2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 232 of 2199
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VISCOUS
FAN/DRIVE1. Fan blades loose - 4.0L. 1. Replace fan blade assembly. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL)
2. Fan blades striking a surrounding
object.2. Locate point of fan blade contact and
repair as necessary.
3. Air obstructions at radiator or air
conditioning condenser.3. Remove obstructions and/or clean debris
or insects from radiator or A/C condenser.
4. Thermal viscous fan drive has
defective bearing - 4.0L4. Replace fan drive. Bearing is not
serviceable. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
INADEQUATE HEATER
PERFORMANCE.1.Thermostat failed in open position
2. Has a Diagnostic trouble Code
(DTC) been set?2. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL -
DESCRIPTION) for correct procedures and
replace thermostat if necessary
3. Coolant level low 3. (Refer to 7 - COOLING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
4. Obstructions in heater hose/
fittings4. Remove heater hoses at both ends and
check for obstructions
5. Heater hose kinked 5. Locate kinked area and repair as
necessary
6. Water pump is not pumping water
to/through the heater core. When
the engine is fully warmed up, both
heater hoses should be hot to the
touch. If only one of the hoses is
hot, the water pump may not be
operating correctly or the heater
core may be plugged. Accessory
drive belt may be slipping causing
poor water pump operation.6. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/WATER
PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). If a
slipping belt is detected, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE
BELTS - REMOVAL). If heater core
obstruction is detected, (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for
cooling system reverse flushing.
STEAM IS COMING
FROM THE FRONT OF
VEHICLE NEAR THE
GRILL AREA WHEN
WEATHER IS WET,
ENGINE IS WARMED UP
AND RUNNING, AND
VEHICLE IS
STATIONARY.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
IS IN NORMAL RANGE1. During wet weather, moisture
(snow, ice or rain condensation) on
the radiator will evaporate when the
thermostat opens. This opening
allows heated water into the radiator.
When the moisture contacts the hot
radiator, steam may be emitted. This
usually occurs in cold weather with
no fan or airflow to blow it away.1. Occasional steam emitting from this area
is normal. No repair is necessary.
COOLANT COLOR 1. Coolant color is not necessarily
an indication of adequate corrosion
or temperature protection. Do not
rely on coolant color for determining
condition of coolant.1. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
COOLANT - DESCRIPTION) for coolant
concentration information. Adjust coolant
mixture as necessary.
WJCOOLING 7 - 9
COOLING (Continued)
Page 233 of 2199
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
COOLANT LEVEL
CHANGES IN COOLANT
RESERVE/OVERFLOW
TANK. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE IS IN NORMAL
RANGE1. Level changes are to be expected
as coolant volume fluctuates with
engine temperature. If the level in
the tank was between the FULL and
ADD marks at normal operating
temperature, the level should return
to within that range after operation
at elevated temperatures.1. A normal condition. No repair is necessary.
FAN RUNS ALL THE
TIME1. Fan control sensors inoperative. 1. Check for DTC's. Verify sensor readings.
2. Fan control solenoid stuck9on9. 2. Check fan operation speeds. Refer to fan
speed operation table.
3. Fan control solenoid harness
damaged.3. Check for DTC 1499. Repair as required.
4. Transmission temperature too
high.4. Check for transmission over temp. DTC.
5. Engine coolant temperature too
high.5. (a) Check coolant level. Correct level as
required.
(b) Thermostat stuck. Replace thermostat.
(c) Water pump failed. Replace water pump.
(d) Coolant flow restricted. Clean radiator.
(e) Air flow over radiator obstructed.Remove
obstruction.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COOLING SYSTEM
LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
A leak detection additive is available through the
parts department that can be added to cooling sys-
tem. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). Pour one ounce of additive into
cooling system. Place heater control unit in HEAT
position. Start and operate engine until radiator
upper hose is warm to touch. Aim the commercially
available black light tool at components to be
checked. If leaks are present, black light will cause
additive to glow a bright green color.
The black light can be used in conjunction with a
pressure tester to determine if any external leaks
exist (Fig. 5).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at normal operating temper-
ature. Recheck the system cold if cause of coolant
loss is not located during the warm engine examina-
tion.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING.
Fig. 5 Leak Detection Using Black LightÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL BLACK LIGHT TOOL
7 - 10 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)
Page 234 of 2199

Carefully remove radiator pressure cap from filler
neck and check coolant level. Push down on cap to
disengage it from stop tabs. Wipe inside of filler neck
and examine lower inside sealing seat for nicks,
cracks, paint, dirt and solder residue. Inspect radia-
tor-to- reserve/overflow tank hose for internal
obstructions. Insert a wire through the hose to be
sure it is not obstructed.
Inspect cams on outside of filler neck. If cams are
damaged, seating of pressure cap valve and tester
seal will be affected.
Attach pressure tester (7700 or an equivalent) to
radiator filler neck (Fig. 6).
Operate tester pump to apply 103.4 kPa (15 psi)
pressure to system. If hoses enlarge excessively or
bulges while testing, replace as necessary. Observe
gauge pointer and determine condition of cooling sys-
tem according to following criteria:
Holds Steady:If pointer remains steady for two
minutes, serious coolant leaks are not present in sys-
tem. However, there could be an internal leak that
does not appear with normal system test pressure. If
it is certain that coolant is being lost and leaks can-
not be detected, inspect for interior leakage or per-
form Internal Leakage Test.
Drops Slowly:Indicates a small leak or seepage
is occurring. Examine all connections for seepage or
slight leakage with a flashlight. Inspect radiator,
hoses, gasket edges and heater. Seal small leak holes
with a Sealer Lubricant (or equivalent). Repair leak
holes and inspect system again with pressure
applied.
Drops Quickly:Indicates that serious leakage is
occurring. Examine system for external leakage. If
leaks are not visible, inspect for internal leakage.
Large radiator leak holes should be repaired by a
reputable radiator repair shop.INTERNAL LEAKAGE INSPECTION
Remove engine oil pan drain plug and drain a
small amount of engine oil. If coolant is present in
the pan, it will drain first because it is heavier than
oil. An alternative method is to operate engine for a
short period to churn the oil. After this is done,
remove engine dipstick and inspect for water glob-
ules. Also inspect transmission dipstick for water
globules and transmission fluid cooler for leakage.
WARNING: WITH RADIATOR PRESSURE TESTER
TOOL INSTALLED ON RADIATOR, DO NOT ALLOW
PRESSURE TO EXCEED 110 KPA (20 PSI). PRES-
SURE WILL BUILD UP QUICKLY IF A COMBUSTION
LEAK IS PRESENT. TO RELEASE PRESSURE,
ROCK TESTER FROM SIDE TO SIDE. WHEN
REMOVING TESTER, DO NOT TURN TESTER MORE
THAN 1/2 TURN IF SYSTEM IS UNDER PRESSURE.
Operate engine without pressure cap on radiator
until thermostat opens. Attach a Pressure Tester to
filler neck. If pressure builds up quickly it indicates a
combustion leak exists. This is usually the result of a
cylinder head gasket leak or crack in engine. Repair
as necessary.
If there is not an immediate pressure increase,
pump the Pressure Tester. Do this until indicated
pressure is within system range of 110 kPa (16 psi).
Fluctuation of gauge pointer indicates compression or
combustion leakage into cooling system.
Because the vehicle is equipped with a catalytic
converter,do notremove spark plug cables or short
out cylinders to isolate compression leak.
If the needle on dial of pressure tester does not
fluctuate, race engine a few times to check for an
abnormal amount of coolant or steam. This would be
emitting from exhaust pipe. Coolant or steam from
exhaust pipe may indicate a faulty cylinder head gas-
ket, cracked engine cylinder block or cylinder head.
A convenient check for exhaust gas leakage into
cooling system is provided by a commercially avail-
able Block Leak Check tool. Follow manufacturers
instructions when using this product.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST - WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE CYLINDER BLOCK
DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAIN-
COCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow thermostat
removal. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE
COOLANT THERMOSTAT - REMOVAL). Remove
Fig. 6 Pressure Testing Cooling SystemÐTypical
1 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
WJCOOLING 7 - 11
COOLING (Continued)
Page 240 of 2199

(3) Install drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(4) Check belt indexing marks (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
(1) Install tensioner assembly to mounting
bracket, align the two dowels on the tensioner with
the mounting bracket and hand start the bolt.
Tighten bolt to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
CAUTION: To prevent damage to coil case, coil
mounting bolts must be torqued.
(2) Install drive belt. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/AC-
CESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).(3) Check belt indexing marks (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
DRIVE BELTS - 4.0L
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING ± SERPENTINE
DRIVE BELT
When diagnosing serpentine drive belts, small
cracks that run across ribbed surface of belt from rib
to rib (Fig. 3), are considered normal. These are not a
reason to replace belt. However, cracks running along
a rib (not across) arenotnormal. Any belt with
cracks running along a rib must be replaced (Fig. 3).
Also replace belt if it has excessive wear, frayed cords
or severe glazing.
Refer to SERPENTINE DRIVE BELT DIAGNOSIS
CHART for further belt diagnosis.
Fig. 2 Automatic Belt Tensioner
1 - IDLER PULLEY TIGHTEN TO 47 N´m (35 FT. LBS.)
2 - AUTOMATIC BELT TENSIONER
3 - GENERATOR MOUNTING BRACKET
Fig. 3 Serpentine Accessory Drive Belt Wear
Patterns
1 - NORMAL CRACKS BELT OK
2 - NOT NORMAL CRACKS REPLACE BELT
WJACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 17
BELT TENSIONERS (Continued)
Page 242 of 2199
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BELT BROKEN (NOTE: IDENTIFY
AND CORRECT PROBLEM
BEFORE NEW BELT IS
INSTALLED)1. Excessive tension. 1. Replace belt and automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Incorrect belt. 2. Replace belt.
3. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation.3. Replace belt.
4. Severe misalignment. 4. Check and replace.
5. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure. 5. Replace defective component
and belt.
NOISE (OBJECTIONABLE
SQUEAL, SQUEAK, OR RUMBLE
IS HEARD OR FELT WHILE
DRIVE BELT IS IN OPERATION)1. Belt slippage. 1. Replace belt or automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Bearing noise. 2. Locate and repair.
3. Belt misalignment. 3. Replace belt.
4. Belt-to-pulley mismatch. 4. Install correct belt.
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
CAUTION: DO NOT LET TENSIONER ARM SNAP
BACK TO THE FREEARM POSITION, SEVERE DAM-
AGE MAY OCCUR TO THE TENSIONER.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Rotate belt tensioner until it contacts its stop.
Remove belt, then slowly rotate the tensioner into
the freearm position. (Fig. 4).
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Check condition of all pulleys.CAUTION: When installing the serpentine accessory
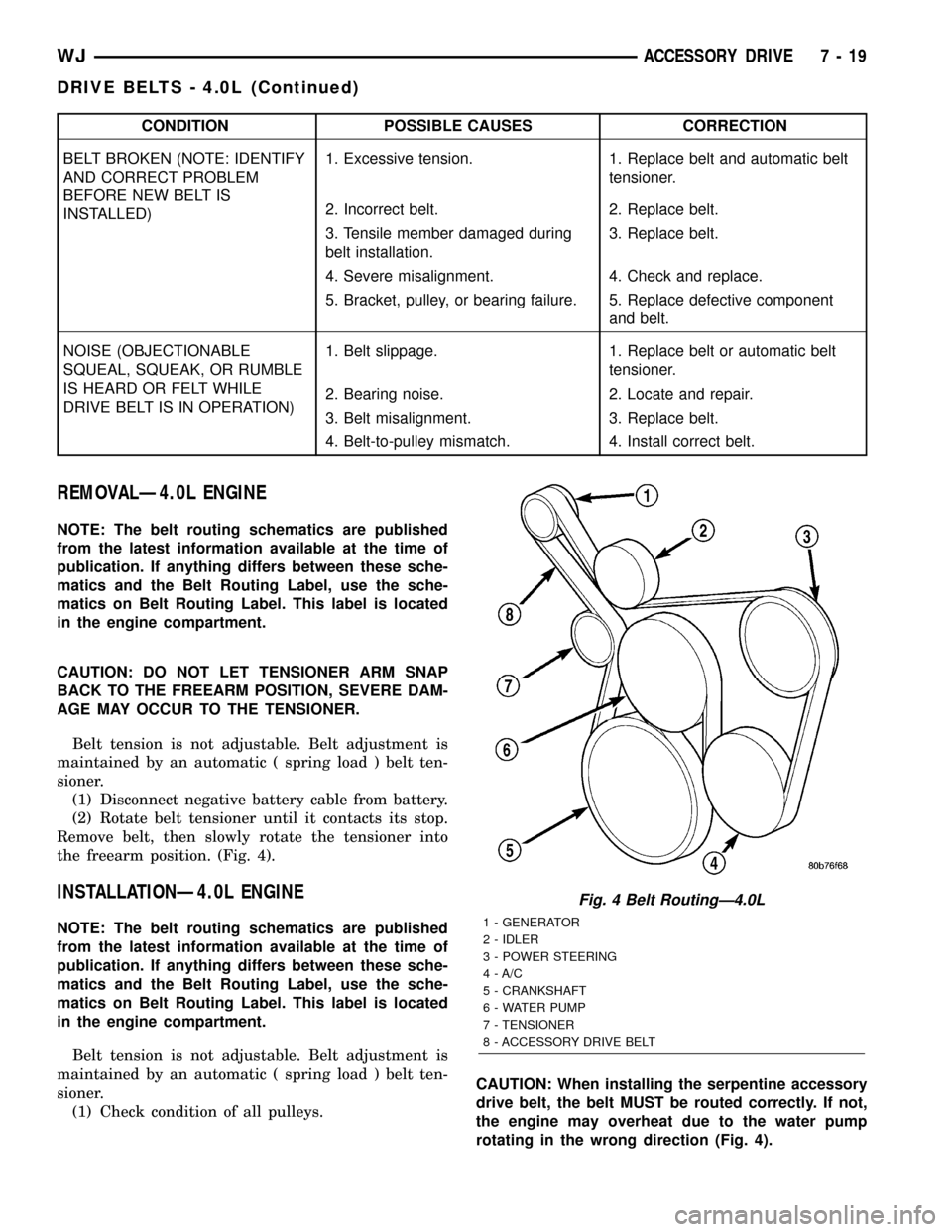
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. If not,
the engine may overheat due to the water pump
rotating in the wrong direction (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4 Belt RoutingÐ4.0L
1 - GENERATOR
2 - IDLER
3 - POWER STEERING
4 - A/C
5 - CRANKSHAFT
6 - WATER PUMP
7 - TENSIONER
8 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
WJACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 19
DRIVE BELTS - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 245 of 2199
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BELT BROKEN (NOTE: IDENTIFY
AND CORRECT PROBLEM
BEFORE NEW BELT IS
INSTALLED)1. Excessive tension. 1. Replace belt and automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Incorrect belt. 2. Replace belt.
3. Tensile member damaged during
belt installation.3. Replace belt.
4. Severe misalignment. 4. Check and replace.
5. Bracket, pulley, or bearing failure. 5. Replace defective component
and belt.
NOISE (OBJECTIONABLE
SQUEAL, SQUEAK, OR RUMBLE
IS HEARD OR FELT WHILE
DRIVE BELT IS IN OPERATION)1. Belt slippage. 1. Replace belt or automatic belt
tensioner.
2. Bearing noise. 2. Locate and repair.
3. Belt misalignment. 3. Replace belt.
4. Belt-to-pulley mismatch. 4. Install correct belt.
REMOVAL - 4.7L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
CAUTION: DO NOT LET TENSIONER ARM SNAP
BACK TO THE FREEARM POSITION, SEVERE DAM-
AGE MAY OCCUR TO THE TENSIONER.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Rotate belt tensioner until it contacts its stop.
Remove belt, then slowly rotate the tensioner into
the freearm position. (Fig. 7).
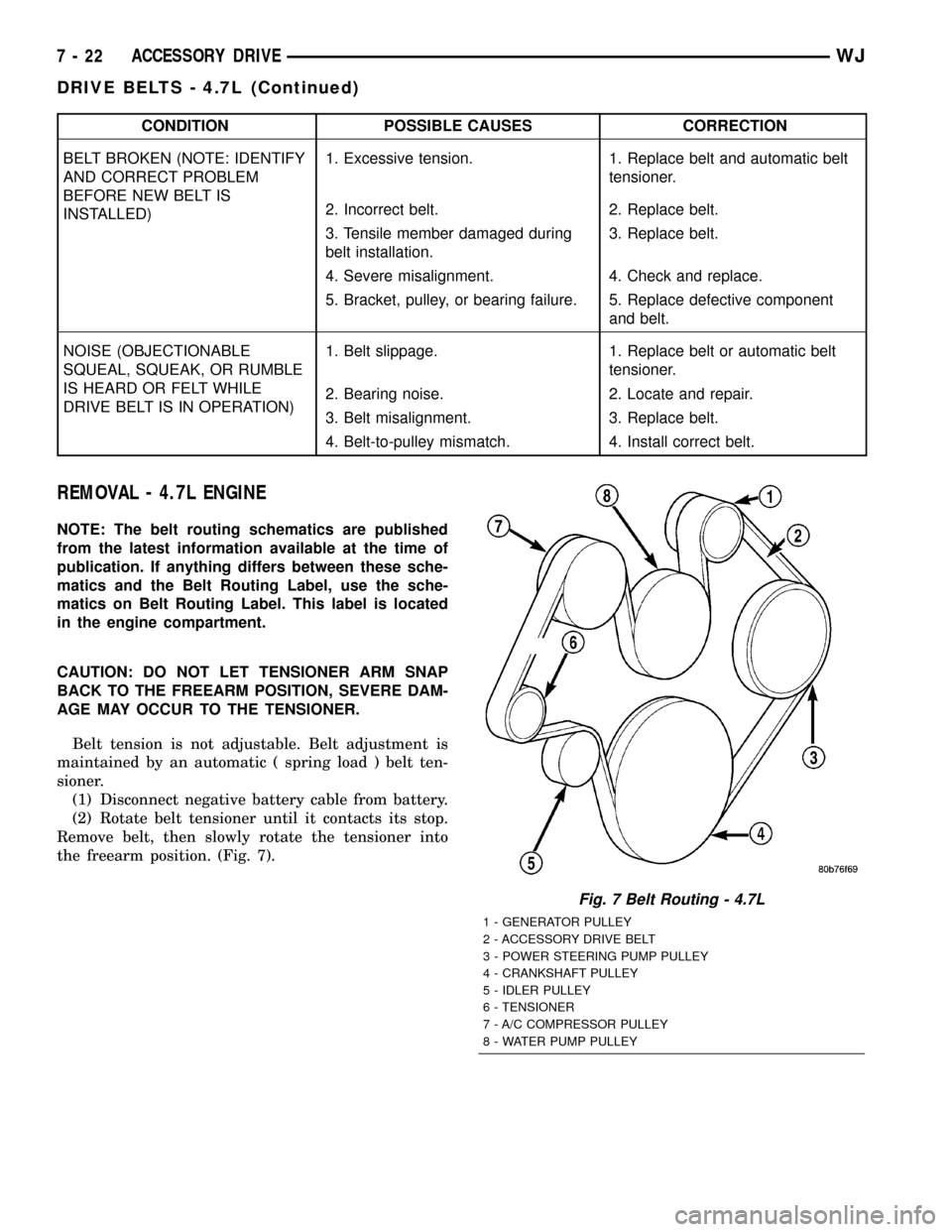
Fig. 7 Belt Routing - 4.7L
1 - GENERATOR PULLEY
2 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT
3 - POWER STEERING PUMP PULLEY
4 - CRANKSHAFT PULLEY
5 - IDLER PULLEY
6 - TENSIONER
7 - A/C COMPRESSOR PULLEY
8 - WATER PUMP PULLEY
7 - 22 ACCESSORY DRIVEWJ
DRIVE BELTS - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 246 of 2199

INSTALLATION - 4.7L ENGINE
NOTE: The belt routing schematics are published
from the latest information available at the time of
publication. If anything differs between these sche-
matics and the Belt Routing Label, use the sche-
matics on Belt Routing Label. This label is located
in the engine compartment.
Belt tension is not adjustable. Belt adjustment is
maintained by an automatic ( spring load ) belt ten-
sioner.
(1) Check condition of all pulleys.
CAUTION: When installing the serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. If not,
the engine may overheat due to the water pump
rotating in the wrong direction (Fig. 7).
(2) Install new belt (Fig. 7). Route the belt around
all pulleys except the idler pulley. Rotate the ten-
sioner arm until it contacts its stop position. Route
the belt around the idler and slowly let the tensioner
rotate into the belt. Make sure the belt is seated onto
all pulleys.(3) With the drive belt installed, inspect the belt
wear indicator (Fig. 8). On 4.7L Engines the gap
between the tang and the housing stop ( measure-
ment A ) must not exceed 24 mm (.94 inches).
Fig. 8 Accessory Drive Belt Wear Indicator
1 - AUTOMATIC TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
WJACCESSORY DRIVE 7 - 23
DRIVE BELTS - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 250 of 2199

(1) Position sensor into the coolant recovery pres-
sure container (Fig. 1).
(2) Connect the coolant level sensor electrical con-
nector (Fig. 2).
(3) Close hood.
COOLANT RECOVERY PRESS
CONTAINER
DESCRIPTION
This system works along with the radiator pres-
sure cap. This is done by using thermal expansion
and contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant
free of trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/ad-
justing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover
minor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-
ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and
returned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reservoir/overflow system has a radia-
tor mounted pressurized cap, an overflow tube and a
plastic coolant reservoir/overflow tank (Fig. 3)
mounted to the right inner fender.
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic fan (Fig. 4) used on vehicles
equipped the 4.7L engine, replaces both the electric
fan and the engine driven mechanical fan. The
hydraulic cooling fan is integral to the fan shroud
and is located between the radiator and the engine.
The power steering pump supplies the hydraulic
fluid and pressure to rotate the cooling fan blade,
while the electrical part of the fan is controlled by
the JTEC.
The hydraulic fan drive (motor) consists of the
three major following components:
²Steering flow control valve
Fig. 1 COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
Fig. 2 COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION
Fig. 3 Coolant Reservoir / Overflow Tank
1 - COOLANT OVERFLOW HOSE
2 - COOLANT RESERVOIR/OVERFLOW TANK
3 - COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR
4 - BOLT
WJENGINE 7 - 27
COOLANT LEVEL SENSOR (Continued)