2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Transmission oil cooler
[x] Cancel search: Transmission oil coolerPage 1647 of 2199

NOTE: Be sure that as the cable is pulled forward
and centered on the throttle lever stud, the cable
housing moves smoothly with the cable. Due to the
angle at which the cable housing enters the spring
housing, the cable housing may bind slightly and
create an incorrect adjustment.
(8) Reconnect the T.V. cable (B) to the throttle
bellcrank lever (C).
(9) Check cable adjustment. Verify transmission
throttle lever and lever on throttle body move simul-
taneously.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 245) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-
vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The torque
converter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid)
pump.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the all transmission fluid
cooler(s) and lines.
Fig. 244 Throttle Valve Cable at Throttle Linkage
1 - THROTTLE LINKAGE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE LOCKING CLIP
3 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
Fig. 245 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE
2 - IMPELLER
3 - HUB
4-STATOR
5 - FRONT COVER
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH DISC
7 - DRIVE PLATE
21 - 128 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE (Continued)
Page 1671 of 2199
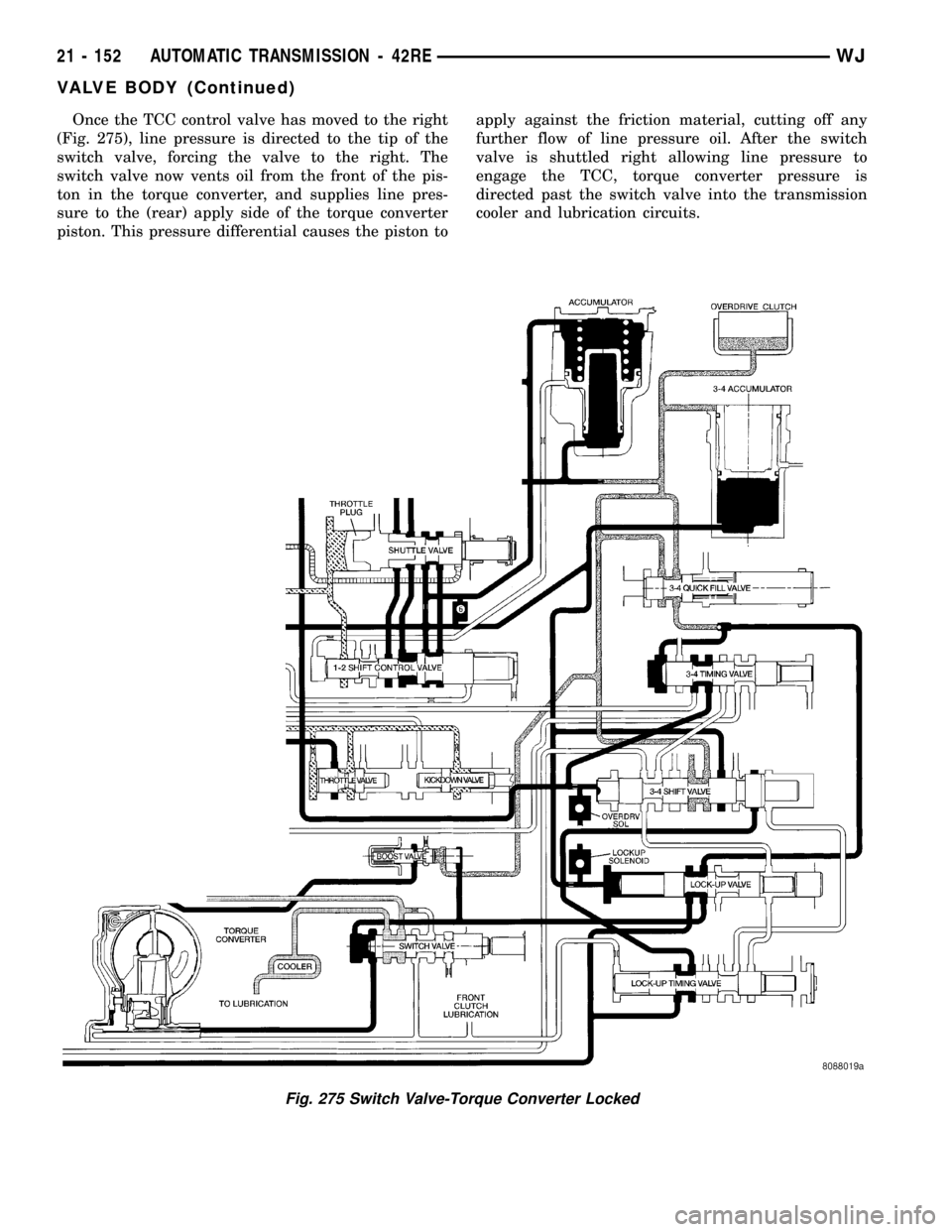
Once the TCC control valve has moved to the right
(Fig. 275), line pressure is directed to the tip of the
switch valve, forcing the valve to the right. The
switch valve now vents oil from the front of the pis-
ton in the torque converter, and supplies line pres-
sure to the (rear) apply side of the torque converter
piston. This pressure differential causes the piston toapply against the friction material, cutting off any
further flow of line pressure oil. After the switch
valve is shuttled right allowing line pressure to
engage the TCC, torque converter pressure is
directed past the switch valve into the transmission
cooler and lubrication circuits.
Fig. 275 Switch Valve-Torque Converter Locked
21 - 152 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1698 of 2199
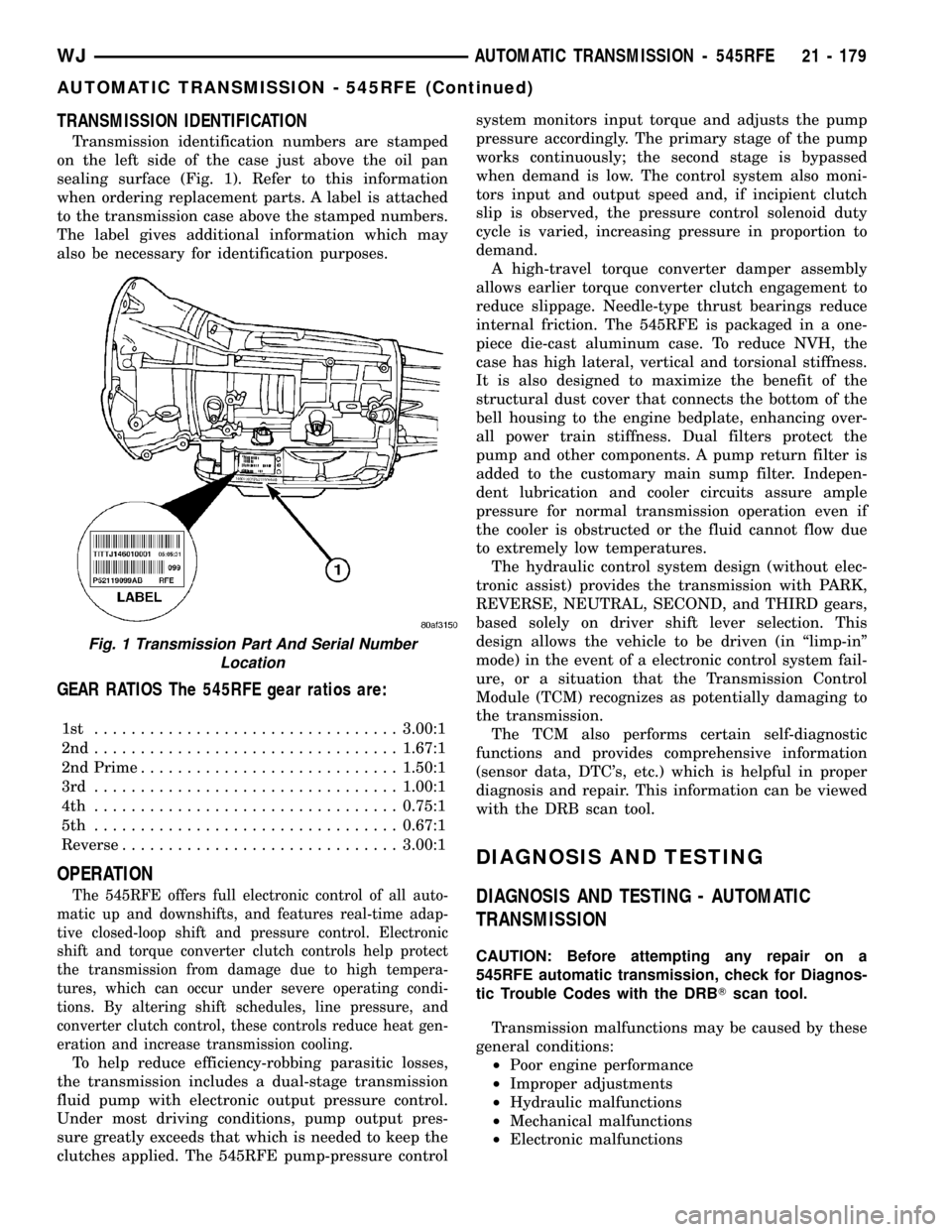
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime............................1.50:1
3rd .................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse..............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 545RFE offers full electronic control of all auto-
matic up and downshifts, and features real-time adap-
tive closed-loop shift and pressure control. Electronic
shift and torque converter clutch controls help protect
the transmission from damage due to high tempera-
tures, which can occur under severe operating condi-
tions. By altering shift schedules, line pressure, and
converter clutch control, these controls reduce heat gen-
eration and increase transmission cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmission includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 545RFE pump-pressure controlsystem monitors input torque and adjusts the pump
pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the pump
works continuously; the second stage is bypassed
when demand is low. The control system also moni-
tors input and output speed and, if incipient clutch
slip is observed, the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle is varied, increasing pressure in proportion to
demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 545RFE is packaged in a one-
piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH, the
case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiffness.
It is also designed to maximize the benefit of the
structural dust cover that connects the bottom of the
bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing over-
all power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a
545RFE automatic transmission, check for Diagnos-
tic Trouble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 179
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1699 of 2199

Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure for
vehicles that are drivable and an alternate procedure for
disabled vehicles (will not back up or move forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform stall test if complaint is based on slug-
gish acceleration. Or, if abnormal throttle opening is
needed to maintain normal speeds with a properly
tuned engine.
(6) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(7)
Perform air-pressure test to check clutch operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2)
Check for broken or disconnected gearshift cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line presure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application chart
provides a basis for analyzing road test results.
CLUTCH APPLICATION CHART
SLP UD OD R 2C 4C L/R OVERRUNNING
P±PARKON
R±REVERSEON ON
N-NEUTRALON
D±OVERDRIVE
FIRSTON ON* ON
SECONDON ON
SECOND PRIMEON ON
THIRDON ON
FOURTHON ON
FIFTHON ON
LIMP-INON ON
2±FIRSTON ON* ON
SECONDON ON
LIMP-INON ON
1±LOWON ON ON
*L/R clutch is on only with the output shaft speed below 150 rpm.
21 - 180 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1700 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at all locations where pressures
exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Only two pressure ports are supplied on the trans-
mission case. The torque converter clutch apply and
release ports are located on the right side of the
transmission case (Fig. 2).
To determine the line pressure, there are two avail-
able methods. The DRBtscan tool can be used to
read line pressure from the line pressure sensor. The
second method is to install Line Pressure Adapter
8259 (Fig. 4) into the transmission case and then
install the pressure gauge and the original sensor
into the adapter. This will allow a comparison of the
DRBtreadings and the gauge reading to determe the
accuracy of the line pressure sensor. The DRBtline
pressure reading should match the gauge reading
within 10 psi.
In order to access any other pressure tap locations,
the transmission oil pan must be removed, the pres-
sure port plugs removed and Valve Body Pressure
Tap Adapter 8258-A (Fig. 5) installed. The extensions
supplied with Adapter 8258-A will allow the installa-
tion of pressure gauges to the valve body. Refer to
(Fig. 3) for correct pressure tap location identifica-
tion.
TEST PROCEDURE
All pressure readings should be taken with the
transmission fluid level full, transmission oil at the
normal operating temperature, and the engine at
1500 rpm. Check the transmission for proper opera-
tion in each gear position that is in question or if a
specific element is in question, check the pressure
readings in at least two gear positions that employ
that element. Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics at
the rear of this section to determine the correct pres-
sures for each element in a given gear position.
Fig. 2 Torque Converter Pressure Locations
1 - TCC RELEASE
2 - TO COOLER
3 - TCC APPLY
4 - FROM COOLER
5 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
Fig. 3 Pressure Tap Locations
Fig. 4 Line Pressure Adapter 8259
1 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR PORT
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - TOOL 8259
4 - PRESSURE TAP
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 181
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1705 of 2199

NOTE: When measuring the input shaft end-play,
two(stops(will be felt. When the input shaft is
pushed inward and the dial indicator zeroed, the
first(stop(felt when the input shaft is pulled out-
ward is the movement of the input shaft in the input
clutch housing hub. This value should not be
included in the end-play measured value and there-
fore must be recorded and subtracted from the dial
indicator reading.
(9) Remove the bolts holding the transmission
extension/adapter housing to the transmission case.
(10) Remove the extension/adapter housing from
the transmission case.
(11) Using Alignment Plate 8261, Adapter 8266-17
from End-Play Tool Set 8266 and Dial Indicator
C-3339, measure and record the output shaft end-
play (Fig. 17).
(12) Remove the bolts holding the transmission oil
pan to the transmission case.
(13) Remove the transmission oil pan from the
transmission case.
(14) Remove the primary oil filter and the oil
cooler return filter (Fig. 18).
(15) Remove the cooler return filter bypass valve.(16) Remove the bolts holding the valve body to
the transmission case (Fig. 19).
(17) Remove the valve body from the transmission
case.
(18) Remove the outer snap-ring securing the
transmission front cover into the transmission case
(Fig. 20).
Fig. 17 Measure Output Shaft End Play
1 - TOOL 8261
2 - TOOL 8266
3 - TOOL C-3339
Fig. 18 Remove Primary Oil and Cooler Filters
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 19 Remove Valve Body Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY TO CASE BOLT (6)
21 - 186 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1709 of 2199

(48) Remove the manual selector shaft seal.
(49) Remove the dipstick tube seal.
CLEANING
The use of crocus cloth is permissible where neces-
sary, providing it is used carefully. When used on
shafts, or valves, use extreme care to avoid rounding
off sharp edges. Sharp edges are vital as they pre-
vent foreign matter from getting between the valve
and valve bore.
Do not reuse oil seals, gaskets, seal rings, or
O-rings during overhaul. Replace these parts as a
matter of course. Also do not reuse snap rings or
E-clips that are bent or distorted. Replace these parts
as well.
Lubricate transmission parts with MopartATF +4,
Type 9602, transmission fluid during overhaul and
assembly. Use petroleum jelly, MopartDoor Ease, or
Ru-Glyde to prelubricate seals, O-rings, and thrust
washers. Petroleum jelly can also be used to hold
parts in place during reassembly.Clean the case in a solvent tank. Flush the case
bores and fluid passages thoroughly with solvent.
Dry the case and all fluid passages with compressed
air. Be sure all solvent is removed from the case and
that all fluid passages are clear.
NOTE: Do not use shop towels or rags to dry the
case (or any other transmission component) unless
they are made from lint-free materials. Lint will stick
to case surfaces and transmission components and
circulate throughout the transmission after assem-
bly. A sufficient quantity of lint can block fluid pas-
sages and interfere with valve body operation.
INSPECTION
Inspect the case for cracks, porous spots, worn
bores, or damaged threads. Damaged threads can be
repaired with Helicoil thread inserts. However, the
case will have to be replaced if it exhibits any type of
damage or wear.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.
(2) Install the cooler filter bypass valve.
(3) Torque the bypass valve to specification. The
valve uses a tapered pipe thread and excessive
torque can damage the transmission case. Tighten
the cooler filter bypass valve to 4.5 N´m (40 in.lbs.).
(4) Install a new selector shaft seal using Seal
Installer 8253 (Fig. 31).
Fig. 30 Manual Shaft/Park Lock Components
1 - GUIDE
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - SHAFT
4 - SPRING
5 - PARK PAWL
6 - MANUAL SHAFT/LEVER
7 - PARK ROD
Fig. 31 Install Selector Shaft
1 - SEAL
2 - TOOL 8253
21 - 190 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1716 of 2199

(51) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(52) Install the primary oil filter and the oil cooler
return filter (Fig. 50). Tighten the screw to hold the
primary oil filter to the valve body to 4.5 N´m (40
in.lbs.). Using Oil Filter Wrench 8321, tighten the
cooler return oil filter to the transmission case to 14
N´m (125 in.lbs.).
(53) Apply RTV silicone to the oil pan and install
the transmission oil pan. Tighten the bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in.lbs.).
(54) Install the input, output, and line pressure
sensors (Fig. 51). Tighten the bolts to 12 N´m (105
in.lbs.).
(55) Install the manual shift lever from the trans-
mission. Torque the retaining cross-bolt to 16 N´m
(140 in.lbs.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Check torque converter hub and hub drive flats
for sharp edges burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the
hub and flats with 320/400 grit paper and crocus
cloth if necessary. Verify that the converter hub
o-ring is properly installed and is free of any debris.
The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump
seal at installation.(2) If a replacement transmission is being
installed, transfer any components necessary, such as
the manual shift lever and shift cable bracket, from
the original transmission onto the replacement trans-
mission.
(3) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(4) Align converter and oil pump.
Fig. 49 Install Valve Body Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY TO CASE BOLT (6)
Fig. 50 Install Primary Oil and Cooler Filters
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 51 Install Input, Output, and Line Pressure
Sensors
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 197
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)