth can be
smoothed with an oilstone. Use 320-400 grit emery to
smooth minor scratches on the shaft bearing sur-
faces. Rough threads on the shaft can be chased if
necessary. Replace the shaft if the threads are dam-
aged, bearing surfaces are scored, or if any sprocket
teeth are cracked or broken.
Examine the drive chain and shaft bearings.
Replace the chain and both sprockets if the chain is
stretched, distorted, or if any of the links bind.
Replace the bearings if rough, or noisy.
LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Inspect annulus gear condition carefully. The gear
is only serviced as part of the front case. If the gear
is damaged, it will be necessary to replace the gear
and front case as an assembly. Do not attempt to
remove the gear (Fig. 50)
FRONT-REAR CASES AND FRONT RETAINER
Inspect the cases and retainer for wear and dam-
age. Clean the sealing surfaces with a scraper and
3M all purpose cleaner. This will ensure proper
sealer adhesion at assembly. Replace the input
retainer seal; do not reuse it.Check case condition. If leaks were a problem, look
for gouges and severe scoring of case sealing sur-
faces. Also make sure the front case mounting studs
are in good condition.
Check the front case mounting studs and vent
tube. The tube can be secured with LoctiteŸ 271 or
680 if loose. The stud threads can be cleaned up with
a die if necessary. Also check condition of the fill/
drain plug threads in the rear case. The threads can
be repaired with a thread chaser or tap if necessary.
Or the threads can be repaired with HelicoilŸ stain-
less steel inserts if required.
OIL PUMP/OIL PICKUP
Examine the oil pump pickup parts. Replace the
pump if any part appears to be worn or damaged. Do
not disassemble the pump as individual parts are not
available. The pump is only available as a complete
assembly. The pickup screen, hose, and tube are the
only serviceable parts and are available separately.
ASSEMBLY
Lubricate transfer case components with automatic
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly (where indi-
cated) during assembly.
CAUTION: The bearing bores in various transfer
case components contain oil feed holes. Make sure
replacement bearings do not block the holes.
Fig. 49 Seal Contact Surface Of Yoke Slinger
1 - FRONT SLINGER (PART OF YOKE)
2 - SEAL CONTACT SURFACE MUST BE CLEAN AND SMOOTH
Fig. 50 Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - FRONT CASE
2 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 295
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 2122 of 2199

NOTE: The blend door sub-assembly is attached to
the housing with 2 screws, and may be removed for
service (Fig. 19).
ASSEMBLY
(1) Place the top half of the HVAC housing on the
bottom half. Be certain that each of the door pivot
pins align with the pivot holes in the HVAC housing.
(2) Install the 10 screws that secure the two hous-
ing halves to each other. Tighten the HVAC housing
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Attach the wire harness electrical connector(s)
to the mounts on the lower case at the blower motor
end of the unit.
(4) Install the 5 clips that secure the two housing
halves to each other. Check doors for binding after
replacement, and after assembly of housing.
(5) Install the screw with plastic washer holding
the lever assembly to the upper case section.
(6) Install the mode door actuator on the left side
of the housing.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: REVIEW THE WARNINGS AND CAU-
TIONS IN PLUMBING BEFORE PERFORMING THE
FOLLOWING OPERATION. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION)Any kinks or sharp bends in the refrigerant plumb-
ing will reduce the capacity of the entire air condi-
tioning system. Kinks and sharp bends reduce the
flow of refrigerant in the system. A good rule for the
flexible hose refrigerant lines is to keep the radius of
all bends at least ten times the diameter of the hose.
In addition, the flexible hose refrigerant lines should
be routed so they are at least 80 millimeters (3
inches) from the exhaust manifold.
High pressures are produced in the refrigerant sys-
tem when the air conditioning compressor is operat-
ing. Extreme care must be exercised to make sure
that each of the refrigerant system connections is
pressure-tight and leak free. It is a good practice to
inspect all flexible hose refrigerant lines at least once
a year to make sure they are in good condition and
properly routed.
(1) Position the HVAC housing to the dash panel.
Be certain that the evaporator condensate drain tube
and the housing mounting studs are inserted into
their correct mounting holes.
(2) Install the HVAC housing mounting nuts to the
studs on the passenger compartment side of the dash
panel. Tighten the nuts to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the HVAC housing wire harness con-
nectors.
(4) Reinstall the rear floor heat ducts to the center
floor heat duct outlets.
(5) Install and tighten the nuts onto the HVAC
housing mounting studs on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. Tighten the nuts to 7 N´m (60
in. lbs.).
(6) Reinstall the PCM to the passenger side dash
panel in the engine compartment. Refer to Electronic
Control Modules for the procedures.
(7) Reinstall the coolant reserve/overflow bottle to
the passenger side inner fender shield. Refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures.
(8) If the vehicle is equipped with the manual tem-
perature control system, connect the HVAC system
vacuum supply line connector to the tee fitting near
the heater core tubes.
(9) Unclamp/unplug the heater core hoses and
tubes. Connect the heater hoses to the heater core
tubes and fill the engine cooling system. Refer to
Cooling for the procedures.
(10) Unplug or remove the tape from the suction
line and the evaporator outlet tube fittings. Connect
the suction line to the evaporator outlet tube.
Tighten retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(11) Unplug or remove the tape from the liquid
line and the evaporator inlet tube fittings. Connect
the liquid line to the evaporator inlet tube. Tighten
retaining nut to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(12) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
Fig. 19 BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY (AZC)
1 - PASSENGER SIDE BLEND DOOR
2 - BLEND DOOR SUB-ASSEMBLY
3 - DOOR PIVOT SHAFT BUSHING
4 - DOOR SHAFT LEVER
5 - DRIVER SIDE BLEND DOOR
WJDISTRIBUTION 24 - 45
HVAC HOUSING (Continued)
Page 2179 of 2199

EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM............................24
DESCRIPTION - CCV SYSTEM...........25
DESCRIPTION - PCV SYSTEM...........25
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L CCV SYSTEM.........26
OPERATION - 4.7L PCV SYSTEM.........26
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - EVAPORATION SYSTEM.......27
CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L................................28
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING........28
INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING....29
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29REMOVAL.............................29
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENABLING
CONDITIONS TO RUN EVAP LEAK
DETECTION TEST.....................32
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
ORVR
DESCRIPTION.........................37
OPERATION...........................37
P C V VA LV E
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV VALVE/PCV
SYSTEM - 4.7L.......................37
REMOVAL - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.............39
INSTALLATION - PCV VALVE - 4.7L.........39
VACUUM LINES
DESCRIPTION.........................39
VAPOR CANISTER
DESCRIPTION.........................39
OPERATION...........................39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - EVAPORATION CONTROL
SYSTEM
The evaporation control system prevents the emis-
sion of fuel tank vapors into the atmosphere. When
fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapors pass
through the control valve, through the fuel manage-
ment valve, and through vent hoses and tubes to a
charcoal filled evaporative canister. The canister tem-
porarily holds the vapors. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) allows intake manifold vacuum todraw vapors into the combustion chambers during
certain operating conditions.
Gas powered engines use a duty cycle purge sys-
tem. The PCM controls vapor flow by operating the
duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid. Refer to Duty Cycle
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
When equipped with certain emissions packages, a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) will be used as part of
the evaporative system for OBD II requirements.
Also refer to Leak Detection Pump.
Vehicles powered with gasoline engines are also
equipped with ORVR (On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery). Refer to ORVR for additional information.
25 - 24 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ